Who does work-based learning benefit –
Who does work-based learning benefit? The answer is simple: everyone. From individuals seeking career advancement to employers looking to attract and retain top talent, work-based learning offers a powerful solution for bridging the gap between education and the real world.
This approach, where practical experience and on-the-job training are interwoven with theoretical knowledge, creates a win-win situation for all involved. Imagine gaining valuable skills while working alongside industry experts, building your professional network, and boosting your confidence – this is the essence of work-based learning.
This method of learning isn’t just about acquiring technical skills; it’s about developing the soft skills employers crave, like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. It’s about gaining practical experience that translates directly to the workplace, making graduates more competitive and prepared for the challenges of today’s job market.
*
Individuals
Work-based learning, also known as experiential learning, offers individuals a unique pathway to career advancement by providing practical experience and valuable insights that traditional education alone may not provide. It’s an approach that bridges the gap between theory and practice, equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to thrive in today’s competitive job market.
Career Advancement
Work-based learning can significantly contribute to career advancement by equipping individuals with industry-specific knowledge and skills, fostering professional networking opportunities, and potentially leading to mentorship.
- Industry-Specific Knowledge and Skills: Work-based learning immerses individuals in real-world work environments, allowing them to gain hands-on experience and develop practical skills that are highly valued by employers. For example, a student pursuing a degree in software engineering could participate in a work-based learning program at a tech company, where they would gain practical experience in coding, software development methodologies, and industry-specific tools.
This experience would make them a more competitive candidate for entry-level positions and accelerate their career growth.
- Professional Networking Opportunities: Work-based learning provides opportunities to connect with industry professionals, build relationships, and expand professional networks. For example, an individual participating in a work-based learning program could attend industry events, meet with potential mentors, and gain insights into career paths and opportunities within their chosen field.
These connections can be invaluable for future job searches and career advancement.
- Potential Mentorship: Work-based learning often involves mentorship from experienced professionals who can guide and support individuals as they develop their skills and explore career options. This mentorship can provide valuable guidance, feedback, and support, helping individuals navigate their career paths and achieve their goals.
Employability Skills
Work-based learning plays a crucial role in enhancing employability skills, particularly soft skills and practical skills that are highly valued by employers.
- Soft Skills: Work-based learning provides opportunities to develop essential soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and critical thinking. For example, an individual participating in a work-based learning program at a marketing agency might learn how to effectively communicate with clients, work collaboratively on projects, and solve complex marketing challenges.
These experiences would enhance their soft skills and make them more valuable to employers.
- Practical Skills: Work-based learning provides hands-on experience in developing practical skills that are essential for success in many industries. For example, an individual participating in a work-based learning program at a financial institution might learn how to use financial software, analyze data, and manage financial projects.
These skills would be highly valuable in the financial services industry and could lead to career advancement opportunities.
- Adaptability: Work-based learning can help individuals adapt to the ever-changing job market demands. By immersing themselves in real-world work environments, individuals gain insights into industry trends, technological advancements, and emerging skills. This exposure can help them stay ahead of the curve and adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
For example, an individual participating in a work-based learning program in the healthcare industry might learn about new technologies and trends in patient care, making them more adaptable to the evolving healthcare landscape.
Confidence and Self-Efficacy
Work-based learning can significantly impact an individual’s confidence and self-efficacy by providing hands-on experience, fostering a sense of accomplishment, and contributing to a stronger sense of purpose and career direction.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Work-based learning allows individuals to contribute to real projects and see the tangible results of their efforts. This sense of accomplishment can boost confidence and motivation, fostering a positive attitude towards work and career development. For example, an individual participating in a work-based learning program at a non-profit organization might contribute to a fundraising campaign and see the positive impact their efforts have on the organization’s mission.
This experience could enhance their sense of accomplishment and purpose.
- Confidence in Abilities: Hands-on experience gained through work-based learning can significantly boost confidence in individual abilities. By applying their knowledge and skills in real-world settings, individuals gain valuable experience and develop a stronger sense of their capabilities. This confidence can be invaluable in job interviews and career pursuits.
- Sense of Purpose: Work-based learning can contribute to a stronger sense of purpose and career direction. By gaining practical experience and exploring different career paths, individuals can gain a better understanding of their interests, skills, and values. This clarity can lead to a stronger sense of purpose and a more fulfilling career path.
2. Employers
Work-based learning (WBL) is a powerful tool for employers, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), to attract, retain, and develop top talent. This approach allows employees to learn new skills and apply them directly in the workplace, fostering a practical and relevant learning experience.
The Benefits of Work-Based Learning for Employers
WBL programs offer a range of advantages for employers, including:
- Attracting and retaining top talent:WBL programs showcase a commitment to employee development, attracting candidates seeking growth opportunities. The practical experience gained through WBL can also lead to higher employee retention rates, as individuals feel valued and invested in.
- Improved employee productivity:WBL programs align learning with specific business needs, ensuring employees gain relevant skills and knowledge that directly impact their work performance. This leads to improved productivity and efficiency within the organization.
- Enhanced employee engagement:By providing opportunities for growth and development, WBL programs can boost employee morale and engagement. Employees feel more motivated and committed when they see their contributions valued and supported.
- Reduced training costs:Traditional classroom-based training can be expensive and time-consuming. WBL programs offer a more cost-effective approach, as learning takes place on the job, minimizing disruption to work schedules.
- Improved business outcomes:By equipping employees with the skills they need to succeed, WBL programs can contribute to improved business outcomes, such as increased sales, enhanced customer service, and improved innovation.
Real-World Examples of Work-Based Learning in SMBs
Several SMBs have successfully implemented WBL programs to attract, retain, and develop talent.
- Example 1:A small marketing agency implemented a mentorship program where experienced employees guided new hires through real-world projects. This program helped new employees gain practical experience and build confidence, leading to higher retention rates and improved performance.
- Example 2:A mid-sized software development company offered employees the opportunity to participate in online courses and certifications related to emerging technologies. This program helped the company stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving tech industry and retain skilled employees who were constantly learning and developing.
Implementing Work-Based Learning Programs in SMBs
SMBs can implement WBL programs in various ways, depending on their specific needs and resources. Here’s a practical guide:
- Identify training needs:Conduct a skills gap analysis to determine the skills and knowledge required for employees to succeed in their roles. This will help you tailor WBL programs to address specific needs.
- Develop a WBL strategy:Define the goals and objectives of your WBL program, including the types of learning activities, delivery methods, and evaluation criteria.
- Choose appropriate learning methods:Consider a variety of methods, including on-the-job training, mentorship, job shadowing, project-based learning, and online courses.
- Provide support and resources:Ensure employees have access to the necessary resources, such as mentors, trainers, and learning materials, to support their learning journey.
- Evaluate and improve:Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your WBL program and make adjustments as needed to ensure it meets the evolving needs of your employees and business.
Call to Action
Investing in work-based learning is a smart strategy for SMBs seeking to attract, retain, and develop top talent. By implementing effective WBL programs, you can empower your employees to grow, contribute, and drive your business forward.
Educational Institutions

Work-based learning provides numerous benefits for educational institutions, enhancing their ability to prepare students for the workforce and strengthen their connections with industry partners.
Curriculum Relevance
Work-based learning helps educational institutions align their curricula with the demands of the modern workplace. By providing students with real-world experiences, institutions can ensure that their programs are relevant and prepare graduates with the skills and knowledge employers seek. This alignment is crucial in today’s rapidly changing job market, where employers often seek candidates with practical experience and the ability to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Strengthening Partnerships
Work-based learning programs foster strong partnerships between educational institutions and industry. These partnerships allow institutions to gain insights into current industry trends, emerging technologies, and the skills employers value. This collaboration enables institutions to adapt their curricula, refine their teaching methods, and ensure their graduates are well-prepared for the workforce.
Types of Work-Based Learning Programs
Educational institutions offer a variety of work-based learning programs to meet the needs of their students and the demands of the industry. Some common types include:
- Internships:These structured programs allow students to gain practical experience in a specific field while working under the supervision of a mentor. Internships provide students with valuable on-the-job training, networking opportunities, and the chance to apply their classroom knowledge in a real-world setting.
- Apprenticeships:Apprenticeships combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction, providing a comprehensive learning experience. These programs are particularly valuable for students pursuing trades or technical fields, offering a structured pathway to develop skills and knowledge required for a specific career.
- Co-op Programs:Co-op programs involve alternating periods of academic study and paid work experience. These programs allow students to gain practical experience and build a professional network while completing their degree. Co-op programs provide students with a valuable opportunity to explore different career paths and gain valuable work experience.
- Service Learning:Service learning programs combine academic study with community service, allowing students to apply their knowledge and skills to address real-world problems. These programs provide students with valuable experiences in teamwork, problem-solving, and civic engagement, enhancing their employability and preparing them for a meaningful career.
4. The Economy
Work-based learning (WBL) goes beyond individual benefits, playing a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape. It acts as a catalyst for economic growth, addresses skills gaps, and fosters a more competitive and resilient workforce, benefiting both developed and developing economies.
4.1. Economic Growth and Innovation
WBL fuels economic growth by aligning education with industry needs, fostering a skilled workforce, and promoting innovation.
- Increased Productivity:WBL equips individuals with practical skills, allowing them to contribute effectively to the workforce, leading to increased productivity and economic output. For instance, in the manufacturing sector, apprenticeships equip workers with the technical expertise needed to operate complex machinery and optimize production processes, contributing to increased efficiency and higher output.
- Innovation:WBL fosters collaboration between industry and academia, facilitating the transfer of knowledge and the development of innovative solutions. This collaboration allows students to gain practical experience in real-world settings, while industry benefits from access to fresh perspectives and talent. For example, in the technology sector, WBL programs involving internships at tech startups expose students to cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, leading to the development of new products and services.
- Entrepreneurship:WBL can encourage entrepreneurship by providing individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to start and run their own businesses. Exposure to real-world challenges and mentorship opportunities through WBL programs can empower individuals to identify business opportunities and develop the skills to navigate the complexities of entrepreneurship.
The success of these ventures further contributes to economic growth and job creation.
5. Specific Industries
Work-based learning (WBL) isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. Its benefits vary significantly depending on the specific industry. Some industries, due to their unique characteristics, see a more profound impact from WBL than others.
5.1. Industries Where Work-Based Learning is Particularly Beneficial
WBL shines in industries with specific demands. These include:
- Industries with high demand for specialized skills and knowledge:Fields like engineering, healthcare, and technology require a deep understanding of specialized knowledge and skills. WBL provides practical experience alongside theoretical learning, bridging the gap between academia and the real world.
- Sectors where practical experience is crucial for career success:In trades like plumbing, carpentry, or automotive repair, hands-on experience is essential for mastery. WBL allows individuals to gain practical skills under the guidance of experienced professionals.
- Industries experiencing rapid technological advancements, requiring constant upskilling:The technology sector is constantly evolving. WBL helps individuals stay ahead of the curve by providing access to cutting-edge technologies and training on the latest tools and techniques.
- Sectors with a strong emphasis on innovation and problem-solving:Industries like design, research, and development benefit from WBL as it fosters creativity and problem-solving skills. Individuals gain valuable insights by working on real-world projects.
Different Learning Styles
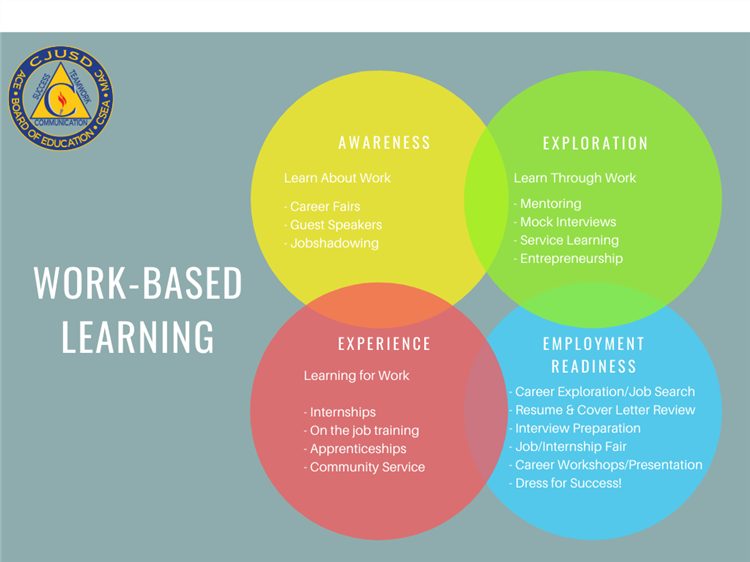
Work-based learning recognizes that individuals learn in different ways. It caters to diverse learning styles, allowing learners to engage with the material in a way that best suits their preferences.
Visual Learners
Visual learners excel when information is presented visually. They retain information better through diagrams, charts, graphs, and other visual aids. Work-based learning programs can cater to visual learners by incorporating these elements into their training materials. For instance, a program for a graphic designer might involve creating presentations, designing marketing materials, or working on visual projects that allow learners to apply their skills and see the tangible results of their work.
Auditory Learners
Auditory learners learn best by listening. They often prefer lectures, discussions, and audio recordings. Work-based learning programs can cater to auditory learners by incorporating these elements into their training. For example, a program for a customer service representative might involve listening to recorded calls, participating in role-playing exercises, or receiving feedback from mentors through audio recordings.
Kinesthetic Learners, Who does work-based learning benefit
Kinesthetic learners learn best by doing. They prefer hands-on activities and practical experiences. Work-based learning programs can cater to kinesthetic learners by providing opportunities for them to actively participate in their learning. For example, a program for a mechanic might involve working on real cars, repairing equipment, or building prototypes.
Advantages of Work-Based Learning for Different Learning Styles
- Visual Learners:Work-based learning programs often provide visual aids, such as presentations, charts, and diagrams, which can help visual learners to better understand and retain information.
- Auditory Learners:Work-based learning programs often involve listening to lectures, participating in discussions, and receiving feedback through audio recordings, which can be beneficial for auditory learners.
- Kinesthetic Learners:Work-based learning programs provide hands-on experiences, allowing kinesthetic learners to actively participate in their learning and apply their knowledge in practical situations.
Lifelong Learning
Work-based learning is a powerful tool for fostering lifelong learning and career development. It provides a dynamic environment where individuals can continuously acquire new skills, knowledge, and experiences, ensuring they remain competitive and adaptable in the ever-evolving job market.
Work-Based Learning Supports Lifelong Learning and Career Development
Work-based learning fosters a culture of continuous learning by integrating practical experience with theoretical knowledge. It allows individuals to apply their skills in real-world settings, receiving feedback and mentorship from experienced professionals. This hands-on approach makes learning more relevant, engaging, and effective, contributing to both personal and professional growth.
Examples of Work-Based Learning Opportunities for Mid-Career Professionals and Those Seeking Career Transitions
Individuals in mid-career or seeking career transitions can benefit from various work-based learning opportunities.
- Mentorship Programs:These programs connect experienced professionals with individuals seeking guidance and support in their career development. Mentors can provide valuable insights, advice, and networking opportunities, helping individuals navigate career changes and acquire new skills.
- Internships and Apprenticeships:These programs offer opportunities to gain hands-on experience in a new field or industry, allowing individuals to explore different career paths and acquire relevant skills. Internships and apprenticeships can be particularly beneficial for those seeking a career change or entering a new industry.
- Professional Development Courses and Workshops:These programs provide focused training on specific skills or knowledge areas, helping individuals enhance their existing skills or acquire new ones relevant to their career goals. Many organizations offer these programs in-house or through partnerships with educational institutions.
- Online Learning Platforms:These platforms offer a wide range of courses and programs covering various topics, from technical skills to soft skills, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule. This flexibility makes online learning a valuable option for individuals juggling work and personal commitments.
Work-based learning isn’t just for the career-minded. It can help anyone develop valuable skills and build confidence. Think about it: if you’re learning by doing, you’re naturally applying what you know. That’s a key principle explored in Hector Ruiz Martin’s book, how do we learn hector ruiz martin.
So, whether you’re a student, a professional looking to upskill, or just someone who wants to learn new things, work-based learning can be a great way to get started.
Role of Work-Based Learning in Adapting to Changing Job Markets and Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements and evolving job markets necessitates continuous learning and adaptation. Work-based learning plays a crucial role in equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to navigate these changes successfully.
- Developing Adaptable Skills:Work-based learning encourages individuals to develop transferable skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration, which are highly valued in the modern workplace. These skills allow individuals to adapt to new technologies and challenges, ensuring their employability in the long term.
- Staying Current with Industry Trends:Work-based learning provides individuals with access to industry experts, allowing them to stay current with the latest trends and technologies. This knowledge helps individuals remain competitive and adaptable in their field, making them valuable assets to their employers.
- Building a Network of Industry Contacts:Through work-based learning opportunities, individuals can build a network of industry contacts, including mentors, colleagues, and potential employers. These connections can provide valuable support and guidance throughout their career journey, opening doors to new opportunities and career advancements.
8. Social Impact: Who Does Work-based Learning Benefit
Work-based learning goes beyond individual benefits, creating ripples of positive change within communities and society as a whole. Its impact extends to fostering economic growth, bridging social divides, and promoting inclusivity.
Positive Social Impact
Work-based learning programs can significantly contribute to the economic development and revitalization of local communities. By providing individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the workforce, these programs can help to create jobs, stimulate economic activity, and improve the overall quality of life.
- Community Level:
- Work-based learning programs can contribute to the economic development and revitalization of local communities by creating jobs and fostering skills development.
- These programs can also help to strengthen the local economy by providing businesses with a pipeline of skilled workers, reducing the need for costly recruitment and training.
- Work-based learning programs can also encourage community engagement by providing opportunities for individuals to learn about different industries and businesses, and to develop valuable connections within their communities.
- Individual Level:
- Work-based learning can empower individuals with valuable skills and knowledge that are directly relevant to the needs of the workforce, increasing their employability and career prospects.
- It can also boost individual confidence, self-efficacy, and career aspirations by providing them with practical experience and a sense of purpose.
Social Mobility & Inclusivity
Work-based learning has the potential to create more equitable access to education and career opportunities, especially for individuals from underrepresented backgrounds. By providing pathways to higher education and professional advancement, it can help to break down barriers and promote social mobility.
- Work-based learning programs can provide pathways to higher education and professional advancement for individuals from underrepresented backgrounds, helping to address issues of equity and access to opportunities.
- These programs can also help to create a more inclusive workforce by providing opportunities for individuals with diverse backgrounds and abilities to develop the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
While work-based learning offers significant benefits, it’s essential to address potential risks and ethical considerations. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in these programs is crucial.
- Potential risks associated with work-based learning include exploitation of workers, inadequate supervision, or lack of proper training.
- Ethical considerations involve ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in work-based learning programs.
- Balancing the needs of employers and the learning objectives of individuals is a challenge that requires careful consideration and planning.
Writing
Work-based learning programs can play a pivotal role in promoting social good and fostering a more equitable society. They provide individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the workforce, while also contributing to the economic development and revitalization of local communities.
By providing pathways to higher education and professional advancement, these programs can help to break down barriers and promote social mobility, creating a more inclusive and equitable society for all.
9. Emerging Trends in Work-Based Learning
Work-based learning is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing demands of the workforce. This section explores some of the most significant trends shaping the future of work-based learning.
Online Platforms
Online platforms are playing an increasingly important role in connecting learners with work-based learning opportunities. These platforms offer a wide range of features and functionalities, catering to diverse learning needs and employer requirements.
- LinkedIn Learning: This platform provides a vast library of online courses and learning resources, covering various topics relevant to professional development. It also offers career coaching and networking opportunities, helping learners build their professional networks and advance their careers. LinkedIn Learning is particularly valuable for individuals seeking to enhance their skills and knowledge in specific areas, and for employers looking to upskill their workforce.
- Coursera: Coursera is a leading online learning platform offering a wide variety of courses from top universities and institutions worldwide. It also features work-based learning programs, including internships and apprenticeships, allowing learners to gain practical experience while studying. Coursera is particularly well-suited for individuals seeking to acquire new skills or advance their education, and for employers seeking to access a global pool of talent.
- Udacity: Udacity focuses on providing industry-relevant skills training in areas such as artificial intelligence, data science, and software engineering. It offers nanodegree programs, which are short, intensive courses designed to prepare learners for specific careers. Udacity is particularly valuable for individuals seeking to acquire in-demand skills and for employers looking to hire skilled professionals in specific technical fields.
These platforms offer numerous benefits for learners and employers. Learners can access a wide range of learning resources, gain practical experience, and build their professional networks. Employers can find qualified candidates, upskill their workforce, and stay competitive in the evolving job market.
However, there are also challenges associated with using these platforms. Learners may need to manage their time effectively and maintain motivation in a self-directed learning environment. Employers need to ensure that the skills and knowledge acquired through these platforms align with their specific needs.
Virtual Internships
Virtual internships are gaining popularity as a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional internships. These internships involve working remotely, often using online collaboration tools and communication technologies.
- Advantages for Learners: Virtual internships offer learners the flexibility to work from anywhere, allowing them to balance their studies or other commitments. They can also gain experience working on real-world projects, build their professional networks, and develop valuable skills, such as communication, collaboration, and problem-solving.
- Advantages for Organizations: Virtual internships provide organizations with access to a wider pool of talent, regardless of location. They can also be more cost-effective than traditional internships, as they eliminate the need for office space and travel expenses. Virtual internships can also help organizations to improve their efficiency and productivity by leveraging remote talent.
- Disadvantages for Learners: Virtual internships may lack the face-to-face interaction and mentorship opportunities offered by traditional internships. Learners may also need to be more self-motivated and disciplined to succeed in a virtual environment.
- Disadvantages for Organizations: Organizations need to invest in technology and infrastructure to support virtual internships.
They also need to ensure that their virtual internship programs are well-structured and provide adequate supervision and support for interns.
Many successful virtual internship programs have been implemented by organizations across various industries. For example, the Virtual Internship Programoffered by the United Nationsprovides students with the opportunity to work on real-world projects related to global development. These programs typically include:
- Structured Training: Providing interns with the necessary training and resources to succeed in a virtual environment.
- Mentorship and Support: Assigning mentors to guide and support interns throughout the internship experience.
- Performance Evaluation: Establishing clear performance expectations and providing regular feedback to interns.
Global Perspective
Work-based learning, a global phenomenon, takes on diverse forms and is influenced by various factors, including economic development, educational systems, and cultural contexts. This section explores how work-based learning models differ across countries, the challenges and opportunities of implementing such programs in a globalized world, and best practices from successful initiatives.
Comparison of Work-Based Learning Models Across Countries
Work-based learning models vary significantly across countries, reflecting their unique educational and economic landscapes.
- Germany:The dual system, a cornerstone of the German education system, combines theoretical instruction at vocational schools with practical training in companies. This model fosters a strong link between education and the workforce, resulting in highly skilled graduates ready for employment.
- United Kingdom:Apprenticeships are a popular work-based learning pathway in the UK, offering on-the-job training and theoretical instruction. The government supports apprenticeship programs through funding and regulations, ensuring quality and standards.
- United States:Work-based learning in the US encompasses a wide range of models, including internships, apprenticeships, and cooperative education. The focus is on developing practical skills and industry-specific knowledge.
- China:China has implemented a “dual-track” system, where students can choose between vocational and academic pathways. This system emphasizes practical skills and vocational training, aligning education with the country’s economic development goals.
Challenges and Opportunities of Implementing Work-Based Learning Programs in a Globalized World
The globalization of the workforce presents both challenges and opportunities for work-based learning.
- Challenge:Ensuring quality and consistency across different countries and regions is crucial to maintaining the credibility of work-based learning programs. Establishing clear standards and guidelines can address this challenge.
- Challenge:Cultural differences can impact the implementation of work-based learning programs. Understanding and respecting local customs and practices is essential for successful program design and delivery.
- Opportunity:Work-based learning can foster international collaboration and knowledge sharing. By connecting students and employers across borders, these programs can promote global understanding and prepare individuals for the interconnected world of work.
- Opportunity:Work-based learning can help address global skills gaps and contribute to workforce development. By providing opportunities for individuals to acquire in-demand skills, these programs can support economic growth and competitiveness.
Best Practices and Lessons Learned from Successful Work-Based Learning Initiatives
Successful work-based learning initiatives around the world offer valuable lessons for program design and implementation.
- Strong Partnerships:Collaborations between educational institutions, employers, and government agencies are essential for effective work-based learning programs. These partnerships ensure alignment between education and industry needs, provide access to resources, and support program sustainability.
- Clear Program Structure:Well-defined program structures, including clear learning objectives, assessments, and mentorship opportunities, provide guidance and support for learners and employers. This helps ensure that participants acquire the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Quality Assurance:Implementing quality assurance mechanisms, such as regular program evaluations and feedback from stakeholders, is crucial for maintaining program standards and effectiveness. This ensures that work-based learning programs meet the needs of learners and employers.
Work-Based Learning and Skills Development

Work-based learning (WBL) is a powerful tool for developing the skills that employers seek, bridging the gap between education and the workplace. By immersing learners in real-world situations, WBL programs equip individuals with the practical knowledge, professional competencies, and essential soft skills necessary for success in today’s dynamic job market.
Examples of Work-Based Learning Programs
WBL programs can take many forms, each designed to foster specific skill development. Here are some examples:
- Internships: These provide students with hands-on experience in their chosen field, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge and gain practical skills under the guidance of experienced professionals.
- Apprenticeships: Combining on-the-job training with classroom instruction, apprenticeships offer structured learning pathways leading to a recognized qualification.
- Mentorship programs: Pairing learners with experienced professionals, mentorship programs provide valuable guidance, support, and networking opportunities, facilitating skills development and career advancement.
- Job shadowing: This involves observing professionals in their daily work environment, gaining insights into industry practices, and understanding the intricacies of different roles.
- Project-based learning: Students collaborate on real-world projects, tackling complex challenges and developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
Skills Development Through Work-Based Learning
WBL fosters the development of essential skills that are highly valued by employers, including:
- Problem-solving: WBL challenges learners to tackle real-world problems, encouraging them to analyze situations, identify solutions, and implement strategies.
- Communication: Working in teams and collaborating with professionals necessitates effective communication skills, including written, verbal, and presentation skills. WBL provides opportunities to refine these abilities.
- Teamwork: WBL programs often involve working in teams, fostering collaboration, conflict resolution, and the ability to contribute effectively to group projects.
- Critical thinking: WBL encourages learners to analyze situations, evaluate information, and make informed decisions, sharpening their critical thinking skills.
- Adaptability: The workplace is constantly evolving, and WBL prepares individuals to adapt to change, embrace new technologies, and learn new skills throughout their careers.
The Future of Work-Based Learning

Work-based learning (WBL) has become increasingly crucial in preparing individuals for the dynamic and ever-evolving job market. As technology advances and the nature of work transforms, WBL will play an even more significant role in equipping learners with the skills and knowledge they need to thrive in the future of work.
Automation and AI Impact
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the workplace at an unprecedented pace, impacting job roles, learning content, and the delivery of education.
- Job Roles:Automation and AI are automating many routine tasks, leading to the displacement of some jobs while creating new roles that require advanced technical skills and cognitive abilities. For example, in manufacturing, robots are taking over repetitive tasks, while the demand for engineers and technicians skilled in programming and maintaining these systems is increasing.
This shift necessitates a focus on developing skills in areas like data analysis, problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity.
- Learning Content:AI-powered tools are enabling personalized learning experiences, tailoring content to individual needs and learning styles. WBL programs will need to incorporate new learning content that addresses the skills required for an automated future, such as AI literacy, data analytics, and digital fluency.
AI can also be used to create adaptive learning platforms that adjust the difficulty and pace of learning based on individual progress.
- Learning Delivery:Automation and AI are changing the way WBL is delivered. Online and blended learning models are becoming increasingly prevalent, allowing learners to access education from anywhere at any time. AI-powered virtual assistants can provide personalized support and guidance to learners, while intelligent tutoring systems can provide tailored feedback and remediation.
Role of Work-Based Learning in Future Work
WBL will be critical in preparing individuals for the future of work by fostering adaptability, resilience, lifelong learning, and essential collaboration and communication skills.
- Adaptability and Resilience:WBL programs can foster adaptability and resilience in learners by providing hands-on experience in real-world settings, allowing them to learn by doing and adapt to changing workplace demands. Experiential learning through internships, apprenticeships, and work-shadowing opportunities helps learners develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and the ability to navigate complex situations.
- Lifelong Learning:WBL can be integrated into a lifelong learning framework, enabling individuals to continuously update their skills and knowledge throughout their careers. WBL programs can provide opportunities for upskilling and reskilling, ensuring learners stay relevant in a rapidly changing job market.
- Collaboration and Communication:WBL programs can emphasize collaboration and communication skills, essential for navigating complex and diverse workplaces. Teamwork projects, group discussions, and mentorship opportunities foster communication and interpersonal skills, preparing learners for collaborative environments.
Emerging Trends in Work-Based Learning
Emerging trends in WBL are shaping the future of education and workforce development.
- Micro-credentials and Skills-Based Learning:Micro-credentials and skills-based learning are gaining traction as employers seek to validate and recognize specific skills acquired through WBL. These credentials can demonstrate specific skills and competencies, making it easier for individuals to showcase their abilities to potential employers.
- Immersive Technologies (VR/AR):Immersive technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are being incorporated into WBL programs to create more engaging and realistic training experiences. VR/AR simulations can provide learners with hands-on practice in real-world scenarios without the risks and costs associated with traditional training methods.
- Employer-Led Learning:Employers are taking a more active role in designing and delivering WBL programs to meet their specific needs and workforce development goals. This trend is driven by the need for customized training that aligns with specific industry requirements and company culture.
Best Practices for Implementing Work-Based Learning
Work-based learning (WBL) programs can be highly effective in preparing individuals for the workforce, but successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. This section will explore best practices for designing and implementing effective WBL programs, including examples of successful initiatives and the importance of ongoing evaluation and improvement.
Defining Clear Learning Objectives and Outcomes
Clearly defining learning objectives and outcomes is essential for any successful WBL program. This ensures that participants gain the knowledge, skills, and experience they need to succeed in their chosen career path.
- Align with Industry Needs:Learning objectives should be aligned with the current and future needs of the industry. This can be achieved through collaboration with employers, industry associations, and other stakeholders. For example, a WBL program for aspiring software developers should include objectives related to current programming languages, software development methodologies, and emerging technologies like cloud computing and artificial intelligence.
- Measurable and Specific:Objectives should be measurable and specific, enabling the program to track participant progress and assess the effectiveness of the program. Instead of vague objectives like “improve communication skills,” a program might aim to “increase participants’ ability to write clear and concise technical documentation, as measured by a post-program writing assessment.”
- Focus on Practical Skills:WBL programs should emphasize practical skills that are directly relevant to the workplace. This can include hands-on training, real-world projects, and opportunities to work with industry professionals.
Creating a Structured Learning Environment
A structured learning environment is crucial for ensuring that WBL programs are effective. This includes establishing clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and fostering a supportive and collaborative learning environment.
- Well-Defined Roles and Responsibilities:Clear roles and responsibilities should be established for all stakeholders involved in the program, including participants, mentors, employers, and educational institutions. This ensures that everyone understands their expectations and responsibilities.
- Regular Feedback and Support:Participants should receive regular feedback from their mentors and employers, as well as opportunities for reflection and self-assessment. This helps them to identify areas for improvement and stay on track with their learning goals.
- Mentorship and Guidance:Providing participants with mentors who can guide them through their WBL experience is essential. Mentors can provide support, guidance, and feedback, helping participants navigate the challenges of the workplace and develop their professional skills.
Developing Partnerships with Employers
Strong partnerships with employers are essential for the success of WBL programs. Employers provide valuable insights into industry needs, offer real-world learning opportunities, and contribute to the development of program curriculum and assessments.
- Identify Suitable Employers:The program should identify employers who are committed to supporting WBL and have a strong track record of providing quality training and development opportunities.
- Develop Clear Agreements:Formal agreements should be established with employers outlining the expectations and responsibilities of each party. This includes defining the learning objectives, the duration of the WBL experience, the level of supervision, and the evaluation process.
- Regular Communication and Collaboration:Regular communication and collaboration between program staff and employers are essential for ensuring that the WBL experience meets the needs of both participants and employers. This can involve regular meetings, site visits, and feedback sessions.
Utilizing Technology for Effective Delivery
Technology can play a significant role in enhancing the effectiveness of WBL programs. This includes using online learning platforms, virtual simulations, and other tools to facilitate learning and communication.
- Online Learning Platforms:Online learning platforms can be used to deliver training materials, track participant progress, and facilitate communication between participants, mentors, and employers.
- Virtual Simulations:Virtual simulations can provide participants with a safe and controlled environment to practice real-world skills. This can be particularly valuable for industries where hands-on training is difficult or expensive.
- Digital Portfolios:Participants can use digital portfolios to document their learning experiences, showcase their skills and achievements, and build their professional brand.
Ongoing Evaluation and Improvement
It is crucial to continuously evaluate and improve WBL programs to ensure they remain relevant, effective, and meet the evolving needs of participants and employers.
- Regular Data Collection:Collect data on participant satisfaction, employer feedback, learning outcomes, and program effectiveness. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and make evidence-based decisions about program design and implementation.
- Feedback Mechanisms:Establish mechanisms for collecting feedback from participants, mentors, employers, and other stakeholders. This feedback can be used to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the program meets the needs of all stakeholders.
- Program Review and Revision:Conduct regular reviews of the program to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This may involve reviewing the program curriculum, learning objectives, assessment methods, and partnership arrangements.
Examples of Successful Work-Based Learning Initiatives
Several successful WBL initiatives have demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach to education and training. These initiatives often share common features, such as strong employer partnerships, clear learning objectives, and a focus on practical skills.
- Apprenticeships:Apprenticeships have been a cornerstone of workforce development for centuries. These programs combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction, providing participants with a comprehensive understanding of their chosen trade. Successful apprenticeship programs often involve partnerships between employers, educational institutions, and industry associations.
- Internships:Internships provide students with valuable work experience and exposure to the workplace. They can be structured as paid or unpaid positions, and they often involve specific learning objectives and projects. Effective internship programs often include mentorship, regular feedback, and opportunities for professional development.
- Work-Study Programs:Work-study programs combine academic study with part-time employment. These programs can provide students with financial assistance, valuable work experience, and opportunities to apply their classroom learning in a real-world setting.
FAQ Overview
What are some examples of work-based learning programs?
Work-based learning encompasses a wide range of programs, including internships, apprenticeships, mentorships, job shadowing, and even volunteer experiences. The specific program will depend on the individual’s goals, the industry, and the educational institution involved.
Is work-based learning only for students?
Absolutely not! Work-based learning can benefit individuals at all stages of their careers, from recent graduates to seasoned professionals seeking to upskill or transition into new roles. It’s a valuable tool for lifelong learning and career development.
How can I find work-based learning opportunities?
Many colleges and universities offer work-based learning programs as part of their curriculum. You can also explore opportunities through online platforms, industry associations, and professional networking events. Don’t be afraid to reach out to companies directly and inquire about internship or mentorship programs.
-*