Which of the following is true of informal learning? It’s a question that sparks curiosity about how we truly learn, beyond the structured walls of classrooms and textbooks. Informal learning, unlike its formal counterpart, unfolds organically through experiences, interactions, and self-driven exploration.
It’s a constant companion in our lives, shaping our knowledge, skills, and perspectives in ways we might not even realize.
From the first time a child imitates a parent’s actions to the seasoned professional absorbing knowledge from a colleague, informal learning weaves itself into the fabric of our daily existence. It’s the casual conversation that sparks a new idea, the hobby that unveils hidden talents, and the online community that connects us with experts in our field.
The beauty of informal learning lies in its adaptability, its ability to cater to individual needs and interests, and its potential to empower us with lifelong learning.
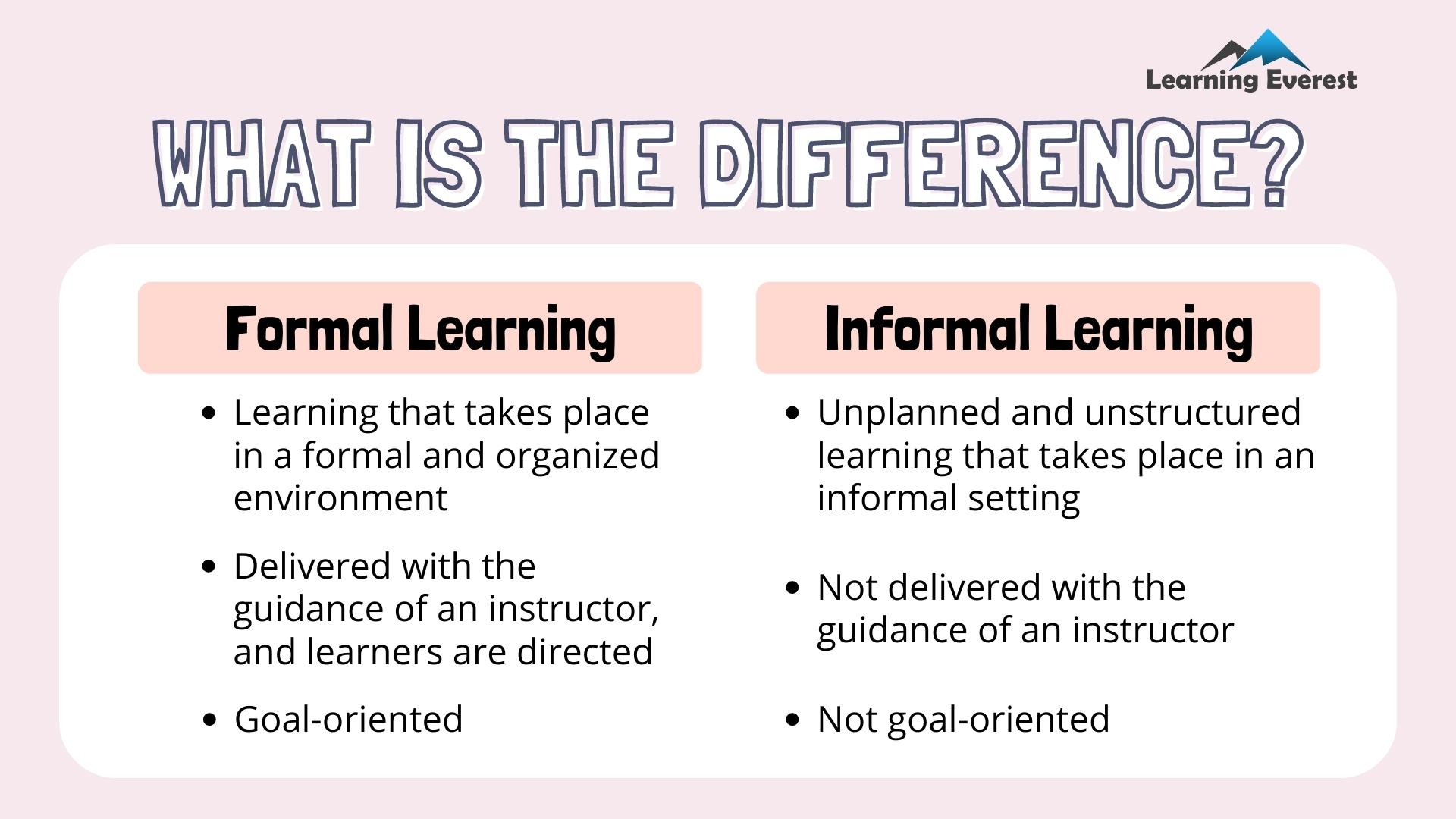
Informal Learning


Informal learning is a continuous and pervasive process that shapes our knowledge, skills, and perspectives throughout our lives. Unlike formal learning, which occurs in structured environments like schools or universities, informal learning is characterized by its lack of a defined curriculum, formal assessment, or predetermined outcomes.
This essay will delve into the multifaceted nature of informal learning, exploring its characteristics, benefits, challenges, and implications for education and the workforce.
Definition and Characteristics
Informal learning encompasses the vast array of learning experiences that occur outside of traditional educational settings. It is a spontaneous and learner-driven process that often arises from everyday interactions, observations, and personal interests. The defining characteristic of informal learning is its lack of structure and formal assessment.
Learners are free to pursue their interests, explore new ideas, and develop their skills at their own pace.Informal learning is often described as being:
- Spontaneous:Informal learning happens organically, without a predetermined plan or schedule. It can arise from unexpected opportunities, such as encountering a new problem or engaging in a conversation with an expert.
- Unstructured:Unlike formal learning, which adheres to a specific curriculum and assessment criteria, informal learning is characterized by its lack of structure. Learners are free to explore their interests and learn in ways that suit their individual learning styles.
- Learner-driven:Informal learning is driven by the learner’s own curiosity, interests, and goals. Learners actively seek out information and experiences that are relevant to their needs and aspirations.
The flexibility and adaptability of informal learning are evident in the diverse range of situations and activities where it takes place. For instance, learning from experiences, such as traveling to a new country or working on a challenging project, provides valuable insights and practical skills.
Observing others, whether it be a skilled craftsman demonstrating their techniques or a mentor sharing their knowledge, can lead to significant learning. Engaging in conversations with peers, colleagues, or experts can expose learners to different perspectives and stimulate critical thinking.
Pursuing hobbies and interests, such as playing a musical instrument or learning a new language, can foster creativity, develop skills, and enhance personal growth.
Benefits and Challenges
Informal learning offers a multitude of benefits, including:
- Increased Motivation:When learners are engaged in activities that they find interesting and relevant, their motivation to learn is naturally enhanced. This can lead to greater persistence, effort, and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills:Informal learning often involves tackling real-world problems and challenges. This hands-on experience helps learners develop critical thinking, analytical, and problem-solving skills that are essential for success in various contexts.
- Enhanced Creativity:The unstructured nature of informal learning allows learners to explore different ideas, experiment with new approaches, and develop their creative thinking skills. This can lead to innovative solutions and original perspectives.
However, informal learning also presents challenges:
- Lack of Structure:The absence of a defined curriculum and assessment criteria can make it difficult to track progress and ensure that learning outcomes are achieved. Learners may need to develop their own strategies for organizing their learning and evaluating their progress.
- Potential for Misinformation:The vast amount of information available through informal channels, such as the internet, can make it difficult to distinguish between accurate and inaccurate information. Learners need to develop critical thinking skills to evaluate the credibility of sources and avoid misinformation.
One of the things that makes informal learning so cool is that it can happen anywhere, anytime. You can learn a new skill just by watching someone else do it, like how to make a killer omelet. Or you might be surprised to find out that even chickens can learn their names, like you can read about here.
So, informal learning is all about being open to new experiences and soaking up knowledge wherever you find it.
- Difficulty in Measuring Learning Outcomes:Assessing the effectiveness of informal learning can be challenging. Traditional methods of assessment, such as standardized tests, may not be suitable for evaluating the skills and knowledge acquired through informal learning. This requires innovative approaches to measuring learning outcomes.
Role of Technology
Technology has played a transformative role in facilitating informal learning, providing access to a wealth of resources and opportunities. Online communities, social media platforms, and educational apps have created new avenues for learners to connect with others, share knowledge, and explore their interests.
- Online Communities:Online forums, discussion groups, and social media platforms provide spaces for learners to connect with others who share their interests, ask questions, and receive support. These communities foster a sense of belonging and create opportunities for peer-to-peer learning.
- Social Media:Social media platforms have become powerful tools for informal learning, enabling learners to access information, engage in discussions, and discover new ideas. They can follow experts in their field, participate in online courses, and connect with like-minded individuals.
- Educational Apps:Educational apps offer gamified learning experiences, interactive simulations, and personalized learning pathways. They can provide learners with engaging content, adaptive assessments, and real-time feedback.
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR), have the potential to further revolutionize informal learning. AI-powered learning platforms can personalize learning experiences, provide tailored recommendations, and offer real-time feedback. VR technologies can create immersive learning environments that allow learners to experience real-world scenarios and develop skills in a safe and engaging way.
Implications for Education and Workforce
Informal learning has significant implications for formal education systems and the workforce. In the context of education, informal learning can complement and enhance traditional classroom experiences.
- Integration with Formal Education:Educators can integrate informal learning activities into their curricula, encouraging students to engage in project-based learning, explore their interests through independent research, and participate in online communities.
- Complementarity to Formal Education:Informal learning can provide students with opportunities to apply their classroom knowledge to real-world contexts, develop practical skills, and explore their passions outside of the traditional curriculum.
In the workforce, informal learning is crucial for preparing individuals for the demands of a rapidly changing job market.
- Development of Transferable Skills:Informal learning experiences can help individuals develop transferable skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, communication, and collaboration, which are highly valued in today’s workforce.
- Adaptability and Lifelong Learning:Informal learning promotes a culture of lifelong learning, enabling individuals to adapt to new technologies, acquire new skills, and remain competitive in the job market.
Informal Learning


Informal learning is a continuous and often unconscious process of acquiring knowledge and skills outside of structured educational settings. It encompasses learning that happens through everyday experiences, interactions, and observations. Unlike formal education, which follows a predetermined curriculum and involves assessments, informal learning is self-directed, flexible, and driven by individual interests and needs.
Defining Informal Learning
Informal learning is a continuous process of acquiring knowledge and skills outside of structured educational settings. It is characterized by its self-directed nature, lack of structured curriculum, and focus on practical application. It can occur anywhere, anytime, and through various means, such as conversations, observations, experiences, and interactions with others.For instance, a young child learning to ride a bicycle by observing and mimicking older siblings is engaging in informal learning.
Similarly, an individual learning a new software program through online tutorials or by observing colleagues is also participating in informal learning. Key characteristics of informal learning include:
- Self-directed: Learners determine their own learning goals, pace, and methods.
- Flexible: Informal learning can occur anytime, anywhere, and in various ways.
- Practical: It focuses on acquiring skills and knowledge that are immediately applicable to real-life situations.
- Experiential: Learning occurs through hands-on activities, real-world experiences, and practical applications.
- Social: Informal learning often involves interactions with others, such as mentors, peers, or experts.
Importance and Benefits
Informal learning plays a crucial role in personal and professional development, contributing to increased knowledge, skills, and adaptability. It enables individuals to acquire knowledge and skills that are not readily available through formal education.
- Enhanced Knowledge and Skills: Informal learning provides opportunities to acquire new knowledge and skills, broaden perspectives, and develop critical thinking abilities. For example, an individual learning a new language through immersion or online resources is engaging in informal learning that enhances their communication skills and cultural understanding.
- Increased Adaptability: The dynamic nature of informal learning allows individuals to adapt to changing circumstances and acquire new skills quickly. In today’s rapidly evolving workplace, informal learning is essential for staying competitive and relevant.
- Personal Growth: Informal learning fosters personal growth by encouraging exploration, self-discovery, and the development of new interests and passions. Individuals who engage in informal learning often report increased confidence, motivation, and a sense of purpose.
- Career Advancement: Informal learning can significantly contribute to career advancement by equipping individuals with the skills and knowledge required for promotion or career transitions. For example, an individual who learns new software skills through online courses or by attending workshops may be better positioned for career advancement in their field.
- Societal Progress: Informal learning promotes societal progress by fostering innovation, creativity, and collaboration. Individuals who engage in informal learning are more likely to contribute to their communities and drive positive change.
Exploring Informal Learning Environments
Informal learning can occur in various environments, both online and offline.
- Online Communities: Online forums, social media groups, and online learning platforms provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others who share similar interests and learn from their experiences. For example, individuals interested in coding can join online communities where they can access tutorials, participate in discussions, and collaborate on projects.
- Social Media Platforms: Social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram can be valuable resources for informal learning. Individuals can follow experts, participate in discussions, and access a wide range of information and resources on various topics.
- Museums and Libraries: Museums and libraries offer opportunities for informal learning through exhibits, lectures, workshops, and access to books and other resources. For example, individuals interested in history can visit museums to learn about different cultures and historical events.
- Workplaces: Workplaces provide ample opportunities for informal learning through mentorship, job shadowing, and on-the-job training. Individuals can learn from experienced colleagues, acquire new skills, and develop their professional networks.
Strategies for Effective Informal Learning
To maximize the benefits of informal learning, individuals can employ various strategies:
- Set Clear Learning Goals: Identifying specific learning goals and objectives helps individuals focus their efforts and track their progress.
- Engage in Active Learning: Actively participating in learning activities, such as asking questions, taking notes, and applying new knowledge, enhances understanding and retention.
- Seek Out Diverse Resources: Exploring various sources of information, such as books, articles, videos, and podcasts, provides a more comprehensive understanding of a topic.
- Reflect on Learning Experiences: Regularly reflecting on learning experiences helps individuals identify areas for improvement and refine their learning strategies.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Informal learning is a lifelong process. Individuals should cultivate a mindset of continuous learning and seek out opportunities to expand their knowledge and skills.
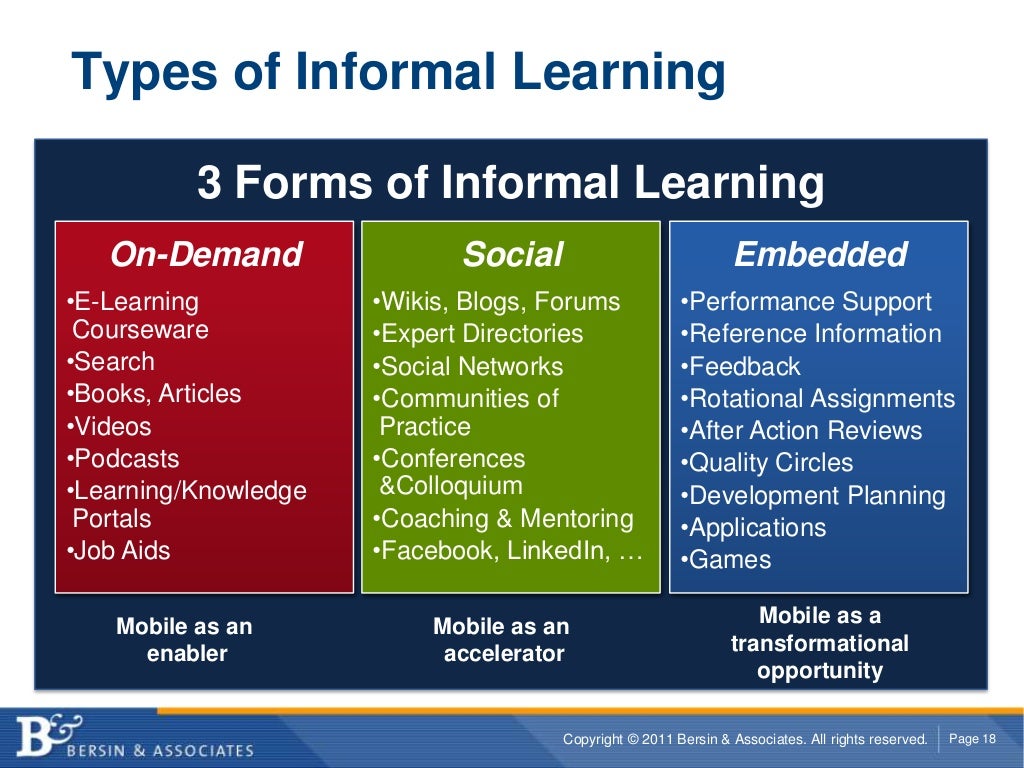
3. Sources and Methods of Informal Learning
Informal learning, the process of acquiring knowledge and skills outside of structured educational settings, plays a crucial role in personal and professional growth. It encompasses a wide range of sources and methods, shaping our understanding of the world and influencing our abilities.
This section explores the diverse avenues through which informal learning takes place, examining the benefits and limitations of each approach.
3.1. Sources of Informal Learning
Informal learning arises from various sources, enriching our knowledge and skills in unexpected ways. These sources can be categorized into real-world experiences, social interactions, online platforms, and self-directed learning.
a. Real-World Experiences
Real-world experiences provide a rich tapestry of learning opportunities, offering practical insights and valuable lessons that go beyond traditional classroom settings.
- Work: The workplace is a fertile ground for informal learning. On-the-job training, problem-solving, and interactions with colleagues foster skill development and knowledge acquisition. For instance, a young engineer might learn new design techniques by observing experienced colleagues working on complex projects.
Similarly, a retail associate might gain valuable customer service skills through interactions with diverse customers. The challenges and successes encountered in the workplace provide valuable lessons that can be applied to future situations.
- Travel: Exploring new cultures, environments, and perspectives through travel can lead to significant informal learning. Exposure to different customs, languages, and ways of life broadens horizons and fosters understanding. For example, a traveler visiting a foreign country might learn about local traditions, history, and cuisine, expanding their knowledge of the world.
The challenges of navigating unfamiliar surroundings and interacting with people from diverse backgrounds can enhance problem-solving skills and adaptability.
- Hobbies and Interests: Pursuing personal interests, such as music, art, or sports, can promote learning outside of formal settings. Engaging in hobbies provides opportunities for exploration, skill development, and self-expression. For instance, a musician might learn about different musical genres and techniques by experimenting with various instruments or attending concerts.
Similarly, an artist might learn about color theory and composition by taking online courses or attending workshops. The dedication and perseverance required to develop a hobby can foster valuable life skills, such as discipline, focus, and resilience.
Real-world experiences offer valuable benefits, including:
- Practical application: Real-world experiences provide opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations, leading to deeper understanding and skill development.
- Contextual learning: Learning in real-world contexts helps individuals connect knowledge to real-life situations, making it more relevant and meaningful.
- Problem-solving: Real-world challenges often require individuals to think critically and creatively to find solutions, fostering problem-solving skills.
However, real-world experiences also have limitations:
- Lack of structure: Real-world experiences can be unstructured and unpredictable, making it difficult to acquire systematic knowledge.
- Potential for bias: Real-world experiences can be influenced by personal biases, leading to incomplete or inaccurate information.
- Limited feedback: Individuals may not always receive feedback on their learning or have opportunities to reflect on their experiences.
b. Social Interactions
Social interactions play a vital role in informal learning, shaping our perspectives, values, and beliefs.
- Family and Friends: Interactions with family and friends contribute to knowledge acquisition and skill development. Through conversations, shared experiences, and guidance from family members, individuals learn about values, traditions, and social norms. For example, a child might learn about cooking, gardening, or financial management by observing and assisting their parents.
Friends can also be valuable sources of information, sharing their experiences, perspectives, and knowledge on various topics.
- Community Groups and Organizations: Participation in clubs, volunteer groups, and other social organizations fosters informal learning. These groups provide opportunities for collaboration, mentorship, and exposure to diverse perspectives. For example, a member of a book club might learn about different literary styles and authors through discussions with fellow members.
Similarly, a volunteer at a local animal shelter might learn about animal care and welfare through hands-on experience and interactions with other volunteers.
- Online Communities: Online forums, social media platforms, and virtual communities facilitate knowledge sharing and learning. Individuals can connect with experts, participate in online discussions, and access a wealth of information on various topics. For example, a student interested in coding might join an online forum to learn from experienced programmers, ask questions, and share their own projects.
Social media platforms can also be used for learning, providing access to educational content, news articles, and expert insights.
Social interactions contribute to informal learning in several ways:
- Knowledge sharing: Social interactions facilitate the exchange of information, perspectives, and experiences, leading to broader understanding.
- Skill development: Collaborating with others on projects or tasks can foster skill development and enhance teamwork abilities.
- Perspective building: Exposure to diverse perspectives through social interactions can challenge existing beliefs and broaden horizons.
c. Online Platforms
The internet has revolutionized informal learning, providing a wealth of resources and opportunities for self-directed learning.
- Educational Websites and Apps: Numerous educational websites and apps offer interactive learning experiences, tutorials, and educational content. For example, Khan Academy provides free online courses on a wide range of subjects, while Duolingo offers language learning tools and exercises.
These platforms provide structured learning opportunities, often with gamified elements to enhance engagement.
- Social Media Platforms: Social media platforms can be used for learning, facilitating information sharing, connecting with experts, and participating in online discussions. For example, individuals can follow experts in their field on Twitter or LinkedIn to stay updated on industry trends and research.
Facebook groups and online forums can provide opportunities for peer learning and discussion.
- Online Courses and MOOCs: Online courses and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) provide structured learning opportunities outside of traditional educational settings. These courses offer a wide range of subjects, from programming and design to history and literature. MOOCs are often offered by reputable universities and institutions, providing access to high-quality educational content.
Online platforms offer several advantages for informal learning:
- Accessibility: Online platforms are readily accessible, allowing individuals to learn from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Flexibility: Online learning allows individuals to learn at their own pace and schedule, fitting learning into busy lives.
- Diversity of content: Online platforms offer a wide range of subjects and resources, catering to diverse interests and learning styles.
However, online platforms also have disadvantages:
- Credibility: Not all online resources are reliable or accurate, requiring careful evaluation of sources.
- Distractions: The internet can be a source of distractions, making it challenging to focus on learning.
- Lack of interaction: Online learning can sometimes lack the personal interaction and feedback found in traditional classroom settings.
d. Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning empowers individuals to take control of their learning process, pursuing their own interests and goals.
- Reading Books and Articles: Independent reading provides opportunities for acquiring knowledge, developing critical thinking skills, and expanding horizons. Individuals can choose books and articles that align with their interests and goals, fostering a love of learning.
- Watching Educational Videos: Educational videos can be a valuable source of information, providing insights on various topics and skills. Platforms like YouTube and Khan Academy offer a wealth of educational content, from documentaries to tutorials.
- Experimentation and Exploration: Hands-on activities and experimentation can contribute to self-directed learning, allowing individuals to test ideas, explore concepts, and gain practical experience. For example, a budding photographer might experiment with different lighting techniques or camera settings to improve their skills.
Self-directed learning requires:
- Motivation: Individuals must be intrinsically motivated to learn and set their own goals.
- Self-discipline: Self-directed learners need to manage their time effectively, set priorities, and stay focused on their learning objectives.
- Effective learning strategies: Individuals must develop effective learning strategies, such as note-taking, summarizing, and reviewing material to retain information.
4. Motivational Factors
Informal learning is not always driven by a formal curriculum or external pressures. Instead, it often arises from intrinsic and extrinsic motivators that shape individuals’ learning choices and strategies. Understanding these motivators is crucial for fostering a more engaged and effective learning environment.
4.1. Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation stems from internal factors, such as curiosity, passion, and personal goals, that drive individuals to learn for the sake of learning.
4.1.1. Curiosity
Curiosity plays a significant role in driving informal learning. It fuels a desire to explore new ideas, understand the world around us, and seek answers to questions that intrigue us.
- In everyday life, curiosity might lead someone to read an article about a topic they find fascinating, watch a documentary about a historical event, or delve into a new hobby.
- In professional settings, curiosity might motivate individuals to attend workshops, read industry publications, or experiment with new technologies.
Curiosity often leads to a deeper understanding of a subject, as individuals are more likely to retain information they actively seek out and engage with.
4.1.2. Passion
Passion is a powerful motivator that can ignite a deep interest in a particular subject or activity. Individuals with strong passions often approach learning with a sense of purpose and dedication.
- Passionate learnersare often self-directed and driven to explore their interests in depth. They may spend hours researching a topic, attending events related to their passion, or connecting with others who share their interests.
- Passion can also lead to a more immersive and engaging learning experience, as individuals are more likely to be motivated and inspired when they are genuinely interested in what they are learning.
4.1.3. Personal Goals
Informal learning can be a powerful tool for achieving personal goals. Individuals may engage in informal learning to acquire new skills, improve their knowledge, or simply expand their horizons.
- For example, someone might take an online course to learn a new language to travel, join a book club to expand their literary horizons, or learn a new craft to pursue a creative outlet.
- Setting and achieving personal goals through informal learningcan be a rewarding and fulfilling experience, as individuals can see the tangible benefits of their efforts.
Role of Technology
Technology has dramatically reshaped the landscape of informal learning, making it more accessible, engaging, and personalized. The rise of online resources, digital tools, and virtual communities has created a dynamic environment where individuals can acquire knowledge and skills outside traditional educational settings.
Impact of Technology on Informal Learning
Technology’s impact on informal learning is profound, enabling individuals to access information, collaborate with others, and tailor their learning experiences to their specific needs.
- Accessibility to Information:The internet has become a vast repository of knowledge, providing access to a wide range of resources, including articles, videos, podcasts, and online courses. This abundance of information empowers individuals to explore their interests and learn about new topics at their own pace.
- Digital Tools for Learning:A plethora of digital tools has emerged to support informal learning, such as learning management systems (LMS), mobile apps, and online simulations. These tools offer interactive learning experiences, personalized feedback, and progress tracking, making learning more engaging and effective.
- Virtual Communities:Online platforms and social media have fostered virtual communities where individuals with shared interests can connect, exchange ideas, and learn from each other. These communities provide a supportive environment for collaborative learning, mentorship, and knowledge sharing.
6. Informal Learning in Different Contexts
Informal learning, the process of acquiring knowledge and skills outside of structured educational settings, thrives in various contexts. From workplaces to communities and even our personal lives, informal learning plays a vital role in shaping our understanding, skills, and overall development.
Informal Learning in Workplaces
Informal learning is becoming increasingly prevalent in modern workplaces, complementing formal training programs and fostering a culture of continuous learning.Informal learning in workplaces can take various forms:
- Mentorship:Experienced employees guide and support junior colleagues, sharing their expertise and insights.
- Peer-to-peer learning:Colleagues collaborate, share knowledge, and learn from each other’s experiences, creating a collaborative learning environment.
- Knowledge sharing initiatives:Organizations facilitate knowledge sharing through platforms like online forums, wikis, and communities of practice, enabling employees to access and contribute to a collective knowledge base.
The impact of informal learning on workplaces is multifaceted:
- Enhanced employee performance:By acquiring new skills and knowledge through informal channels, employees can improve their performance and adapt to evolving job demands.
- Increased job satisfaction:Employees who engage in informal learning feel more valued and motivated, leading to higher job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
- Organizational innovation:Informal learning fosters creativity and innovation, as employees can share ideas, experiment with new approaches, and develop solutions to complex challenges.
Organizations can foster a culture of informal learning by:
- Creating opportunities for interaction:Encouraging collaboration, mentorship, and peer-to-peer learning through dedicated programs and initiatives.
- Providing access to resources:Making relevant learning materials, tools, and technologies readily available to employees.
- Recognizing and rewarding informal learning:Acknowledging and rewarding employees’ efforts in engaging in informal learning activities.
Informal Learning in Educational Institutions
Informal learning plays a crucial role in complementing formal education within schools and universities, providing students with opportunities to explore their interests, develop critical thinking skills, and engage in real-world experiences.Examples of informal learning in educational institutions include:
- Student-led initiatives:Students organize clubs, societies, and projects, pursuing their passions and learning through hands-on experiences.
- Extracurricular activities:Sports, arts, and other extracurricular activities provide opportunities for students to develop teamwork, leadership, and other valuable skills.
- Community engagement programs:Schools and universities partner with local communities, enabling students to engage in service learning and gain practical experience.
Informal learning in educational settings has a significant impact on student development:
- Increased student engagement:Informal learning activities make learning more engaging and relevant, fostering a sense of ownership and motivation among students.
- Enhanced critical thinking skills:Informal learning encourages students to think critically, solve problems creatively, and develop independent learning skills.
- Improved overall well-being:Engaging in informal learning activities promotes social interaction, emotional intelligence, and overall well-being among students.
Integrating informal learning practices into existing educational frameworks presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Balancing formal and informal learning:Finding the right balance between structured learning and informal exploration is crucial for a holistic educational experience.
- Assessing informal learning:Developing effective methods to assess the learning outcomes and impact of informal learning activities is essential.
- Providing support and resources:Ensuring adequate resources, mentorship, and guidance for students to engage in meaningful informal learning experiences is vital.
Informal Learning in Communities
Informal learning plays a vital role in community development, fostering social cohesion, cultural preservation, and economic growth.Examples of informal learning in communities include:
- Community centers:These centers provide spaces for residents to gather, learn new skills, and participate in community activities.
- Workshops and classes:Local organizations and individuals offer workshops and classes on a wide range of topics, from gardening to technology to arts and crafts.
- Volunteer programs:Community members volunteer their time and skills to support local initiatives, gaining valuable experience and contributing to their community.
Informal learning has a significant impact on communities:
- Enhanced community cohesion:Informal learning fosters social interaction and collaboration, strengthening community bonds and promoting a sense of belonging.
- Increased social capital:Informal learning activities build trust, networks, and shared knowledge, enhancing the overall social capital of a community.
- Economic development:By equipping individuals with new skills and knowledge, informal learning can contribute to economic development and job creation within communities.
Supporting and promoting informal learning initiatives within communities presents challenges and opportunities:
- Resource allocation:Ensuring adequate funding and resources for community-based informal learning programs is essential.
- Accessibility:Making informal learning opportunities accessible to all members of the community, regardless of age, background, or ability, is crucial.
- Collaboration and partnerships:Fostering collaboration between community organizations, schools, and other stakeholders is vital for creating a vibrant and sustainable informal learning ecosystem.
Informal Learning in Personal Lives
Informal learning shapes our individual growth and development outside of formal educational settings, enabling us to pursue our passions, acquire new skills, and expand our horizons.Examples of informal learning in personal lives include:
- Hobbies:Engaging in hobbies like painting, music, or gardening provides opportunities for learning, creativity, and personal fulfillment.
- Personal projects:Pursuing personal projects, such as writing a book, learning a new language, or building a website, fosters self-directed learning and a sense of accomplishment.
- Self-directed learning:Utilizing online resources, books, and other materials to learn new skills or expand knowledge independently.
Informal learning has a profound impact on our personal lives:
- Enhanced personal skills:Informal learning allows us to develop skills that are not necessarily taught in formal settings, such as problem-solving, creativity, and communication.
- Knowledge acquisition:Informal learning enables us to acquire new knowledge and perspectives, expanding our understanding of the world and ourselves.
- Improved overall well-being:Engaging in informal learning activities can promote a sense of purpose, satisfaction, and overall well-being.
Facilitating self-directed informal learning in the digital age presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Information overload:Navigating the vast amount of information available online and identifying reliable sources can be challenging.
- Distractions:The digital environment can be distracting, making it difficult to focus on learning goals.
- Digital literacy:Developing digital literacy skills, including critical thinking, information evaluation, and online safety, is crucial for effective self-directed learning.
Measuring and Evaluating Informal Learning
Informal learning, as we’ve explored, is a powerful force in personal and professional development. However, its very nature—spontaneous, often unplanned, and diverse—presents challenges when it comes to measuring its impact. This section delves into methods and approaches to assess the effectiveness and impact of informal learning, addressing the unique difficulties it presents and exploring tools and frameworks for evaluation.
Challenges of Measuring Informal Learning Outcomes
The inherent characteristics of informal learning make traditional assessment methods, often designed for structured learning environments, less effective. Here are some key challenges:
- Defining Learning Outcomes:Informal learning often lacks clearly defined objectives. It’s more about exploration, discovery, and the acquisition of skills or knowledge that may not be easily quantifiable. For example, a person learning to code through online tutorials may not have a specific set of skills in mind, but rather a desire to gain a general understanding of programming.
- Identifying and Tracking Learning Experiences:Informal learning can occur across a wide range of settings and through diverse activities. Tracking and documenting these experiences can be difficult. Consider someone learning about photography by watching YouTube videos, attending workshops, and experimenting with their camera.
Documenting all these experiences for evaluation can be challenging.
- Attributing Learning to Informal Sources:It’s often difficult to isolate the specific impact of informal learning from other sources of knowledge and skills. An individual’s professional success might be due to a combination of formal education, on-the-job training, and informal learning. Attributing specific achievements to informal learning alone can be problematic.
Alternative Assessment Strategies
Given the challenges of traditional methods, alternative approaches are necessary to evaluate informal learning. These strategies focus on understanding the process and outcomes of learning, rather than simply measuring quantifiable results:
- Self-Assessment:Encourage learners to reflect on their learning experiences and identify the skills and knowledge they’ve gained. This can involve journaling, creating portfolios, or engaging in self-evaluation tools.
- Portfolio Assessment:This method involves collecting evidence of learning, such as projects, presentations, or articles, to demonstrate the learner’s growth and development. It provides a holistic view of their learning journey.
- Peer Assessment:Learners can provide feedback to each other on their work and learning experiences. This collaborative approach can help identify areas of strength and areas for improvement.
- Observation and Interviews:Observing learners in action and conducting interviews can provide valuable insights into their learning processes and outcomes. This method allows for a more qualitative assessment of informal learning.
Tools and Frameworks for Evaluating Informal Learning
Several tools and frameworks can assist in evaluating informal learning experiences and outcomes. Here are some examples:
- Informal Learning Inventory:This tool helps individuals identify their informal learning activities and assess their impact on their skills and knowledge. It can be used to track learning experiences over time.
- The 70-20-10 Model:This framework suggests that 70% of learning occurs through on-the-job experiences, 20% through interactions with others, and 10% through formal training. This model emphasizes the importance of informal learning in professional development.
- The GROW Model:This coaching tool can be used to facilitate self-reflection and identify learning goals, current reality, options for improvement, and a plan for action. It can be adapted for evaluating informal learning experiences.
Strategies for Fostering Informal Learning
Informal learning thrives when individuals and organizations actively cultivate an environment that encourages exploration, knowledge sharing, and continuous learning. This section will explore strategies for promoting informal learning in various settings.
Creating Environments that Encourage Curiosity and Exploration
Encouraging curiosity and exploration is crucial for fostering informal learning. This involves creating an environment where individuals feel comfortable asking questions, experimenting, and taking risks. Several strategies can help cultivate this environment:
- Promote a culture of questioning: Encourage individuals to ask questions, even if they seem basic or obvious. Create a safe space where people feel comfortable expressing their curiosity without fear of judgment.
- Provide opportunities for experimentation: Offer individuals opportunities to try new things, make mistakes, and learn from their experiences. This could involve setting up “playgrounds” where people can experiment with new tools and technologies or providing access to resources that allow for exploration.
- Foster a growth mindset: Encourage individuals to view challenges as opportunities for learning and growth. This involves emphasizing the importance of effort, perseverance, and learning from mistakes.
Fostering Knowledge Sharing
Knowledge sharing is a cornerstone of informal learning. Individuals learn from each other by sharing their experiences, insights, and perspectives. Here are some strategies for fostering knowledge sharing:
- Create platforms for knowledge sharing: Establish online forums, discussion groups, or knowledge bases where individuals can share their knowledge and expertise. This could involve using online platforms like Slack, Yammer, or internal wikis.
- Encourage peer-to-peer learning: Promote opportunities for individuals to learn from each other through mentoring, coaching, or peer-to-peer training sessions.
- Recognize and reward knowledge sharing: Acknowledge and reward individuals who actively share their knowledge and expertise. This could involve providing recognition, incentives, or opportunities for advancement.
Encouraging Continuous Learning
Informal learning is an ongoing process. Organizations should provide opportunities and resources for individuals to continue learning throughout their careers. Here are some strategies for encouraging continuous learning:
- Provide access to learning resources: Offer access to online courses, books, articles, and other learning materials that support continuous learning. This could involve subscribing to online learning platforms or providing access to internal libraries and databases.
- Encourage participation in conferences and workshops: Support individuals’ participation in industry conferences, workshops, and other learning events. This provides opportunities for networking, learning from experts, and staying up-to-date on industry trends.
- Promote a culture of continuous learning: Create a culture where learning is valued and encouraged. This involves setting expectations for continuous learning, providing opportunities for professional development, and recognizing individuals who are committed to lifelong learning.
The Future of Informal Learning: Which Of The Following Is True Of Informal Learning
The future of informal learning is brimming with exciting possibilities, driven by technological advancements and evolving learning paradigms. Emerging trends are transforming how individuals acquire knowledge and skills, leading to a more personalized, accessible, and engaging learning experience.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of informal learning. AI-powered learning platforms can personalize learning experiences, providing customized content and recommendations based on individual needs and learning styles.
- AI-powered chatbots can offer real-time assistance and guidance, answering questions and providing personalized feedback.
- AI algorithms can analyze learning data to identify knowledge gaps and recommend relevant learning resources.
- AI-driven adaptive learning platforms can adjust the difficulty level of learning materials in real-time, ensuring that learners are challenged but not overwhelmed.
The Rise of Virtual Reality, Which of the following is true of informal learning
Virtual reality (VR) is emerging as a powerful tool for creating immersive and engaging learning experiences. VR environments can simulate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- VR simulations can provide hands-on training for complex tasks, such as surgery or piloting an aircraft.
- VR can be used to create interactive museum exhibits and historical reenactments, bringing learning to life.
- VR can facilitate collaborative learning experiences, allowing learners to interact with each other in virtual environments.
Personalized Learning Platforms
Personalized learning platforms are gaining popularity, providing learners with tailored learning experiences based on their individual needs, interests, and learning styles. These platforms leverage data analytics and AI to create personalized learning paths and recommendations.
- Personalized learning platforms can provide learners with access to a vast library of learning resources, including videos, articles, and interactive exercises.
- Learners can track their progress and receive personalized feedback, helping them stay motivated and on track.
- Personalized learning platforms can connect learners with peers and mentors, fostering a sense of community and support.
Detailed FAQs
What are some examples of informal learning in everyday life?
Examples include learning a new recipe from a friend, picking up a new language through immersion, gaining practical skills from a hobby, or acquiring knowledge through online forums and social media.
How can I make the most of informal learning opportunities?
Be curious, seek out new experiences, engage in conversations, experiment with different learning methods, and reflect on your learning journey.
Is informal learning as valuable as formal education?
While formal education provides structured knowledge and credentials, informal learning complements and enriches our learning experiences. It helps us develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and adaptability skills, which are highly valued in today’s world.
How can technology enhance informal learning?
Technology provides access to vast online resources, educational platforms, virtual communities, and personalized learning experiences, making informal learning more accessible and engaging.