Which are the most difficult languages to learn – Which languages are the hardest to learn sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The quest to decipher the complexities of foreign tongues is a fascinating journey, one that often leads us down winding paths of cultural exploration and linguistic discovery.
From the intricate tones of Mandarin to the intricate grammar of Hungarian, the world is a tapestry of languages, each with its unique challenges and rewards.
This exploration delves into the factors that make some languages notoriously difficult to learn, examining linguistic features, cultural context, and the availability of learning resources. We’ll explore the subjective nature of language learning, acknowledging that what one person finds challenging, another may find relatively easy.
We’ll also uncover the power of motivation, mindset, and the transformative impact of technology on our ability to conquer new languages.
Defining Difficulty
The idea of “difficult languages” is a common one, but it’s crucial to understand that language learning difficulty is not a fixed or objective measure. Instead, it’s a subjective experience influenced by various factors unique to each learner.
Subjectivity of Language Learning
The perceived difficulty of a language can vary greatly from person to person. For instance, a native Spanish speaker might find Portuguese relatively easy to learn due to its similarities, while a native English speaker might find it more challenging.
Similarly, someone with a strong background in linguistics might find the complexities of a language like Finnish fascinating, while another learner might find it overwhelming.Personal experiences and perspectives play a significant role in shaping how challenging a language appears. Previous language learning experiences, cultural exposure, and even personal motivations can influence how readily a learner embraces the challenges of a new language.
Factors Influencing Learning Experiences
Several factors can influence the overall learning experience and contribute to the perceived difficulty of a language.
Native Language
Language families and their relationships can significantly impact learning difficulty. Languages within the same family often share similarities in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, making them easier to learn for speakers of related languages. For example, a native Spanish speaker might find learning Italian or Portuguese relatively straightforward due to their shared Latin roots.
Conversely, languages from different families, such as English and Japanese, often have very different grammatical structures and sound systems, leading to greater challenges for learners.
Learning Style
Learning styles are another crucial factor influencing language acquisition. Visual learners might excel at learning through flashcards and diagrams, while auditory learners might prefer listening to audio recordings and engaging in conversations. Kinesthetic learners might benefit from hands-on activities like role-playing and using physical objects to represent vocabulary.
Understanding your preferred learning style allows you to tailor your learning strategies to maximize your success.
Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is arguably the most important factor in language learning. When you are genuinely interested in a language, have clear goals, or feel a personal connection to the culture, you are more likely to persevere through challenges and find joy in the learning process.
Factors like interest, goals, and personal connections to a language can significantly influence your learning success.
Challenging Language Features
While the subjective nature of language learning is important, certain language features can objectively pose challenges for learners.
Pronunciation
Pronunciation can be a significant hurdle for learners. Different languages have unique sound systems, tones, and accents. Languages like Mandarin Chinese, with its four tones, or Arabic, with its complex consonant sounds, can present significant challenges for learners unfamiliar with these features.
Grammar
Grammatical structures can also be challenging. Verb conjugation, word order, and gender agreement are just a few examples of grammatical features that can vary significantly between languages. Languages like German, with its complex noun declension system, or Finnish, with its numerous grammatical cases, can be particularly challenging in this regard.
Vocabulary
Most languages have a vast vocabulary, making memorizing new words and phrases a significant undertaking. The sheer number of words and their associated meanings can be overwhelming for learners, especially in the initial stages. Effective vocabulary acquisition strategies, such as using flashcards, spaced repetition, and contextual learning, are essential for building a strong vocabulary foundation.
Linguistic Complexity
Beyond the sheer number of speakers, another key factor in language learning difficulty is linguistic complexity. This refers to the inherent structure and features of a language, which can make it more or less challenging to grasp for speakers of other languages.
Linguistic Features Contributing to Difficulty
Several linguistic features contribute to the complexity of a language. These features can be grouped and analyzed to understand how they impact learning difficulty.
| Feature | Description | Example | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Writing System | The way a language is written, including the alphabet, script, and symbols. | Arabic uses a right-to-left script, with characters that connect and change form depending on their position in a word. | High for speakers of languages with different writing systems. |
| Grammar | The rules governing sentence structure, word order, and verb conjugation. | In German, verbs are often placed at the end of a sentence, while in English, they typically come before the object. | High for languages with complex grammatical rules, especially for verb conjugation and word order. |
| Pronunciation | The sounds of a language, including vowels, consonants, and tones. | Mandarin Chinese has four tones, which can change the meaning of a word. | High for languages with sounds that are not present in the learner’s native language. |
| Vocabulary | The words and phrases used in a language. | Japanese has many homophones, words that sound the same but have different meanings. | High for languages with large and complex vocabularies. |
| Sentence Structure | The arrangement of words and phrases in a sentence. | In Latin, the subject of a sentence can come after the verb, unlike in English. | High for languages with complex sentence structures. |
| Tonal Languages | Languages where the pitch of a word changes its meaning. | In Thai, the same word pronounced with different tones can mean “to eat,” “to buy,” or “to die.” | High for speakers of non-tonal languages. |
Comparison of Language Family Complexity
Language families, groups of languages with a common ancestor, can also be compared based on their complexity. For instance, the Indo-European family, which includes English, French, Spanish, and German, is generally considered to have relatively simpler grammar compared to the Semitic family, which includes Arabic and Hebrew.
The Semitic family features complex verb conjugation and noun morphology, which can be challenging for learners. Similarly, the Sino-Tibetan family, which includes Chinese, Tibetan, and Burmese, often presents challenges due to its tonal nature and complex writing systems.
3. Cultural Immersion

Language learning is not just about memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules. It’s about understanding the culture that surrounds the language. Cultural immersion is crucial for achieving fluency and truly appreciating the richness of a language.
3.1 Importance of Cultural Context
Cultural context plays a vital role in understanding the nuances of language. It provides a framework for interpreting meaning beyond the literal words. For example, idioms and metaphors are often rooted in cultural experiences and traditions. The phrase “kick the bucket” in English refers to death, but its meaning is not immediately obvious without understanding the cultural context.
Similarly, metaphors like “raining cats and dogs” or “a fish out of water” rely on shared cultural experiences for their effectiveness.Humor is another area where cultural context is essential. Jokes often rely on cultural references, shared beliefs, and social norms.
What might be funny in one culture might be offensive or incomprehensible in another. Neglecting cultural context can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and even social blunders. For example, using a phrase that is considered polite in one culture might be seen as disrespectful in another.
3.2 Impact of Cultural Norms and Values
Cultural norms and values shape communication styles, influencing how people interact with each other. These norms can vary significantly across cultures, affecting factors like politeness, directness, and formality.For instance, in some cultures, direct communication is valued, while in others, indirect communication is preferred.
This can lead to misunderstandings if individuals from different cultures are not aware of these differences. Similarly, levels of formality in language can vary depending on the relationship between speakers and the social context.Understanding cultural values can enhance intercultural communication skills.
By being aware of the different ways people communicate and the underlying cultural norms, individuals can avoid misunderstandings and build stronger relationships.
3.3 Examples of Cultural Immersion
There are many ways to immerse oneself in a new culture. Activities like watching movies, reading literature, and interacting with native speakers can provide valuable insights into the culture and language.Participating in cultural events, festivals, and celebrations can also be a rewarding way to experience a new culture firsthand.
These events offer opportunities to observe cultural traditions, interact with locals, and learn about the history and values of the culture.For example, attending a traditional dance performance or a religious ceremony can provide a deeper understanding of the culture’s beliefs and practices.
Similarly, participating in a local festival or celebration can provide insights into the culture’s traditions and values.Cultural immersion can significantly improve language proficiency and cultural understanding. By engaging with the culture in a meaningful way, learners can develop a deeper understanding of the language and its nuances.
4. Learning Resources
The availability and quality of learning resources can significantly impact the ease and effectiveness of learning a new language. This section will analyze the learning resources available for two target languages, focusing on the types of resources and their effectiveness in facilitating language acquisition.
4.1 Availability and Quality of Learning Resources
This section explores the range and quality of learning resources available for two target languages, comparing the abundance, variety, and quality of resources for each.
- Textbooks: These provide a structured approach to language learning, covering grammar, vocabulary, and often cultural aspects.
- Online Courses: These offer flexible learning opportunities, with varying levels of interaction and support.
- Language Exchange Platforms: These connect learners with native speakers for conversational practice.
- Immersion Schools: These provide a full-immersion environment, promoting rapid language acquisition.
- Language Learning Apps: These offer gamified learning experiences, focusing on vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
| Resource Type | Target Language 1 | Target Language 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Textbooks | Abundant, high quality | Limited, mixed quality |
| Online Courses | Varied, some excellent | Few, mostly beginner level |
| Language Exchange Platforms | Numerous, active communities | Limited options, less active |
| Immersion Schools | Widely available, reputable programs | Limited availability, fewer options |
| Language Learning Apps | Many options, diverse features | Fewer options, limited features |
4.2 Effectiveness of Different Learning Methods
This section compares the effectiveness of different learning methods, considering their strengths and weaknesses in facilitating specific learning outcomes.
- Textbooks:
- Pros: Structured learning, comprehensive grammar coverage.
- Cons: Can be dry and repetitive, limited real-world application.
- Online Courses:
- Pros: Flexible learning, interactive elements, access to diverse instructors.
- Cons: Can lack personal interaction, quality varies significantly.
- Language Exchange Programs:
- Pros: Immersive practice, natural language acquisition, cultural exchange.
- Cons: Requires commitment, potential for uneven language proficiency among participants.
- Immersion Schools:
- Pros: Full immersion, rapid language acquisition, cultural immersion.
- Cons: Can be expensive, requires significant time commitment.
- Language Learning Apps:
- Pros: Gamified learning, convenient access, focused on specific skills.
- Cons: Can be limited in scope, may not provide comprehensive language learning.
4.3 Challenges Associated with Limited Resources
This section identifies challenges associated with limited learning resources and suggests potential solutions to overcome them.
- Challenge: Lack of authentic materials for pronunciation practice.
- Solution: Utilize online resources like YouTube videos, podcasts, and language exchange platforms with native speakers.
- Challenge: Limited access to qualified instructors.
- Solution: Explore online tutoring platforms, language exchange groups, or seek out local language communities.
- Challenge: Difficulty in finding comprehensive learning materials for advanced learners.
- Solution: Seek out specialized textbooks, online courses, or engage in self-directed learning using authentic materials like books, articles, and movies.
- Challenge: Lack of opportunities for cultural immersion.
- Solution: Engage in online cultural exchange programs, attend cultural events, or connect with native speakers online.
Language Families and Their Characteristics

Understanding the family tree of languages can offer valuable insights into their similarities, differences, and inherent complexities. Languages within the same family often share common roots, vocabulary, and grammatical structures, making them easier to learn for speakers of related languages.
Language Families and Their Characteristics
Language families group languages with shared ancestry, reflecting their historical evolution and common linguistic features. This classification helps understand the relationships between languages and their potential learning difficulties.
| Family | Languages | Characteristics | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indo-European | English, Spanish, French, German, Hindi, Russian | Rich in verb conjugation, complex noun declension, and extensive vocabulary. | Generally considered moderately difficult for native English speakers, with variations depending on the specific language. |
| Sino-Tibetan | Mandarin Chinese, Cantonese, Tibetan | Tonal languages with a complex writing system and a focus on grammatical particles. | Considered very difficult for native English speakers due to the tonal system and unfamiliar writing system. |
| Afro-Asiatic | Arabic, Hebrew, Amharic, Berber | Semitic languages have a complex verb system and a focus on root consonants. | Generally considered difficult for native English speakers, with Arabic being particularly challenging due to its script and grammatical structures. |
| Austronesian | Malay, Indonesian, Tagalog, Hawaiian | Highly agglutinative languages with complex verb morphology and a focus on prefixes and suffixes. | Generally considered moderately difficult for native English speakers, with variations depending on the specific language. |
The difficulty level is subjective and can vary depending on the learner’s native language, motivation, and learning methods. However, languages within the same family often share similarities that can make learning easier for speakers of related languages. For instance, a Spanish speaker might find Portuguese relatively easier to learn than Japanese due to shared vocabulary and grammatical structures.
Conversely, languages from different families, such as English and Japanese, often present greater challenges due to their distinct linguistic features and lack of shared ancestry. This table provides a general overview of language families and their characteristics. It is important to remember that each language has its own unique features and complexities, and the difficulty level can vary significantly depending on the individual learner.
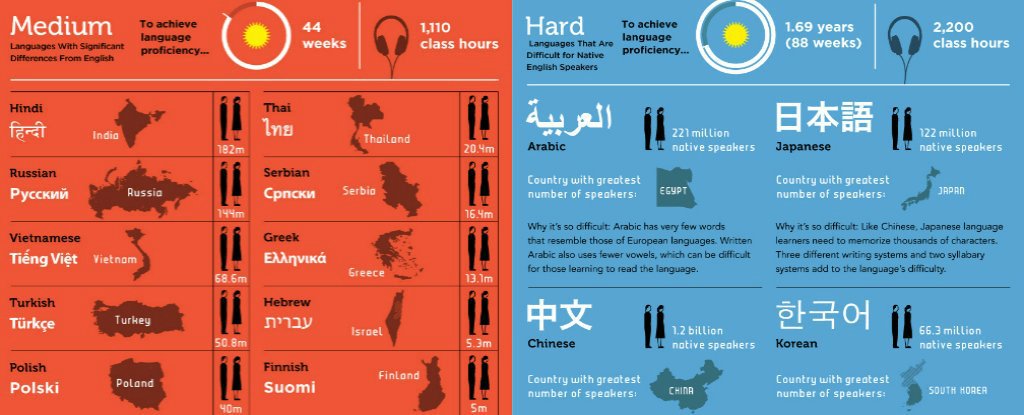
Commonly Cited Difficult Languages
It’s natural to wonder which languages are considered the most challenging to learn. While the difficulty of learning a language is subjective and depends on various factors, certain languages are consistently mentioned as being particularly tough.
Languages Often Deemed Difficult
The perceived difficulty of a language is often attributed to factors like grammar complexity, writing system, pronunciation, and cultural differences. Here are some languages frequently cited as difficult for English speakers:
| Language | Family | Difficulty Factors | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandarin Chinese | Sino-Tibetan | Tonal system, complex writing system (characters), different grammatical structures | “你好” (nǐ hǎo)
|
| Japanese | Japonic | Three writing systems (hiragana, katakana, kanji), complex grammar, honorifics | “こんにちは” (konnichiwa)
|
| Arabic | Semitic | Right-to-left writing, complex verb conjugation, different alphabet | “مرحبا” (marhabaan) Trying to figure out which languages are the toughest to learn? It’s a bit like asking how long it takes to learn a manual – it really depends on your background and the manual itself! How long does it take to learn manual is a similar question, with the answer depending on the complexity of the manual and your familiarity with the subject. Similarly, languages like Mandarin or Arabic have different levels of difficulty for different learners. So, the best way to figure out how hard a language will be for you is to dive in and see how it feels!
|
| Korean | Koreanic | Unique writing system (Hangul), complex grammar, different sentence structure | “안녕하세요” (annyeonghaseyo)
|
| Hungarian | Uralic | Complex grammar with numerous suffixes, different word order, vowel harmony | “Szia”
|
| Finnish | Uralic | Complex grammar with agglutination, vowel harmony, different sentence structure | “Hei”
|
| Icelandic | North Germanic | Complex grammar, archaic vocabulary, distinct pronunciation | “Hæ”
|
| Polish | West Slavic | Complex grammar, numerous declensions, different pronunciation | “Cześć”
|
| Russian | East Slavic | Complex grammar, Cyrillic alphabet, different pronunciation | “Привет” (privet)
|
| Greek | Indo-European | Complex grammar, different alphabet, distinct pronunciation | “Γειά σου” (ya sou)
|
7. Tips for Learning Difficult Languages
Learning a challenging language can feel like climbing a steep mountain. It requires dedication, persistence, and a well-planned approach. But don’t worry, you’re not alone on this journey. With the right strategies, you can conquer any language learning challenge and unlock the doors to a new world of communication and cultural understanding.
Setting Goals and Motivation
It’s essential to set realistic and achievable goals to stay motivated and make progress. Break down your language learning journey into smaller, manageable steps. For example, instead of aiming to become fluent in a year, focus on achieving specific milestones like learning basic greetings, mastering verb conjugations, or reading a short story.
- Tip:Set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Explanation:SMART goals provide clarity, direction, and a sense of accomplishment as you progress.
- Example:Instead of saying, “I want to learn Japanese,” you could say, “I want to learn how to introduce myself and ask basic questions in Japanese within the next three months.”
- Tip:Find a language buddy or join a language learning group.
- Explanation:Having someone to learn with can provide support, motivation, and a sense of accountability.
- Example:You could find a language exchange partner online or join a local language meetup group.
- Tip:Reward yourself for reaching milestones.
- Explanation:Positive reinforcement can help you stay motivated and engaged.
- Example:You could treat yourself to a delicious meal, watch a movie in the target language, or buy yourself a new book in that language.
Vocabulary Acquisition
Expanding your vocabulary is crucial for understanding and expressing yourself in a new language. Don’t try to memorize everything at once. Focus on learning words and phrases that are relevant to your interests and goals.
- Tip:Use flashcards or spaced repetition software.
- Explanation:These tools help you learn new words efficiently by reviewing them at spaced intervals.
- Example:Popular spaced repetition software includes Anki and Memrise.
- Tip:Learn words in context.
- Explanation:This helps you understand the nuances of word usage and remember them more easily.
- Example:Instead of just memorizing the word “beautiful,” learn it in a sentence like “The sunset was beautiful.”
- Tip:Create a vocabulary notebook or use a digital vocabulary tracker.
- Explanation:This helps you organize your vocabulary and track your progress.
- Example:You could write down new words with their definitions, example sentences, and related words.
Grammar Mastery
Grammar is the foundation of any language. Understanding grammatical structures and rules is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences and communicating effectively.
- Tip:Use grammar exercises and online resources.
- Explanation:These resources can help you practice applying grammar rules in different contexts.
- Example:Websites like Grammarly and Duolingo offer interactive grammar exercises.
- Tip:Break down complex grammatical concepts into smaller, manageable parts.
- Explanation:This makes learning grammar less overwhelming and more accessible.
- Example:Instead of trying to learn all verb tenses at once, focus on mastering one tense at a time.
- Tip:Find a language partner or tutor.
- Explanation:A language partner can help you practice your grammar skills in real-time and provide feedback.
- Example:You could find a language partner online or through a local language exchange program.
Pronunciation and Speaking
Pronunciation is crucial for clear communication and understanding. Even if your grammar is perfect, your pronunciation can make it difficult for others to understand you.
- Tip:Use phonetic transcriptions and pronunciation practice apps.
- Explanation:These tools can help you learn the correct pronunciation of sounds and words.
- Example:Apps like Forvo and Babbel offer pronunciation practice features.
- Tip:Record yourself speaking and listen back to identify areas for improvement.
- Explanation:This helps you become more aware of your pronunciation and identify any mistakes.
- Example:You could use your phone’s voice recorder or a dedicated recording app.
- Tip:Practice speaking with native speakers or language partners.
- Explanation:This is the best way to improve your pronunciation and fluency.
- Example:You could find a language partner online or through a local language exchange program.
Immersion and Practice
Immersion is a powerful tool for language learning. Surrounding yourself with the target language can accelerate your progress and enhance your understanding.
- Tip:Watch movies, TV shows, and documentaries in the target language.
- Explanation:This helps you get accustomed to the sounds and rhythms of the language.
- Example:You could watch movies with subtitles or use language learning apps like Netflix and Duolingo.
- Tip:Listen to music and podcasts in the target language.
- Explanation:This helps you learn new vocabulary and improve your listening comprehension.
- Example:You could listen to music on Spotify or Apple Music or find podcasts on platforms like Stitcher and Google Podcasts.
- Tip:Read books, articles, and websites in the target language.
- Explanation:This helps you expand your vocabulary and improve your reading comprehension.
- Example:You could start with children’s books or graded readers and gradually move on to more challenging texts.
Overcoming Discouragement
Learning a new language can be challenging, and it’s natural to experience moments of frustration and setbacks. But don’t give up! Remember that progress is not always linear.
- Tip:Celebrate small victories.
- Explanation:This helps you stay motivated and recognize your progress.
- Example:You could celebrate learning a new verb, understanding a conversation, or reading a page of a book in the target language.
- Tip:Don’t be afraid to make mistakes.
- Explanation:Mistakes are a part of the learning process. They provide opportunities for growth and improvement.
- Example:Don’t be afraid to ask questions and seek clarification when you’re unsure about something.
- Tip:Find a language learning community or online forum.
- Explanation:Connecting with other learners can provide support, motivation, and a sense of belonging.
- Example:You could join a language learning group on Facebook or Reddit.
The Impact of Technology on Language Learning
Technology has revolutionized the way we learn languages, offering a plethora of tools and resources that were previously unimaginable. From language learning apps to online communities, technology has made language acquisition more accessible, engaging, and effective than ever before.
The Role of Technology in Language Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in language learning by providing a wide range of tools and resources that enhance the learning experience. These tools can be categorized based on their functions, advantages, and disadvantages.
| Technology | Function | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language Learning Apps | Provide interactive lessons, exercises, and games to improve vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. | Convenient, accessible, and often personalized to the learner’s needs. | Can be repetitive and lack real-world context. |
| Online Dictionaries and Translators | Provide definitions, translations, and pronunciation guides for words and phrases. | Instant access to information and support for understanding new words. | Can lead to over-reliance and hinder the development of independent language skills. |
| Language Exchange Platforms | Connect learners with native speakers for conversation practice and cultural exchange. | Immersive and authentic language practice with native speakers. | Can be challenging to find reliable and compatible partners. |
| Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) | Create immersive learning environments that simulate real-world scenarios. | Engaging and interactive, allowing learners to practice language skills in realistic contexts. | Can be expensive and require specialized equipment. |
| Language Learning Websites and Blogs | Offer comprehensive resources, including lessons, articles, and videos on various language topics. | Wide range of information and perspectives on language learning. | Can be overwhelming and lack structure for structured learning. |
Technology Simplifying Language Acquisition
Technology simplifies language acquisition by making learning more accessible, engaging, and efficient.
“Technology has democratized language learning, allowing individuals to access resources and connect with others regardless of their location or background.”
For example, language learning apps provide personalized learning paths, adaptive exercises, and interactive games that cater to individual learning styles and preferences. This personalized approach allows learners to focus on their specific needs and weaknesses, leading to faster progress. Additionally, technology allows learners to access authentic language materials, such as movies, music, and news articles, which provides them with exposure to real-world language use and helps them develop fluency and natural communication skills.
Technology Complicating Language Acquisition
While technology offers numerous benefits, it can also complicate language acquisition by creating distractions, fostering over-reliance on technology, and hindering the development of essential language skills.
“The over-reliance on technology can lead to a superficial understanding of the language and hinder the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.”
For instance, the use of online translators can lead to a lack of effort in memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules, hindering the development of independent language skills. Additionally, the constant stream of notifications and distractions from social media and other online platforms can hinder focus and concentration, making it difficult for learners to engage fully with language learning materials.
9. The Importance of Motivation and Mindset
The journey of learning a new language is often described as a marathon, not a sprint. While dedication and effort are essential, they are not enough to ensure success. Motivation and mindset play a crucial role in driving learners to persevere through challenges and achieve their language learning goals.
The Power of Motivation
Motivation is the driving force behind our actions. It determines how much effort we invest, how long we persist, and ultimately, how much we learn. There are two main types of motivation: intrinsic and extrinsic.Intrinsic motivation stems from a genuine interest in the language itself, a desire to explore new cultures, or a personal satisfaction in mastering a challenging skill.
This type of motivation is often described as “self-driven” and leads to a deeper level of engagement. Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, is driven by external rewards or pressures, such as getting a promotion, impressing others, or avoiding punishment.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation:| Type of Motivation | Benefits | Drawbacks ||—|—|—|| Intrinsic Motivation | Higher engagement, greater persistence, increased enjoyment, deeper understanding, improved learning outcomes | Can be challenging to sustain over the long term, may not be present in all learners || Extrinsic Motivation | Can provide initial impetus, can be helpful in short-term goals, can be used to create incentives | Can lead to superficial learning, can be demotivating if rewards are not received, can create dependence on external factors |
Mindset Matters, Which are the most difficult languages to learn
The power of a growth mindset in language learning cannot be overstated. A growth mindset believes that abilities can be developed through effort and dedication. Learners with a growth mindset embrace challenges as opportunities for learning and growth. They are not afraid of making mistakes, as they see them as stepping stones towards improvement.
> “The most important thing is to enjoy your work. When you enjoy your work, you will be more motivated to learn and grow.”
Carol Dweck, renowned psychologist and researcher
Cultivating Motivation
Maintaining motivation over the long term is crucial for success in language learning. Here are some practical strategies that learners can employ:
- Set Realistic Goals: Avoid setting overly ambitious goals that can lead to discouragement. Start with small, achievable goals and gradually increase the difficulty as you progress.
- Find Language Learning Buddies: Connect with other learners who share your passion for the language. Sharing experiences, challenges, and successes can provide encouragement and motivation.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge your progress and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small they may seem. This reinforces your sense of accomplishment and motivates you to continue learning.
- Make Learning Enjoyable: Find ways to make language learning fun and engaging. Explore different learning methods, listen to music, watch movies, read books, or participate in language exchange programs.
- Vary Your Learning Activities: Avoid monotony by incorporating a variety of learning activities into your routine. This keeps your learning experience fresh and prevents boredom.
Overcoming Challenges
Language learning is not always smooth sailing. Learners often face challenges that can test their motivation and mindset. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them: Q: What can I do if I’m afraid of making mistakes?A:Remember that mistakes are a natural part of the learning process.
Embrace them as opportunities for growth. Focus on the progress you’re making, not on the mistakes you’re making. Q: How can I avoid feeling overwhelmed by the amount of material?A:Break down your learning goals into smaller, manageable steps. Focus on one skill or concept at a time and gradually build your knowledge and fluency.
Q: What if I hit a plateau in my progress?A:Don’t get discouraged! Plateaus are a normal part of the learning curve. Reassess your learning strategies, try new methods, or seek guidance from a tutor or language exchange partner.
The Impact of Beliefs
Research has shown that positive beliefs about one’s ability to learn a language can significantly impact performance and confidence. Learners who believe they can succeed are more likely to persevere through challenges and achieve their goals. Conversely, negative beliefs can create self-doubt and hinder progress.
Cultivating a positive mindset by focusing on your strengths and past successes can empower you to overcome challenges and achieve your language learning goals.
The Personal Journey of Language Learning
The pursuit of learning a new language is a deeply personal journey, shaped by individual experiences, motivations, and challenges. It’s not just about mastering grammar and vocabulary; it’s about connecting with a new culture, expanding your worldview, and unlocking new opportunities.
Experiences of Language Learners
Understanding the challenges and successes of language learners provides valuable insights into the process of language acquisition. The table below showcases the diverse experiences of individuals who have embarked on the journey of learning a new language.
| Learner | Language | Challenges | Successes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarah | Mandarin Chinese | Tonal system, complex writing system, cultural differences | Ability to communicate with family in China, increased understanding of Chinese culture |
| David | Arabic | Right-to-left writing system, unfamiliar sounds, complex grammar | Reading Arabic literature, making friends with Arabic speakers, increased awareness of Middle Eastern culture |
| Maria | Japanese | Honorifics, complex writing system, cultural nuances | Enjoying Japanese films and music, understanding Japanese customs, increased confidence in intercultural communication |
| John | Spanish | Verb conjugations, gendered nouns, pronunciation | Travelling through Latin America, communicating with Spanish speakers, increased career opportunities |
Stories of Successful Language Acquisition
Language learning is often a journey marked by perseverance and the adoption of effective strategies. The following stories illustrate the power of dedication and the strategies employed by successful language learners.
“I started learning Japanese because I was fascinated by the culture and wanted to understand anime and manga better. I struggled with the writing system at first, but I found that creating flashcards and practicing regularly helped me memorize the characters. I also immersed myself in Japanese media, watching movies and listening to music. After a few years, I was able to read and write Japanese at a basic level, and I even started to understand some spoken Japanese.”Emily, a Japanese language learner.
“I was always intimidated by the idea of learning Mandarin Chinese, but I realized that it was something I truly wanted to do. I started with online resources and language exchange partners. I found that speaking with native speakers, even if it was just a few minutes a day, helped me improve my fluency. I also joined a local Chinese language class, which gave me the opportunity to practice with other learners and get feedback from a teacher.”
Michael, a Mandarin Chinese language learner.
The Benefits of Learning Difficult Languages
Embarking on the journey of learning a challenging language can be a daunting endeavor, but the rewards are truly profound. The act of mastering a complex linguistic system goes beyond simply acquiring new vocabulary and grammar rules; it unlocks a wealth of personal and professional benefits that enrich our lives in unexpected ways.
Personal Benefits
Learning a difficult language has a profound impact on personal growth and self-confidence. The process of overcoming the challenges of mastering a complex linguistic system fosters a sense of accomplishment and resilience. The ability to communicate effectively in a language that is significantly different from one’s native tongue instills a deep sense of pride and self-assurance.
- Enhanced Cognitive Abilities: Learning a new language has been shown to enhance cognitive abilities, including memory, problem-solving, and critical thinking. The brain is constantly challenged to process new information, make connections between concepts, and adapt to different linguistic structures, which strengthens these cognitive functions.
For example, memorizing vocabulary words and grammatical rules exercises memory, while understanding complex sentence structures and deciphering cultural nuances enhances problem-solving and critical thinking skills. The process of acquiring a new language stimulates brain plasticity, creating new neural pathways and improving cognitive flexibility.
- Psychological Benefits: Expanding one’s linguistic repertoire can have significant psychological benefits. The ability to communicate with people from different cultures and backgrounds fosters a sense of empathy and understanding. It breaks down barriers and promotes a more inclusive worldview. Learning a difficult language can also be a powerful tool for personal growth and self-discovery.
It challenges individuals to step outside of their comfort zones, embrace new perspectives, and develop a deeper appreciation for the diversity of human experience.
Professional Benefits
In today’s globalized world, multilingualism is a highly sought-after skill that opens doors to new career opportunities and enhances job prospects.
- Enhanced Job Prospects: In many industries, multilingualism is highly valued. For example, in fields such as international business, diplomacy, healthcare, and education, fluency in multiple languages is often a prerequisite for employment. Learning a difficult language can make one a more competitive candidate in the global job market, as it demonstrates a commitment to cross-cultural communication and a willingness to adapt to diverse work environments.
- Fostering Cross-Cultural Understanding: Language learning plays a crucial role in fostering cross-cultural understanding and communication. Fluency in a difficult language enables individuals to navigate diverse cultural contexts more effectively. It allows for deeper engagement with different perspectives, customs, and traditions. For example, a businessperson fluent in Mandarin Chinese can navigate complex business negotiations in China with greater sensitivity and understanding.
Multilingualism can facilitate international collaborations, cultural exchange, and promote a more harmonious global community.
The Future of Language Learning: Which Are The Most Difficult Languages To Learn
The landscape of language learning is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing learner needs. We’re witnessing a shift from traditional classroom settings to a more personalized, interactive, and accessible approach.
Emerging Trends in Language Learning
These trends are reshaping how we learn languages, offering more engaging and effective methods.
Trend Description Impact Example Personalized Learning Tailoring learning experiences to individual needs and learning styles, using adaptive technology and AI. Increased engagement, faster progress, and improved learning outcomes. Duolingo’s personalized learning paths based on user performance and goals. Gamification Incorporating game mechanics and design principles into language learning platforms to make learning more enjoyable and motivating. Increased engagement, improved motivation, and better retention of language skills. Memrise’s use of games and challenges to make learning vocabulary fun and interactive. Immersive Technologies Utilizing virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create immersive learning environments that simulate real-life situations. Enhanced language acquisition through realistic practice, improved cultural understanding, and increased motivation. VR language learning platforms that allow users to practice conversations in virtual settings. Artificial Intelligence (AI) AI-powered language learning tools that provide personalized feedback, adaptive learning paths, and conversational practice. Improved language fluency, personalized learning experiences, and access to real-time feedback. Chatbots that simulate conversations with native speakers, providing instant feedback and practice opportunities.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence
AI is revolutionizing language learning by offering personalized experiences and real-time feedback. AI-powered tools can analyze learner data, identify strengths and weaknesses, and provide customized learning paths. Chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly used for conversational practice, allowing learners to interact with native speakers in a safe and controlled environment.
This technology has the potential to make language learning more accessible and effective for individuals with diverse learning styles and needs.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some of the most common reasons why people find certain languages difficult to learn?
Many factors contribute to the perceived difficulty of a language, including the distance from your native language, the complexity of the writing system, grammar rules, pronunciation, and the availability of learning resources. For example, a language with a complex tonal system, like Mandarin Chinese, can be challenging for speakers of languages without tones.
Similarly, languages with highly complex grammar rules, such as Hungarian or Finnish, can pose significant challenges.
Is it true that some languages are inherently harder to learn than others?
It’s a common misconception that some languages are inherently “harder” than others. While some languages may present more challenges for certain learners, it ultimately depends on individual factors like native language, learning style, motivation, and the learner’s previous experience with language learning.
What’s important is to choose a language that interests you and that you’re motivated to learn.
What are some tips for staying motivated when learning a difficult language?
Maintaining motivation is crucial for success in language learning. Here are a few tips: Set realistic goals, find a language learning buddy, celebrate milestones, immerse yourself in the language through movies, music, and books, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes.
Remember that learning a language is a journey, not a race, and progress takes time and effort.