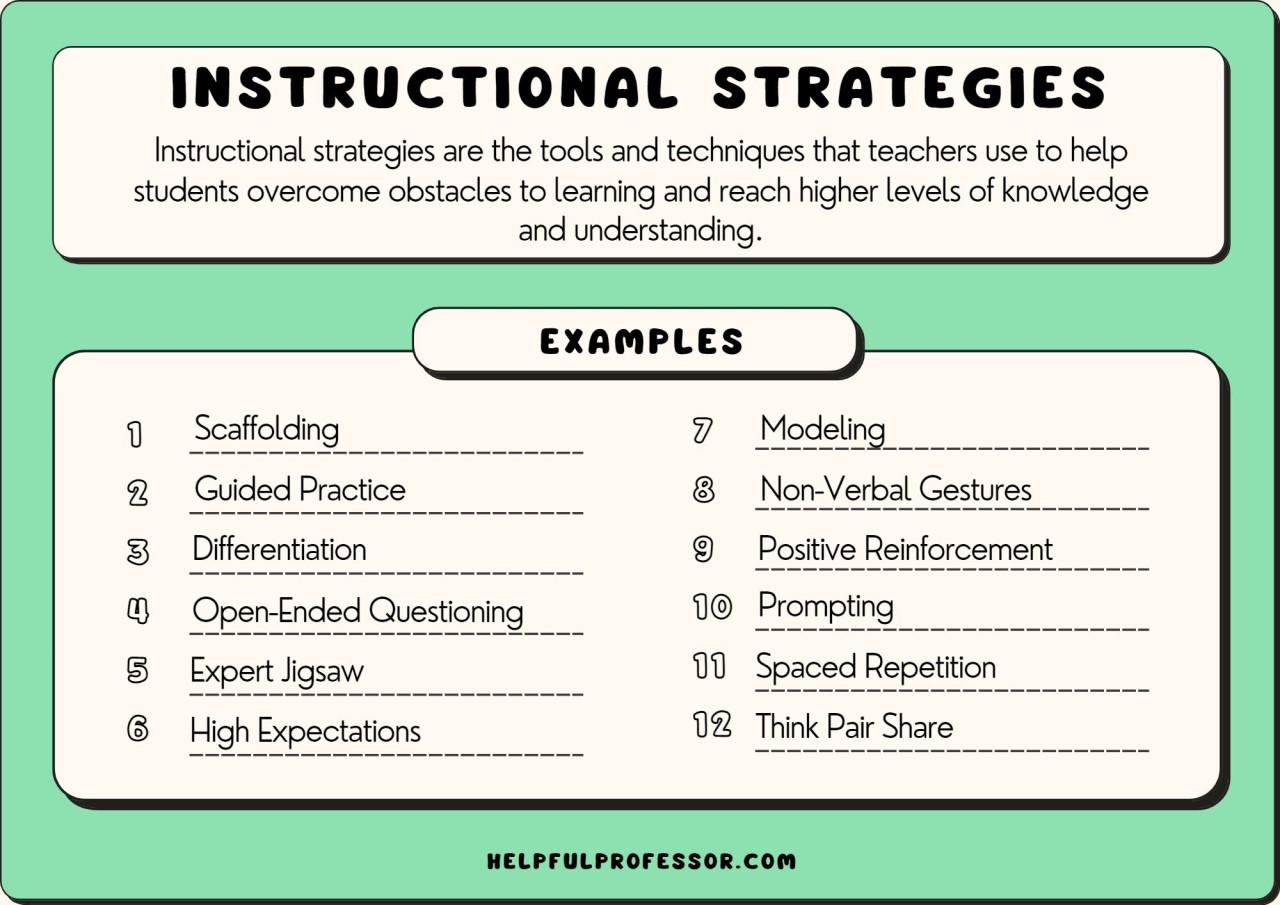
What is applied learning? It’s more than just memorizing facts; it’s about taking what you learn and using it to solve real-world problems. Imagine a scientist studying a disease in a lab, then applying that knowledge to develop a new treatment.
That’s applied learning in action! It’s about bridging the gap between theory and practice, making learning relevant and engaging.
Applied learning encourages active participation, hands-on experiences, and critical thinking. It goes beyond traditional lectures and textbooks, allowing students to explore concepts through projects, case studies, and real-world scenarios. This approach helps them develop essential skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and communication, skills that are highly valued in today’s dynamic world.
Defining Applied Learning
Imagine you’re learning how to bake a cake. You could read a recipe, memorize the ingredients and steps, and even recite them perfectly. But would you actually know how to bake a cake? Probably not. Applied learning is like actually baking the cake, using your knowledge and skills to create something real.
It’s about taking what you learn in the classroom and applying it to real-world situations.
Applied learning is all about putting your knowledge into practice, like learning to play a musical instrument. But some instruments are way harder to master than others! If you’re looking for a real challenge, check out this list of what are the hardest instruments to learn.
The more you apply yourself, the better you’ll become, no matter how challenging the instrument!
The Core Principles of Applied Learning
Applied learning focuses on active engagement and real-world application. It’s not about simply memorizing facts, but about understanding how those facts work in practice.
- Active Engagement:Applied learning emphasizes active participation in the learning process. This could involve hands-on activities, problem-solving, group projects, or real-world simulations.
- Real-World Relevance:Applied learning connects classroom knowledge to real-world situations. It helps students see how their learning applies to their lives and future careers.
- Problem-Solving:Applied learning encourages students to think critically and solve problems using the knowledge and skills they’ve acquired.
- Feedback and Reflection:Applied learning involves regular feedback and reflection to help students understand their progress and identify areas for improvement.
Contrasting Applied Learning with Traditional Theoretical Learning
Traditional theoretical learning focuses on the acquisition of knowledge through lectures, textbooks, and memorization. It emphasizes understanding concepts and theories, but may not always connect these concepts to real-world applications.
- Learning Objectives:Traditional learning aims to impart knowledge and understanding of theoretical concepts. Applied learning focuses on developing practical skills and applying knowledge to solve real-world problems.
- Learning Methods:Traditional learning relies heavily on lectures, textbooks, and assessments that test recall of information. Applied learning uses hands-on activities, projects, simulations, and real-world experiences to engage students.
| Learning Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Theoretical Learning | Provides a strong foundation in theoretical concepts. Enables students to understand complex ideas and theories. | May not be engaging for all students. Can feel disconnected from real-world applications. |
| Applied Learning | Develops practical skills and real-world experience. Makes learning more engaging and relevant. | May require more resources and time to implement. Can be challenging to assess learning outcomes. |
Real-World Examples of Applied Learning
Applied learning is prevalent in various fields, demonstrating its effectiveness in developing practical skills and knowledge.
- Healthcare:A nursing student participating in a simulation where they practice administering medication to a patient. This allows them to apply their theoretical knowledge in a safe and controlled environment, developing critical thinking and decision-making skills.
- Engineering:An engineering student designing and building a bridge using real-world materials and constraints. This project allows them to apply their knowledge of physics, mathematics, and engineering principles to a practical problem, fostering problem-solving and creativity.
- Art:An art student creating a mural for a local community center. This project allows them to apply their artistic skills and knowledge to a real-world context, promoting collaboration, communication, and cultural understanding.
Importance of Applied Learning

Applied learning, as we have established, is a powerful approach to education that emphasizes hands-on experience and real-world application. But beyond its definition, lies its profound significance in shaping individuals and propelling professional success. This section delves into the multifaceted benefits of applied learning.
Benefits for Individual Development
Applied learning is a catalyst for individual growth, fostering a range of valuable skills and traits.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities:Applied learning challenges individuals to tackle real-world problems, encouraging them to analyze situations, develop creative solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. This iterative process hones their critical thinking skills and equips them with the ability to navigate complex scenarios.
- Increased Confidence and Self-Efficacy:By engaging in practical tasks and projects, individuals gain firsthand experience and build confidence in their abilities. This sense of accomplishment reinforces their belief in their potential and encourages them to take on new challenges.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration Skills:Many applied learning experiences involve teamwork and collaboration. Individuals learn to communicate effectively, listen actively, and work together to achieve common goals. These skills are essential for success in any professional setting.
- Development of Adaptability and Resilience:Real-world situations are rarely predictable, and applied learning prepares individuals to embrace change and adapt to new circumstances. They learn to think on their feet, overcome obstacles, and persevere through challenges, developing resilience and adaptability.
Impact on Professional Success
The benefits of applied learning extend beyond individual development and have a direct impact on professional success.
- Increased Employability:Employers value candidates with practical skills and experience. Applied learning provides individuals with the hands-on knowledge and real-world applications that employers seek, making them highly competitive in the job market.
- Improved Job Performance:Applied learning equips individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in their chosen fields. They are better prepared to handle real-world challenges, solve problems effectively, and contribute meaningfully to their organizations.
- Enhanced Career Advancement Opportunities:Individuals with applied learning experience are often seen as valuable assets by employers. They are more likely to be promoted, offered leadership roles, and given opportunities for professional growth and development.
Fostering Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Applied learning cultivates critical thinking and problem-solving skills by placing individuals in situations where they must analyze information, evaluate options, and make informed decisions.
- Developing Analytical Skills:Applied learning encourages individuals to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components. They learn to identify key factors, gather relevant information, and analyze data to form logical conclusions.
- Promoting Creative Thinking:Applied learning challenges individuals to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. They are encouraged to explore different perspectives, consider alternative approaches, and develop creative strategies.
- Enhancing Decision-Making Abilities:Applied learning provides opportunities for individuals to practice making decisions based on available information and their own judgment. They learn to weigh the pros and cons of different options, consider potential consequences, and make informed choices.
Methods of Applied Learning
Applied learning methods are the diverse approaches educators use to connect classroom knowledge with real-world applications, fostering deeper understanding and practical skills. These methods encourage active learning, problem-solving, and critical thinking, preparing students for success beyond the academic realm.
Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered approach where learners engage in complex, real-world projects that require them to apply knowledge and skills from various disciplines.
- Advantages:
- Develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills.
- Encourages self-directed learning and ownership of the learning process.
- Provides opportunities for authentic assessment of skills and knowledge.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive to implement.
- May require significant planning and teacher expertise.
- Can be challenging to manage student groups and ensure equitable participation.
Examples:
- In a science class, students could design and build a model solar car, applying principles of physics and engineering.
- In a history class, students could create a museum exhibit about a historical event, researching and presenting information in a compelling way.
Case Studies
Case studies present real-world scenarios or situations that learners analyze and solve using their knowledge and critical thinking skills.
- Advantages:
- Offers opportunities for students to apply theoretical concepts to practical situations.
- Encourages critical thinking, analysis, and decision-making skills.
- Provides a platform for exploring ethical dilemmas and real-world complexities.
- Disadvantages:
- May require significant preparation and research to develop compelling case studies.
- Can be challenging to ensure the case studies are relevant and engaging for all learners.
- May not provide opportunities for hands-on application or practical skill development.
Examples:
- In a business class, students could analyze a case study about a company facing a financial crisis, applying their knowledge of accounting and finance to propose solutions.
- In a psychology class, students could examine a case study of a patient with a specific mental health disorder, applying their understanding of psychological theories to diagnose and recommend treatment options.
Internships
Internships provide students with practical work experience in their field of study, allowing them to apply their academic knowledge in a real-world setting.
- Advantages:
- Provides valuable hands-on experience and exposure to industry practices.
- Develops professional skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving.
- Facilitates networking and potential career opportunities.
- Disadvantages:
- Can be challenging to secure internships, especially in competitive fields.
- May require students to balance their academic responsibilities with internship commitments.
- Not all internships provide meaningful or relevant experiences.
Examples:
- A computer science student could intern at a software company, developing and testing applications.
- A journalism student could intern at a newspaper or magazine, writing articles and conducting interviews.
Simulation Games
Simulation games provide interactive, engaging experiences that allow learners to practice skills and make decisions in a safe and controlled environment.
- Advantages:
- Offers opportunities for hands-on learning and skill development.
- Encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
- Provides immediate feedback and opportunities for reflection and improvement.
- Disadvantages:
- May not accurately reflect real-world complexities or challenges.
- Can be limited in scope and may not address all aspects of a particular skill or concept.
- May require specialized software or equipment to implement.
Examples:
- In a business class, students could play a business simulation game, making decisions about pricing, marketing, and production.
- In a healthcare class, students could participate in a medical simulation game, practicing patient care and decision-making in a simulated clinical setting.
4. Applied Learning in Education
Applied learning, as we’ve seen, is a powerful approach to education that goes beyond rote memorization and focuses on real-world application. Let’s explore how applied learning is implemented across various educational levels, from K-12 to higher education, and delve into curriculum design strategies that promote this active and engaging learning style.
4.1. K-12 Education
Applied learning in K-12 education is particularly valuable for developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, essential for success in the 21st century.
- Applied learning in grades 6-8 fosters a deeper understanding of concepts by allowing students to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. This approach encourages students to think critically, solve problems creatively, and collaborate effectively. Real-world projects, such as designing a sustainable community garden, conducting a local environmental impact study, or creating a business plan for a school fundraiser, provide hands-on experiences that connect classroom learning to practical applications.
These projects allow students to explore their interests, develop valuable skills, and build confidence in their abilities.
Implementing applied learning in under-resourced schools can be challenging, but not insurmountable.
- Lack of resources, including access to technology, can hinder the implementation of applied learning projects. However, creative solutions can be found. Schools can leverage community partnerships, collaborate with local businesses and organizations, and explore innovative funding opportunities to secure the necessary resources.
Teacher training is another critical factor in successful applied learning. Providing teachers with the professional development and support they need to effectively implement applied learning strategies is essential. This can include workshops, mentorship programs, and access to online resources.
Community partnerships play a crucial role in enriching applied learning experiences for elementary school students.
- Collaborations with local businesses, museums, and community organizations can provide students with access to real-world experts, facilities, and resources. For example, a partnership with a local farm could offer students hands-on experience in agriculture, while a collaboration with a museum could provide opportunities for historical research and artifact analysis.
These partnerships not only enrich the curriculum but also expose students to diverse career paths and community resources.
4.2. Higher Education
Applied learning is a cornerstone of many university programs, particularly in fields like engineering, where practical application is essential.
- Engineering programs often incorporate applied learning through capstone projects, where students work in teams to design, build, and test solutions to real-world problems. These projects provide valuable experience in problem-solving, teamwork, and project management. Internships are another crucial component of applied learning in engineering.
Students gain hands-on experience in their field of study, apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, and build valuable professional networks.
The integration of applied learning in business administration programs varies depending on the learning environment.
- In traditional classroom settings, applied learning can be implemented through case studies, simulations, and group projects. These activities provide students with the opportunity to analyze real-world business scenarios, apply theoretical concepts, and develop critical thinking and decision-making skills. Online learning environments offer unique opportunities for applied learning through interactive simulations, virtual internships, and online collaboration tools.
These technologies allow students to engage in real-time business scenarios, collaborate with peers from diverse backgrounds, and develop essential digital skills.
Applied learning significantly impacts student engagement and career readiness in higher education.
- By providing students with hands-on experiences and real-world applications, applied learning fosters a deeper understanding of concepts, enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills, and develops valuable professional skills. These experiences make learning more relevant and engaging, motivating students to take ownership of their education and prepare for successful careers.
4.3. Curriculum Design
Designing a curriculum that effectively incorporates applied learning requires careful consideration of learning objectives, project ideas, and assessment methods.
- A high school biology course focusing on environmental sustainability could incorporate applied learning through a project-based approach. Students could work in teams to design and implement a school-wide composting program, conduct a local water quality analysis, or create a community garden.
These projects would allow students to apply their knowledge of biology to real-world problems, develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, and make a positive impact on their community.
A college-level history course can incorporate applied learning through a lesson plan that combines primary source analysis and community engagement.
- Students could analyze primary sources related to a specific historical event, such as letters, diaries, or photographs, and then use their findings to create a museum exhibit or a public presentation for the local community. This activity would allow students to engage in historical research, develop critical thinking and communication skills, and share their learning with a wider audience.
Evaluating student work in applied learning projects requires a rubric that assesses both content knowledge and process skills.
- A rubric for an applied learning project in a secondary school English language arts course could focus on communication skills, creativity, and critical thinking. The rubric would assess students’ ability to communicate effectively in writing and orally, to demonstrate originality and innovation in their work, and to analyze and synthesize information from multiple sources.
Applied Learning in the Workplace: What Is Applied Learning
![]()
Applied learning isn’t just for classrooms; it’s a vital tool for companies to boost employee skills and drive success. It’s all about putting theory into practice, giving employees the chance to learn by doing and apply their knowledge to real-world challenges.
Examples of Applied Learning in Companies
Companies use a variety of methods to incorporate applied learning into their training programs. Here are some examples:
- On-the-Job Training:This classic approach involves employees learning by working alongside experienced colleagues, gaining practical skills and knowledge through direct experience. For example, a new sales representative might shadow a seasoned team member during customer calls and presentations to learn the ropes.
- Mentorship Programs:Pairing new employees with experienced mentors provides guidance, support, and practical advice, fostering professional growth and skill development. A junior software developer might be mentored by a senior developer, receiving guidance on coding practices and project management.
- Case Studies:Companies often use real-world business cases to challenge employees to analyze problems, develop solutions, and present their recommendations. This simulates real-life situations and allows employees to apply their knowledge in a structured environment.
- Simulations and Role-Playing:These techniques recreate realistic workplace scenarios, allowing employees to practice their skills in a safe and controlled setting. For example, a customer service representative might participate in a simulated phone call to handle a difficult customer interaction.
- Project-Based Learning:Employees work on real projects, collaborating with teams and applying their skills to solve practical problems. This fosters teamwork, problem-solving, and a sense of ownership. A marketing team might be tasked with developing a new campaign, applying their marketing knowledge and creativity to achieve specific goals.
Benefits of Applied Learning for Professional Development
Applied learning offers numerous benefits for employee development and organizational growth:
- Enhanced Skills and Knowledge:Employees gain practical skills and knowledge that are directly applicable to their roles, improving their performance and contributing to organizational success. A marketing team using project-based learning to develop a new campaign gains valuable experience in market research, content creation, and campaign execution.
- Increased Confidence and Motivation:Experiencing success through hands-on learning boosts employee confidence and motivation. Seeing the direct impact of their learning on real-world projects inspires employees to continue growing and contributing.
- Improved Problem-Solving Abilities:Applied learning challenges employees to think critically, analyze problems, and develop solutions, enhancing their problem-solving skills and decision-making abilities. A team working on a case study involving a product launch learns to identify potential challenges, analyze market trends, and develop strategies to mitigate risks.
- Greater Job Satisfaction:Employees who feel empowered to apply their knowledge and contribute to real projects experience greater job satisfaction and are more likely to remain with the company. A software developer who participates in a project to build a new application feels a sense of accomplishment and pride in their work, contributing to their overall job satisfaction.
Solving Real-World Business Problems with Applied Learning
Applied learning can be a powerful tool for tackling real-world business challenges. By applying their knowledge and skills to specific problems, employees can generate innovative solutions and drive positive outcomes for the organization.
- Product Development:A team of engineers using project-based learning to develop a new product can leverage their technical expertise and knowledge of customer needs to create a successful product that meets market demands.
- Marketing Campaigns:A marketing team applying case studies and simulations to develop a new marketing campaign can test different strategies, analyze results, and optimize their approach for maximum impact.
- Customer Service Improvement:Customer service representatives using role-playing scenarios to practice handling difficult customer interactions can develop effective communication skills and improve their ability to resolve customer issues.
- Operational Efficiency:Employees using applied learning to identify and implement process improvements can streamline workflows, reduce costs, and enhance operational efficiency. A team analyzing production processes might identify opportunities to automate tasks or optimize resource allocation.
6. Challenges of Applied Learning
Implementing an applied learning program can be a rewarding experience, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. These challenges are often tied to the specific context of the implementation, whether it be in a school district, a rural community, or a corporate setting.
Understanding these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them is essential for successful implementation.
Potential Challenges in School Districts
- Lack of Teacher Training:Teachers may need additional training to effectively design and implement applied learning projects. This training should focus on pedagogical approaches, assessment strategies, and how to integrate real-world experiences into the curriculum.
- Limited Resources:Schools may face limitations in resources, such as funding, materials, and access to community partners. Creative solutions, like partnerships with local businesses, community organizations, or crowdfunding initiatives, can help address this challenge.
- Curriculum Alignment:Integrating applied learning projects into the existing curriculum can be challenging. Schools should ensure that applied learning projects are aligned with learning standards and assessments. This might involve revising existing curriculum or creating new units specifically designed for applied learning.
- Parental Support:Some parents may be hesitant about applied learning, especially if it involves activities outside the traditional classroom setting. Open communication with parents, showcasing the benefits of applied learning, and involving them in the process can help build support.
- Assessment and Evaluation:Assessing student learning in applied learning contexts can be different from traditional methods. Schools need to develop appropriate assessment strategies that measure both knowledge and skills gained through hands-on experiences.
Challenges in Rural vs. Urban Settings
| Challenge | Rural Setting | Urban Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Access to Resources | Limited access to specialized equipment, technology, and experts. | Greater access to resources, but potential for overcrowding and competition for resources. |
| Community Engagement | Stronger community ties, but potential for limited resources and expertise. | Diverse community, but potential for challenges in building relationships and finding relevant partnerships. |
| Student Demographics | More homogeneous student population, but potential for limited exposure to diverse perspectives. | Diverse student population, but potential for challenges in meeting the needs of all students. |
Equity in Applied Learning Programs
The “Project-Based Learning for All” initiative, developed by the Buck Institute for Education, provides a compelling example of a successful applied learning program that addressed equity concerns. This initiative focuses on providing equitable access to project-based learning opportunities for all students, regardless of their background or socioeconomic status.
Key strategies employed include:
- Universal Design for Learning:The program emphasizes the use of universal design principles to ensure that all students can access and participate in project-based learning activities.
- Culturally Responsive Teaching:The program encourages teachers to incorporate culturally relevant content and learning experiences into project-based learning activities.
- Collaborative Partnerships:The program fosters partnerships with community organizations and businesses to provide students with real-world learning experiences and mentorship opportunities.
- Professional Development:The program provides teachers with ongoing professional development to support their implementation of equitable project-based learning practices.
Challenges in High School History Projects
Designing an applied learning project for a high school history class can present unique challenges in ensuring equitable access and meaningful participation. Here are some potential challenges and solutions:
- Access to Materials:Some students may lack access to necessary materials, such as computers, internet access, or specialized equipment. Solutions include providing access to school computers and labs, offering alternative ways to complete the project (e.g., using physical materials or collaborating with peers), and working with parents or community organizations to provide resources.
- Support and Guidance:Students may need varying levels of support and guidance to complete the project. Teachers can provide differentiated instruction, offer small group tutoring, and create opportunities for peer-to-peer support.
- Differentiated Instruction:Students may have different learning styles and interests. Teachers can design projects that allow students to explore their interests and demonstrate their learning in different ways. This might involve offering multiple project options, providing flexible deadlines, and allowing students to choose their own research topics.
Impact of Applied Learning on Student Engagement and Achievement
A study by the National Center for Research in Applied Learning (NCRAL) found that students who participated in applied learning programs showed significant increases in engagement, motivation, and academic achievement. The study highlighted the importance of:
- Authentic Learning Experiences:Students are more engaged when they see the relevance of what they are learning to real-world situations.
- Collaborative Learning:Working in groups and collaborating with peers can enhance engagement and learning.
- Student Choice and Ownership:Allowing students to make choices about their projects and take ownership of their learning can increase motivation and engagement.
7. Future of Applied Learning
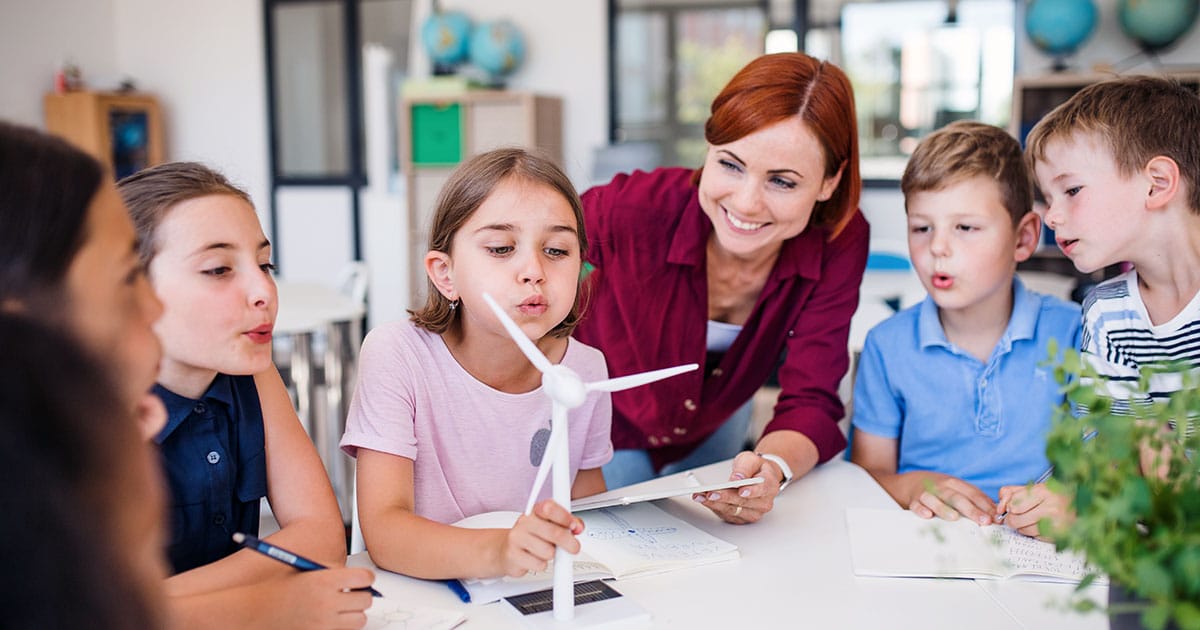

The future of applied learning is bright, driven by a convergence of emerging trends and the transformative power of technology. These advancements are poised to revolutionize how we learn, work, and solve real-world problems.
Emerging Trends in Applied Learning
The landscape of applied learning is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging that are shaping how knowledge is acquired and applied.
| Trend | Description | Evidence | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Learning | Personalized learning tailors educational experiences to individual needs, interests, and learning styles. This approach utilizes data analytics, adaptive learning platforms, and AI-powered tools to provide customized learning paths and feedback. | A study by the National Center for Education Statistics found that students who participated in personalized learning programs demonstrated significant improvements in academic performance. | Personalized learning fosters student engagement, improves academic outcomes, and prepares individuals for the demands of a rapidly changing workforce. |
| Experiential Learning | Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that allow learners to apply theoretical concepts in practical settings. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills. | A research paper published in the Journal of Experiential Education highlighted the effectiveness of experiential learning in promoting student engagement and developing practical skills. | Experiential learning bridges the gap between theory and practice, enhances employability, and prepares individuals for the challenges of the modern workplace. |
| Interdisciplinary Learning | Interdisciplinary learning integrates knowledge and skills from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems. This approach encourages students to think critically, collaborate, and develop solutions that transcend traditional subject boundaries. | A report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine emphasized the importance of interdisciplinary learning in preparing students for careers in STEM fields and other sectors. | Interdisciplinary learning fosters innovation, creativity, and the ability to solve complex problems, which are essential for success in a globalized and interconnected world. |
Role of Technology in Applied Learning
Emerging technologies are playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of applied learning, offering new opportunities to enhance learning experiences, personalize instruction, and bridge the gap between theory and practice.
“Technology is not just a tool; it is a powerful catalyst for innovation and transformation in applied learning.”
* Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI-powered tools can personalize learning pathways, provide real-time feedback, and offer adaptive support to learners. AI can analyze student data to identify strengths and weaknesses, recommend relevant resources, and create customized learning experiences.
Virtual Reality (VR)
VR offers immersive and engaging learning environments that simulate real-world situations. Students can experience scenarios, practice skills, and gain practical knowledge in a safe and controlled environment.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing learning experiences by providing interactive content, visualizations, and real-time feedback. AR can be used to create interactive simulations, provide contextual information, and enhance hands-on learning activities.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent systems for managing learning credentials, tracking student progress, and ensuring the authenticity of educational materials.
Impact of Applied Learning on Education and the Workforce
Applied learning is poised to have a profound impact on education and the workforce, transforming how individuals learn, work, and contribute to society.
“Applied learning is not just about acquiring knowledge; it is about developing the skills and competencies needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.”
* Development of In-Demand Skills:Applied learning fosters the development of critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration skills, which are highly sought after by employers in today’s job market.
Enhanced Employability
Applied learning prepares individuals for the demands of the modern workplace by equipping them with practical skills, real-world experience, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Applied learning encourages students to think creatively, solve problems, and develop innovative solutions, fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
Lifelong Learning
Applied learning promotes a culture of lifelong learning, empowering individuals to adapt to new technologies, acquire new skills, and remain competitive in a rapidly changing job market.
Applied Learning in Different Disciplines
Applied learning is a versatile approach that can be adapted to various disciplines, enriching the learning experience and fostering deeper understanding. This section explores the unique ways applied learning is implemented across STEM, humanities, and social sciences, highlighting the specific challenges and opportunities each field presents.
Applied Learning in STEM
Applied learning in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) focuses on practical application of theoretical knowledge through hands-on projects, experiments, and real-world problem-solving.
- Engineering:Students design and build prototypes, solve engineering challenges, and work in teams to develop innovative solutions.
- Computer Science:Students develop software applications, design websites, and engage in coding challenges, applying their knowledge to create tangible products.
- Biology:Students conduct experiments in laboratories, analyze data, and participate in field research, gaining practical experience in scientific methodology.
Applied learning in STEM provides opportunities for students to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaborative skills. It also helps them gain practical experience and prepare for future careers in STEM-related fields.
Applied Learning in Humanities
Applied learning in the humanities focuses on connecting theoretical concepts to real-world issues and engaging students in critical analysis and creative expression.
- History:Students analyze primary sources, conduct historical research, and create multimedia presentations, applying historical knowledge to contemporary issues.
- Literature:Students analyze literary works, participate in debates and discussions, and engage in creative writing projects, developing critical thinking and communication skills.
- Art:Students create artwork, engage in performance art, and analyze art history, developing creativity, critical thinking, and communication skills.
Applied learning in the humanities helps students develop critical thinking, communication, and creative skills, preparing them for careers in fields like journalism, education, and the arts.
Applied Learning in Social Sciences
Applied learning in social sciences focuses on applying theoretical knowledge to real-world social issues, fostering empathy, and promoting social change.
- Psychology:Students conduct research on human behavior, analyze data, and apply psychological principles to address social issues, gaining practical experience in research and analysis.
- Sociology:Students study social phenomena, conduct interviews and surveys, and analyze data, developing critical thinking and research skills to understand and address social problems.
- Political Science:Students analyze political systems, engage in political campaigns, and participate in community activism, applying political knowledge to real-world issues and promoting civic engagement.
Applied learning in the social sciences prepares students for careers in social work, policy analysis, and community development, fostering their ability to understand and address complex social issues.
Case Studies of Applied Learning
Applied learning shines brightest when it’s put into practice. Case studies provide a window into real-world scenarios where applied learning has made a tangible difference. By examining these case studies, we can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of different applied learning approaches and identify key takeaways for broader implementation.
Case Study: Project-Based Learning in STEM Education
Project-based learning (PBL) is a popular approach to applied learning, particularly in STEM fields. One noteworthy case study involves a high school in California that implemented a PBL curriculum in its biology classes. Students were tasked with designing and conducting experiments to investigate the effects of pollution on local waterways.
This project-based approach encouraged students to apply scientific concepts and critical thinking skills in a real-world context. They had to research, plan, execute, and analyze their experiments, culminating in presentations of their findings to the community. The outcomes were impressive: students demonstrated a deeper understanding of biological principles, developed valuable research skills, and gained a sense of ownership over their learning.
- Improved Academic Performance:Students in the PBL group consistently outperformed their peers in traditional lecture-based classes on standardized tests and assessments.
- Enhanced Engagement:The hands-on nature of PBL fostered greater student engagement and motivation, leading to increased participation and a positive learning environment.
- Development of 21st-Century Skills:The project required students to collaborate, communicate effectively, and solve problems creatively, equipping them with essential skills for the modern workforce.
This case study highlights the potential of PBL to enhance STEM education by bridging the gap between theory and practice. It demonstrates that students can learn effectively by applying their knowledge to real-world challenges, fostering deeper understanding, critical thinking, and practical skills.
Measuring the Impact of Applied Learning

It’s essential to measure the impact of applied learning programs to ensure their effectiveness and optimize their future development. By understanding how well these programs achieve their goals, we can make informed decisions about resource allocation, program design, and implementation strategies.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Applied Learning Programs
Various methods can be employed to assess the effectiveness of applied learning programs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Pre- and Post-Tests:These tests measure student knowledge and skills before and after participating in an applied learning program. They can help determine the program’s impact on knowledge acquisition and skill development.
- Strengths:Reliable, objective, and relatively easy to administer.
- Weaknesses:May not fully capture the development of practical skills or the application of knowledge in real-world settings.
- Surveys:Surveys can gather feedback from students, instructors, and employers about their experiences with the applied learning program.
- Strengths:Provide insights into student satisfaction, engagement, and perceptions of program effectiveness.
- Weaknesses:May be subjective and influenced by biases.
- Focus Groups:Focus groups provide a platform for in-depth discussions with students and stakeholders about their experiences with the program.
- Strengths:Offer rich qualitative data and allow for exploration of complex issues.
- Weaknesses:Can be time-consuming and difficult to generalize findings.
- Interviews:Individual interviews can provide more detailed information about student experiences and perceptions than surveys or focus groups.
- Strengths:Offer a deeper understanding of individual perspectives and experiences.
- Weaknesses:Can be time-consuming and difficult to analyze.
- Performance Evaluations:Performance evaluations assess student performance on real-world projects or tasks.
- Strengths:Provide a direct measure of practical skills and knowledge application.
- Weaknesses:May be subjective and influenced by factors beyond the student’s control.
- Portfolio Reviews:Portfolio reviews evaluate student work samples, such as projects, presentations, and written reports.
- Strengths:Provide a comprehensive assessment of student learning and progress.
- Weaknesses:Can be time-consuming to review and may not be suitable for all types of applied learning programs.
Key Metrics for Evaluating the Impact of Applied Learning
Several key metrics can be used to evaluate the impact of applied learning programs, focusing on the acquisition of practical skills, knowledge application, and problem-solving abilities.
- Performance on Real-World Projects:This metric assesses student performance on projects that simulate real-world work experiences.
- Strengths:Provides a direct measure of practical skills and knowledge application.
- Weaknesses:May not be suitable for all types of applied learning programs.
- Improvement in Job Readiness:This metric measures the extent to which the applied learning program has improved student readiness for the workforce.
- Strengths:Provides a valuable measure of program effectiveness.
- Weaknesses:Can be challenging to measure objectively.
- Increased Confidence in Applying Knowledge:This metric measures student confidence in applying their knowledge to real-world situations.
- Strengths:Provides a valuable measure of student self-efficacy.
- Weaknesses:May be subjective and influenced by biases.
- Attendance Rates and Participation Levels:These metrics can indicate student engagement and motivation in the applied learning program.
- Strengths:Easy to measure and provide a basic indication of student interest.
- Weaknesses:May not reflect the quality of student engagement or learning.
- Self-Reported Learning Gains:This metric measures student perceptions of their learning gains through the applied learning program.
- Strengths:Provides insights into student perspectives on program effectiveness.
- Weaknesses:May be subjective and influenced by biases.
- Satisfaction with the Program:This metric measures student satisfaction with the applied learning program.
- Strengths:Provides valuable feedback for program improvement.
- Weaknesses:May not reflect the actual impact of the program on student learning.
- Career Advancement and Salary Increases:These metrics measure the long-term impact of applied learning on student career success.
- Strengths:Provide a powerful measure of program effectiveness.
- Weaknesses:Can be challenging to track and may be influenced by factors beyond the applied learning program.
Examples of Measuring the Impact of Applied Learning
Several real-world case studies demonstrate the value of measuring the impact of applied learning programs.
- Case Study 1:A university implemented a new applied learning program in its engineering department. The program involved students working on real-world projects for local businesses. The university used a combination of performance evaluations, student surveys, and employer feedback to assess the program’s impact.
- Metrics:Performance evaluations, student surveys, employer feedback.
- Findings:The program significantly improved student practical skills and job readiness. Employers were highly satisfied with the students’ work and reported that they were well-prepared for the workforce.
- Case Study 2:A high school implemented a new applied learning program in its science department. The program involved students conducting research projects in collaboration with local scientists. The school used a combination of pre- and post-tests, student portfolios, and self-reported learning gains to assess the program’s impact.
- Metrics:Pre- and post-tests, student portfolios, self-reported learning gains.
- Findings:The program significantly improved student understanding of scientific concepts and their ability to apply scientific knowledge to real-world problems. Students reported high levels of satisfaction with the program and felt that it had enhanced their learning experience.
The Importance of Measuring the Impact of Applied Learning Programs
Measuring the impact of applied learning programs is crucial for several reasons.
- Improved Program Quality:By evaluating program effectiveness, we can identify areas for improvement and ensure that programs are meeting their intended goals.
- Increased Accountability:Measuring impact helps to hold program stakeholders accountable for program outcomes and demonstrates the value of applied learning.
- Informed Decision-Making:Data on program impact can inform decisions about resource allocation, program design, and implementation strategies.
- Enhanced Advocacy:Evidence of program effectiveness can be used to advocate for increased funding and support for applied learning initiatives.
Best Practices for Assessing the Effectiveness of Applied Learning Programs
Several best practices can be used to ensure that assessments of applied learning programs are rigorous and reliable.
- Use a Multi-Method Approach:Combine different assessment methods to capture a comprehensive picture of program impact.
- Involve Stakeholders:Engage students, instructors, employers, and other stakeholders in the assessment process.
- Use Valid and Reliable Measures:Ensure that assessment measures are aligned with program goals and are reliable and valid.
- Collect Data Over Time:Track program impact over time to identify trends and measure long-term outcomes.
- Disseminate Findings:Share findings with program stakeholders and the broader community to promote transparency and accountability.
Resources for Applied Learning
Embarking on the journey of implementing applied learning requires access to a wealth of resources that can guide your efforts, provide practical strategies, and offer real-world examples. Whether you’re an individual seeking to enhance your learning experience or an organization aiming to integrate applied learning into your programs, there are numerous resources available to support your endeavors.
Websites
Websites dedicated to applied learning serve as valuable hubs for information, guidance, and inspiration. They offer practical advice, research findings, case studies, and connections to a community of practitioners.
- The Applied Learning Institute– [https://www.appliedlearning.org](https://www.appliedlearning.org) – This website is a leading resource for applied learning, providing a comprehensive overview of the field, practical guidance for educators and organizations, and a collection of case studies showcasing successful implementations.
- The National Center for Applied Learning– [https://www.ncal.org](https://www.ncal.org) – The National Center for Applied Learning is a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting and supporting applied learning initiatives across various sectors. Their website offers resources, research, and professional development opportunities for educators, practitioners, and organizations.
- The Association for Experiential Education– [https://www.aee.org](https://www.aee.org) – The Association for Experiential Education is a professional organization that promotes experiential learning and its application in various settings. Their website offers resources, publications, and networking opportunities for professionals interested in experiential learning and applied learning.
Books
Books provide in-depth insights, theoretical frameworks, and practical methodologies for implementing applied learning. They offer valuable guidance for educators, trainers, and organizations looking to design and implement effective applied learning experiences.
- “Learning by Doing: A Guide to Applied Learning”– This comprehensive guide covers theoretical frameworks, practical strategies, and real-world examples of applied learning implementation. It provides a roadmap for educators and organizations seeking to integrate applied learning into their programs.
- “Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development”– This book by David A. Kolb explores the theory and practice of experiential learning, a key component of applied learning. It offers insights into the learning cycle and its application in various settings.
- “The Art of Problem Solving”– This book by Sandor Lehoczky and Bruce R. Sherwood delves into the principles and techniques of problem-solving, a core skill in applied learning. It provides practical strategies and exercises for developing problem-solving abilities.
Articles
Articles from academic journals, industry publications, and online platforms offer valuable insights into specific aspects of applied learning, including research findings, practical applications, and emerging trends.
- “The Impact of Applied Learning on Student Engagement”– This article explores the positive effects of applied learning on student engagement and motivation, highlighting its role in fostering active learning and deeper understanding.
- “Designing Effective Applied Learning Experiences”– This article provides practical guidance for educators and trainers on designing and implementing engaging applied learning experiences that promote student learning and development.
- “The Future of Applied Learning in the Workplace”– This article examines the evolving role of applied learning in the workplace, highlighting its importance in developing essential skills for the 21st century.
Organizations, What is applied learning
Organizations actively promoting and supporting applied learning initiatives play a crucial role in fostering innovation and collaboration in the field. They offer training programs, resources, and networking opportunities for individuals and organizations seeking to implement applied learning strategies.
- The National Institute for Applied Learning– This organization provides training programs, resources, and support to educators and organizations seeking to implement applied learning. They offer workshops, conferences, and online resources on various aspects of applied learning.
- The International Society for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning– This society promotes scholarship and innovation in teaching and learning, including applied learning. They offer conferences, publications, and networking opportunities for educators and researchers interested in applied learning.
- The Center for Applied Learning and Technology– This center focuses on promoting and supporting the integration of technology in applied learning. They offer resources, training programs, and research on the use of technology to enhance applied learning experiences.
Applied Learning and Lifelong Learning
Imagine a world where learning isn’t confined to classrooms or specific periods in life. Lifelong learning is all about embracing a continuous journey of personal and professional growth, and applied learning plays a crucial role in making this journey both effective and engaging.
Defining Applied Learning and Lifelong Learning
Applied learning is about putting knowledge into practice, using it to solve real-world problems. It’s about learning by doing, by engaging in hands-on activities, projects, and case studies. Lifelong learning, on the other hand, is about continuously acquiring new knowledge and skills throughout your life, regardless of age or career stage.
It’s a commitment to personal and professional development that goes beyond formal education.
The Role of Applied Learning in Lifelong Learning
Applied learning is the fuel that powers lifelong learning. It’s the practical application that makes learning relevant and meaningful. By engaging in applied learning, you’re not just passively absorbing information; you’re actively using it to create, innovate, and solve problems.
This active engagement makes learning more effective and enjoyable.
Examples of Applied Learning in Lifelong Learning
Let’s consider a few examples of how applied learning can be incorporated into different stages of life and career paths:
- Early Career:A recent graduate pursuing a career in software development could participate in hackathons, contribute to open-source projects, or build their own personal projects. These experiences provide hands-on practice and demonstrate their skills to potential employers.
- Mid-Career:A marketing professional might enroll in a digital marketing course and then apply their newfound knowledge by launching a social media campaign for their company. This practical application reinforces the learning and leads to tangible results.
- Retirement:A retired teacher could volunteer at a local school, sharing their knowledge and experience with younger generations. This volunteer work provides a meaningful outlet for continued learning and skill development.
Benefits of Applied Learning for Lifelong Learning
The benefits of applied learning for lifelong learning are numerous:
- Enhanced Adaptability:Applied learning helps you develop the skills and knowledge needed to adapt to changing circumstances and embrace new technologies.
- Skill Development:By applying your learning, you gain practical experience and develop essential skills that are highly valued in the workplace.
- Career Advancement:Applied learning can lead to promotions, salary increases, and new career opportunities. It demonstrates your commitment to continuous learning and your ability to make a real-world impact.
Applied Learning for Social Impact
Applied learning, by its very nature, focuses on real-world application. This makes it a powerful tool for addressing societal challenges and creating positive social change. By engaging learners in hands-on projects that tackle real-world issues, applied learning can equip individuals with the skills, knowledge, and mindset needed to become agents of change.
Applied Learning for Social Justice
Applied learning can play a crucial role in promoting social justice by empowering individuals to challenge inequalities and advocate for change. Here are some ways applied learning can be used to address social justice issues:
- Community-based projects:Students can engage in projects that address local social justice issues, such as poverty, homelessness, or racial discrimination. For example, students might partner with local organizations to provide services to underserved communities, conduct research on social justice issues, or advocate for policy changes.
- Social entrepreneurship:Applied learning can foster social entrepreneurship by encouraging students to develop innovative solutions to social problems. Students can learn about social business models, design sustainable solutions, and create businesses that address social needs. For example, students might develop a mobile app to connect low-income families with food banks or create a social enterprise that provides affordable housing solutions.
- Critical thinking and reflection:Applied learning encourages students to critically analyze social issues, question assumptions, and develop informed perspectives. By engaging in projects that challenge social norms and inequalities, students can develop a deeper understanding of social justice and its importance.
Applied Learning for Sustainability
Applied learning can be a powerful tool for promoting sustainability by encouraging individuals to develop solutions to environmental challenges and adopt sustainable practices. Here are some examples:
- Environmental projects:Students can participate in projects that address environmental issues such as climate change, pollution, and resource depletion. For example, students might conduct research on renewable energy sources, design sustainable building practices, or develop campaigns to promote environmental awareness.
- Green business practices:Applied learning can help students develop sustainable business practices by integrating environmental considerations into their decision-making processes. Students can learn about green supply chains, sustainable manufacturing processes, and eco-friendly product design.
- Community engagement:Applied learning can encourage students to engage in community initiatives that promote sustainability. Students can participate in local gardening projects, organize community clean-ups, or advocate for sustainable policies.
FAQ
What are some examples of applied learning in different fields?
In healthcare, medical students might participate in clinical rotations, applying their theoretical knowledge to real patient care. In engineering, students might design and build prototypes to solve engineering challenges. In art, students might create art installations that address social issues.
How can I incorporate applied learning into my own learning?
There are many ways to incorporate applied learning! You can volunteer in your community, participate in internships, take online courses that involve projects, or even start your own personal projects related to your interests. The key is to find ways to apply what you learn to real-world situations.
Is applied learning only for students?
Not at all! Applied learning is relevant for people of all ages and backgrounds. Professionals can use applied learning to enhance their skills, solve workplace problems, and stay ahead in their fields. Even hobbies can be a form of applied learning, allowing you to put your knowledge and skills into practice.