What is an asynchronous learning day –
What is an asynchronous learning day? Imagine a school day where students aren’t all gathered in a classroom at the same time. Instead, they engage with learning materials and activities independently, at their own pace, and often using technology. This flexible approach, sometimes called “flipped learning” or “blended learning,” is becoming increasingly popular in education.
Asynchronous learning days offer a unique opportunity to personalize learning experiences, cater to diverse learning styles, and empower students to take ownership of their education. They allow students to explore topics in depth, revisit challenging concepts, and work at their own speed, all while fostering independence and self-directed learning.
*
Definition of Asynchronous Learning Day
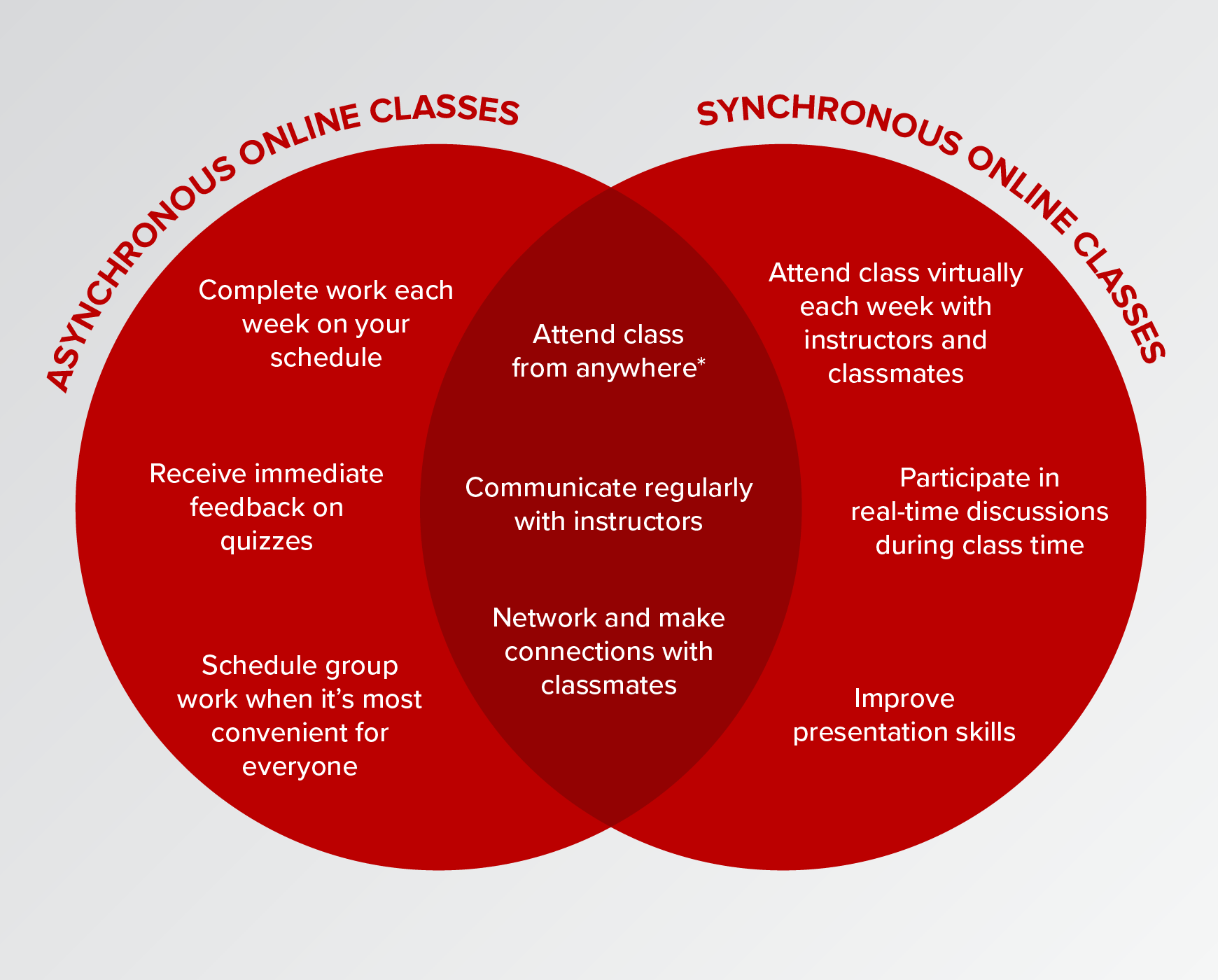
An asynchronous learning day is a day where students engage in learning activities independently, at their own pace, and outside of a traditional classroom setting. Unlike synchronous learning, where everyone learns together in real-time, asynchronous learning allows students to access and complete their work whenever and wherever it suits them.
It’s a crucial element of blended learning models, where online and offline learning experiences are combined to create a flexible and personalized learning environment.
Key Characteristics of Asynchronous Learning Day
Asynchronous learning days are characterized by their flexibility, self-paced nature, and reliance on technology. They provide students with the freedom to learn at their own pace, allowing them to spend more time on challenging topics or move ahead quickly on concepts they understand.
Technology plays a vital role in delivering content and activities, providing access to a wide range of resources like online videos, interactive simulations, and digital textbooks. This allows for individualization, enabling students to choose the learning materials and activities that best suit their needs and learning styles.
Examples of Activities During an Asynchronous Learning Day
The activities that occur during an asynchronous learning day can be categorized into three main types: content consumption, active learning, and collaborative learning.
- Content Consumption: Students access and engage with learning materials at their own pace. Examples include:
- Reading online articles or chapters from digital textbooks.
- Watching educational videos on platforms like Khan Academy or YouTube.
- Listening to podcasts or audiobooks related to the topic.
- Interacting with interactive simulations that provide hands-on experience with concepts.
- Active Learning: Students actively engage with the material and demonstrate their understanding. Examples include:
- Completing online quizzes or assessments to test their comprehension.
- Participating in online discussion forums where they can share their thoughts and ask questions.
- Working on individual projects or assignments that require research, analysis, and critical thinking.
- Submitting assignments or completing tasks through online platforms like Google Classroom or Canvas.
- Collaborative Learning: Students work together on projects or activities, even when they are physically separated. Examples include:
- Engaging in online group projects where students collaborate on a shared document or presentation.
- Participating in virtual group discussions using tools like Zoom or Google Meet.
- Collaborating on shared documents using platforms like Google Docs or Microsoft Word Online.
Potential Benefits of Asynchronous Learning Days for Students
Asynchronous learning days offer numerous benefits for students, promoting flexibility, self-paced learning, and personalized learning experiences. Students can learn at their own pace, focusing on areas that require more attention while moving quickly through topics they understand. This individualized approach caters to diverse learning styles and needs, allowing students to choose the learning materials and activities that work best for them.
By providing students with greater control over their learning, asynchronous learning days empower them to take ownership of their education and develop their self-directed learning skills.
Benefits of Asynchronous Learning Days
Asynchronous learning days offer numerous advantages for students, fostering flexibility, personalized learning, and enhanced engagement. By providing opportunities for independent study, students can manage their time effectively, explore topics at their own pace, and develop essential self-directed learning skills.
Supporting Diverse Learning Styles
Asynchronous learning caters to different learning styles by offering a variety of learning materials and activities. Students can choose the methods that best suit their preferences and needs.
- Visual Learners:Asynchronous learning provides opportunities for visual learners to engage with materials like videos, infographics, and presentations. They can pause, rewind, and revisit information as needed, enhancing comprehension.
- Auditory Learners:Audio recordings, podcasts, and online lectures cater to auditory learners. They can listen to content at their own pace and absorb information through sound.
- Kinesthetic Learners:Asynchronous activities that involve hands-on projects, simulations, or interactive games cater to kinesthetic learners. These activities provide opportunities for active learning and practical application of concepts.
Enhancing Student Engagement
Asynchronous learning can enhance student engagement by providing opportunities for self-directed learning, personalized experiences, and collaborative projects.
- Self-Directed Learning:Students can take ownership of their learning by choosing topics, exploring resources, and completing activities at their own pace. This fosters a sense of responsibility and autonomy, increasing engagement.
- Personalized Experiences:Asynchronous learning allows students to tailor their learning experience to their individual needs and interests. They can choose from a variety of resources and activities, focusing on areas where they need more support or exploring topics that pique their curiosity.
- Collaborative Projects:Asynchronous learning platforms facilitate online collaboration. Students can work together on projects, share ideas, and provide feedback, fostering a sense of community and engagement.
Implementing Asynchronous Learning Days
Planning and implementing asynchronous learning days requires careful consideration to ensure a smooth and successful transition for both students and teachers. This involves defining clear goals, creating engaging content, and establishing effective communication channels.
Planning Asynchronous Learning Days, What is an asynchronous learning day
Planning asynchronous learning days involves establishing clear goals, selecting appropriate learning activities, and developing a schedule that aligns with the curriculum.
- Define Learning Objectives:Clearly articulate the learning objectives for each asynchronous learning day. This ensures that students understand the expected outcomes and can focus their efforts accordingly.
- Choose Engaging Activities:Select a variety of engaging learning activities that cater to different learning styles and interests. This could include online videos, interactive simulations, podcasts, or self-paced projects.
- Develop a Schedule:Create a structured schedule that Artikels the activities for each asynchronous learning day. This provides students with a clear roadmap and helps them manage their time effectively.
Creating Engaging Content
Creating engaging content is essential for keeping students motivated and engaged during asynchronous learning days. This involves selecting appropriate formats, incorporating multimedia elements, and providing opportunities for interaction.
- Select Appropriate Formats:Choose formats that are suitable for the learning objectives and student audience. This could include videos, articles, podcasts, interactive simulations, or online quizzes.
- Incorporate Multimedia Elements:Utilize multimedia elements, such as images, videos, and audio recordings, to enhance the learning experience and make the content more engaging.
- Provide Opportunities for Interaction:Include opportunities for students to interact with the content, such as online discussions, forums, or collaborative projects.
Communicating with Students and Parents
Clear and consistent communication is crucial for successful implementation of asynchronous learning days. This involves informing students and parents about the purpose, expectations, and support available.
- Inform Students and Parents:Provide clear information about the purpose, expectations, and schedule of asynchronous learning days. This can be done through email, newsletters, or school websites.
- Establish Communication Channels:Establish clear communication channels for students and parents to ask questions, seek support, and provide feedback. This could include email, online forums, or designated office hours.
- Provide Support Resources:Offer students and parents access to support resources, such as online tutorials, FAQs, or technical assistance. This ensures that everyone has the necessary tools to succeed.
Role of Technology in Asynchronous Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping asynchronous learning environments, enabling educators to deliver engaging and flexible learning experiences. By leveraging technology, asynchronous learning overcomes the limitations of traditional synchronous learning, where all learners must be present at the same time and location.
Technology’s Impact on Asynchronous Learning
Technology empowers educators to create learning experiences that cater to diverse learner needs and preferences. Here’s how technology enhances flexibility and accessibility:
- Flexible Learning:Asynchronous learning allows learners to access educational materials and complete assignments at their own pace, anytime and anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for students with busy schedules, working professionals, and learners with diverse learning styles.
- Increased Accessibility:Technology removes geographical barriers, allowing learners from different locations and backgrounds to participate in online learning communities. This is especially important for students who may not have access to traditional brick-and-mortar educational institutions.
Technology’s impact on learner engagement and motivation is significant. Interactive learning platforms, multimedia content, and gamified learning experiences create a more engaging and motivating learning environment. This is in contrast to traditional synchronous learning, which can often be perceived as passive and less stimulating.
Key Technological Tools and Platforms
Here’s a table outlining some of the key technological tools and platforms used for asynchronous learning:
| Tool/Platform | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Management System (LMS) | Provides a central hub for course materials, assignments, communication, and assessments. | Moodle, Canvas, Blackboard |
| Video Conferencing Software | Facilitates real-time video and audio communication, allowing for virtual meetings, lectures, and group discussions. | Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams |
| Online Discussion Forums | Enables asynchronous communication and collaboration among learners and instructors. | Canvas Discussion Boards, Moodle Forums, Piazza |
| Collaborative Document Editing Tools | Allows learners to work together on documents, presentations, and other projects in real-time. | Google Docs, Microsoft Word Online, Dropbox Paper |
| Interactive Learning Platforms | Offer a variety of interactive learning experiences, including simulations, games, and quizzes. | Kahoot!, Quizlet, Khan Academy |
| Multimedia Content Creation Tools | Empower learners to create and share multimedia content, such as videos, podcasts, and presentations. | YouTube, Audacity, Canva |
Technology and Communication/Collaboration
Technology plays a crucial role in facilitating communication and collaboration in asynchronous learning environments. Online discussion forums, instant messaging platforms, and collaborative document editing tools enable learners to connect with each other and their instructors, fostering a sense of community and shared learning.
- Online Discussion Forums:These platforms provide a space for learners to engage in discussions, ask questions, share insights, and provide feedback on course materials. They promote peer-to-peer learning and knowledge sharing, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
- Collaborative Document Editing Tools:These tools allow learners to work together on documents, presentations, and other projects in real-time, regardless of their physical location. This enhances group projects, shared tasks, and collaborative writing experiences.
Summary
Technology is a vital component of asynchronous learning, enabling educators to create flexible, accessible, and engaging learning experiences. By leveraging technology, asynchronous learning overcomes the limitations of traditional synchronous learning, fostering greater learner autonomy, accessibility, and engagement. While technology offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider potential challenges, such as digital equity, technical support, and the need for effective pedagogical practices to ensure successful implementation.
Challenges of Asynchronous Learning: What Is An Asynchronous Learning Day

While asynchronous learning offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge and address potential challenges to ensure student success. These challenges can arise from various factors, including student motivation, technological access, and effective communication.
By understanding these challenges and implementing strategies to mitigate them, educators can create a supportive and engaging asynchronous learning environment that fosters student learning and well-being.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Maintaining student engagement and motivation is crucial in asynchronous learning. Without the structure and immediate feedback of a traditional classroom setting, students may struggle to stay on track and complete assignments.
- Lack of direct interaction:Asynchronous learning often lacks the immediate feedback and interaction that students receive in a traditional classroom setting. This can lead to a feeling of isolation and decreased motivation, particularly for students who thrive in collaborative environments.
- Time management challenges:Students may struggle to manage their time effectively and prioritize asynchronous learning activities, especially if they have other commitments or responsibilities. This can lead to procrastination and missed deadlines.
- Difficulty staying focused:Students may find it challenging to stay focused and engaged with asynchronous learning materials, especially if they are not accustomed to independent learning. Distractions at home or in their learning environment can also hinder their ability to concentrate.
Technical Issues and Access
Asynchronous learning relies heavily on technology, which can create challenges for students who lack access to reliable internet or devices. Additionally, technical difficulties can disrupt learning and create frustration.
- Unequal access to technology:Not all students have equal access to reliable internet connections, computers, or other necessary technology. This can create a digital divide and hinder their ability to participate fully in asynchronous learning.
- Technical difficulties:Technical issues, such as internet outages, software glitches, or device malfunctions, can disrupt asynchronous learning and create frustration for students. This can lead to missed deadlines and a sense of discouragement.
- Lack of technical skills:Some students may lack the necessary technical skills to navigate online learning platforms, access resources, or complete assignments. This can create a barrier to their success in asynchronous learning.
Communication and Support
Effective communication and support are crucial for student success in asynchronous learning. Students need clear instructions, regular feedback, and access to support resources to navigate the learning process effectively.
- Miscommunication and lack of clarity:Asynchronous learning requires clear and concise communication to ensure that students understand expectations and instructions. Miscommunication can lead to confusion, frustration, and poor performance.
- Limited opportunities for feedback:Asynchronous learning can make it more difficult for students to receive timely and personalized feedback on their work. This can hinder their learning progress and make it challenging to identify areas for improvement.
- Lack of support systems:Students may feel isolated and lack access to the same level of support that they would receive in a traditional classroom setting. This can make it more difficult to address challenges and stay motivated.
Asynchronous Learning in Different Educational Settings
Asynchronous learning has become increasingly prevalent in various educational settings, from K-12 schools to higher education institutions and online learning platforms. Its flexibility and accessibility make it an attractive option for learners with diverse needs and schedules. This section explores how asynchronous learning is implemented in different educational contexts, highlighting the unique approaches, considerations, and challenges associated with each.
Asynchronous Learning in K-12 Education
Asynchronous learning in K-12 education presents opportunities to personalize learning experiences and cater to diverse student needs. Here are some ways asynchronous learning is implemented:
- Flipped Classroom:This approach involves students watching lectures or reviewing material at home, allowing class time for interactive activities, projects, and collaborative learning. Asynchronous learning through video lectures, online simulations, and interactive exercises allows students to learn at their own pace and revisit concepts as needed.
- Online Learning Platforms:Educational platforms like Khan Academy, Coursera, and Edpuzzle provide access to a vast library of asynchronous learning resources, including video lessons, interactive quizzes, and practice exercises. These platforms allow students to learn independently and receive immediate feedback on their progress.
- Blended Learning:This model combines asynchronous online learning with traditional classroom instruction. Students can access online materials for homework assignments, review concepts, and complete assessments outside of class. This allows for more flexible scheduling and personalized learning experiences.
Asynchronous Learning in Higher Education
Higher education institutions are increasingly adopting asynchronous learning strategies to enhance flexibility and accessibility for students.
- Online Courses:Many universities offer fully online degree programs and individual courses, relying heavily on asynchronous learning components. This includes pre-recorded lectures, discussion forums, online assignments, and virtual office hours. Students can access materials and participate in discussions at their convenience.
An asynchronous learning day is like having a flexible school schedule where you can complete your work at your own pace. Think of it like learning a new language, like Hebrew, where you can study at your own pace and on your own time.
You can check out this article about whether Hebrew is a difficult language to learn: is hebrew a difficult language to learn. So, an asynchronous learning day gives you the freedom to work on your studies, just like you can learn Hebrew, without being tied to a fixed classroom schedule.
- Hybrid Courses:Hybrid courses blend online and face-to-face instruction. Asynchronous components may include online readings, quizzes, and discussions, while synchronous elements include live lectures, group projects, and laboratory sessions. This approach provides flexibility while maintaining a sense of community and direct interaction with instructors.
- Independent Study:Asynchronous learning is crucial for independent study programs, allowing students to pursue specialized topics or research projects at their own pace. Students can access online resources, collaborate with mentors, and submit assignments asynchronously, fostering self-directed learning and exploration.
Asynchronous Learning in Online Learning
Online learning platforms heavily rely on asynchronous learning strategies to cater to a diverse student population and provide flexibility.
- Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs):MOOCs are designed for large-scale online learning, relying heavily on asynchronous learning components. Pre-recorded lectures, interactive exercises, and discussion forums allow students from around the world to participate at their own pace and interact with peers and instructors.
- Personalized Learning:Asynchronous learning in online platforms enables personalized learning experiences, allowing students to progress through content at their own pace and focus on areas where they need additional support. Adaptive learning technologies and personalized learning pathways provide customized feedback and guidance based on individual needs.
- Virtual Communities:Online learning platforms often foster virtual communities through asynchronous discussions and forums. Students can engage with peers, ask questions, and share insights outside of scheduled class times, promoting collaboration and peer-to-peer learning.
Challenges of Asynchronous Learning in Different Educational Settings
While asynchronous learning offers numerous benefits, certain challenges need to be addressed in different educational settings:
- Maintaining Engagement:Engaging students in asynchronous learning environments can be challenging. Students may require motivation and structure to stay on track with their learning. Strategies such as interactive activities, gamification, and regular feedback can help.
- Technical Barriers:Access to technology and reliable internet connections is crucial for successful asynchronous learning. Schools and universities must ensure equitable access to technology and provide support for students facing technical challenges.
- Social Interaction:Asynchronous learning can limit opportunities for social interaction and collaboration among students. Creating online spaces for discussion, group projects, and virtual meetups can foster a sense of community and collaboration.
- Assessment and Feedback:Assessing student learning in asynchronous environments requires innovative approaches. Online quizzes, project submissions, and discussion forum participation can provide insights into student understanding, but ensuring accurate and timely feedback is crucial.
Asynchronous Learning and Student Engagement
Asynchronous learning offers flexibility and convenience for students, but it also presents unique challenges in maintaining student engagement and motivation. This section delves into the impact of asynchronous learning on student engagement, exploring how it influences participation, motivation, time management, and ultimately, learning outcomes.
Engagement in Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning can significantly impact student participation in class discussions and online forums. While the flexibility of asynchronous learning allows students to contribute at their own pace and convenience, it can also lead to a decrease in real-time interaction and the feeling of a shared learning experience.
Factors Affecting Engagement
- Accessibility and Convenience:Asynchronous learning provides flexibility for students to participate in discussions and forums at times that suit their schedules. This accessibility can lead to increased participation, especially for students with busy schedules or time constraints.
- Structure and Organization:Clear guidelines, well-organized forums, and timely feedback from instructors are crucial for maintaining engagement in asynchronous discussions.
- Variety and Interactivity:Incorporating a variety of discussion formats, including video responses, polls, and interactive activities, can help to keep students engaged and motivated.
- Peer Interaction:Encouraging peer-to-peer interaction and collaboration in online forums can foster a sense of community and promote active participation.
Motivation in Asynchronous Learning
Understanding the factors that influence student motivation in asynchronous learning environments is crucial for maximizing engagement and achieving desired learning outcomes.
Factors Affecting Motivation
- Clear Expectations and Goals:Students are more motivated when they understand the learning objectives, expectations, and how the asynchronous activities contribute to their overall understanding.
- Meaningful Content and Relevance:Connecting the asynchronous learning materials to real-world applications or personal interests can make learning more engaging and meaningful.
- Personalized Learning Experiences:Offering opportunities for students to choose topics, activities, or learning paths that align with their interests and learning styles can enhance motivation.
- Feedback and Recognition:Timely and constructive feedback from instructors and peers can provide students with a sense of accomplishment and motivate them to continue participating.
Time Management in Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning can impact students’ ability to manage their time effectively, both positively and negatively.
Time Management Considerations
- Flexibility and Self-Direction:Asynchronous learning empowers students to manage their learning time based on their individual schedules and preferences.
- Procrastination and Time Management Skills:Students need to develop strong time management skills to avoid procrastination and ensure they complete assigned tasks within deadlines.
- Structured Learning Environments:Providing clear deadlines, structured learning plans, and regular reminders can help students stay on track and manage their time effectively.
Learning Outcomes in Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning can lead to similar or different learning outcomes compared to traditional synchronous learning, depending on the design and implementation of the learning activities.
Factors Influencing Learning Outcomes
- Active Learning Strategies:Incorporating active learning strategies, such as problem-solving, case studies, and simulations, can promote deeper understanding and application of knowledge in asynchronous environments.
- Quality of Learning Materials:Well-designed and engaging learning materials, including videos, interactive exercises, and multimedia resources, are essential for effective asynchronous learning.
- Assessment and Evaluation:Appropriate assessment methods, including formative and summative assessments, should be used to measure learning outcomes and provide feedback to students.
Asynchronous Learning and Teacher Roles

Asynchronous learning may seem to lessen the direct involvement of teachers, but it actually demands a different set of skills and responsibilities. Teachers play a crucial role in shaping effective asynchronous learning experiences, ensuring that students have the resources and support they need to thrive in this flexible learning environment.
Designing and Delivering Asynchronous Learning Content
Teachers need to meticulously design and deliver asynchronous learning content to make it engaging and effective. This requires understanding the learning objectives and tailoring the content to meet diverse learning styles and needs.
- Clear Learning Objectives:Teachers must clearly define the learning objectives for each asynchronous learning module, ensuring that students understand what they are expected to learn.
- Varied Content Formats:Teachers should employ a variety of content formats, such as videos, podcasts, interactive simulations, and online quizzes, to keep students engaged and cater to different learning preferences.
- Chunking and Sequencing:Breaking down complex information into smaller, manageable chunks helps students process information more effectively.
- Accessibility and Usability:Teachers must ensure that all learning materials are accessible to all students, regardless of their learning abilities or disabilities. This includes providing transcripts for videos, captions for multimedia content, and alternative formats for text-based materials.
Providing Support and Guidance
While asynchronous learning allows for flexibility, students may still require support and guidance. Teachers play a vital role in ensuring that students have access to the necessary resources and assistance during asynchronous learning periods.
- Regular Check-Ins:Teachers should schedule regular check-ins with students, either through online forums, video conferencing, or email, to address any questions, concerns, or difficulties.
- Clear Communication:Teachers should communicate clearly and consistently with students regarding expectations, deadlines, and available resources.
- Collaborative Learning Opportunities:Teachers can create opportunities for students to collaborate and support each other during asynchronous learning periods. This could include online discussion forums, group projects, or peer-to-peer learning activities.
10. Future Trends in Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing educational needs. Emerging trends like personalized learning, adaptive technology, and microlearning are shaping the future of education and creating new possibilities for engaging and effective learning experiences.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning is a key trend in asynchronous learning, tailoring learning paths to individual student needs and learning styles. AI-powered platforms can analyze student data, such as performance, learning preferences, and interests, to create customized learning experiences. For example, platforms like Khan Academy and Duolingo use AI to recommend learning resources and adjust the difficulty level based on individual progress.
These platforms also offer personalized feedback and support, providing students with individualized guidance and encouragement.
Adaptive Technology
Adaptive learning platforms play a crucial role in adjusting content difficulty and pacing based on student performance. These platforms use algorithms to assess student understanding and provide immediate feedback, allowing students to progress at their own pace. Examples include platforms like DreamBox Learning for math and IXL for various subjects.
Adaptive technology can enhance student engagement by providing a personalized and challenging learning experience. It can also improve knowledge retention by focusing on areas where students need additional support.
Microlearning
Microlearning involves delivering bite-sized content modules that focus on specific skills or concepts. These modules can be accessed asynchronously, allowing students to learn at their own pace and on their own time. Microlearning addresses the challenges of knowledge retention and information overload by breaking down complex topics into manageable chunks.
Examples include platforms like LinkedIn Learning and Coursera, which offer short, focused learning modules on a wide range of topics. Microlearning is also valuable for skills development and professional development, allowing individuals to acquire new skills or update existing knowledge in a flexible and accessible manner.
Case Studies of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning days are becoming increasingly common in schools and universities around the world. These days offer students the opportunity to learn at their own pace and in their own way, while also providing teachers with valuable time for professional development and planning.
To understand the potential and challenges of asynchronous learning days, it’s crucial to examine real-world examples of successful implementations. This section explores case studies from different educational settings, highlighting key factors that contributed to their success and providing insights for future implementation.
Case Studies of Asynchronous Learning Days
To understand the practical implications and effectiveness of asynchronous learning days, let’s delve into specific examples from different educational institutions.
Case Study 1: [School Name], [Location]- Elementary School
This elementary school implemented asynchronous learning days as part of their response to the COVID-19 pandemic. The school’s primary goal was to provide students with continuity of learning while ensuring the safety of everyone involved.
- Context:Pandemic Response
- Design and Structure:Asynchronous learning days were designed around a blend of online learning platforms, pre-recorded video lessons, and independent student activities. The school utilized a learning management system (LMS) to deliver content, facilitate communication, and provide feedback. Teachers created engaging video lessons that students could access at their own pace.
Independent activities included worksheets, online games, and creative projects that allowed students to explore topics in a hands-on manner.
- Targeted Learning Outcomes:The school focused on maintaining students’ academic progress, fostering their independence, and developing their self-directed learning skills. Students were expected to complete assigned tasks, demonstrate their understanding through online quizzes or projects, and participate in online discussions.
- Key Success Factors:
- Student Engagement:The school incorporated a variety of engaging activities and resources, including interactive games, multimedia presentations, and hands-on projects, to keep students motivated and on track.
- Teacher Support:Teachers provided clear instructions, regular feedback, and support to students through online forums, video conferencing, and email. They also collaborated to create and share resources.
- Technology Infrastructure:The school invested in reliable technology infrastructure and provided students with access to devices and internet connectivity. They ensured that all students had the necessary tools to participate in online learning.
- Assessment and Feedback:The school implemented a combination of formative and summative assessments, including online quizzes, project submissions, and participation in online discussions. Feedback was provided promptly through the LMS and video conferencing sessions.
- Communication and Collaboration:The school maintained open communication channels between teachers, students, and parents. Regular updates were provided through the LMS, email, and phone calls.
- Lessons Learned:The school learned the importance of providing clear instructions, ensuring accessibility to technology, and offering ongoing support to students and teachers. They also emphasized the need for regular communication and collaboration to address any challenges and maintain a sense of community.
Case Study 2: [School Name], [Location]
High School
This high school implemented asynchronous learning days as part of a curriculum innovation initiative. The school aimed to personalize learning experiences, promote student autonomy, and prepare students for the demands of the 21st-century workforce.
- Context:Curriculum Innovation
- Design and Structure:Asynchronous learning days were structured around student-led activities, independent research projects, and online collaboration tools. Students had the freedom to choose from a range of activities that aligned with their interests and learning goals. The school provided a platform for students to share their work, collaborate with peers, and receive feedback from teachers.
- Targeted Learning Outcomes:The school aimed to develop students’ critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills. They also wanted to foster students’ self-directed learning habits, creativity, and innovation. Students were expected to demonstrate their understanding through presentations, projects, and online discussions.
- Key Success Factors:
- Student Engagement:Students were highly engaged in asynchronous learning days due to the personalized nature of the activities and the opportunity to explore their interests. The school also encouraged student-led projects and presentations, which provided students with a sense of ownership and responsibility for their learning.
- Teacher Support:Teachers provided guidance and support to students during asynchronous learning days. They offered feedback on projects, facilitated online discussions, and encouraged students to pursue their interests. They also collaborated to create a variety of resources and activities for students to choose from.
- Technology Infrastructure:The school invested in robust technology infrastructure, including a robust LMS, video conferencing tools, and online collaboration platforms. This enabled students to access resources, communicate with peers and teachers, and share their work effectively.
- Assessment and Feedback:Assessment during asynchronous learning days focused on students’ ability to apply their knowledge, solve problems, and communicate their findings effectively. Feedback was provided through online platforms, individual consultations, and peer reviews.
- Communication and Collaboration:The school fostered a collaborative learning environment through online forums, group projects, and peer-to-peer feedback. Students were encouraged to communicate their ideas, share resources, and support each other’s learning.
- Lessons Learned:The school learned the importance of providing students with choices, fostering a collaborative learning environment, and providing adequate technology infrastructure. They also emphasized the need for ongoing teacher support and feedback to guide students’ learning and ensure that they were meeting learning objectives.
Case Study 3: [School Name], [Location]
University
This university implemented asynchronous learning days as part of a teacher professional development initiative. The goal was to provide teachers with time to collaborate, learn new teaching strategies, and develop innovative curriculum materials.
- Context:Teacher Professional Development
- Design and Structure:Asynchronous learning days were structured around online workshops, webinars, and self-paced learning modules. Teachers were provided with access to a variety of resources, including videos, articles, and interactive simulations. They also had the opportunity to participate in online discussions with colleagues and experts in the field.
- Targeted Learning Outcomes:The university aimed to enhance teachers’ pedagogical skills, knowledge of educational technology, and ability to design engaging and effective learning experiences. Teachers were expected to apply the new skills and knowledge they gained during asynchronous learning days to their classrooms.
- Key Success Factors:
- Teacher Engagement:Teachers were highly engaged in asynchronous learning days due to the flexibility and convenience of online learning. They appreciated the opportunity to learn at their own pace and access resources that were relevant to their specific needs.
- Teacher Support:The university provided technical support, guidance, and resources to teachers during asynchronous learning days. They also offered opportunities for teachers to connect with colleagues and share best practices.
- Technology Infrastructure:The university invested in a user-friendly LMS, reliable video conferencing tools, and a variety of online learning resources. This ensured that teachers had access to the necessary tools and resources to participate in asynchronous learning activities.
- Assessment and Feedback:The university used a variety of methods to assess teachers’ learning, including online quizzes, participation in discussions, and project submissions. Feedback was provided through the LMS and individual consultations.
- Communication and Collaboration:The university fostered a collaborative learning environment through online forums, group projects, and peer-to-peer feedback. Teachers were encouraged to share their ideas, resources, and best practices.
- Lessons Learned:The university learned the importance of providing teachers with flexible and accessible learning opportunities, offering ongoing support and guidance, and fostering a collaborative learning environment. They also emphasized the need for a robust technology infrastructure and effective communication strategies to ensure the success of asynchronous learning days.
Best Practices for Asynchronous Learning

Asynchronous learning offers flexibility and autonomy, but effective implementation requires careful planning and execution. This section explores best practices for designing and delivering engaging and successful asynchronous learning experiences.
Content Delivery
Delivering high-quality content is paramount in asynchronous learning. Students rely on the materials provided to learn effectively. The following strategies ensure clear, accessible, and engaging content delivery.
- Chunk content into manageable units: Break down complex topics into smaller, digestible units to prevent information overload. This promotes focused learning and allows students to process information at their own pace.
- Use diverse media formats: Employ a variety of media formats like videos, audio recordings, interactive simulations, and infographics to cater to different learning styles and preferences. This can enhance engagement and comprehension.
- Provide clear instructions and learning objectives: Ensure students understand what is expected of them by clearly stating learning objectives and providing detailed instructions for each activity. This helps them navigate the learning process effectively.
- Make content accessible: Ensure materials are accessible to all students, regardless of disabilities or technological limitations. Consider providing transcripts for videos, alternative formats for documents, and captions for multimedia content.
Student Engagement
Engaging students in asynchronous learning is crucial to maintain their motivation and ensure active learning. The following strategies promote student participation and interaction.
- Incorporate interactive elements: Include quizzes, polls, discussion forums, and collaborative projects to encourage active participation and interaction among students. This fosters a sense of community and encourages peer learning.
- Provide opportunities for feedback and reflection: Offer opportunities for students to reflect on their learning and receive feedback from instructors and peers. This helps them identify areas for improvement and promotes self-directed learning.
- Offer personalized learning paths: Allow students to choose learning paths that align with their interests and learning styles. This fosters a sense of ownership and autonomy, enhancing motivation and engagement.
- Use gamification techniques: Incorporate game mechanics like points, badges, and leaderboards to motivate students and make learning more enjoyable. This can be particularly effective for engaging younger learners.
Assessment
Assessment in asynchronous learning should be aligned with learning objectives and provide meaningful feedback. The following strategies promote effective assessment in asynchronous learning.
- Use a variety of assessment methods: Employ a range of assessment methods like quizzes, projects, essays, and discussions to assess different learning outcomes. This provides a comprehensive understanding of student learning.
- Provide timely and constructive feedback: Offer timely and specific feedback on student work, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement. This helps students track their progress and refine their learning.
- Offer opportunities for self-assessment: Encourage students to reflect on their learning and assess their own progress. This promotes metacognition and self-directed learning.
- Use technology to streamline assessment: Leverage technology tools for automated grading, online submission, and feedback delivery. This can save time and enhance efficiency in assessment.
Research on Asynchronous Learning
Research on asynchronous learning has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of online and blended learning models. Studies have explored the effectiveness of asynchronous learning across various educational settings and disciplines, providing valuable insights into its impact on student outcomes and the future of education.
Effectiveness of Asynchronous Learning
A substantial body of research suggests that asynchronous learning can be an effective pedagogical approach. Studies have consistently shown that asynchronous learning can be as effective as traditional face-to-face instruction in terms of student learning outcomes, particularly in terms of knowledge acquisition and skill development.
For example, a meta-analysis of 52 studies by Bernard et al. (2014) found that asynchronous learning was as effective as traditional instruction in terms of student achievement in various subjects, including mathematics, science, and language arts. The researchers concluded that asynchronous learning can be a viable alternative to traditional instruction, particularly for students who prefer a flexible learning environment.
Impact on Student Achievement, Engagement, and Satisfaction
Asynchronous learning has been found to have a positive impact on student achievement, engagement, and satisfaction. Studies have shown that students who participate in asynchronous learning activities tend to perform better academically, demonstrate higher levels of engagement, and report higher levels of satisfaction with their learning experience.A study by Garrison and Kanuka (2004) found that students who participated in asynchronous online discussions demonstrated higher levels of critical thinking and problem-solving skills compared to those who did not.
The researchers attributed this finding to the opportunity for students to reflect on their ideas and engage in more in-depth discussions in an asynchronous environment.
Future Directions for Research
While there is a growing body of research on asynchronous learning, several areas warrant further investigation. Future research should focus on:
- Exploring the impact of different asynchronous learning modalities, such as online forums, video lectures, and interactive simulations, on student outcomes.
- Investigating the role of learner characteristics, such as learning styles and prior knowledge, in influencing the effectiveness of asynchronous learning.
- Developing and testing innovative asynchronous learning strategies that promote deeper learning and engagement.
- Examining the ethical implications of asynchronous learning, such as issues related to accessibility, equity, and student privacy.
Future research in asynchronous learning is crucial for optimizing its effectiveness and ensuring that it is used to create engaging and equitable learning experiences for all students.
Asynchronous Learning and Student Diversity
Asynchronous learning offers numerous benefits for educators and students alike, but it’s crucial to recognize and address the diverse needs of learners to ensure inclusivity and equitable access to quality education.
Importance of Considering Student Diversity
Designing asynchronous learning experiences that effectively cater to a diverse student population is essential. This requires a deep understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities presented by factors such as learning styles, cultural backgrounds, language proficiency, disabilities, socioeconomic status, and prior academic experiences.
- Learning Styles:Some students may thrive with visual learning materials like videos and infographics, while others prefer auditory learning through podcasts or audio lectures. Kinesthetic learners might benefit from interactive simulations or hands-on activities that encourage active engagement.
- Cultural Backgrounds:Students from different cultures may have varying expectations and preferences for learning. Understanding cultural norms and values can help tailor asynchronous activities to resonate with diverse learners.
- Language Proficiency:Students with limited English proficiency might require additional support, such as translated materials, captioned videos, or opportunities for peer-to-peer language support.
- Disabilities:Students with disabilities may need specific accommodations, such as text-to-speech software, closed captions, or alternative assessment methods. It’s essential to consult with students and their support systems to understand their individual needs.
- Socioeconomic Status:Access to technology and reliable internet connectivity can be a significant barrier for students from low-income backgrounds. Ensuring equitable access to resources and technology is crucial for successful asynchronous learning.
- Prior Academic Experiences:Students with different academic backgrounds may have varying levels of prior knowledge and skills. Providing differentiated learning materials and opportunities for remediation can help address these gaps.
Strategies for Accessibility and Equity
To ensure that asynchronous learning is accessible and equitable for all students, educators can implement strategies that address potential barriers related to technology, time, and learning styles.
Technology
- Alternative Access Methods:Providing options like text-to-speech software, closed captions, and screen readers can make digital materials accessible to students with visual or auditory impairments.
- Different Devices:Offering a range of devices, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones, can accommodate students’ individual preferences and technical capabilities.
- Compatibility with Assistive Technologies:Ensure that all learning materials and platforms are compatible with assistive technologies commonly used by students with disabilities.
Time
- Flexible Deadlines:Allowing students to complete assignments at their own pace, within reasonable timeframes, can accommodate individual schedules and responsibilities.
- Break Down Large Assignments:Dividing large assignments into smaller, manageable chunks can reduce overwhelm and promote a sense of progress.
- Live Q&A Sessions:Offering live question-and-answer sessions can provide real-time support and clarification for students who need it.
Learning Styles
- Diverse Learning Materials:Providing a variety of learning materials, including videos, podcasts, interactive simulations, and text-based resources, can cater to different learning preferences.
- Options for Engagement:Offering different levels of engagement, such as active participation in discussions or passive observation of materials, can accommodate individual learning styles.
Adapting Asynchronous Learning Activities
Common asynchronous learning activities, such as online discussions, video lectures, and group projects, can be adapted to meet the needs of diverse learners.
Online Discussions
- Multiple Formats for Participation:Encourage participation through various formats, including text, audio, and video, to accommodate different communication styles and comfort levels.
- Prompts that Encourage Diverse Perspectives:Design discussion prompts that promote critical thinking, empathy, and respect for diverse viewpoints.
- Accessibility Features:Utilize accessibility features like text-to-speech and closed captions to make discussions accessible to all students.
Video Lectures
- Transcripts and Closed Captions:Provide transcripts and closed captions for all video lectures to enhance accessibility for students with auditory impairments or language differences.
- Summaries and Key Takeaways:Offer summaries and key takeaways at the end of each video to help students retain important information.
- Interactive Elements:Incorporate interactive elements, such as quizzes, polls, or embedded links to relevant resources, to enhance engagement and understanding.
Group Projects
- Flexible Group Formation Options:Allow students to choose their group members or provide options for self-selected or teacher-assigned groups, considering individual preferences and strengths.
- Clear Guidelines and Rubrics:Provide clear guidelines and rubrics for group projects to ensure that all students understand expectations and assessment criteria.
- Accessible Collaboration Tools:Use collaboration tools that are accessible to all students, regardless of their technical skills or disabilities.
Designing Asynchronous Learning Activities for Students with Learning Disabilities
When designing asynchronous learning activities for students with learning disabilities, it’s crucial to consider their individual needs and provide appropriate accommodations.
- Clear and Concise Instructions:Use clear and concise language in all instructions and materials, avoiding jargon or complex sentence structures.
- Step-by-Step Guidance:Provide step-by-step guidance for completing assignments, breaking down tasks into manageable chunks.
- Opportunities for Practice and Feedback:Offer opportunities for practice and feedback throughout the learning process, allowing students to develop skills and receive support.
- Alternative Assessment Options:Provide alternative assessment options, such as oral presentations, demonstrations, or portfolios, to accommodate different learning styles and abilities.
Questions Often Asked
What are the main benefits of asynchronous learning days for students?
Asynchronous learning days offer several benefits, including increased flexibility, personalized learning experiences, and the ability to work at one’s own pace. They also allow students to access learning materials and activities from anywhere with an internet connection, making education more accessible.
How can teachers effectively implement asynchronous learning days?
Teachers can implement asynchronous learning days by carefully planning the activities, providing clear instructions, and offering adequate support to students. They should also consider using a variety of online tools and platforms to engage students and facilitate communication.
What are some examples of asynchronous learning activities?
Examples of asynchronous learning activities include online quizzes, watching educational videos, completing interactive simulations, participating in online discussions, and working on individual projects. The possibilities are endless!
-*