Is learning guitar hard? Absolutely, but it’s also incredibly rewarding. The journey to becoming a guitarist is a mix of challenges and triumphs, with every chord learned and song mastered bringing a sense of accomplishment. Whether you’re drawn to the melodic beauty of classical music or the energetic rhythms of rock, the guitar offers a world of musical expression waiting to be explored.
This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of guitar playing, from understanding the basics to mastering chords, strumming patterns, and even venturing into scales and melodies. We’ll address common challenges faced by beginners and provide strategies to stay motivated along the way.
Get ready to embark on a musical adventure!
The Basics of Guitar Playing

Learning to play the guitar is an exciting journey that can bring you immense joy and satisfaction. But before you start strumming your favorite tunes, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of guitar playing.
Understanding the Parts of a Guitar
The guitar is a fascinating instrument with various parts that work together to produce sound. Knowing the functions of these parts will help you better understand how the guitar works.
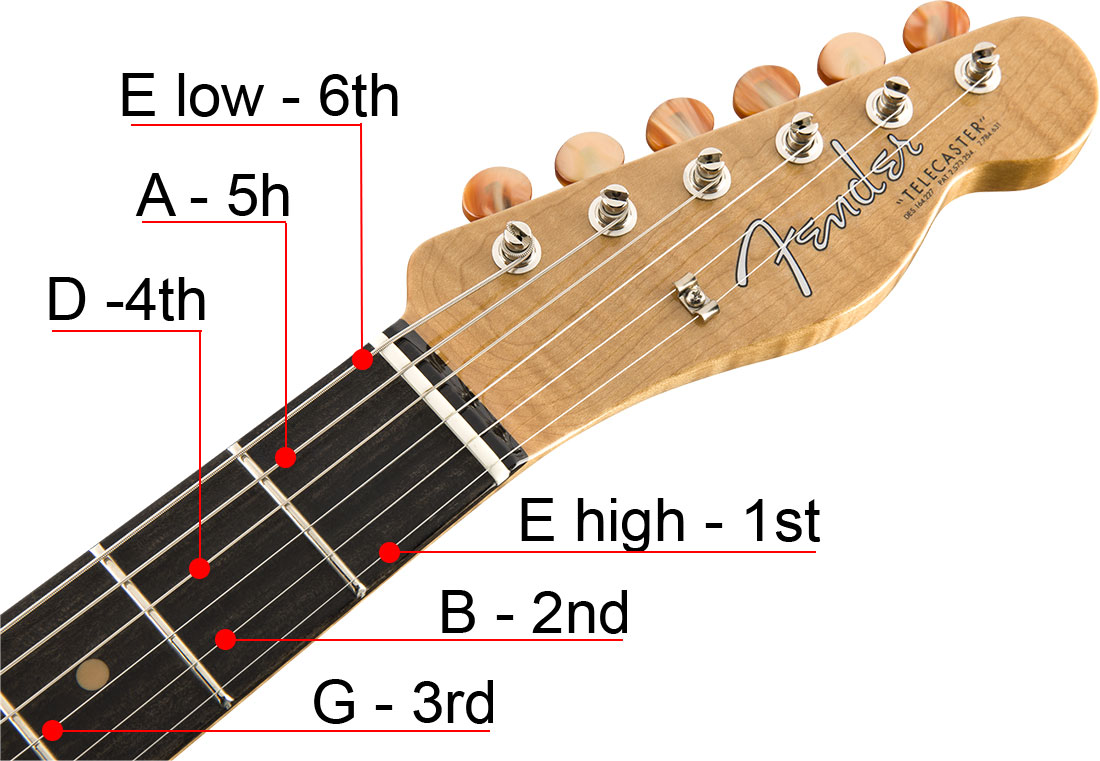
- Headstock:The topmost part of the guitar, where the tuning pegs are located. These pegs are used to adjust the tension of the strings, which determines the pitch of the notes.
- Nut:A small piece of material located at the end of the fretboard, where the strings rest. It determines the distance between the strings and the first fret.
- Fretboard:A strip of wood with metal frets that divide the neck into sections. Each fret represents a specific note. By pressing down on a string at a particular fret, you change the length of the vibrating string, producing a different note.
- Neck:The long, wooden part of the guitar that connects the headstock to the body. It holds the fretboard and the strings.
- Body:The main part of the guitar that resonates and amplifies the sound produced by the strings. The body shape and materials can significantly influence the guitar’s tone.
- Bridge:A structure located on the body of the guitar where the strings are attached. It helps to transfer the vibrations from the strings to the body, producing sound.
- Strings:Six strings made of different materials that are stretched across the neck and body. Each string produces a different pitch when plucked or strummed.
Holding the Guitar Correctly
Holding the guitar correctly is crucial for comfort, playing efficiency, and avoiding injuries.
- Sit down comfortably:Choose a chair that provides good back support and allows you to keep your feet flat on the floor. Position yourself so that the guitar rests comfortably on your lap.
- Adjust the strap:If you’re using a strap, adjust it so that the guitar hangs at a comfortable height. It should be high enough to allow you to reach all the frets easily but low enough to avoid strain on your shoulders.
- Position your left hand:Place your left hand on the neck of the guitar, with your thumb behind the neck and your fingers resting lightly on the strings. Your fingers should be curved and relaxed, not stiff.
- Position your right hand:For strumming, place your right hand on the strings near the bridge, with your thumb resting on the back of the neck. Your fingers should be relaxed and ready to strum. For picking, use your right hand fingers to pluck individual strings.
Tuning Your Guitar
Tuning your guitar is essential before playing, as it ensures that the strings are at the correct pitch. You can use a tuner or tune by ear.
- Using a Tuner:Electronic tuners are widely available and provide an accurate way to tune your guitar. Simply pluck each string and the tuner will display the pitch. Adjust the tuning pegs until the string is in tune.
- Tuning by Ear:Tuning by ear requires practice and a good ear for music. You can use a reference source, such as a piano or another tuned instrument, to find the correct pitch for each string. Adjust the tuning pegs until the string matches the reference pitch.
The Importance of Posture and Hand Positioning
Proper posture and hand positioning are vital for comfortable and efficient guitar playing.
- Posture:Maintain a straight back and relaxed shoulders. Avoid slouching or hunching over the guitar, as this can lead to discomfort and pain.
- Hand Positioning:Keep your left hand fingers curved and relaxed, and avoid pressing too hard on the strings. Use your thumb to support the back of the neck, providing stability and control. For your right hand, keep your fingers relaxed and use a light touch when strumming or picking.
Learning Basic Chords

Learning chords is a fundamental step in mastering the guitar. It opens up a world of musical possibilities, allowing you to play songs, accompany singers, and even create your own melodies.
Identifying Common and Beginner-Friendly Chords
To begin your chord-learning journey, it’s essential to focus on a few foundational chords. These chords are relatively easy to grasp and form the basis for playing countless songs. Here are five common and beginner-friendly guitar chords:* G Major:This chord is formed by placing your index finger on the 3rd fret of the low E string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, and ring finger on the 3rd fret of the D string.
The notes in a G major chord are G, B, and D.* C Major:This chord is formed by placing your index finger on the 1st fret of the A string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the D string, and ring finger on the 3rd fret of the G string.
The notes in a C major chord are C, E, and G.* D Major:This chord is formed by placing your index finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, middle finger on the 3rd fret of the D string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the G string.
The notes in a D major chord are D, F#, and A.* E Major:This chord is formed by placing your index finger on the 1st fret of the B string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the E string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the A string.
The notes in an E major chord are E, G#, and B.* A Major:This chord is formed by placing your index finger on the 2nd fret of the E string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the D string.
The notes in an A major chord are A, C#, and E.
Designing a Practice Routine
Consistency is key when learning guitar chords. Dedicate a specific time each day for practice. Start with a warm-up routine that focuses on finger stretching and exercises. Then, focus on mastering each individual chord. Here’s a sample practice routine:* Warm-up (5 minutes):Spend a few minutes stretching your fingers and wrists to prepare them for playing.* Individual Chord Practice (10 minutes):Practice each chord separately, focusing on proper finger placement and clear sound.
Aim for 30 seconds of practice per chord.* Chord Transitions (10 minutes):Practice transitioning between chords smoothly. Start with simple two-chord combinations and gradually increase the complexity.* Playing Along with Melodies (10 minutes):Find simple melodies or songs that use the chords you’re learning. Try playing along with them, focusing on strumming patterns and keeping a steady rhythm.
Proper Finger Placement and Strumming Patterns
G Major:
Finger Placement
Index finger on the 3rd fret of the low E string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, and ring finger on the 3rd fret of the D string.
Strumming Pattern
Down-up-down-up, starting with a downstroke. C Major:
Finger Placement
Index finger on the 1st fret of the A string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the D string, and ring finger on the 3rd fret of the G string.
Strumming Pattern
Down-up-down-up, starting with a downstroke. D Major:
Finger Placement
Index finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, middle finger on the 3rd fret of the D string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the G string.
Strumming Pattern
Down-up-down-up, starting with a downstroke. E Major:
Finger Placement
Index finger on the 1st fret of the B string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the E string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the A string.
Strumming Pattern
Down-up-down-up, starting with a downstroke. A Major:
Finger Placement
Index finger on the 2nd fret of the E string, middle finger on the 2nd fret of the A string, and ring finger on the 2nd fret of the D string.
Strumming Pattern
Down-up-down-up, starting with a downstroke.
Overcoming Challenges
Learning chords can be challenging, but it’s important to persevere. Common challenges include:* Finger Pain:Practice regularly and gradually increase the duration of your practice sessions. Take breaks when needed and stretch your fingers.* Difficulty Transitioning Between Chords:Practice chord transitions slowly and deliberately. Focus on smooth finger movements and clear sound.* Memorizing Finger Placements:Use visual aids like chord diagrams and practice regularly.
You can also create flashcards or use online resources to help you memorize finger placements.
The Experience of Mastering Basic Chords
Mastering these basic chords is a rewarding experience. As you gain proficiency, you’ll notice a significant improvement in your playing ability. You’ll be able to play along with more songs, create your own music, and express yourself creatively. The sense of accomplishment you feel upon mastering these chords will motivate you to continue your guitar journey and explore more complex techniques.
Mastering Guitar Strumming
Strumming is the foundation of many guitar styles, from folk and rock to blues and country. It’s the rhythmic pulse that gives your music life and energy. Mastering strumming techniques will allow you to play a wide range of songs and develop your own unique style.
Different Strumming Patterns and Variations
Understanding basic strumming patterns is crucial. They serve as a starting point for creating more complex and diverse rhythms.Here are some common patterns:
- Down-Up:This is the most basic pattern, alternating between downstrokes and upstrokes. It’s a good starting point for beginners.
- Down-Down-Up-Up:This pattern adds a little more rhythm and complexity, with two downstrokes followed by two upstrokes.
- Down-Up-Down-Down:This pattern emphasizes the downstroke, creating a heavier sound.
- Down-Up-Down-Up-Down:This pattern is a variation of the basic down-up pattern, with an extra downstroke added for emphasis.
You can further expand these patterns by:
- Adding Mutes:Muting strings with your picking hand can create a percussive effect and add variation to your strumming.
- Using Accents:Strumming harder on certain beats can emphasize those beats and create a more dynamic rhythm.
- Changing the Direction:You can reverse the direction of a pattern (e.g., up-down instead of down-up) to create a different feel.
Comparing Strumming Techniques for Different Musical Styles
Different musical styles often employ specific strumming techniques. Here’s a comparison:
| Style | Strumming Technique | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Folk | Down-Up, Down-Down-Up-Up, Muting | Simple, rhythmic, often with a focus on downstrokes |
| Rock | Down-Up, Down-Up-Down-Down, Accents | Energetic, powerful, with emphasis on downstrokes and accents |
| Blues | Down-Up, Down-Down-Up-Up, Muting, Accents | Grooving, often with a syncopated feel, using mutes and accents |
| Country | Down-Up, Down-Down-Up-Up, Muting, Accents | Simple, rhythmic, often with a focus on downstrokes and mutes |
Developing Smooth and Rhythmic Strumming
Smooth and rhythmic strumming is essential for creating a pleasing musical experience. Here are some tips:
- Practice Regularly:Consistent practice is key to developing muscle memory and improving your strumming technique.
- Focus on Timing:Pay close attention to the timing of your strums, ensuring they land on the correct beats.
- Use a Metronome:A metronome helps you develop a steady tempo and improve your timing.
- Relax Your Wrist:A relaxed wrist allows for smoother and more controlled strumming.
- Experiment with Different Picks:Different picks have different thicknesses and shapes, which can affect your strumming sound.
The Importance of Timing and Counting in Strumming
Timing is crucial for strumming. You need to know when to strum down and when to strum up to create the desired rhythm.
Counting Beats:Counting beats helps you maintain a steady tempo and understand the rhythm of the music.
For example, a common time signature in music is 4/4 time, which means there are four beats in each measure. You can count these beats as “1, 2, 3, 4” to keep your strumming in time.
Learning Guitar Scales and Melodies
Learning scales and melodies is an important step in your guitar journey. Scales provide the foundation for playing different musical styles, while melodies allow you to express your creativity and create compelling music.
Mastering Guitar Scales
Understanding scales is essential for playing guitar. Scales are a sequence of notes that form the basis of melodies and harmonies. Each scale has a unique pattern of intervals that determines its sound. Here is a table outlining the major scales and their corresponding finger patterns for the first five frets on the guitar:
| Scale | Finger Pattern |
|---|---|
| C Major | I
|
| D Major | II
|
| E Major | III
|
| F Major | IV
|
| G Major | I
|
| A Major | II
|
| B Major | III
|
The root note of a scale is the first note in the sequence. For example, in the C Major scale, C is the root note. Each scale pattern is based on the root note and its corresponding intervals.
Practicing Scales Effectively
Consistent practice is key to mastering scales. Practice scales methodically, playing them both ascending and descending. Focus on smooth transitions between notes, ensuring that each note is played clearly and accurately.
“Practice scales by playing them slowly and accurately, gradually increasing the tempo as you become more comfortable. Use a metronome to maintain a consistent beat and develop a sense of rhythm.”
Creating Melodies with Scales
Scales are the building blocks of melodies. By using notes from a scale, you can create a variety of melodic phrases.
Playing Simple Melodies
Start with a single note from the scale, such as the root note. Then, add another note from the scale to create a two-note phrase. Experiment with different note combinations and rhythmic variations.
“Start with the root note (C) and add a note from the scale (e.g., D, E, or G) to create a two-note phrase. Experiment with different note combinations and rhythmic variations.”
Scales and Chords
Scales are closely related to chords. Chords are made up of multiple notes played simultaneously, and scales contain all the notes within a corresponding chord.
“The C Major scale (C, D, E, F, G, A, B) contains all the notes in the C Major chord (C, E, G).”
Improvising with Scales
Scales can be used to create improvisations and solos. By using the notes from a scale, you can create unique melodic phrases and explore different musical ideas.
“Try playing a series of arpeggios (C-E-G-C) while incorporating notes from the C Major scale to create a melodic phrase.”
Applying Scales to Real Music
Many popular songs utilize scales. By analyzing these songs, you can identify the scales used and understand how they contribute to the overall musical structure.
“Listen to the song ‘Imagine’ by John Lennon. The melody in the chorus utilizes the C Major scale, and you can hear the notes from the C Major chord being played in the accompaniment.”
Developing Finger Strength and Dexterity

Finger strength and dexterity are crucial for guitarists, enabling them to play complex chords, intricate melodies, and fast-paced riffs with ease. Building these skills requires consistent practice and targeted exercises that strengthen the muscles in your hands and fingers.
Finger Strength Exercises
Strengthening your fingers is essential for playing the guitar comfortably and effectively. Here are some exercises that can help you build finger strength:
- Hand Grippers:Hand grippers are excellent tools for building grip strength, which is essential for playing chords and holding down strings. There are various types of hand grippers, including spring-loaded grippers, adjustable grippers, and powerball grippers. When using a hand gripper, focus on squeezing it firmly and slowly releasing it, ensuring a controlled movement.
- Finger Extensions and Curls:Finger extensions and curls are simple yet effective exercises that isolate and strengthen individual fingers. For finger extensions, start with your hand relaxed and your fingers straight. Extend each finger one at a time, keeping the other fingers relaxed. For finger curls, start with your fingers extended and curl each finger down towards your palm, keeping the other fingers straight.
Repeat these exercises for each finger, focusing on controlled movements and maintaining proper form.
- Resistance Bands:Resistance bands offer a versatile way to strengthen your fingers and improve dexterity. Wrap a resistance band around your fingers, keeping your hand relaxed. You can then perform various exercises, such as finger extensions, curls, and lateral movements. Adjust the tension of the band based on your strength level, gradually increasing the resistance as your fingers get stronger.
Dexterity Drills, Is learning guitar hard
Dexterity refers to the ability to move your fingers independently and with precision. Developing dexterity is crucial for playing fast passages, executing complex fingerpicking patterns, and performing intricate guitar techniques. Here are some drills that can enhance your finger dexterity:
- Finger Tapping:Finger tapping exercises involve tapping your fingers on a surface, focusing on speed and accuracy. Start with a simple pattern, such as tapping each finger in sequence, and gradually increase the speed and complexity of the pattern. You can also try tapping different rhythms and patterns, challenging your fingers to move quickly and precisely.
- Finger Isolation:Finger isolation drills aim to improve the independent movement of each finger. One common exercise involves placing your hand flat on a table and lifting each finger one at a time, keeping the other fingers relaxed. You can also try playing scales or arpeggios with each finger independently, focusing on isolating the movement of each finger.
- Object Manipulation:Activities like juggling, coin stacking, or playing with small objects can enhance finger dexterity. These activities require precise hand-eye coordination and fine motor control, which translates to improved finger dexterity on the guitar.
Importance of Practice and Repetition
Consistent practice is crucial for developing finger strength and dexterity. Regular practice strengthens the neural pathways in your brain, improving finger coordination and muscle memory. Repetition plays a vital role in building muscle memory, allowing your fingers to move automatically and efficiently.
- Neural Pathways:As you practice guitar exercises, you’re essentially creating new neural pathways in your brain. These pathways connect the motor cortex (responsible for movement) to the muscles in your fingers. The more you practice, the stronger these pathways become, enabling your fingers to move with greater coordination and precision.
- Muscle Memory:Muscle memory is the ability of your muscles to perform movements automatically without conscious thought. Repetition is essential for building muscle memory. The more you practice a particular exercise or technique, the more your muscles will remember the movements, allowing you to play with greater speed and accuracy.
- Progressive Difficulty:Gradually increasing the difficulty of exercises is essential for challenging your fingers and improving your skills. Start with simple exercises and gradually increase the speed, complexity, and duration of the exercises. This gradual progression ensures that your fingers are constantly challenged and adapt to new demands.
Fingerpicking and Alternate Picking
Fingerpicking and alternate picking are two common techniques used by guitarists. Mastering these techniques requires both finger strength and dexterity.
- Fingerpicking Techniques:Fingerpicking involves using your fingers to pluck individual strings. There are various fingerpicking techniques, but two common ones are the thumb-and-finger method and the three-finger method. The thumb-and-finger method involves using your thumb to pluck the bass strings and your index, middle, and ring fingers to pluck the treble strings.
The three-finger method involves using your index, middle, and ring fingers to pluck all the strings, with the thumb providing support.
- Alternate Picking Technique:Alternate picking involves using a pick to pluck the strings, alternating between downstrokes and upstrokes. This technique is commonly used for playing lead guitar parts and fast riffs. The key to alternate picking is to maintain a consistent rhythm and alternate between downstrokes and upstrokes smoothly.
- Picking Patterns:Practicing picking patterns is an excellent way to improve your fingerpicking and alternate picking skills. Start with simple patterns and gradually increase the complexity and speed. You can also experiment with different picking patterns to challenge your fingers and explore new sounds.
Avoiding Finger Injuries
It’s essential to prioritize finger health to prevent injuries and ensure long-term playing enjoyment. Here are some tips for avoiding finger injuries:
- Proper Posture:Maintaining good posture while playing the guitar is crucial for preventing strain on your fingers, wrists, and shoulders. Ensure that your back is straight, your shoulders are relaxed, and your elbows are at a comfortable angle. Avoid hunching over the guitar or straining your fingers to reach the strings.
- Warm-up and Cool-down:Warming up your fingers before playing and cooling down afterward is essential for preventing injuries. Start with some simple finger stretches and exercises to loosen up your muscles and increase blood flow. After playing, gently stretch your fingers and wrists to reduce muscle tension.
- Rest and Recovery:Allowing your fingers adequate rest is essential for preventing overuse injuries. Take breaks during long practice sessions to avoid straining your fingers. If you experience any pain or discomfort, stop playing and give your fingers time to recover.
Learning Guitar Tablature
Guitar tablature, often shortened to “tabs,” is a way to represent music for guitar using a visual system that’s different from traditional musical notation. It’s a popular method for learning guitar, especially for beginners, as it’s often easier to understand and follow than sheet music.
Understanding Guitar Tablature
Guitar tablature is a visual representation of the guitar’s fretboard. Each line in a tab represents a string on the guitar, with the top line representing the highest-pitched string (usually the thinnest) and the bottom line representing the lowest-pitched string (usually the thickest).
Numbers on the lines indicate the fret you should press down on that string to play a note.
- String Lines:The six horizontal lines represent the six strings of a guitar. The top line represents the high E string, and the bottom line represents the low E string.
- Fret Numbers:Numbers on the lines indicate the fret you should press down on that string. The numbers correspond to the frets on the guitar neck, starting with 1 for the first fret and increasing as you move up the neck.
- Tablature for a Single Note:A single number on a line represents a single note. For example, “5” on the third line would indicate playing the fifth fret on the A string.
- Tablature for Multiple Notes:Multiple numbers on a line represent playing multiple notes at the same time. For example, “3, 5, 7” on the second line would indicate playing the third, fifth, and seventh frets on the D string.
- Silence:A blank space on a line indicates that the string should be left open or not played.
- Other Symbols:Tabs can also include symbols for strumming patterns, bending notes, and other guitar techniques.
Reading and Understanding Guitar Tabs
Reading guitar tabs is a straightforward process once you understand the basics. The key is to visualize the guitar neck and the position of your fingers on the fretboard.
- String Lines:Identify the string lines by remembering that the top line is the high E string and the bottom line is the low E string.
- Fret Numbers:Look at the numbers on each line to determine which frets to press down on.
- Rhythm:Guitar tabs usually include a rhythm section, often represented by a grid or time signature. This helps you understand the timing of the notes.
- Practice:The best way to learn how to read guitar tabs is to practice. Start with simple tabs and gradually work your way up to more complex ones.
Using Tabs to Learn Songs and Guitar Parts
Guitar tabs are a great resource for learning songs and guitar parts. They can help you understand the chords, melodies, and rhythms of a song, making it easier to play along.
- Find Tabs Online:Many websites and apps offer free guitar tabs for a wide variety of songs. Popular sites include Ultimate Guitar, Songsterr, and Chordify.
- Practice with Tabs:Use tabs to practice playing along with recordings of your favorite songs. This will help you develop your timing and coordination.
- Break Down Difficult Parts:If you come across a difficult section in a tab, break it down into smaller parts and practice each section individually.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Tabs
Using guitar tabs has both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Easier to Learn:Tabs are generally easier to read and understand than traditional sheet music, especially for beginners.
- Visual Representation:Tabs provide a visual representation of the guitar fretboard, making it easier to understand where to place your fingers.
- Widely Available:Tabs are widely available online and in print, making it easy to find them for a variety of songs.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Musical Information:Tabs do not provide information about dynamics, tempo, or other musical elements that are important for a full understanding of a piece of music.
- Over-Reliance on Tabs:Over-reliance on tabs can hinder the development of music theory and ear training skills.
- Inaccuracies:Some tabs online may be inaccurate or incomplete, leading to frustration and confusion.
7. Learning from Guitar Teachers and Resources
Learning guitar doesn’t have to be a solitary journey. There are fantastic resources and teachers available to guide you along the way. Whether you prefer the structure of lessons or the freedom of self-study, you can find a learning path that suits your style and helps you achieve your guitar goals.
7.1 The Value of Professional Guidance
A good guitar teacher can be an invaluable asset to your musical journey. They provide personalized feedback, help you develop proper technique, and guide you through the sometimes-confusing world of music theory.
- Personalized Feedback:A teacher can identify your strengths and weaknesses and tailor lessons to your specific needs. They’ll help you overcome obstacles, refine your technique, and make sure you’re on the right track.
- Structured Learning:Lessons provide a structured framework for your learning. You’ll work through a curriculum, learn new skills systematically, and build a solid foundation for your guitar playing.
- Overcoming Common Obstacles:Every guitarist encounters challenges. A teacher can help you overcome common obstacles like finger pain, bad habits, and frustration. They’ll provide encouragement, support, and practical solutions.
- Developing Proper Technique:Good technique is essential for efficient playing and preventing injuries. A teacher will guide you on proper hand positioning, finger placement, and strumming techniques, ensuring you develop healthy habits from the start.
- Understanding Music Theory:Music theory can seem daunting, but it’s essential for understanding how music works. A teacher can break down complex concepts into manageable pieces and help you apply theory to your guitar playing.
Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning guitar can be a rewarding journey, but it’s also a challenging one. It’s normal to encounter obstacles along the way, but don’t let them discourage you! By understanding common challenges and developing effective strategies, you can stay motivated and make steady progress.
Challenges Faced by Beginner Guitarists
Beginner guitarists often face a variety of hurdles, both technical and emotional. Recognizing these challenges is the first step toward overcoming them.
| Challenge | Cause | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sore Fingers | Lack of finger strength and calluses | Experiencing pain or discomfort when pressing down on strings. |
| Difficulty Coordinating Hands | Lack of practice and coordination between left and right hands | Struggling to strum chords while simultaneously pressing down on the strings with the left hand. |
| Frustration with Progress | Unrealistic expectations or comparing oneself to others | Feeling discouraged because progress seems slow or not as rapid as expected. |
| Lack of Motivation | Feeling overwhelmed or bored with practice routine | Losing interest in practicing regularly or feeling uninspired to learn new songs. |
| Fear of Making Mistakes | Perfectionism or fear of judgment | Hesitating to play in front of others or avoiding challenging songs due to fear of errors. |
Strategies for Overcoming Frustration and Staying Motivated
It’s essential to have a positive mindset and effective strategies to deal with the inevitable frustrations that come with learning guitar.
- Focus on Progress, Not Perfection:Celebrate small victories and acknowledge your progress, even if it seems insignificant. Remember that every step forward, no matter how small, contributes to your overall development.
- Practice Patience and Self-Compassion:Learning guitar takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and avoid comparing your progress to others. Everyone learns at their own pace.
- Break Down Goals into Smaller Steps:Instead of aiming for a large, intimidating goal, break it down into smaller, more manageable steps. This makes the journey feel less overwhelming and gives you a sense of accomplishment as you achieve each milestone.
- Find a Supportive Community:Connect with other guitarists, either online or in person. Sharing experiences and receiving encouragement from others can boost motivation and help you stay on track.
- Take Breaks When Needed:It’s okay to step away from the guitar if you’re feeling overwhelmed or frustrated. Taking a break can help you return with a fresh perspective and renewed enthusiasm.
Setting realistic goals is crucial for staying motivated. Breaking down large goals into smaller, achievable steps creates a sense of progress and accomplishment. This approach helps maintain enthusiasm and prevent discouragement.
- Celebrate Learning a New Chord:Reward yourself with a small treat or a break after successfully mastering a new chord.
- Record Yourself Playing:Listen back to your recordings and acknowledge how far you’ve come since you started. This can be a powerful reminder of your progress.
- Share Your Music with Friends and Family:Performing for others, even if it’s just a simple song, can be a rewarding experience and boost your confidence.
Maintaining a Consistent Practice Routine
Regular practice is essential for developing guitar skills and achieving your goals. Establishing a consistent routine helps build good habits and ensures steady progress.
- Schedule Dedicated Practice Time:Treat practice time as an important appointment and block it out in your calendar. This helps create a sense of commitment and ensures that you prioritize practice.
- Create a Dedicated Practice Space:Having a designated space for practicing can help you focus and avoid distractions. Ensure your space is comfortable and has everything you need, such as your guitar, picks, and a tuner.
- Start Small and Gradually Increase Duration:Begin with short practice sessions and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable. It’s better to practice consistently for shorter periods than to have sporadic long sessions.
- Break Down Practice into Smaller Sessions:Instead of trying to practice for a long time all at once, break down your practice into shorter, focused sessions. This helps maintain concentration and prevent burnout.
- Find a Practice Buddy:Practicing with a friend can provide motivation, accountability, and a sense of camaraderie. You can also learn from each other and offer support.
Consistent practice is crucial for skill development and progress. It allows your muscle memory to develop, helps you master techniques, and reinforces what you’ve learned. The more you practice, the faster you’ll progress and the more confident you’ll become.
Overcoming a Challenge: A Story
Sarah, a beginner guitarist, was struggling with her left-hand coordination. She couldn’t seem to press down on the strings cleanly while strumming with her right hand. Frustration started to creep in, and she felt like giving up.Sarah remembered the advice from her guitar teacher: “Focus on progress, not perfection.” She started breaking down her practice into smaller, more manageable chunks.
Instead of trying to play a whole song, she focused on practicing individual chords and strumming patterns. She also practiced patience and self-compassion, reminding herself that everyone learns at their own pace.Sarah celebrated her small victories. When she finally mastered a new chord, she rewarded herself with a cup of tea and a break.
She also started recording herself playing, which helped her track her progress and identify areas for improvement.Over time, Sarah’s coordination improved, and her frustration turned into excitement. She realized that the key to success was consistent practice, patience, and a positive mindset.
The challenges she faced had only made her more determined to achieve her goals.
Exploring Different Guitar Genres and Styles
The beauty of the guitar lies in its versatility, allowing you to express yourself across a wide range of musical styles. From the bluesy grit of rock and roll to the intricate melodies of classical music, each genre has its own unique set of techniques and influences.
Exploring these diverse styles can expand your musical horizons, inspire creativity, and deepen your understanding of the instrument.
Guitar Genres and Their Characteristics
Different guitar genres have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Let’s explore some popular genres and their key features:
- Rock:Characterized by powerful chords, driving rhythms, and often distorted electric guitar sounds. Rock guitarists use techniques like palm muting, power chords, and aggressive picking to create a dynamic and energetic sound.
- Blues:Rooted in African American musical traditions, blues is known for its soulful melodies, expressive bends, and use of the pentatonic scale. Blues guitarists often use techniques like slide guitar, vibrato, and rhythmic phrasing to convey emotion and improvisation.
- Jazz:Jazz guitar emphasizes improvisation, complex chord progressions, and a focus on melody and harmony. Jazz guitarists use techniques like single-note lines, chord voicings, and sophisticated fingerpicking to create a unique and improvisational sound.
- Country:Country guitar is characterized by its use of acoustic guitars, open tunings, and traditional strumming patterns. Country guitarists often use techniques like flatpicking, fingerpicking, and slide guitar to create a warm and melodic sound.
- Metal:Metal guitar is known for its heavy riffs, fast tempos, and aggressive distortion. Metal guitarists use techniques like tremolo picking, pinch harmonics, and complex chord progressions to create a powerful and intense sound.
- Classical:Classical guitar music features intricate melodies, complex harmonies, and precise fingerwork. Classical guitarists use techniques like fingerpicking, arpeggios, and sophisticated scales to create a beautiful and expressive sound.
Influential Guitarists in Different Genres
Each guitar genre has its own iconic figures who have shaped the sound and style of their respective musical traditions.
- Rock:Jimi Hendrix, Eric Clapton, Jimmy Page, Eddie Van Halen, Slash
- Blues:B.B. King, Muddy Waters, Albert King, Stevie Ray Vaughan, Eric Clapton
- Jazz:Django Reinhardt, Charlie Christian, Wes Montgomery, Pat Metheny, John McLaughlin
- Country:Chet Atkins, Merle Haggard, Marty Stuart, Vince Gill, Keith Richards
- Metal:Tony Iommi, Randy Rhoads, Dimebag Darrell, Kirk Hammett, James Hetfield
- Classical:Andrés Segovia, Julian Bream, John Williams, Christopher Parkening, Sharon Isbin
Exploring Different Guitar Styles
Experimenting with different guitar styles is a rewarding journey that can broaden your musical horizons. Here are some tips for exploring and experimenting with different guitar styles:
- Listen to a variety of music:Immerse yourself in the sounds of different genres. Pay attention to the guitar techniques, chord progressions, and overall feel of each style.
- Learn from guitarists:Study the techniques and approaches of influential guitarists in the styles you’re interested in. Watch videos, listen to recordings, and analyze their playing.
- Practice techniques:Dedicate time to practicing specific techniques associated with different genres. For example, if you’re interested in blues, focus on bending, vibrato, and slide guitar.
- Find a community:Connect with other guitarists who share your interest in different styles. Join online forums, attend workshops, or jam with others to share ideas and learn from each other.
- Be patient and persistent:Mastering a new style takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and keep practicing. The more you explore, the more you’ll discover your own unique voice on the guitar.
The Importance of Listening and Musicality
Learning guitar is more than just mastering finger dexterity and technique. It’s about developing a deep understanding of music and expressing yourself creatively. One crucial aspect of this journey is cultivating musicality, and a key ingredient in that is listening.
Listening actively to music is like learning a new language. It allows you to grasp the nuances of rhythm, melody, harmony, and the emotions conveyed through sound. This understanding forms the foundation for your own musical expression on the guitar.
Active Listening and Identifying Key Elements
Active listening goes beyond simply hearing the music; it involves paying close attention to its components. Here are some tips for developing this skill:
- Focus on the Rhythm:Pay attention to the tempo, the beat, and how the music is divided into measures. Notice the patterns and variations in the rhythm. You can tap your foot or count along to help you internalize the rhythm.
- Identify the Melody:Listen closely to the main melody line, the tune that is most prominent. Try to sing along with it or hum the melody. This helps you understand the melodic structure and the way the notes flow.
- Recognize the Harmony:Notice the chords being played. How do they change? How do they create different moods and feelings? Listen for the bass line, which often provides a grounding element for the harmony.
- Analyze the Dynamics:Pay attention to the volume changes, the crescendos (getting louder) and diminuendos (getting softer). How do these dynamics affect the emotional impact of the music?
Playing and Listening: A Symbiotic Relationship
Listening and playing are interconnected aspects of guitar learning. By listening to music, you absorb musical ideas, techniques, and styles. This knowledge then informs your playing, shaping your own musical voice.
- Learning from the Masters:Listen to guitarists you admire and analyze their playing. Pay attention to their technique, phrasing, and musicality. Try to emulate their style and learn from their approach.
- Expanding Your Musical Horizons:Explore different genres and styles of music. This broadens your musical vocabulary and exposes you to new techniques, rhythms, and melodies. It can also inspire you to create your own unique sound.
- Developing Your Ear:Listen to music with the intention of identifying the chords and melodies being played. This can help you develop your ear training skills, which are essential for playing by ear and improvising.
Examples of How Listening Enhances Guitar Playing
- Understanding Chord Progressions:By listening to different songs, you’ll start to recognize common chord progressions. This knowledge will help you create your own chord sequences and accompany other musicians.
- Improving Your Timing and Rhythm:Listening to music with a strong beat will help you develop your sense of rhythm and timing. This is crucial for playing in time with other musicians and for creating a solid foundation for your music.
- Developing Your Phrasing and Improvisation:Listening to guitarists who are skilled improvisers can inspire you to develop your own unique phrasing and improvisation skills. Pay attention to their melodic ideas, their use of scales and arpeggios, and their ability to create interesting musical lines.
The Benefits of Playing Guitar
/teaching-young-boy-guitar-10140747-58e5285b3df78c5162b342ba.jpg)
Learning to play the guitar is a rewarding experience that offers numerous benefits, enriching not only your musical life but also your cognitive, emotional, and social well-being. It’s an investment in yourself that can unlock hidden talents, boost your confidence, and bring joy to your life.
This blog post will delve into the transformative power of guitar playing, exploring its profound impact on various aspects of your life.
Cognitive Benefits of Playing Guitar
Playing the guitar is a mentally stimulating activity that can significantly enhance cognitive skills. The process of learning and playing engages different areas of the brain, promoting neuroplasticity and improving cognitive function.
- Improved Memory:Learning guitar involves memorizing chords, scales, and musical pieces. This process strengthens the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory formation and retrieval. Research has shown that musicians, including guitarists, tend to have better verbal memory and working memory compared to non-musicians.
- Enhanced Attention Span:Guitar playing requires sustained focus and attention to detail. It trains your brain to concentrate on the task at hand, filtering out distractions and improving your overall attention span. Studies have found that musicians exhibit improved auditory attention and selective attention, which are essential for everyday tasks and academic performance.
- Increased Problem-Solving Abilities:Learning guitar involves deciphering musical notation, figuring out chord progressions, and improvising melodies. This process engages the prefrontal cortex, the brain region responsible for executive functions, including planning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
| Brain Region | Function | Role in Guitar Playing |
|---|---|---|
| Hippocampus | Memory formation and retrieval | Memorizing chords, scales, and musical pieces |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Executive functions, including planning, decision-making, and problem-solving | Deciphering musical notation, figuring out chord progressions, and improvising melodies |
| Auditory Cortex | Processing sound information | Recognizing and interpreting musical sounds |
| Motor Cortex | Controlling voluntary movements | Coordinating finger movements for playing chords and melodies |
Emotional Benefits of Playing Guitar
Beyond cognitive benefits, playing guitar offers profound emotional advantages, serving as a powerful tool for stress relief, emotional expression, and self-discovery.
- Stress Reduction:Engaging in music, particularly playing an instrument like the guitar, can trigger the release of endorphins, natural mood boosters that have stress-reducing effects. Research suggests that listening to and playing music can lower levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, promoting relaxation and well-being.
- Emotional Expression and Release:Music has long been recognized as a universal language that transcends words. Playing guitar allows individuals to express their emotions, whether it’s joy, sadness, anger, or love, through music. This cathartic experience can be incredibly therapeutic, providing an outlet for emotional release and processing.
- Improved Mood and Self-Esteem:The sense of accomplishment and satisfaction that comes with mastering new guitar skills can significantly boost mood and self-esteem. Learning to play an instrument can provide a sense of purpose, challenge, and achievement, contributing to a more positive self-image.
“Music is a powerful tool for healing and transformation. It can soothe the soul, uplift the spirit, and connect us to something greater than ourselves.”
Unknown
Social Benefits of Playing Guitar
Music has always been a unifying force, bringing people together and fostering social connections. Playing guitar can create opportunities for collaboration, community engagement, and enhanced communication skills.
- Collaboration and Community Engagement:Playing guitar often involves joining bands, performing in groups, or participating in jam sessions. These activities foster a sense of community and collaboration, allowing individuals to connect with like-minded people who share a passion for music.
- Enhanced Communication and Social Skills:Learning guitar can improve communication skills by encouraging individuals to express themselves through music. It also develops social skills by providing opportunities to interact with others in a musical setting, fostering teamwork and cooperation.
The Role of Practice and Persistence: Is Learning Guitar Hard
Becoming a proficient guitarist requires more than just talent; it demands consistent and dedicated practice. Just like any skill, playing the guitar is a journey of learning, refinement, and mastery. Regular practice is the key that unlocks the door to guitar proficiency, allowing you to transform from a beginner to a confident musician.
Unlocking Guitar Mastery: The Power of Consistent Practice
Consistent practice is the foundation of guitar mastery. It’s the secret ingredient that transforms raw talent into tangible skills. When you practice regularly, you’re not just playing scales or strumming chords; you’re building muscle memory, refining your technique, and deepening your understanding of music theory.Imagine your fingers dancing across the fretboard, effortlessly navigating complex chords and melodies.
This is the result of consistent practice. Through repetition, your brain and muscles develop a symbiotic relationship, making playing the guitar feel increasingly natural and intuitive. The more you practice, the stronger your fingers become, the smoother your transitions between chords, and the more fluid your melodies.
Beyond technical proficiency, consistent practice fosters a deeper understanding of music theory. As you play scales and explore different chords, you begin to recognize patterns and relationships within music. This newfound knowledge empowers you to create your own melodies, improvise, and even compose your own songs.
Deliberate Practice: A Focused Approach to Guitar Learning
Deliberate practice is a targeted and structured approach to guitar learning. It involves setting specific goals for each practice session, focusing on areas that require improvement, and actively seeking feedback to track progress. Unlike traditional practice, which can often be passive and unfocused, deliberate practice emphasizes conscious effort and purposeful engagement.
Deliberate Practice vs. Traditional Practice
| Deliberate Practice | Traditional Practice | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Specific areas for improvement | General playing or familiar songs |
| Goal Setting | Clearly defined goals for each session | Vague or no specific goals |
| Feedback | Active seeking and analysis of feedback | Minimal or no feedback |
| Structure | Structured and organized practice sessions | Unstructured and often haphazard |
| Effectiveness | Rapid and noticeable improvement | Slower progress and plateaus |
Sample Weekly Practice Schedule for Beginner Guitarists
Here’s a sample weekly practice schedule for beginner guitarists, focusing on different aspects of guitar playing:
Monday: Fingerpicking Fundamentals
Warm-up
Play a simple scale like C major for 5 minutes.
Exercise
Practice fingerpicking patterns like “The Travis Picking” for 10 minutes.
Song
Learning guitar can feel daunting at first, but it’s all about finding the right rhythm. Just like a drummer needs to understand the connection between the cymbal, scimitar, and drums, cymbal scimitar drum connections , you need to grasp the relationship between chords, melodies, and rhythms on the guitar.
It’s all about practice and patience, and you’ll be strumming your way to success in no time!
Learn a fingerpicking song like “House of the Rising Sun” for 15 minutes.
Tuesday: Strumming Mastery
Warm-up
Play a basic strumming pattern for 5 minutes.
Exercise
Practice different strumming patterns like “down-up-down-down” for 10 minutes.
Song
Learn a song with a strumming pattern like “Blowin’ in the Wind” for 15 minutes.
Wednesday: Scale Exploration
Warm-up
Play a C major scale for 5 minutes.
Exercise
Practice different scales like D major, G major, and A minor for 10 minutes.
Song
Try to play a simple melody using a scale you’ve learned for 15 minutes.
Thursday: Chord Progressions
Warm-up
Play a simple chord progression like C-G-Am-F for 5 minutes.
Exercise
Practice transitioning between different chords for 10 minutes.
Song
Learn a song with a basic chord progression like “Let It Be” for 15 minutes.
Friday: Finger Strength and Dexterity
Warm-up
Play a fingerpicking exercise for 5 minutes.
Exercise
Practice exercises that build finger strength and dexterity, like “Spider Walk” for 10 minutes.
Song
Play a song that requires precise fingerwork for 15 minutes.
Saturday: Open Mic Night
Warm-up
Play a few songs you’ve learned for 5 minutes.
Performance
Play a song or two at an open mic night for 15 minutes.
Sunday: Rest and Relaxation
Rest
Give your hands a break and relax for the day.
The Journey of a Guitarist: A Story of Perseverance
John, a young aspiring guitarist, had always been drawn to the soulful sounds of the blues. He spent countless hours practicing, but progress seemed slow. His fingers fumbled on the fretboard, his chords sounded muddy, and his melodies lacked the emotion he longed to express.
Discouragement crept in, whispering doubts about his ability.But John refused to give up. He understood that guitar mastery was a marathon, not a sprint. He embraced the challenges as opportunities for growth, and he found inspiration in the stories of legendary guitarists who had faced similar struggles.
He sought guidance from experienced players, practiced with unwavering dedication, and immersed himself in the world of blues music.Slowly but surely, John’s skills began to blossom. His fingers gained strength and dexterity, his chords became clear and resonant, and his melodies echoed with the raw emotion of the blues.
He learned to embrace the imperfections, recognizing that they were part of his unique musical journey. John’s story is a testament to the power of perseverance. It reminds us that the path to guitar mastery is paved with challenges, but it’s the unwavering commitment to practice and the unwavering belief in oneself that ultimately leads to success.
The Importance of Enjoyment and Passion
Learning guitar should be an enjoyable journey, not a chore. Passion fuels your dedication, making the inevitable challenges feel less daunting and propelling you forward.
Finding Music You Love
When you discover music that resonates with you, it becomes a source of inspiration. You’ll find yourself eager to learn the songs you adore, pushing you to practice more and improve your skills. Whether it’s classic rock, blues, jazz, or something else entirely, embrace the music that ignites your passion.
The Journey of Learning Guitar
Learning guitar is a rewarding journey that takes time, dedication, and perseverance. It’s a process of gradual improvement, with different stages of learning presenting unique challenges and opportunities.
Navigating the Stages of Learning
Understanding the different stages of learning can help you set realistic expectations and stay motivated throughout the journey.
- Beginner Stage:The initial stage focuses on mastering the basics, including holding the guitar correctly, learning basic chords, and strumming patterns. This stage can be exciting and challenging, as you grapple with new concepts and develop fundamental skills.
- Intermediate Stage:As you progress, you’ll start to explore more complex chords, scales, and strumming techniques. This stage involves developing your musical ear, improving finger dexterity, and expanding your repertoire of songs.
- Advanced Stage:The advanced stage is where you delve deeper into musical theory, improvisation, and advanced techniques. You’ll start to develop your own unique style and explore different genres and musical influences.
Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning guitar can be challenging at times, but it’s important to stay motivated and overcome obstacles.
- Set Realistic Goals:Don’t expect to become a virtuoso overnight. Break down your learning goals into smaller, achievable steps.
- Find a Supportive Community:Connect with other guitarists, either online or in person, to share your experiences, get feedback, and stay inspired.
- Celebrate Progress:Acknowledge your achievements, no matter how small they may seem. Every step forward is a cause for celebration.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask for Help:If you’re struggling with a particular concept, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a teacher, mentor, or online resources.
The Importance of Setting Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is crucial for maintaining motivation and enjoying the learning process.
- Understand the Time Commitment:Learning guitar requires consistent practice and dedication. It’s important to be realistic about the time you can commit to practicing.
- Embrace the Learning Curve:Learning guitar is a gradual process, and there will be times when you feel frustrated or stuck. Embrace these challenges as opportunities for growth.
- Focus on Progress, Not Perfection:Don’t strive for perfection, as it can lead to discouragement. Instead, focus on making progress, even if it’s small steps at a time.
The Ongoing Nature of Learning
Learning guitar is a lifelong journey of continuous improvement.
- Embrace the Challenge:Don’t be afraid to tackle new techniques and genres. The more you challenge yourself, the more you’ll grow as a musician.
- Never Stop Learning:There’s always something new to learn about guitar playing. Explore different styles, techniques, and musical theories to expand your horizons.
- Embrace the Journey:Enjoy the process of learning and becoming a better guitarist. The journey is just as important as the destination.
Guitar Resources and Communities
The guitar world is vast and exciting, with countless resources and communities available to help you on your musical journey. From online platforms offering lessons and gear reviews to supportive online forums, there’s a wealth of information and camaraderie waiting to be explored.
Online Resources
Online resources provide a treasure trove of guitar knowledge, offering lessons, tools, and inspiration for players of all levels.
- Lessons and Tutorials:
- JustinGuitar:A comprehensive website with free lessons for beginners to advanced players, covering various guitar styles and techniques. [website name: justinGuitar.com]
- Fender Play:An online platform offering structured guitar lessons with interactive exercises and personalized feedback. [website name: fender.com/play]
- Guitar Tricks:A subscription-based service with thousands of video lessons, covering everything from basic chords to advanced improvisation techniques. [website name: guitar tricks.com]
- Marty Music:A YouTube channel and website featuring engaging guitar lessons, song tutorials, and gear reviews. [website name: martymusic.com]
- Tablature and Sheet Music:
- Ultimate Guitar:A popular website with a vast database of guitar tabs, chords, and sheet music for various songs. [website name: ultimate-guitar.com]
- Songsterr:An online platform offering interactive tabs, allowing you to play along with backing tracks and adjust the tempo. [website name: songsterr.com]
- Guitar Gear Reviews:
- Guitar World:A well-established magazine and website providing reviews of guitars, amps, pedals, and other guitar gear. [website name: guitarworld.com]
- Premier Guitar:A website offering in-depth gear reviews, interviews with guitarists, and articles on guitar techniques. [website name: premierguitar.com]
- Guitar News and Articles:
- Guitar Player:A magazine and website featuring news, interviews, and articles on the guitar world. [website name: guitarplayer.com]
- MusicRadar:A website covering news and reviews related to music technology, including guitars, amps, and software. [website name: musicradar.com]
- Community Forums:
- The Gear Page:A popular forum for guitarists to discuss gear, techniques, and music. [website name: thegearpage.net]
- Reddit’s r/Guitar:A subreddit dedicated to all things guitar, offering a platform for discussions, questions, and sharing. [website name: reddit.com/r/guitar]
Guitar Books
Guitar books provide valuable insights into technique, theory, and specific genres, enriching your musical knowledge and skills.
- Technique and Theory:
- “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Playing Guitar” by Michael New:A comprehensive guide for beginners, covering basic chords, scales, and techniques. [book title: The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Playing Guitar]
- “Guitar Theory for Dummies” by Mark Phillips:An accessible introduction to music theory, explaining scales, chords, and other fundamental concepts. [book title: Guitar Theory for Dummies]
- Specific Genres:
- “The Ultimate Blues Guitar Book” by Jerry Ragovoy:A guide to blues guitar, covering techniques, licks, and classic blues songs. [book title: The Ultimate Blues Guitar Book]
- “The Complete Book of Rock Guitar” by Michael New:A comprehensive guide to rock guitar, covering techniques, riffs, and solos. [book title: The Complete Book of Rock Guitar]
- Improvisation:
- “The Jazz Improvisation Handbook” by Ted Greene:A classic text on jazz improvisation, offering exercises and insights into melodic and harmonic concepts. [book title: The Jazz Improvisation Handbook]
Guitar Learning Apps
Guitar learning apps offer interactive lessons, tools, and resources to enhance your practice and learning experience.
- Interactive Lessons:
- Fender Play:Offers structured lessons with interactive exercises and personalized feedback, providing a guided learning experience. [app name: Fender Play]
- Yousician:Uses AI technology to analyze your playing and provide feedback, offering personalized lessons and exercises. [app name: Yousician]
- Chord and Scale Diagrams:
- Chord! by Anytune:Provides a comprehensive library of chord diagrams, allowing you to explore different chords and progressions. [app name: Chord! by Anytune]
- GuitarTuna:Offers a tuner, metronome, and a library of chord and scale diagrams, supporting your practice and learning. [app name: GuitarTuna]
- Metronome and Tuner:
- Metronome Beats:A simple and effective metronome app, allowing you to set the tempo and practice your timing. [app name: Metronome Beats]
- GuitarTuna:Includes a tuner and metronome, offering a convenient tool for tuning your guitar and practicing with a steady beat. [app name: GuitarTuna]
- Recording and Practice Tools:
- AmpliTube:A virtual amp and effects modeling app, allowing you to experiment with different tones and practice with backing tracks. [app name: AmpliTube]
- GarageBand:A comprehensive music creation app, allowing you to record your guitar playing, experiment with effects, and create multi-track recordings. [app name: GarageBand]
Online Guitar Communities
Joining online guitar communities can provide a supportive and engaging environment for your musical journey.
- Benefits:
- Sharing Knowledge and Experience:Connect with other guitarists, exchange tips, and learn from their experiences. [website name: ultimate-guitar.com]
- Getting Feedback and Advice:Seek advice from experienced players, get feedback on your playing, and improve your technique. [website name: thegearpage.net]
- Finding Motivation and Inspiration:Connect with a community of passionate guitarists, share your progress, and find inspiration to keep practicing. [website name: reddit.com/r/guitar]
- Connecting with Other Guitarists:Build relationships with like-minded musicians, share your love for music, and find opportunities to collaborate. [website name: fender.com/play]
- Finding Supportive Communities:
- Look for Active and Welcoming Communities:Choose forums or groups with regular activity and a friendly atmosphere. [website name: thegearpage.net]
- Focus on Your Learning Goals:Find communities that align with your interests and goals, whether it’s blues, rock, or classical guitar. [website name: ultimate-guitar.com]
- Avoid Negativity and Toxicity:Seek communities that promote positive learning and avoid negativity or toxic behavior. [website name: reddit.com/r/guitar]
- Embrace Diversity in Skill Levels:Join communities that welcome guitarists of all skill levels, from beginners to advanced players. [website name: fender.com/play]
- Enhancing Learning:
- Motivational Support and Encouragement:Receive encouragement from fellow guitarists, share your progress, and stay motivated. [website name: reddit.com/r/guitar]
- Sharing Practice Tips and Strategies:Learn from other guitarists’ practice routines, share your own strategies, and improve your learning process. [website name: thegearpage.net]
- Learning from Different Perspectives:Gain insights from diverse guitarists with different backgrounds and experiences, expanding your musical horizons. [website name: fender.com/play]
- Building a Sense of Community and Belonging:Connect with other guitarists, share your passion for music, and build a sense of belonging within a supportive community. [website name: ultimate-guitar.com]
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the best way to choose a guitar for a beginner?
Start with an acoustic guitar. They’re affordable, versatile, and great for learning basic chords and strumming. Look for a guitar with a comfortable size and a good sound quality. Don’t be afraid to try out different models before making a decision.
How much time should I practice each day?
Aim for 15-30 minutes of focused practice daily. Consistency is key. Short, regular sessions are more effective than long, infrequent ones.
Is it necessary to take lessons?
While self-learning is possible, lessons can provide valuable guidance and feedback. A good teacher can help you develop proper technique and avoid bad habits.
What are some good resources for learning guitar online?
There are many excellent online resources available, including websites like JustinGuitar.com, YouTube channels like Fender Play, and apps like Yousician.