What do you learn in a communications class? It’s not just about talking and writing—it’s about understanding the complexities of human interaction, the power of language, and the art of building connections. From the fundamentals of verbal and nonverbal communication to exploring theories and applying practical skills, this course delves into the multifaceted world of how we communicate and its impact on our lives.
You’ll discover different communication types, learn how to listen effectively, and gain valuable insights into public speaking, writing, and providing feedback. The course also explores communication theories, interpersonal dynamics, group communication, and the role of communication in various contexts, including organizations, mass media, and a globalized world.
By understanding the principles and strategies of effective communication, you’ll develop the skills to navigate relationships, build trust, and achieve your goals.
Communication Fundamentals
Communication is the lifeblood of any successful interaction, whether it’s between individuals, groups, or organizations. Understanding the different types of communication and how to use them effectively is crucial for building strong relationships, achieving goals, and navigating the complexities of modern life.
Types of Communication
Communication can be broadly categorized into four main types: verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual. Each type has its unique characteristics and strengths, and understanding these differences is essential for effective communication.
- Verbal Communication:This involves the use of spoken words to convey messages. It includes both formal and informal language, depending on the context. For instance, a job interview requires formal language, while a casual conversation with friends uses informal language.
- Nonverbal Communication:This encompasses all forms of communication that do not involve spoken words. It includes body language (gestures, facial expressions, posture), tone of voice, and physical appearance. Nonverbal cues can often be more powerful than verbal communication, as they convey emotions and attitudes that words may not express.
For example, a firm handshake can convey confidence, while a slumped posture can indicate disinterest.
- Written Communication:This involves the use of written words to convey messages. It includes letters, emails, reports, and other forms of written documents. Written communication allows for careful consideration and planning of messages, making it ideal for conveying complex information or formal requests.
For example, a business proposal or a legal contract requires clear and concise written communication.
- Visual Communication:This involves the use of visual elements to convey messages. It includes images, graphs, charts, and videos. Visual communication is highly effective in capturing attention, conveying information quickly, and enhancing understanding. For example, a presentation using slides with images and graphs can be more engaging and informative than a purely verbal presentation.
Communication in Different Contexts
The effectiveness of communication depends heavily on the context in which it takes place. Different contexts require different communication styles and strategies.
- Workplace:In a professional setting, clear and concise communication is paramount. Verbal communication is often used for meetings and presentations, while written communication is essential for emails, reports, and memos. Nonverbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact and using appropriate body language, is also crucial for building rapport and conveying professionalism.
For example, a manager delivering a presentation needs to use clear and confident verbal communication, while a team working on a project needs to communicate effectively through written memos and emails to ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Family:Family communication is often more informal than professional communication. While verbal communication is still important, nonverbal communication plays a significant role in expressing love, support, and understanding. Active listening, empathy, and clear communication are crucial for resolving conflicts and maintaining healthy relationships within the family.
For example, a family dinner can involve sharing stories and listening attentively to each other, while a family meeting might require open and honest communication to address issues and make decisions.
- Social Gatherings:Social communication often involves a mix of verbal and nonverbal cues. It’s important to be mindful of social norms and adjust your communication style accordingly. Active listening, empathy, and humor are key elements of successful social communication. For example, at a party, you might engage in small talk with strangers, while at a friend’s birthday celebration, you might share personal anecdotes and jokes.
- Public Speaking:Public speaking requires a combination of strong verbal communication skills, effective nonverbal cues, and engaging visual aids. Clear articulation, confident delivery, and audience engagement are essential for successful public speaking. For example, a politician delivering a speech needs to use persuasive language and captivating nonverbal cues to connect with the audience, while a teacher presenting a lecture needs to use clear explanations and visual aids to enhance understanding.
Importance of Effective Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful relationships, both personal and professional. It fosters trust, understanding, and collaboration, leading to positive outcomes in various aspects of life.
- Personal Life:Effective communication is essential for building strong and lasting relationships. It allows individuals to express their thoughts and feelings clearly, understand the perspectives of others, and resolve conflicts constructively. Open and honest communication fosters trust, empathy, and intimacy, leading to deeper connections and greater satisfaction in personal relationships.
For example, a couple who communicates openly and honestly is more likely to resolve conflicts peacefully and build a strong and lasting relationship.
- Professional Life:In the professional sphere, effective communication is crucial for career advancement, teamwork, and overall success. Clear and concise communication helps individuals to convey their ideas effectively, build strong working relationships, and navigate complex situations. Effective communication skills are highly valued by employers, as they contribute to increased productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
For example, a salesperson who communicates effectively with customers is more likely to build rapport, close deals, and achieve sales targets.
“The single biggest problem in communication is the illusion that it has taken place.”
George Bernard Shaw
2. Communication Skills: What Do You Learn In A Communications Class
Communication skills are essential for effective interactions in all aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional settings. They enable us to convey our thoughts and ideas clearly, build strong connections, and achieve our goals. This section explores key communication skills that are crucial for success in various domains.
2.1 Active Listening
Active listening is a crucial communication skill that involves paying full attention to the speaker and demonstrating understanding. It goes beyond simply hearing the words; it encompasses engaging with the message, interpreting the speaker’s intent, and responding appropriately.
- Key Elements of Active Listening:
- Paying Attention:Focus on the speaker, minimize distractions, and maintain eye contact.
- Asking Questions:Clarify points you don’t understand and demonstrate your interest.
- Summarizing:Paraphrase the speaker’s message to ensure you comprehend it correctly.
- Nonverbal Cues:Use appropriate body language, such as nodding, leaning in, and maintaining an open posture.
- Empathy:Try to understand the speaker’s perspective and emotions.
- Examples of Active Listening in a Professional Setting:
- During Meetings:Engage actively by taking notes, asking clarifying questions, and summarizing key points.
- Client Interactions:Listen attentively to client concerns, acknowledge their feelings, and respond with empathy and solutions.
- Feedback Sessions:Focus on the speaker’s message, ask for clarification, and demonstrate understanding of their perspective.
2.2 Public Speaking
Public speaking is the art of delivering a speech to an audience. It involves careful preparation, effective delivery, and engaging with the listeners. While many people find public speaking daunting, with practice and the right strategies, it can become a powerful tool for communication and persuasion.
- Steps Involved in Preparing and Delivering an Effective Public Speech:
- Planning and Research:Define your purpose, identify your audience, and gather relevant information.
- Structuring the Speech:Organize your thoughts logically, using an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Writing the Speech:Craft clear, concise, and engaging language.
- Rehearsing:Practice your speech multiple times to ensure fluency and confidence.
- Delivery:Use a natural and enthusiastic tone, maintain eye contact, and use gestures effectively.
- Tips for Managing Stage Fright:
- Preparation:Thorough preparation can boost confidence and reduce anxiety.
- Deep Breathing:Take deep breaths to calm your nerves and relax your body.
- Positive Visualization:Imagine yourself delivering a successful speech.
- Focus on the Audience:Connect with your listeners and focus on sharing your message.
- Engaging the Audience:
- Storytelling:Use anecdotes and stories to make your message relatable and memorable.
- Visual Aids:Incorporate visuals, such as slides or props, to enhance your presentation.
- Questions and Interaction:Encourage audience participation through questions and discussions.
- Humor:Use appropriate humor to lighten the mood and keep the audience engaged.
2.3 Writing
Clear and concise writing is essential for effective professional communication. It ensures that your message is understood accurately, efficiently, and persuasively. Different writing styles are appropriate for various situations, and understanding their nuances is crucial for achieving your communication goals.
- Importance of Clear and Concise Writing:
- Clarity:Use precise language and avoid jargon or technical terms that your audience may not understand.
- Conciseness:Get to the point quickly and avoid unnecessary words or phrases.
- Organization:Structure your writing logically, using headings, subheadings, and bullet points.
- Professionalism:Maintain a professional tone and avoid slang or informal language.
- Different Writing Styles:
- Formal Writing:Used for official documents, reports, and academic papers. It features a formal tone, complex sentence structure, and objective language.
- Informal Writing:Used for personal communication, such as emails to friends or colleagues. It features a casual tone, simpler sentence structure, and may include slang or contractions.
- Persuasive Writing:Used to convince the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take action. It features strong arguments, compelling evidence, and persuasive language.
- Appropriate Applications:
- Formal Writing:Business proposals, research papers, legal documents.
- Informal Writing:Personal emails, social media posts, text messages.
- Persuasive Writing:Marketing materials, sales pitches, fundraising appeals.
2.4 Feedback
Feedback is an integral part of effective communication. It provides valuable insights into our performance, helps us identify areas for improvement, and fosters growth. Different types of feedback have distinct impacts on communication, and understanding these nuances is crucial for giving and receiving feedback constructively.
| Type of Feedback | Impact on Communication |
|---|---|
| Positive Feedback | Reinforces positive behaviors, motivates individuals, and builds confidence. |
| Constructive Feedback | Identifies areas for improvement, provides specific suggestions, and encourages growth. |
| Negative Feedback | Can be demotivating, discouraging, and damage relationships if not delivered effectively. |
- Providing Constructive Feedback Effectively:
- Focus on Specific Behaviors:Avoid general statements and provide concrete examples.
- Be Timely:Provide feedback as soon as possible after the event.
- Use “I” Statements:Focus on your observations and feelings rather than making accusations.
- Offer Solutions:Suggest ways to improve or address the issue.
- Maintain a Positive Tone:Even when delivering negative feedback, maintain a respectful and constructive approach.
- Receiver’s Perspective:
- Listen Actively:Pay attention to the feedback and ask clarifying questions.
- Don’t Take it Personally:Focus on the message and avoid getting defensive.
- Seek Clarification:If you don’t understand the feedback, ask for further explanation.
- Consider the Feedback:Reflect on the message and consider how you can apply it.
- Express Gratitude:Thank the sender for their feedback and acknowledge their effort.
3. Communication Theories
Communication theories provide frameworks for understanding how messages are created, transmitted, received, and interpreted. They offer valuable insights into the complexities of human interaction and can help us improve our communication skills in various contexts.
3.1. Shannon-Weaver Model
The Shannon-Weaver model, developed by Claude Shannon and Warren Weaver in 1949, is a linear model of communication that focuses on the technical aspects of transmitting information.
- The model depicts communication as a one-way process, starting with a sender who encodes a message and transmits it through a channel to a receiver who decodes the message.
- Noise, which can be any interference that distorts the message, is also a key component of the model.
- Feedback, the receiver’s response to the message, is not included in the original model but is often considered a crucial aspect of effective communication.
The Shannon-Weaver model is widely used in fields such as engineering, computer science, and telecommunications.
- Its strengths lie in its clarity, simplicity, and focus on the technical aspects of communication.
- It provides a basic understanding of how messages are transmitted and received, and it can be useful for analyzing communication problems in technical settings.
However, the model also has limitations:
- It is a linear model that does not account for the interactive and dynamic nature of communication.
- It does not adequately address the role of meaning-making, which is central to human communication.
- It fails to consider the influence of context, which can significantly impact the interpretation of messages.
An example of how the Shannon-Weaver model can be applied to a real-world communication situation is a phone call:
- The sender is the person making the call, who encodes their message into spoken words.
- The channel is the telephone line.
- The receiver is the person receiving the call, who decodes the message by listening to the spoken words.
- Noise could include background noise, static on the line, or misunderstandings due to accents or dialects.
- Feedback could be the receiver’s verbal response or their tone of voice.
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, encompassing the exchange of thoughts, feelings, and ideas between two or more individuals. This form of communication plays a crucial role in building relationships, resolving conflicts, and achieving shared goals. Understanding the dynamics of interpersonal communication is essential for effective and meaningful connections.
Self-Disclosure
Self-disclosure involves revealing personal information about oneself to others. This process can build trust and intimacy, fostering a deeper understanding between individuals. It can be categorized into different levels, ranging from superficial to highly personal information.
- Superficial Level: This level involves sharing basic information about oneself, such as hobbies, interests, or work. It is typically used in casual interactions and helps build a foundation for deeper connections.
- Personal Level: This level involves sharing more intimate information, such as personal experiences, values, or beliefs. It requires a greater level of trust and can strengthen the bond between individuals.
- Intimate Level: This level involves sharing highly personal and sensitive information, such as vulnerabilities, fears, or dreams. It is reserved for close relationships and can create a deep sense of connection and understanding.
The level of self-disclosure is influenced by factors such as the nature of the relationship, the context of the interaction, and the individual’s comfort level. It is important to note that self-disclosure should be reciprocal and appropriate to the relationship.
Conflict Resolution
Conflict is an inevitable part of interpersonal communication. It arises when individuals have differing opinions, perspectives, or goals. Effective conflict resolution involves understanding the root causes of the conflict, communicating effectively, and finding mutually acceptable solutions.
- Active Listening: Listening attentively to the other person’s perspective is crucial for understanding their needs and concerns. It involves paying full attention, asking clarifying questions, and demonstrating empathy.
- Assertive Communication: Assertive communication involves expressing one’s needs and opinions clearly and respectfully, while acknowledging the other person’s perspective. It avoids aggression or passivity and promotes a more balanced and productive exchange.
- Compromise and Negotiation: Finding mutually acceptable solutions often involves compromise and negotiation. This requires both parties to be willing to make concessions and find common ground.
Effective conflict resolution skills are essential for maintaining healthy relationships and achieving positive outcomes.
Relationship Building
Interpersonal communication plays a vital role in building and maintaining relationships. Effective communication fosters trust, intimacy, and a sense of connection between individuals.
- Active Listening: Demonstrating genuine interest in the other person’s thoughts and feelings is essential for building trust and intimacy. It involves paying full attention, asking clarifying questions, and reflecting on what they have said.
- Empathy and Understanding: Putting oneself in the other person’s shoes and understanding their perspective is crucial for building empathy and strengthening the bond between individuals.
- Shared Experiences and Interests: Engaging in shared activities, interests, or hobbies can create opportunities for connection and strengthen the relationship. It provides common ground and fosters a sense of shared identity.
Building strong and healthy relationships requires consistent effort and commitment to effective communication.
Communication Styles
Different individuals have distinct communication styles that reflect their personality, values, and cultural background. Understanding these styles can enhance communication effectiveness and foster more harmonious interactions.
- Assertive: This style involves expressing one’s needs and opinions clearly and respectfully, while acknowledging the other person’s perspective. It is characterized by directness, honesty, and confidence.
- Passive: This style involves avoiding conflict and often putting the needs of others before their own. It can be characterized by indirectness, hesitancy, and a lack of assertiveness.
- Aggressive: This style involves expressing one’s needs and opinions in a forceful and domineering manner, often at the expense of others. It can be characterized by hostility, blame, and disrespect.
- Passive-Aggressive: This style involves expressing anger or resentment indirectly, through subtle behaviors or sarcasm. It can be characterized by manipulation, avoidance, and a lack of direct communication.
It is important to be aware of one’s own communication style and the styles of others to promote effective and respectful interactions.
Scenario
Imagine a workplace scenario where a team is working on a major project with tight deadlines. One team member, known for their passive communication style, is struggling to voice their concerns about the project’s feasibility. As a result, their concerns go unaddressed, leading to potential delays and misunderstandings.
This scenario highlights the importance of effective interpersonal communication skills, particularly assertiveness, in resolving conflicts and ensuring project success.
5. Group Communication
Group communication is a vital aspect of our personal and professional lives. It involves the exchange of information, ideas, and perspectives between two or more individuals working towards a common goal. Understanding the dynamics of group communication, including its challenges and opportunities, is crucial for effective collaboration and achieving desired outcomes.
Challenges and Opportunities
The effectiveness of group communication can be significantly impacted by various factors, including group size, member diversity, and the complexity of the task at hand. Understanding these factors can help us navigate potential challenges and leverage opportunities for successful collaboration.
- Scenario: A team working on a complex project with members from diverse backgrounds and expertise.
- Challenges:
- Communication barriers due to cultural differences, language variations, and differing communication styles.
- Difficulty in coordinating efforts and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Potential for misunderstandings and conflicts arising from differing perspectives and approaches.
- Opportunities:
- A rich pool of knowledge and perspectives, leading to innovative solutions and creative problem-solving.
- Enhanced learning and growth through exposure to diverse viewpoints and experiences.
- Increased adaptability and resilience in responding to complex and changing situations.
- Scenario: A student group collaborating on a presentation with limited time and resources.
- Challenges:
- Time constraints and limited resources can lead to rushed decisions and compromises.
- Difficulty in coordinating schedules and ensuring everyone contributes equally.
- Potential for conflicts arising from competing priorities and differing opinions.
- Opportunities:
- Shared workload and collaborative problem-solving, leading to a more efficient and effective outcome.
- Development of essential teamwork and time management skills.
- Learning from each other’s strengths and weaknesses, fostering individual growth and development.
- Scenario: A community organization planning an event with a large volunteer base.
- Challenges:
- Coordination difficulties in managing a large group of volunteers with varying levels of commitment and experience.
- Potential for miscommunication and confusion due to the size and complexity of the project.
- Challenges in ensuring everyone feels valued and included in the decision-making process.
- Opportunities:
- A diverse range of skills and perspectives, leading to a more comprehensive and successful event.
- Increased community engagement and ownership of the event, fostering a sense of belonging and shared purpose.
- Opportunity for individual growth and development through leadership and collaboration experiences.
- Introduction:This is where you grab the audience’s attention, introduce your topic, and state your main points.
- Body:The body of your speech is where you develop your main points, provide evidence, and support your claims. Each main point should have its own section with clear transitions between them.
- Conclusion:The conclusion summarizes your main points, reiterates your thesis, and leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
- Vocal Tone:Speak clearly and at a moderate pace. Vary your pitch and volume to keep the audience engaged.
- Body Language:Maintain eye contact with your audience, use hand gestures to emphasize points, and stand tall and confidently.
- Visual Aids:Use visual aids, such as slides or props, to illustrate your points and make your speech more engaging.
- Ask questions:Encourage audience participation by asking questions related to your topic.
- Use stories and anecdotes:Relatable stories and anecdotes can make your speech more memorable and connect with your audience on a personal level.
- Be enthusiastic:Your enthusiasm for your topic will be contagious and inspire your audience.
- Formal channels are often hierarchical, meaning information flows from superiors to subordinates or vice versa.
- Informal channels, on the other hand, can be more fluid and often involve information sharing among colleagues or across different departments.
- Open and transparent communication fosters trust and collaboration, leading to higher employee morale and productivity.
- Effective communication can also help to align employees around shared goals and values, creating a sense of purpose and direction.
- Conversely, poor communication can lead to misunderstandings, conflict, and decreased productivity.
- Leaders who are skilled communicators can build strong relationships with their employees, fostering a culture of open dialogue and feedback.
- Effective communication is also essential for decision-making. When information is shared openly and transparently, leaders can make informed decisions that are supported by their teams.
- Print Media:Print media includes newspapers, magazines, books, and other printed materials. It has been a dominant form of mass communication for centuries, offering in-depth coverage and analysis of events.
- Broadcast Media:Broadcast media encompasses radio and television, which transmit information and entertainment through audio and video signals. Broadcast media offers immediate access to news and events, making it a powerful tool for public communication.
- Digital Media:Digital media includes websites, social media platforms, blogs, and online streaming services. The rise of digital media has revolutionized mass communication, providing a vast and interactive platform for information sharing and communication.
- Agenda Setting:Mass media can influence the public’s perception of the importance of issues by focusing on specific topics and events. This process, known as agenda setting, shapes public discourse and priorities.
- Framing:Mass media can frame events and issues in specific ways, influencing how people interpret and understand information. This framing effect can impact public opinion and policy decisions.
- Cultural Influence:Mass media plays a significant role in shaping cultural trends and values. It introduces new ideas, fashions, and behaviors, influencing people’s lifestyles and preferences.
- Convergence:Technology has blurred the lines between different forms of media, leading to the convergence of print, broadcast, and digital media. This convergence has created new opportunities for information sharing and entertainment.
- Social Media:Social media platforms have emerged as powerful tools for communication and information dissemination. They provide a platform for individuals to share their thoughts, experiences, and news, fostering a more participatory and interactive media landscape.
- Mobile Media:The proliferation of smartphones and mobile devices has led to the rise of mobile media, allowing people to access information and entertainment anytime and anywhere. This has significantly increased the reach and accessibility of mass communication.
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn have become integral to modern communication. They facilitate the sharing of information, news, and personal updates, fostering online communities and social connections.
- Email: Email remains a cornerstone of professional and personal communication, offering a reliable and efficient way to exchange messages, documents, and files.
- Video Conferencing: Technologies like Zoom, Skype, and Google Meet have transformed remote collaboration, allowing individuals to participate in meetings and presentations virtually, regardless of their physical location.
- Instant Messaging: Applications such as WhatsApp, Telegram, and Messenger provide real-time text-based communication, enabling quick and informal exchanges.
- Mobile Phones: Smartphones have become ubiquitous, offering a range of communication tools, including texting, calling, video calls, and internet access, making it possible to connect with anyone, anywhere, at any time.
- Increased Reach and Accessibility: These technologies break down geographical barriers, enabling communication with individuals and groups across the globe.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Real-time communication tools facilitate seamless collaboration on projects, regardless of location, fostering shared understanding and productivity.
- Faster Information Dissemination: Instantaneous communication enables rapid sharing of news, updates, and information, promoting transparency and efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Communication technologies can significantly reduce communication costs, especially for businesses, by eliminating the need for travel and traditional methods like postal mail.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined communication processes, facilitated by technology, can lead to faster decision-making, improved productivity, and enhanced efficiency in various tasks.
- Privacy Concerns: Sharing information online raises concerns about data privacy and security, as personal information can be accessed or misused without proper safeguards.
- Misinformation and Disinformation: The rapid spread of information online can lead to the dissemination of misinformation and disinformation, potentially influencing public opinion and decision-making.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology and digital literacy can create a digital divide, excluding certain individuals and communities from the benefits of these technologies.
- Over-reliance and Dependence: Excessive reliance on communication technologies can lead to decreased face-to-face interaction, potentially impacting social skills and interpersonal relationships.
- Distraction and Reduced Focus: Constant access to communication technologies can lead to distractions, impacting concentration and productivity, particularly in work and academic settings.
- Honesty: This involves being truthful and transparent in our communication. It means avoiding deception, manipulation, and withholding crucial information.
- Respect: Respecting others means valuing their perspectives, even if we disagree. It involves being courteous, considerate, and avoiding language that is demeaning or offensive.
- Fairness: Fairness in communication involves being impartial and giving everyone a fair opportunity to be heard. It means avoiding bias, prejudice, and discrimination in our communication.
- Advertising: Ethical considerations in advertising focus on honesty and transparency. Ads should not mislead consumers, use deceptive claims, or exploit vulnerabilities.
- Journalism: Journalism ethics prioritize accuracy, fairness, and truthfulness. Journalists should strive for objectivity, avoid bias, and ensure their reporting is based on verifiable facts.
- Social Media: Ethical communication on social media involves being mindful of the impact of our posts and interactions. It includes avoiding spreading misinformation, cyberbullying, and engaging in respectful online conversations.
- Plagiarism: Presenting someone else’s work as your own is a blatant violation of ethical communication. It undermines the integrity of the original creator and can lead to academic or professional sanctions.
- Misinformation and Disinformation: Deliberately spreading false or misleading information can have devastating consequences, eroding trust and causing harm.
- Cyberbullying: Using electronic communication to harass, threaten, or humiliate others is unethical and can have a significant impact on the victim’s well-being.
- Language barriers can create misunderstandings and impede clear communication. Even when using a common language, different dialects, accents, and slang can create confusion.
- Cultural norms, such as appropriate greetings, body language, and levels of formality, vary significantly across cultures. What is considered polite in one culture might be offensive in another.
- Communication styles also differ across cultures. Some cultures favor direct communication, while others prefer indirect approaches. This can lead to misinterpretations and misunderstandings.
- Effective intercultural communication promotes understanding, empathy, and respect, fostering stronger relationships and collaborations.
- It helps avoid misunderstandings and conflicts, leading to smoother interactions and more successful outcomes.
- It enhances personal and professional growth, allowing individuals to adapt to diverse environments and work effectively with people from different backgrounds.
- Active listening involves paying full attention to the speaker, understanding their perspective, and asking clarifying questions. It demonstrates respect and encourages open communication.
- Cultural sensitivity involves being aware of and respecting cultural differences, avoiding stereotypes and biases. It requires understanding that different cultures have different norms and values.
- Non-verbal communication, such as body language, facial expressions, and gestures, can vary significantly across cultures. Being aware of these differences can help avoid misinterpretations and misunderstandings.
- Using clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or slang, and employing visual aids can enhance communication clarity, especially when communicating with individuals from different linguistic backgrounds.
- Empathy and understanding are crucial for effective communication in a diverse world. Putting yourself in the other person’s shoes and trying to understand their perspective can lead to more meaningful and productive conversations.
- Be aware of your own cultural biases and how they might influence your perceptions and communication.
- Practice active listening, paying attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues.
- Develop cultural sensitivity, recognizing and respecting cultural differences.
- Be mindful of nonverbal communication, as it can vary significantly across cultures.
- Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or slang.
- Be patient and understanding, allowing time for cultural differences to be acknowledged and respected.
- Seek feedback and clarification to ensure understanding.
- The Civil Rights Movement: Led by Martin Luther King Jr., the Civil Rights Movement utilized non-violent communication strategies like peaceful protests, sit-ins, and boycotts to challenge racial segregation and discrimination in the United States. These strategies effectively brought attention to the injustices faced by African Americans and galvanized public support for the movement’s goals.
- The Indian Independence Movement: Mahatma Gandhi’s leadership in the Indian independence movement exemplified the power of non-violent communication. His philosophy of Satyagraha (truth force) emphasized non-violent resistance through civil disobedience, peaceful protests, and fasting. These strategies helped mobilize the Indian population and ultimately led to India’s independence from British rule.
- Impact: Non-violent communication strategies have been instrumental in achieving social change goals. By promoting empathy and understanding, they foster dialogue and cooperation, creating a conducive environment for positive change. Non-violent communication can also be a powerful tool for de-escalating conflict and building bridges between opposing groups.
- Limitations: While non-violent communication has proven effective in many instances, it is not without limitations. In situations where there is a power imbalance or where violence is used by opposing forces, non-violent communication may not be sufficient to achieve change.
Additionally, maintaining non-violent communication strategies can be challenging in the face of provocation or hostility.
- Traditional Media: Traditional media outlets like television, radio, and newspapers have long played a significant role in shaping public opinion and influencing social movements. They provide a platform for reaching a broad audience and can amplify the message of social movements.
However, traditional media often has a gatekeeping function, controlling the narrative and potentially limiting the reach of smaller or less mainstream movements.
- Social Media: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have revolutionized the way social movements operate. They provide a powerful tool for mobilization, allowing activists to connect with a wider audience, share information, and organize events quickly and efficiently.
Social media also enables decentralized communication, empowering individuals and grassroots movements to bypass traditional media gatekeepers and share their message directly with the public.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: Social media offers advantages like greater reach, accessibility, and the ability to bypass traditional media control. However, it also presents challenges, including the spread of misinformation, echo chambers, and the potential for censorship. Traditional media, while offering greater control over messaging, may struggle to keep up with the rapid pace of social media and may face limitations in reaching younger audiences.
- Role of Technology: The evolution of social media has been shaped by advancements in technology. The rise of mobile devices, high-speed internet, and social media algorithms has made it easier for people to access information, connect with others, and participate in social movements.
This has significantly impacted the reach, speed, and effectiveness of social media in driving social change.
- Literary devices, such as metaphor, simile, imagery, and symbolism, act as communication tools, enriching the reader’s understanding and creating evocative imagery.
- For example, in Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet,” the use of metaphor, like “Juliet is the sun,” not only paints a vivid picture of Juliet’s beauty but also conveys Romeo’s intense admiration and love.
- Similarly, the use of symbolism in Nathaniel Hawthorne’s “The Scarlet Letter,” where the scarlet letter “A” represents Hester’s sin and its societal implications, adds layers of meaning to the narrative, inviting readers to interpret the text on multiple levels.
- Dialogue, a crucial element in literature, plays a vital role in revealing characters’ personalities, motivations, and relationships.
- In Shakespeare’s plays, the dialogue is often poetic and formal, reflecting the Elizabethan era’s linguistic style.
- In contrast, modern novels often employ more colloquial and realistic dialogue, mirroring contemporary speech patterns.
- Cinematography, the art of capturing images on film, plays a crucial role in establishing mood, setting, and character.
- The use of wide-angle shots in “The Lord of the Rings” creates a sense of epic scale and grandeur, while close-up shots in “The Silence of the Lambs” intensify the tension and psychological impact of the scenes.
- Editing, the process of assembling and arranging shots, controls the pace and flow of the film, influencing the audience’s perception and understanding of the narrative.
- In “Pulp Fiction,” Quentin Tarantino’s non-linear editing style creates a sense of disorientation and surprise, challenging conventional storytelling techniques.
- Sound design, including dialogue, music, and sound effects, enhances the film’s emotional impact and creates a more immersive experience.
- The use of suspenseful music in “Jaws” heightens the fear and anticipation, while the iconic “Star Wars” theme music evokes a sense of wonder and adventure.
- Acting, the art of portraying characters, brings life and authenticity to the film, allowing the audience to connect with the characters on an emotional level.
- Marlon Brando’s performance in “A Streetcar Named Desire” is a masterclass in conveying raw emotion and vulnerability, while Daniel Day-Lewis’s transformative portrayal of Abraham Lincoln in “Lincoln” showcases the power of acting to embody historical figures.
Communications classes teach you how to express yourself effectively, whether it’s through writing, speaking, or even visual media. You’ll learn about different communication styles, how to tailor your message to your audience, and how to use technology to enhance your communication.
It’s all about understanding how to connect with others, and that’s something you can even learn online! In fact, you might be interested in learning more about what is e learning day , which celebrates the benefits of online learning.
Ultimately, communications skills are valuable in any career path, as they help you build relationships and get your ideas across.
- Marlon Brando’s performance in “A Streetcar Named Desire” is a masterclass in conveying raw emotion and vulnerability, while Daniel Day-Lewis’s transformative portrayal of Abraham Lincoln in “Lincoln” showcases the power of acting to embody historical figures.
- Melody, the sequence of notes, creates a sense of flow and direction, influencing the emotional impact of the music.
- The uplifting melody of “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen evokes feelings of hope and redemption, while the melancholic melody of “Yesterday” by The Beatles evokes feelings of longing and nostalgia.
- Harmony, the simultaneous sounding of notes, creates a sense of richness and complexity, adding depth to the emotional experience.
- The lush harmonies in a classical symphony can evoke feelings of grandeur and awe, while the simple harmonies in a folk song can create a sense of intimacy and connection.
- Rhythm, the pattern of sounds and silences, creates a sense of energy and movement, influencing the emotional impact of the music.
- The driving rhythm of a rock song can evoke feelings of excitement and energy, while the slow, deliberate rhythm of a ballad can evoke feelings of sadness and contemplation.
- Instrumentation, the use of different instruments, creates a unique sonic landscape, influencing the emotional character of the music.
- The soaring strings of a violin can evoke feelings of passion and romance, while the earthy sounds of a bass guitar can evoke feelings of power and intensity.
- Art can challenge societal norms, raising awareness about important issues and prompting dialogue and reflection.
- For example, the works of feminist artists like Judy Chicago and Cindy Sherman challenged traditional representations of women in art, raising awareness about gender inequality and promoting feminist perspectives.
- Art can inspire activism and social movements, mobilizing people to fight for justice and equality.
- The iconic image of “Tank Man” in Tiananmen Square, captured by Jeff Widener, became a symbol of resistance and courage, inspiring people around the world to fight for freedom and democracy.
- Art can offer a platform for marginalized voices, giving expression to experiences and perspectives that are often silenced or ignored.
- The work of African American artists like Jacob Lawrence and Kara Walker addressed themes of racism and social injustice, giving voice to the experiences of Black Americans and challenging dominant narratives.
- Choose an art form that resonates with you, such as a short story, poem, or song.
- Consider using metaphors, similes, imagery, and symbolism to create a vivid and evocative experience for your audience.
- Focus on a specific theme or idea that you want to communicate through your art.
- For example, you could write a poem about the feeling of being overwhelmed by information in the digital age, using metaphors to describe the sensory overload and the struggle to find meaning in a sea of data.
- Consider your intended audience and tailor your language and style accordingly.
- For example, if you are writing a song for a specific genre, you might use certain musical conventions and lyrical themes that are associated with that genre.
- Active Listening:Healthcare providers should actively listen to patients’ concerns and questions, demonstrating empathy and understanding. This involves paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues.
- Clear and Concise Explanations:Healthcare providers should explain medical information in a clear, concise, and understandable manner, avoiding technical jargon. They should also use visual aids and other tools to enhance comprehension.
- Patient Education:Educating patients about their conditions, treatment options, and self-management strategies empowers them to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care.
- Open Communication:Encourage patients to ask questions and express their concerns freely, creating a safe and open environment for communication.
- Collaborative Decision-Making:Involving patients in decision-making regarding their care fosters trust and empowers them to take ownership of their health.
- Empathy and Compassion:Healthcare providers should demonstrate empathy and compassion, acknowledging patients’ emotions and providing emotional support.
- Cultural Sensitivity:Healthcare providers should be sensitive to cultural differences and adapt their communication style accordingly, ensuring effective communication with diverse patient populations.
- AI-powered chatbots are increasingly used by businesses to provide instant customer support, answer frequently asked questions, and automate tasks, streamlining interactions and improving response times.
- Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant leverage AI to understand and respond to voice commands, making it easier to access information, control smart devices, and manage schedules.
- AI-powered translation services, such as Google Translate and DeepL, are breaking down language barriers by providing real-time translations, facilitating communication across diverse cultures and languages.
- While AI can improve efficiency, there are concerns about potential job displacement as AI systems automate tasks traditionally performed by humans.
- The personalization offered by AI raises privacy concerns, as data about user preferences and communication patterns is collected and analyzed.
- Bias can be embedded in AI algorithms, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in communication scenarios, highlighting the need for ethical development and responsible use.
Group Roles and Communication Influence
Within a group, individuals often assume specific roles that influence their communication style and behavior. Understanding these roles and their impact on group dynamics is crucial for fostering effective communication and achieving shared goals.
| Group Role | Communication Style/Behavior | Facilitating Communication | Hindering Communication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leader | Often takes initiative, sets the agenda, and facilitates discussions. They are typically assertive, confident, and able to motivate others. | Provides direction and clarity, encourages participation, and helps resolve conflicts. | Can become overly dominant, stifle creativity, and fail to listen to others’ perspectives. |
| Task-Oriented | Focuses on achieving goals, staying on track, and meeting deadlines. They are typically organized, efficient, and detail-oriented. | Keeps the group focused on the task at hand, ensures progress is made, and helps manage time effectively. | Can be inflexible, resist change, and fail to consider the needs of others. |
| Relationship-Oriented | Prioritizes building relationships, fostering a positive team environment, and ensuring everyone feels valued and included. They are typically empathetic, supportive, and good listeners. | Creates a sense of trust and belonging, promotes open communication, and helps resolve conflicts constructively. | Can be overly sensitive, avoid difficult conversations, and fail to address performance issues. |
| Innovator | Brings creative ideas and solutions to the table, challenges the status quo, and encourages out-of-the-box thinking. They are typically imaginative, risk-taking, and open to new ideas. | Stimulates creativity and innovation, expands the group’s perspective, and helps generate new solutions. | Can be unrealistic, impractical, and fail to consider the feasibility of their ideas. |
| Skeptic | Questions assumptions, challenges ideas, and provides critical feedback. They are typically analytical, objective, and focused on finding flaws. | Ensures thorough analysis, identifies potential problems, and promotes a more balanced perspective. | Can be overly critical, negative, and discourage creativity and innovation. |
Effective Group Communication Strategies
Effective group communication is essential for successful collaboration, decision-making, and conflict resolution. By adopting specific strategies, groups can foster a positive and productive communication environment.
Leadership
Leaders play a crucial role in shaping the communication dynamics within a group. > How can leaders foster open and inclusive communication within a group?Leaders can create a safe and supportive environment where all members feel comfortable sharing their ideas and perspectives. They can actively listen to everyone’s input, acknowledge and respect differing viewpoints, and encourage open dialogue.
> What strategies can leaders use to encourage active participation from all members?Leaders can use various techniques to ensure everyone’s voice is heard. They can use structured communication methods, such as round-robin discussions, to ensure everyone has an opportunity to speak. They can also encourage active listening and provide positive reinforcement for participation.
Decision-Making
Effective group decision-making requires a collaborative approach that ensures everyone’s input is considered and respected.> What are some effective methods for making group decisions that ensure everyone’s input is considered?Groups can use a variety of decision-making methods, such as consensus-building, majority vote, or expert opinion, depending on the complexity of the decision and the group’s dynamics.
> How can groups avoid groupthink and ensure a diversity of perspectives?Groupthink occurs when members prioritize conformity over critical thinking and independent judgment. To avoid groupthink, groups can encourage dissenting opinions, assign a devil’s advocate role, and ensure everyone has an opportunity to express their views without fear of judgment.
Conflict Management
Conflicts are inevitable in group communication, but they can be a valuable opportunity for growth and learning if managed effectively.> What are some constructive approaches to addressing conflict within a group?Groups can use a variety of conflict resolution strategies, such as active listening, compromise, and mediation. It is important to focus on understanding the underlying issues, finding common ground, and reaching a mutually acceptable solution.> How can groups use conflict as an opportunity for growth and learning?Conflicts can provide valuable insights into differing perspectives, communication styles, and group dynamics.
By addressing conflicts constructively, groups can improve their communication skills, build stronger relationships, and develop a more cohesive and resilient team.
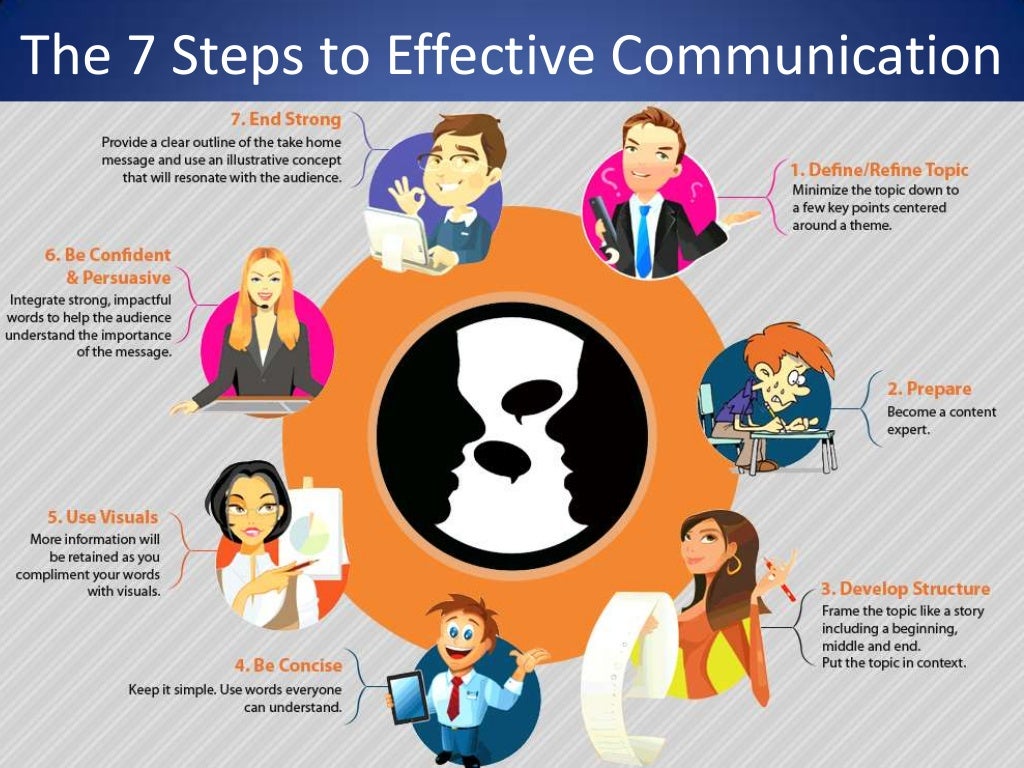
Public Speaking

Public speaking is a crucial communication skill that involves delivering a prepared speech to an audience. It’s a skill that can be learned and improved with practice and a deep understanding of its components.
Key Elements of a Successful Public Speech
A successful public speech is a well-structured presentation that engages the audience and effectively conveys the speaker’s message. There are three key elements: structure, delivery, and audience engagement.
Structure
The structure of a speech provides a framework for organizing your thoughts and ensuring a logical flow of information. It typically follows a three-part structure:
Delivery
Delivery refers to how you present your speech. It includes your vocal tone, body language, and visual aids. A good delivery is confident, clear, and engaging.
Audience Engagement
Engaging your audience is crucial for a successful speech. This involves connecting with them on an emotional level and making them feel like they are part of the conversation.
Types of Public Speeches
Public speeches can be categorized into different types based on their purpose. Here are some common types:
Informative Speeches
Informative speeches aim to educate the audience on a specific topic. They present factual information, explain concepts, and provide insights.
Example:A speech on the history of the internet.
Persuasive Speeches
Persuasive speeches aim to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take a specific action. They present arguments, evidence, and appeals to persuade the audience.
Example:A speech advocating for climate change action.
Ceremonial Speeches
Ceremonial speeches are delivered on special occasions, such as weddings, graduations, or funerals. They often express gratitude, celebrate achievements, or commemorate events.
Example:A best man’s speech at a wedding.
Overcoming Stage Fright
Stage fright, also known as public speaking anxiety, is a common experience. It’s the fear of speaking in front of an audience. However, there are strategies for overcoming stage fright:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Practice your speech thoroughly | Familiarity with your material will boost your confidence and reduce anxiety. |
| Visualize success | Imagine yourself delivering your speech confidently and effectively. |
| Focus on your audience | Connect with your audience and remember that they are there to listen to you. |
| Deep breathing exercises | Take slow, deep breaths to calm your nerves and reduce physical symptoms of anxiety. |
| Positive self-talk | Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations about your abilities. |
Organizational Communication
Organizational communication is the lifeblood of any successful company. It’s how information flows, decisions are made, and relationships are built. This area of communication focuses on how communication functions within an organization.
Communication Channels and Processes
Communication channels are the pathways through which information travels within an organization. These channels can be formal, like company emails or meetings, or informal, like casual conversations in the breakroom.
The effectiveness of communication within an organization depends on the choice of appropriate channels and the efficiency of communication processes.
Impact of Communication on Organizational Culture and Performance
Communication plays a critical role in shaping an organization’s culture. It influences how employees perceive their work environment, their relationships with colleagues, and their overall commitment to the company.
Importance of Communication for Leadership and Decision-Making
Leaders rely on effective communication to inspire and motivate their teams, to convey strategic direction, and to ensure that decisions are understood and implemented effectively.
Mass Communication

Mass communication refers to the process of transmitting information and ideas to a large audience through various channels, including print, broadcast, and digital media. It plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion, disseminating news and information, and influencing cultural trends.
Forms of Mass Communication
Mass communication encompasses various forms, each with its unique characteristics and reach.
The Role of Mass Communication in Shaping Public Opinion and Culture
Mass communication plays a significant role in shaping public opinion and influencing cultural trends. It serves as a primary source of information and entertainment, influencing people’s beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors.
The Impact of Technology on Mass Communication
Technological advancements have significantly impacted mass communication, leading to new forms of media and changing the way information is created, disseminated, and consumed.
Communication and Technology
In today’s digital age, communication technologies have revolutionized how we interact with each other, both personally and professionally. These technologies have made it easier to connect with people across the globe, share information instantaneously, and collaborate on projects in real-time.
However, they also present unique challenges and considerations that must be understood to utilize them effectively.
Types of Communication Technologies
The landscape of communication technologies is vast and ever-evolving. Some of the most common and influential technologies include:
Benefits of Communication Technologies
Communication technologies offer numerous advantages, enhancing our ability to connect, share information, and collaborate:
Drawbacks of Communication Technologies
Despite their numerous benefits, communication technologies also present potential drawbacks:
Effectiveness of Communication Technologies
The effectiveness of different communication technologies can vary depending on the specific communication purpose:
| Communication Technology | Purpose | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Formal communication, sharing documents | High | |
| Video Conferencing | Meetings, presentations, remote collaboration | High |
| Instant Messaging | Informal communication, quick exchanges | High |
| Social Media | Sharing news, updates, building communities | Moderate |
| Mobile Phones | Personal communication, emergencies | High |
Choosing the right communication technology is crucial for effective communication. Consider the purpose, audience, and context to determine the most appropriate tool.
Communication Ethics

Communication ethics are a set of principles that guide our communication behaviors, ensuring they are responsible, respectful, and considerate of others. It’s about making conscious choices in how we communicate, aiming for positive outcomes and avoiding harmful consequences.
Ethical Principles of Communication
These principles are the foundation of ethical communication.
Ethical Considerations in Different Communication Contexts, What do you learn in a communications class
Ethical communication is crucial in various contexts.
Examples of Unethical Communication Practices
Unethical communication practices can have severe consequences, impacting individuals and society as a whole.
Communication in a Globalized World
Our world is increasingly interconnected, with people from diverse cultures interacting more than ever before. This globalization presents both challenges and opportunities for effective communication. Understanding how cultural differences impact communication is crucial for navigating this complex landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities of Communicating Across Cultures
The world of business has become truly global, with companies operating across borders and collaborating with partners from diverse backgrounds. This presents unique challenges and opportunities for communication.
| Communication Style | Western Cultures | Eastern Cultures |
|---|---|---|
| Directness | Direct and explicit communication, valuing clarity and efficiency. | Indirect and subtle communication, valuing harmony and avoiding confrontation. |
| Body Language | Open body language, direct eye contact, and assertive gestures. | More reserved body language, avoiding direct eye contact, and using more subtle gestures. |
| Time Perception | Linear time perception, focusing on schedules and deadlines. | Circular time perception, valuing relationships and flexibility over strict schedules. |
| Decision-Making | Individualistic decision-making, valuing autonomy and independence. | Collective decision-making, valuing consensus and group harmony. |
Importance of Intercultural Communication Competence
In a globalized world, intercultural communication competence is essential for building strong relationships, fostering collaboration, and achieving success in various settings. It enables individuals to understand and appreciate cultural differences, communicate effectively across cultures, and navigate diverse social contexts.
“The single biggest problem in communication is the illusion that it has taken place.”
George Bernard Shaw
This quote highlights the importance of active listening, clear communication, and understanding different perspectives to ensure that communication is truly effective. In a globalized world, where interactions across cultures are increasingly common, this message becomes even more relevant.
Strategies for Effective Communication in a Diverse World
Developing effective communication strategies for a diverse world requires embracing cultural sensitivity, active listening, and non-verbal communication skills.
Key Principles of Effective Intercultural Communication
Effective intercultural communication is built on a foundation of understanding, respect, and empathy. It requires individuals to be mindful of their own cultural biases, actively listen to others, and adapt their communication style to different cultural contexts.
12. Communication and Social Change
Communication plays a crucial role in driving social change. It allows individuals and groups to raise awareness about social issues, mobilize support, and advocate for change. This section explores how communication, particularly non-violent communication and media, contribute to shaping social movements and influencing societal transformations.
The Role of Non-Violent Communication in Social Change
Non-violent communication, a method of communication emphasizing empathy and understanding, has proven effective in fostering social change. By focusing on needs and feelings rather than blame and judgment, it promotes dialogue, builds bridges, and encourages cooperation.
Impact of Traditional and Social Media on Social Movements
Traditional media (TV, radio, print) and social media have distinct impacts on social movements, influencing their mobilization, messaging, and overall impact.
Communication and the Arts
Communication and the arts are intricately intertwined, each enriching and influencing the other. Art, in its diverse forms, provides a powerful platform for communication, allowing artists to express their ideas, emotions, and perspectives in ways that transcend language.
The Language of Literature
Literary works, through their intricate use of language and narrative structure, offer profound insights into human experience and the complexities of communication.
Film as a Visual Language
Film, as a visual medium, utilizes a unique language of imagery, sound, and editing to convey meaning and evoke emotions.
Music’s Emotional Power
Music, a universal language, has the power to evoke a wide range of emotions and experiences without relying on spoken words.
Art as a Catalyst for Change
Art, in its various forms, has a long history of serving as a powerful tool for social commentary and promoting social change.
Writing a Creative Piece
Writing a creative piece allows you to explore the theme of communication in the arts and express your own ideas and emotions through the power of language.
Communication and Health
Communication is essential in healthcare settings, playing a vital role in ensuring effective patient care and achieving positive health outcomes. It facilitates understanding between healthcare providers and patients, enabling the delivery of appropriate treatment and promoting patient well-being.
The Importance of Communication in Healthcare Settings
Effective communication is crucial for a successful healthcare system. It allows for the accurate exchange of information, fostering trust and collaboration among healthcare professionals, patients, and their families. This leads to better patient care, improved health outcomes, and increased patient satisfaction.
The Role of Communication in Patient-Provider Relationships
The patient-provider relationship is built on effective communication. Open and honest dialogue between patients and healthcare providers is essential for establishing trust, understanding patients’ needs and concerns, and developing personalized treatment plans.
Effective communication fosters a sense of partnership between patients and providers, empowering patients to actively participate in their care.
Communication Strategies for Improving Patient Care and Health Outcomes
Several communication strategies can enhance patient care and health outcomes:
15. Communication and the Future
The world of communication is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology that are reshaping how we connect and interact. Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality are at the forefront of this transformation, ushering in a future where communication will be more personalized, accessible, and globally connected than ever before.
AI’s Role in Communication
Artificial intelligence is already deeply integrated into communication tools and platforms, enhancing efficiency and personalization.
The benefits of AI in communication are undeniable, but it’s crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks.
Helpful Answers
What are some common communication challenges in the workplace?
Common workplace communication challenges include miscommunication, conflicting perspectives, lack of clarity, ineffective feedback, and cultural differences.
How can I improve my nonverbal communication skills?
Focus on maintaining eye contact, using appropriate body language, and paying attention to your tone of voice. Be aware of your facial expressions and gestures, as they can convey a lot about your emotions and intentions.
Is it important to study communication if I’m not going into a communication-related field?
Absolutely! Effective communication is essential in all aspects of life, from personal relationships to professional success. Understanding communication principles can help you build stronger connections, resolve conflicts, and navigate various situations effectively.