Side of brain for creativity – When it comes to creativity, the right side of your brain takes center stage. This fascinating region is responsible for divergent thinking, problem-solving, and imagination – the essential ingredients for generating new ideas and expressing yourself creatively.
In this article, we’ll delve into the right brain’s role in creativity, exploring how it interacts with the left brain, and uncovering strategies to tap into its creative potential.
Creative Hemispheres
Creativity is a complex cognitive process that involves the interaction of different brain regions. While the right hemisphere is often associated with creativity, the left hemisphere also plays a significant role.
In right-handed individuals, the left hemisphere is dominant for language and logical thinking. However, the right hemisphere is responsible for visual-spatial processing, intuition, and emotional expression. Both hemispheres work together to support creative thinking.
Dominant Hemisphere for Creativity
- Right hemisphere: Visual-spatial processing, intuition, emotional expression
Contributions of the Non-Dominant Hemisphere
- Left hemisphere: Language, logical thinking
Interaction of Brain Activity
- Creative tasks engage both hemispheres, with different regions specializing in specific aspects of the process.
- For example, the prefrontal cortex is involved in planning and decision-making, while the temporal lobes are involved in memory and language processing.
Hemispheric Connectivity
- The corpus callosum, a bundle of nerve fibers, connects the two hemispheres.
- Stronger hemispheric connectivity is associated with greater creative ability.
Brain Regions for Creativity
Creativity, a complex and multifaceted cognitive process, involves the interplay of various brain regions. These regions work in harmony to facilitate divergent thinking, problem-solving, and the generation of novel ideas.
The key brain regions associated with creativity include:
- Prefrontal Cortex:The prefrontal cortex, particularly the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), is involved in executive functions such as planning, decision-making, and working memory. It plays a crucial role in the generation and evaluation of creative ideas.
- Temporal Lobes:The temporal lobes, especially the medial temporal lobes, are associated with memory, language, and emotional processing. They contribute to the retrieval of relevant information, the formation of associations, and the generation of novel combinations.
- Parietal Lobes:The parietal lobes, particularly the posterior parietal cortex, are involved in spatial reasoning, attention, and sensory processing. They facilitate the manipulation of mental representations and the integration of different sensory inputs.
- Default Mode Network (DMN):The DMN is a group of brain regions that are active when an individual is at rest or engaged in self-referential thinking. It is believed to be involved in the generation of spontaneous thoughts and the integration of diverse ideas.
Neural Networks and Creativity
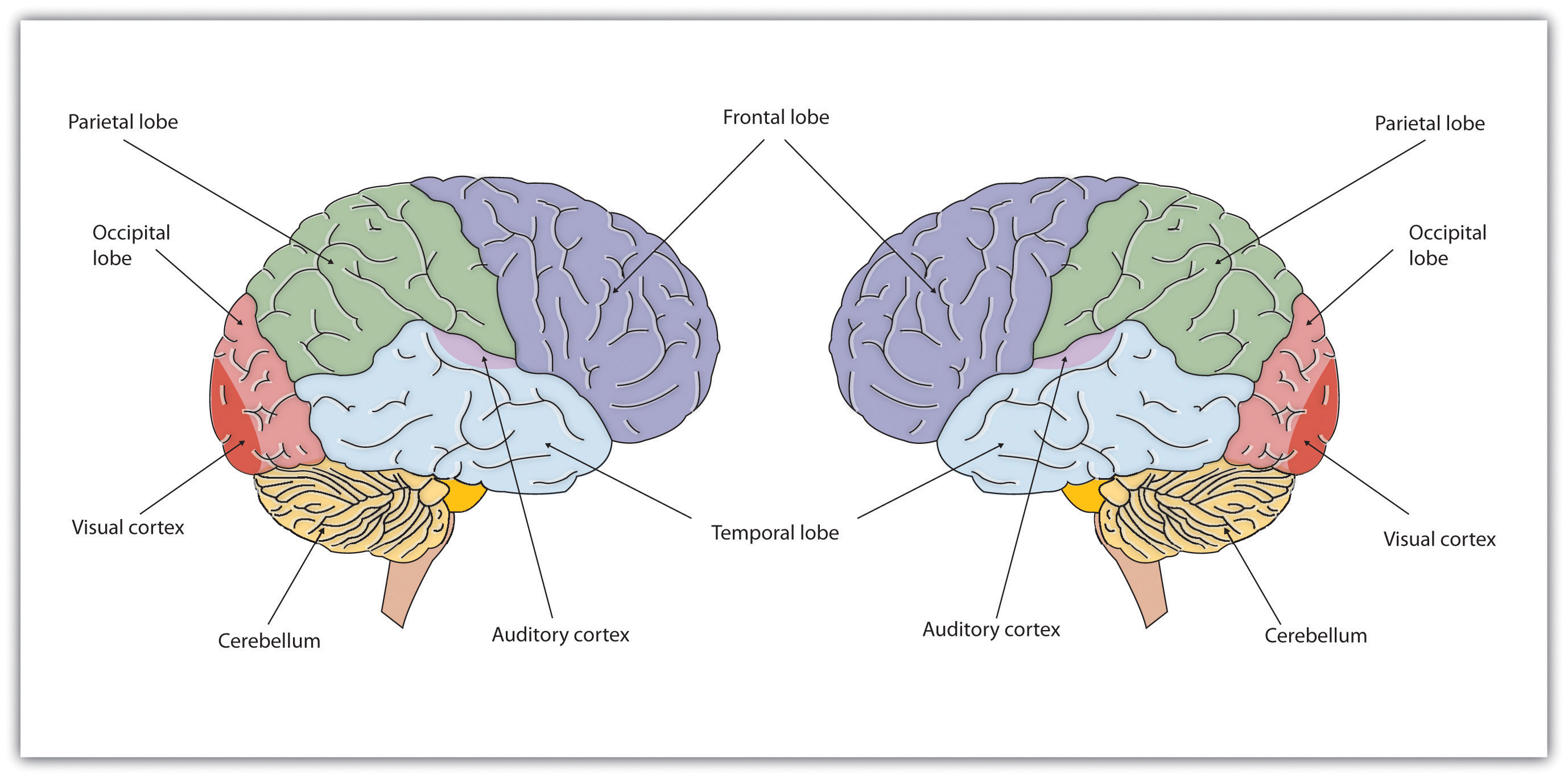
Neural networks are complex systems of interconnected neurons that process and transmit information in the brain. They play a crucial role in creativity by facilitating the generation and evaluation of new ideas.One key neural network involved in creativity is the default mode network (DMN).
The DMN is active when the brain is at rest, and it is thought to be involved in self-reflection, autobiographical memory, and imagination. When engaged in creative tasks, the DMN shows increased activity, suggesting that it is involved in the generation of new ideas.Another neural network involved in creativity is the executive attention network (EAN).
The EAN is responsible for controlling attention and working memory. It is thought to be involved in the evaluation and selection of new ideas. When engaged in creative tasks, the EAN shows increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions such as planning, decision-making, and problem-solving.Together, the DMN and EAN work together to facilitate divergent thinking and problem-solving.
The DMN generates new ideas, while the EAN evaluates and selects the most promising ones. This interplay between the two networks is essential for creative thought.
Cognitive Processes and Creativity

Creativity is a complex process that involves a variety of cognitive processes, such as imagination, intuition, and insight. These processes work together to generate new ideas, solve problems, and make decisions.
Imagination
Imagination is the ability to generate new ideas and images. It is essential for creativity because it allows us to think outside the box and come up with new solutions to problems. For example, a designer might use their imagination to visualize a new product design, or a scientist might use their imagination to come up with a new theory.
Intuition
Intuition is the ability to make quick judgments without conscious reasoning. It is often thought of as a “gut feeling” or a “sixth sense.” Intuition can be helpful for creativity because it can help us to make decisions quickly and efficiently.
For example, an entrepreneur might use their intuition to decide whether or not to invest in a new business venture.
Insight
Insight is the sudden realization of a solution to a problem. It is often described as an “aha!” moment. Insight can be helpful for creativity because it can help us to overcome obstacles and find new solutions to problems. For example, a mathematician might have an insight that helps them to solve a difficult equation.
Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is the ability to generate multiple solutions to a problem. It is essential for creativity because it allows us to explore different possibilities and come up with new ideas. For example, a brainstorming session is a good way to encourage divergent thinking.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is the ability to find solutions to problems. It is essential for creativity because it allows us to overcome obstacles and achieve our goals. For example, a scientist might use their problem-solving skills to develop a new cure for a disease.
Decision-Making
Decision-making is the ability to choose the best course of action. It is essential for creativity because it allows us to make decisions about which ideas to pursue and which ones to abandon. For example, a designer might use their decision-making skills to choose the best design for a new product.
Environmental Factors and Creativity
The environment plays a significant role in shaping creativity. From upbringing to education and social interactions, external factors can profoundly influence an individual’s creative abilities.
Upbringing
The home environment can nurture or stifle creativity. Supportive parents who encourage exploration, experimentation, and divergent thinking foster a positive atmosphere for creative development. Conversely, restrictive environments may suppress creativity by imposing rigid expectations and discouraging risk-taking.
Education
Educational institutions can provide opportunities for creative expression and problem-solving. Schools that emphasize critical thinking, collaboration, and project-based learning foster creativity. However, rigid curricula and standardized testing can sometimes hinder creativity by emphasizing conformity over innovation.
Social Interactions
Social interactions can influence creativity both positively and negatively. Exposure to diverse perspectives, collaborations with others, and constructive criticism can stimulate creative thinking. However, social pressures, groupthink, and fear of judgment can also inhibit creativity.
– Personality Traits and Creativity: Side Of Brain For Creativity
Personality traits play a significant role in shaping an individual’s creative potential. Certain traits, such as openness, curiosity, and risk-taking, are consistently associated with higher levels of creativity.
Studies show that creativity often stems from the right side of the brain. If you’re looking to tap into that creative side, check out creative ground. This online platform offers workshops, resources, and a community to help you nurture your creativity.
By engaging with creative ground, you can harness the power of your right brain and unleash your creative potential.
Openness, a key trait in creative individuals, involves a willingness to embrace new experiences, ideas, and perspectives. It allows individuals to consider diverse possibilities and challenge conventional thinking, fostering a fertile ground for creative solutions.
Curiosity
Curiosity, an insatiable drive to explore and seek knowledge, fuels creativity. Curious individuals are constantly questioning, investigating, and seeking out new information, expanding their mental horizons and enriching their reservoir of ideas.
Risk-Taking
Risk-taking is an essential ingredient in the creative process. It involves the willingness to venture into uncharted territory, experiment with new approaches, and embrace the potential for failure. Creative individuals are not afraid to step outside of their comfort zones, recognizing that innovation often requires taking calculated risks.
Relationship between Personality Traits and Creative Output
The relationship between personality traits and creative output is complex and varies across different domains, such as art, science, and music. In general, individuals with high levels of openness, curiosity, and risk-taking tend to exhibit greater creative achievements in their respective fields.
Environmental Factors and Creative Personality Traits
Environmental factors can significantly influence the development of creative personality traits. Supportive environments that encourage exploration, experimentation, and risk-taking can foster the growth of these traits. In contrast, restrictive or highly structured environments may stifle creativity by suppressing the expression of these traits.
Examples of Creative Approaches
- An artist with a high level of openness may incorporate unconventional materials and techniques into their work, challenging traditional artistic norms.
- A scientist with a strong sense of curiosity may pursue research in an unexplored field, driven by a desire to uncover new knowledge.
- A musician with a penchant for risk-taking may experiment with novel musical forms, blending different genres and creating innovative soundscapes.
Creative Expression
Creative expression is the outward manifestation of one’s creative ideas and emotions. It encompasses various forms, including art, music, writing, and performance.
Each form of creative expression offers unique ways to convey emotions and ideas. Art allows visual representation of concepts and emotions through painting, sculpture, and other mediums. Music expresses emotions and ideas through organized sound, melody, and rhythm. Writing provides a medium for storytelling, poetry, and other literary forms to convey complex ideas and emotions.
Performance
Performance encompasses various forms, including theater, dance, and music. It allows artists to express themselves and engage with an audience in real-time. Performance provides a dynamic and interactive platform for conveying emotions and ideas, often involving a collaborative effort between performers.
Measuring Creativity
Measuring creativity presents unique challenges due to its multifaceted nature. Creativity encompasses diverse cognitive processes, making it difficult to quantify using traditional assessment methods. Despite these challenges, various approaches have been developed to assess creative abilities and potential.
Divergent Thinking Tests, Side of brain for creativity
Divergent thinking tests measure an individual’s ability to generate multiple unique and unconventional solutions to problems. Examples include:
- Alternative Uses Test:Participants list as many different uses as possible for a common object.
- Word Association Test:Participants provide as many words as they can that are related to a given word.
Advantages:
- Objectively quantifiable.
- Useful for screening large groups.
Disadvantages:
- May not capture real-world creative potential.
- Can be influenced by prior knowledge and cultural factors.
Problem-Solving Exercises
Problem-solving exercises assess an individual’s ability to approach and solve problems in innovative ways. Examples include:
- Lateral Thinking Puzzles:Participants solve unconventional problems using indirect or unconventional approaches.
- Case Studies:Participants analyze complex scenarios and propose creative solutions.
Advantages:
- Simulates real-world problem-solving situations.
- Evaluates both divergent and convergent thinking.
Disadvantages:
- Can be time-consuming to administer.
- Scoring may be subjective and dependent on the evaluator’s expertise.
Artistic Expression Evaluations
Artistic expression evaluations assess creativity through the production of original works of art, music, or literature. Examples include:
- Drawing or Painting:Participants create visual representations of their ideas and concepts.
- Music Composition:Participants create original musical pieces.
- Creative Writing:Participants write short stories, poems, or other forms of literature.
Advantages:
- Allows for subjective interpretation and expression.
- Can capture real-world creative potential.
Disadvantages:
- Highly subjective and difficult to quantify.
- May be influenced by prior training and experience.
Creative Writing Prompts
Creative writing prompts assess an individual’s ability to generate original and engaging written content. Examples include:
- Story Starters:Participants continue or complete a story based on a given prompt.
- Poetry Writing:Participants create poems based on specific themes or constraints.
Advantages:
- Provides a structured way to assess creative writing skills.
- Can evaluate both divergent and convergent thinking.
Disadvantages:
- May not capture real-world creative potential.
- Scoring may be subjective and dependent on the evaluator’s expertise.
Innovation Challenges
Innovation challenges involve participants in solving real-world problems through innovative solutions. Examples include:
- Design Competitions:Participants create innovative designs for products, services, or systems.
- Hackathons:Participants collaborate to develop creative solutions to specific problems within a limited time frame.
Advantages:
- Simulates real-world creative problem-solving.
- Can lead to tangible outcomes and practical applications.
Disadvantages:
- Can be resource-intensive to organize.
- May be influenced by group dynamics and team composition.
Guidelines for Developing a Comprehensive Assessment Plan
To develop a comprehensive assessment plan for measuring creativity, consider the following guidelines:
- Use multiple assessment methods:Combine different assessment methods to capture various aspects of creativity.
- Consider the context:Tailor the assessment plan to the specific purpose and context of the evaluation.
- Involve multiple raters:Utilize multiple raters to reduce subjectivity and ensure reliability.
- Provide clear instructions and criteria:Ensure participants understand the assessment tasks and expectations.
- Consider time constraints:Determine appropriate time limits for each assessment method.
Summary Table of Assessment Methods
| Assessment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Divergent Thinking Tests | Objectively quantifiable, useful for screening | May not capture real-world creativity, influenced by prior knowledge |
| Problem-Solving Exercises | Simulates real-world situations, evaluates divergent and convergent thinking | Time-consuming, subjective scoring |
| Artistic Expression Evaluations | Allows for subjective interpretation, captures real-world creativity | Highly subjective, influenced by prior training |
| Creative Writing Prompts | Structured way to assess writing skills, evaluates divergent and convergent thinking | May not capture real-world creativity, subjective scoring |
| Innovation Challenges | Simulates real-world problem-solving, leads to tangible outcomes | Resource-intensive, influenced by group dynamics |
– Creativity in Different Domains
Creativity manifests in diverse domains, each with unique characteristics and challenges. Science, technology, business, and the arts showcase the multifaceted nature of creative expression.
In science, creativity drives groundbreaking discoveries and theories. Scientists generate novel hypotheses, design innovative experiments, and interpret complex data, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.
Technology
Technological advancements are fueled by creative thinking. Engineers and designers conceptualize new products, processes, and systems that enhance our lives. Creativity in technology often involves problem-solving, innovation, and the ability to envision future possibilities.
Business
Business creativity drives innovation, market expansion, and customer satisfaction. Entrepreneurs and business leaders generate new ideas, develop unique products or services, and implement strategies that differentiate their organizations in competitive markets.
Arts
Creativity in the arts encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including visual arts, music, literature, and performing arts. Artists express their unique perspectives, emotions, and ideas through various mediums, fostering cultural expression and emotional resonance.
Creativity and Innovation
Creativity is the foundation for innovation. Creative ideas lead to innovative solutions and products that can transform industries and improve lives. For example, the invention of the telephone, the computer, and the internet were all sparked by creative thinking.
Key Characteristics of Creative Individuals
Creative individuals often possess certain key characteristics, such as:
- Open-mindedness and willingness to take risks
- Curiosity and a thirst for knowledge
- Imagination and the ability to think outside the box
- Perseverance and the ability to overcome obstacles
- Collaboration and the ability to work well with others
These traits contribute to innovation by allowing individuals to generate new ideas, explore different possibilities, and bring their creations to life.
Collaboration and Diverse Perspectives
Collaboration and diverse perspectives are also essential for fostering creativity and innovation. When people with different backgrounds and expertise work together, they can bring a wider range of ideas and perspectives to the table. This can lead to more innovative solutions and products that meet the needs of a broader audience.
Enhancing Creativity
Creativity is a skill that can be learned and enhanced. There are a number of strategies that you can use to boost your creativity, including brainstorming, mind mapping, lateral thinking, and writing prompts.
Creativity Enhancement Strategies
- Brainstorming:Generates a large number of ideas by gathering a group of people and having them generate as many ideas as possible on a given topic.
- Mind Mapping:Helps to visualize and connect ideas by starting with a central topic and then branching out to related ideas.
- Lateral Thinking:Encourages unconventional thinking by challenging assumptions and looking for alternative perspectives.
- Writing Prompts:Stimulates creativity by providing a starting point to get your creative juices flowing.
Fostering a Creative Environment
In addition to using creativity enhancement strategies, you can also create a more creative environment by:
- Encouraging open communication and idea sharing.
- Providing time and space for employees to think creatively.
- Celebrating and rewarding creativity.
Resources for Further Exploration
Future of Creativity
The future of creativity is a topic of great interest and speculation. As technology advances, new tools and techniques are emerging that have the potential to impact the way we create and innovate. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two of the most promising technologies in this regard.
AI and ML can be used to automate tasks that are currently performed by humans, freeing up our time and resources to focus on more creative endeavors. For example, AI can be used to generate new ideas, create artwork, and even write music.
ML can be used to identify patterns and trends in data, which can help us to better understand the creative process and develop new strategies for fostering creativity.
Role of AI and ML in Enhancing Human Creativity
- AI can be used to generate new ideas and concepts that can be further developed by humans.
- AI can be used to create realistic and immersive virtual environments that can inspire creativity and innovation.
- AI can be used to analyze data and identify patterns that can help us to better understand the creative process.
- ML can be used to develop new tools and techniques that can help us to create and innovate more effectively.
Case Studies of Creative Individuals
By examining the creative processes and achievements of notable individuals, we can uncover valuable patterns and lessons that can inform our understanding of creativity.
These case studies offer insights into the diverse ways that creativity manifests itself, the challenges and obstacles that creative individuals face, and the strategies they employ to overcome them.
Common Patterns and Lessons Learned
- Persistence and resilience:Creative individuals often face setbacks and failures, but they persist in their pursuit of their creative goals.
- Openness to new experiences:Creative individuals are often willing to explore new ideas and experiences, which can provide them with fresh perspectives and inspiration.
- Collaboration and networking:Creative individuals often benefit from collaborating with others and building a network of support.
- Self-belief and confidence:Creative individuals believe in their own abilities and are willing to take risks to pursue their creative vision.
- Intrinsic motivation:Creative individuals are often driven by an internal desire to create, rather than by external rewards or recognition.
Popular Questions
What are the key functions of the right brain in creativity?
The right brain excels in visual-spatial processing, pattern recognition, and emotional expression, which are crucial for generating and evaluating creative ideas.
How can I tap into the creative power of my right brain?
Engage in activities that stimulate your right brain, such as drawing, painting, playing music, or brainstorming with others.
Is it possible to improve my creativity by strengthening my right brain?
Yes, engaging in activities that challenge and stimulate your right brain can help enhance its creative functions over time.