Is it easy to learn guitar –
Is it easy to learn guitar? The answer, like most things in life, is a bit nuanced. While some people pick it up quickly, others find it a challenging journey. The truth is, learning guitar is an adventure, a path of discovery that’s as much about personal growth as it is about mastering chords and melodies.
Whether you’re drawn to the soulful sounds of acoustic guitar, the raw power of electric riffs, or the intricate beauty of classical fingerpicking, the journey is filled with its own unique rewards.
This guide is designed to help you navigate the early stages of learning guitar, addressing common questions, challenges, and misconceptions. We’ll explore the factors that influence learning difficulty, provide practical tips for beginners, and offer insights into how to stay motivated and make progress.
Get ready to embark on a musical adventure – your guitar journey starts here!
The Appeal of Guitar Learning
The guitar, with its timeless melodies and captivating rhythms, has been a source of inspiration and artistic expression for generations. Its allure transcends cultural boundaries, drawing people from all walks of life to its strings. Whether you’re a seasoned musician or a curious beginner, the guitar holds a unique appeal that continues to captivate hearts and ignite passions.
Reasons for Learning Guitar
The reasons people choose to learn guitar are as diverse as the individuals themselves. Some are drawn to the sheer joy of creating music, while others seek a creative outlet for self-expression. The guitar provides a platform for both, allowing individuals to translate their emotions and experiences into captivating melodies.
- Musical Expression:The guitar offers a vast array of musical styles, from the soulful blues to the intricate classical pieces, providing a canvas for expressing a wide spectrum of emotions.
- Stress Relief:The act of playing guitar can be a powerful stress reliever. Focusing on the physical movements and the intricate melodies can help clear the mind and provide a sense of calm.
- Cognitive Enhancement:Learning guitar challenges the brain, improving memory, coordination, and problem-solving skills. It also enhances creativity and spatial reasoning.
- Social Connection:Guitar playing can be a social activity, fostering connections with other musicians and creating opportunities for shared musical experiences.
- Sense of Accomplishment:Mastering a new skill like guitar playing can provide a sense of accomplishment and boost self-esteem.
Benefits of Playing Guitar
The benefits of playing guitar extend far beyond musical proficiency. The act of learning and playing can have a profound impact on an individual’s well-being and overall development.
- Improved Mood:Playing guitar releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Enhanced Creativity:The guitar encourages creative thinking and problem-solving, fostering innovation and originality.
- Increased Focus:Learning guitar requires concentration and attention to detail, which can improve focus and attention span.
- Improved Memory:Learning guitar involves memorizing chords, scales, and melodies, which strengthens memory and cognitive function.
- Social Skills:Playing guitar can be a social activity, enhancing communication skills and fostering relationships.
Factors Influencing Learning Difficulty

Learning guitar is a journey that varies greatly from person to person. While the appeal of playing guitar is undeniable, the path to mastery is influenced by a complex interplay of personal factors and the specific style of guitar you choose to learn.
Personal Factors
Personal factors play a significant role in determining how easily you can learn guitar. These factors include your musical background, natural aptitude, and dedication to practice.
Musical Background
Prior musical experience can significantly impact your guitar learning journey. If you’ve already played other instruments or have a background in singing, you’ll likely have a head start.
- Initial Learning Pace:Individuals with prior musical experience tend to pick up guitar fundamentals faster. They understand basic musical concepts like rhythm, melody, and harmony, allowing them to grasp new techniques more quickly.
- Understanding Musical Concepts:Existing musical knowledge translates directly to guitar learning. You’ll have a better grasp of musical notation, scales, chords, and music theory, accelerating your understanding of guitar-specific concepts.
- Adapting to New Techniques:Having played other instruments helps you adapt to new techniques more easily. You’re familiar with the physicality of playing an instrument, making it easier to learn fingerpicking, strumming, or other guitar-specific techniques.
- Motivation and Engagement:A background in music often leads to greater motivation and engagement. You’ll be more likely to enjoy the learning process and persevere through challenges.
| Factor | Prior Musical Experience | No Prior Musical Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Learning Pace | Faster | Slower |
| Understanding Musical Concepts | Easier | More Challenging |
| Adapting to New Techniques | Quicker | Slower |
| Motivation and Engagement | Higher | Potentially Lower |
Natural Aptitude
Natural aptitude plays a role in how quickly and easily you can learn guitar. This includes factors like musical ear, hand-eye coordination, and memory.
- Musical Ear:A good musical ear allows you to recognize and reproduce pitches and melodies by ear, which can be helpful for learning songs and improvising. This ability can make it easier to pick up new scales, chords, and melodies.
- Hand-Eye Coordination:Good hand-eye coordination is crucial for playing guitar. It allows you to move your fingers accurately and precisely on the fretboard, while coordinating with the other hand to strum or pick the strings.
- Memory:A good memory helps you learn and retain new musical patterns, scales, chords, and songs. It’s essential for memorizing fingerings, chord progressions, and musical pieces.
Individuals with a strong musical ear may find it easier to learn by ear, while those with excellent hand-eye coordination might excel at intricate fingerpicking techniques.
Dedication and Practice Habits
Dedication and consistent practice are paramount to guitar mastery. The more time you dedicate to practicing, the faster you’ll progress.
- Relationship between Dedication, Practice Time, and Proficiency:The more you practice, the more you reinforce muscle memory and develop your skills. Consistent practice allows you to build upon your existing knowledge and refine your technique.
- Impact of Different Practice Schedules:Daily practice is generally considered the most effective, as it allows you to maintain momentum and build upon your progress. Weekly practice can also be effective, but it’s important to ensure consistent practice sessions. Sporadic practice, on the other hand, can lead to slower progress and difficulty retaining information.
- Setting Realistic Practice Goals and Effective Strategies:Setting realistic practice goals is crucial for staying motivated and preventing burnout. It’s also important to incorporate effective practice strategies, such as focusing on specific techniques, breaking down complex songs into smaller sections, and practicing with a metronome to improve rhythm and timing.
Guitar Style Factors
The style of guitar you choose to learn can also significantly impact the learning process.
Classical Guitar
Classical guitar presents unique challenges, requiring a specific approach to learning.
- Fingerpicking Techniques:Classical guitar emphasizes fingerpicking, where you use individual fingers to pluck the strings, creating a complex and nuanced sound. This technique requires precise finger coordination and dexterity, which can be challenging to master.
- Complex Musical Notation:Classical guitar music is typically written in standard musical notation, which involves learning to read notes on a staff and understanding various musical symbols. This can be a steep learning curve for beginners.
- Focus on Classical Repertoire:Classical guitar repertoire often includes complex pieces that require advanced technique and musical understanding. This can be challenging for beginners, but it also provides opportunities to develop a deep understanding of classical music.
Acoustic Guitar
Learning acoustic guitar offers a different experience compared to classical guitar.
- Techniques:Acoustic guitar techniques are more diverse than classical guitar, encompassing fingerpicking, strumming, and various picking patterns. While fingerpicking is still important, acoustic guitar often emphasizes strumming, which involves using a pick or your fingers to create a rhythmic pattern across multiple strings.
- Musical Styles:Acoustic guitar is used in a wide range of musical genres, including folk, blues, country, and pop. This allows for greater flexibility in terms of musical styles and repertoire.
- Typical Repertoire:Acoustic guitar repertoire is diverse, ranging from folk songs to contemporary pop hits. This allows for a more personalized learning experience, catering to your individual musical preferences.
Electric Guitar
Electric guitar offers its own set of challenges and advantages.
- Distortion Effects:Electric guitar often utilizes distortion effects, which can be challenging to master. These effects require understanding how to control the amount of distortion and how to use it effectively in different musical contexts.
- Learning Guitar Solos:Electric guitar is often associated with playing solos, which require advanced picking techniques and improvisation skills. Learning to play guitar solos can be a challenging but rewarding aspect of electric guitar playing.
- Mastering Different Picking Techniques:Electric guitar players use a variety of picking techniques, including alternate picking, downpicking, and sweep picking. Mastering these techniques is essential for achieving a clean and precise sound.
| Factor | Acoustic Guitar | Electric Guitar |
|---|---|---|
| Techniques | Fingerpicking, strumming, various picking patterns | Alternate picking, downpicking, sweep picking, distortion effects |
| Musical Styles | Folk, blues, country, pop | Rock, metal, blues, jazz |
| Typical Repertoire | Folk songs, contemporary pop hits | Rock classics, metal riffs, blues solos |
Early Stages of Guitar Learning
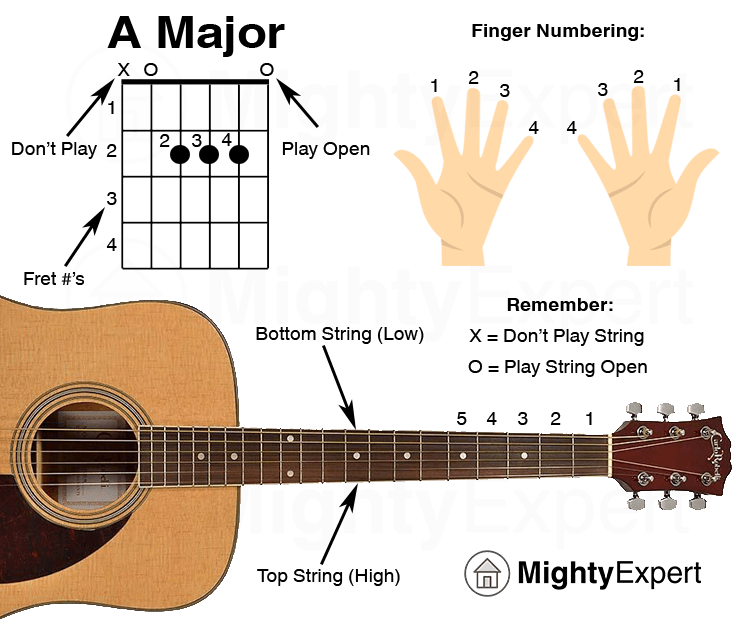
The early stages of guitar learning are crucial for establishing a strong foundation and developing essential skills. Mastering these initial steps will pave the way for a smooth and enjoyable learning journey.
Essential Skills for Beginners
The first step in learning guitar is to develop a basic understanding of proper posture, hand positioning, and basic chords. These skills are fundamental for playing comfortably and efficiently.
Posture
Maintaining good posture while playing guitar is essential for comfort, preventing strain, and ensuring proper technique.
- Sitting Posture:When sitting, choose a chair that provides adequate support and allows you to keep your back straight and your feet flat on the floor. Position the guitar so that the body rests comfortably on your lap, with the neck angled slightly upwards.
- Standing Posture:When standing, keep your feet shoulder-width apart, with your knees slightly bent. The guitar should be held close to your body, with the strap adjusted to a comfortable height that allows for easy access to the fretboard.
Hand Positioning
Proper hand positioning is key to playing accurate notes and chords.
- Left Hand:Place your left hand on the fretboard, with your thumb behind the neck, gently supporting the back of the neck. The fingers should be curved and relaxed, with only the fingertips pressing down on the strings.
- Right Hand:For strumming, hold the pick between your thumb and index finger, with a relaxed wrist. For fingerpicking, use your thumb and fingers to pluck individual strings, with a gentle and precise motion.
Basic Chords
Learning basic chords is the foundation of playing guitar.
- G Chord:
– Place your index finger on the 3rd fret of the low E string.
– Place your middle finger on the 2nd fret of the A string.
– Place your pinky finger on the 3rd fret of the high E string.
– The D and G strings are played open.
- C Chord:
– Place your index finger on the 1st fret of the A string.
– Place your middle finger on the 2nd fret of the D string.
– Place your pinky finger on the 3rd fret of the G string.
– The E and B strings are played open.
- D Chord:
– Place your index finger on the 2nd fret of the A string.
– Place your middle finger on the 3rd fret of the D string.
– Place your pinky finger on the 2nd fret of the G string.
– The E and B strings are played open.
- E Chord:
– Place your index finger on the 1st fret of the A string.
– Place your middle finger on the 2nd fret of the D string.
– Place your pinky finger on the 2nd fret of the G string.
– Place your ring finger on the 1st fret of the B string.
– The low E string is played open.
Setting Up Your Guitar
Before you can start playing, you need to tune your guitar and ensure that the strings are in good condition.
Tuning
Tuning your guitar is essential for playing in tune.
- Using a Tuner:A guitar tuner is a device that listens to the sound of each string and displays the corresponding note. Tune each string to the standard tuning, which is E-A-D-G-B-E from the lowest to the highest string.
- Tuning by Ear:If you don’t have a tuner, you can tune your guitar by ear using a reference source, such as a piano or an online tuning website.
Stringing
Guitar strings are available in various materials and gauges, each with its own characteristics.
- String Types:Common guitar string materials include steel, nylon, and bronze. Steel strings are typically used for electric guitars, while nylon strings are common on acoustic guitars.
- String Gauge:The gauge refers to the thickness of the string. Thicker strings produce a deeper and fuller sound, while thinner strings offer a brighter and more articulate tone.
Learning Basic Chords
Once you have your guitar tuned and set up, it’s time to learn some basic chords.
Chord Charts
Chord charts are diagrams that show you how to place your fingers on the fretboard to form a chord.
Learning guitar can feel like a long journey, but it’s all about taking those first steps. If you’re wondering about the bass, it’s often considered a bit easier to pick up, with fewer strings and simpler chords. Check out this article to see if is bass easy to learn for you.
Ultimately, the key to success with any instrument is dedication and practice, so don’t get discouraged if it takes time to master those guitar riffs!
- Format:Chord charts typically show the fretboard from the top, with the strings numbered 1-6 from lowest to highest. The dots represent the frets, and the numbers indicate the fingers used to play the chord.
Practice Techniques
Practice is key to mastering chords and developing muscle memory.
- Repetition:Repeat each chord multiple times, focusing on accurate finger placement and clear sound.
- Finger Exercises:Practice individual finger movements, such as moving from one fret to another or switching between different chords.
- Chord Progressions:Learn and practice simple chord progressions, which involve switching between different chords in a specific sequence.
Finding Resources and Lessons
There are numerous resources available to help you learn guitar, from online tutorials to in-person lessons.
Online Tutorials
Online tutorials offer a convenient and affordable way to learn guitar.
- Reputable Platforms:Websites such as Fender Play, JustinGuitar, and Guitar Tricks offer structured lessons and interactive exercises.
- YouTube Channels:Popular YouTube channels like Marty Music, Andrew Huang, and Rick Beato provide a wide range of tutorials, tips, and techniques.
Guitar Teachers
Learning from a guitar teacher can provide personalized instruction and feedback.
- Benefits:A teacher can help you identify and correct mistakes, develop good technique, and learn at your own pace.
- Finding Teachers:Look for local music schools, guitar shops, or online directories that list qualified guitar teachers.
Guitar Books
Guitar books offer a comprehensive guide to learning guitar, with detailed instructions, exercises, and theory.
- Beginner-Friendly Books:“Hal Leonard Guitar Method” and “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Playing Guitar” are popular choices for beginners.
Overcoming Challenges and Building Skills
Learning guitar can be a rewarding journey, but it’s not without its hurdles. You’ll likely encounter moments of frustration, finger pain, and waning motivation. However, with the right approach and a bit of perseverance, you can overcome these challenges and build a strong foundation in guitar playing.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
It’s crucial to remember that everyone learns at their own pace, and there will be times when you feel like giving up. But don’t let those moments deter you. Here are some strategies that can help you stay motivated and keep progressing:
- Practice Regularly:Consistency is key. Even short, daily practice sessions are more effective than infrequent, lengthy ones. Set aside a specific time each day for practice and stick to it as much as possible.
- Set Achievable Goals:Break down your learning into smaller, manageable goals. Instead of aiming to master a complex song right away, focus on learning a specific chord progression, a new strumming pattern, or a short melody. Celebrating each accomplishment will keep you motivated.
- Seek Support:Don’t be afraid to reach out for help. Connect with other guitarists, join online forums, or consider taking lessons from a qualified instructor. Sharing your journey and learning from others can provide valuable insights and encouragement.
- Be Patient and Kind to Yourself:Learning guitar takes time and effort. There will be days when you feel like you’re not making progress. Don’t get discouraged. Remember that every practice session, no matter how small, contributes to your overall development. Be patient with yourself and celebrate your successes along the way.
The Importance of Rhythm and Metronome Practice
A strong sense of rhythm is fundamental to guitar playing. It helps you play in time with other musicians, creates a solid foundation for your music, and enhances your overall musicality.
- Practice with a Metronome:A metronome is a valuable tool for developing your rhythm. It provides a consistent beat that helps you stay on time and develop a steady tempo. Start by practicing simple exercises and gradually incorporate more complex rhythms as you progress.
- Listen to Music Actively:Pay attention to the rhythms in the music you listen to. Try to identify the different beats, accents, and time signatures. This will help you develop a better understanding of rhythm and how it works in different musical styles.
Expanding Guitar Skills
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you’re ready to dive into the world of advanced guitar techniques. These techniques will not only enhance your playing but also unlock a whole new dimension of musical expression.
Learning Advanced Techniques
Learning advanced guitar techniques involves a gradual process of understanding the mechanics, practicing consistently, and applying them creatively. Here’s a breakdown of some common advanced techniques and how to approach them:
Strumming Patterns
Strumming patterns are rhythmic sequences of downstrokes and upstrokes that add depth and texture to your playing. Mastering different strumming patterns can transform simple chords into captivating melodies.
- Start with basic patterns like alternating down-up strokes and gradually introduce variations like eighth-note patterns and syncopated rhythms.
- Practice strumming patterns with different tempos and dynamics to develop your timing and control.
- Experiment with different pick angles and strumming techniques to find your own unique sound.
Fingerpicking
Fingerpicking involves using individual fingers to pluck strings, creating intricate melodies and harmonies. This technique allows for greater control and expressiveness compared to strumming.
- Begin by learning basic fingerpicking patterns, such as the “Travis Picking” technique, which uses thumb and index finger to create a rhythmic base while other fingers play the melody.
- Practice fingerpicking exercises that focus on finger independence and coordination, such as picking individual strings in sequence or playing scales using individual fingers.
- Gradually incorporate fingerpicking into your playing, starting with simple melodies and progressing to more complex arrangements.
Scales
Scales are sequences of notes that form the foundation of melodies and harmonies. Learning scales helps you understand the structure of music and develop your improvisation skills.
- Start with major and minor scales, which are the most common scales in Western music.
- Practice playing scales in different positions on the fretboard, both ascending and descending.
- Experiment with different fingerings and techniques to find the most comfortable and efficient way to play scales.
Developing a Practice Routine
A structured practice routine is essential for mastering advanced techniques. It allows you to focus on specific areas of improvement and track your progress.
- Start each practice session with warm-up exercises, such as scales, arpeggios, and finger stretches, to prepare your hands for playing.
- Allocate specific time slots for each technique you’re working on, such as strumming, fingerpicking, or scales.
- Break down complex techniques into smaller, manageable steps and practice each step individually before combining them.
- Use a metronome to develop your timing and rhythm.
- Record yourself playing to identify areas for improvement and track your progress.
Exploring Different Genres
Exposure to various musical genres can broaden your musical horizons and inspire creativity.
- Listen to and analyze music from different genres, such as blues, rock, jazz, classical, and folk.
- Try learning songs from different genres to understand the unique stylistic elements and techniques used in each genre.
- Experiment with different guitar styles, such as slide guitar, fingerstyle guitar, and electric guitar techniques.
The Role of Resources and Technology: Is It Easy To Learn Guitar
The journey of learning guitar is greatly enhanced by the vast array of resources and technological tools available today. From online platforms to physical materials, these resources offer valuable support and guidance throughout your learning experience.
Online Courses and Platforms
Online courses and platforms have revolutionized guitar learning, providing flexible and accessible learning options. These platforms offer structured lessons, interactive exercises, and personalized feedback, catering to different learning styles and skill levels.
- Coursera:This platform hosts a variety of guitar courses, from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced techniques, taught by renowned instructors.
- Udemy:Offers a wide selection of guitar courses, covering various genres and styles, with flexible learning schedules and affordable pricing.
- Fender Play:A subscription-based platform designed specifically for guitar learning, featuring interactive lessons, song tutorials, and personalized learning paths.
Apps
Guitar learning apps provide convenient and engaging tools for practice and skill development. These apps offer interactive exercises, chord diagrams, tuner functionality, and even opportunities to connect with other guitarists.
- GuitarTuna:A popular app that accurately tunes your guitar and provides helpful feedback on your tuning accuracy.
- Yousician:An interactive app that uses gamification to engage learners, providing feedback on their playing and offering personalized lessons.
- Ultimate Guitar Tabs:A comprehensive app that provides access to a vast library of guitar tabs and chords for a wide range of songs.
Books
Traditional guitar books offer a structured and comprehensive approach to learning, providing detailed explanations of theory, techniques, and exercises. These books can serve as valuable companions for both beginners and experienced guitarists.
- Hal Leonard Guitar Method:A popular and comprehensive method book that guides beginners through the fundamentals of guitar playing.
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Playing Guitar:A user-friendly guide that covers essential guitar skills and concepts in an accessible format.
- Guitar for Dummies:A practical and informative book that provides clear explanations and helpful tips for guitar learners of all levels.
Traditional Guitar Lessons vs. Online Learning Platforms
While traditional guitar lessons provide personalized instruction and direct feedback from a qualified teacher, online learning platforms offer flexibility, affordability, and access to a wide range of resources.
Traditional lessons offer the benefit of personalized feedback and tailored instruction from a qualified teacher. However, online learning platforms provide flexibility, affordability, and access to a wide range of resources.
Technology’s Role in Guitar Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in supporting the guitar learning process, offering tools that enhance practice, improve accuracy, and foster a sense of community.
Guitar Tuners
Guitar tuners are essential for ensuring accurate tuning, which is fundamental for playing in tune and achieving a pleasant sound. Electronic tuners provide quick and precise tuning, while smartphone apps offer convenient and portable tuning solutions.
Recording Software
Recording software allows guitarists to capture their playing, enabling self-evaluation and identifying areas for improvement. This software also provides opportunities for experimentation with different sounds and effects.
Online Communities
Online guitar communities provide a platform for connecting with other guitarists, sharing knowledge, seeking advice, and finding inspiration. These communities offer valuable resources, support, and motivation for guitar learners.
The Importance of Enjoyment and Persistence in Learning Guitar

Learning guitar should be a journey filled with joy and discovery, not a chore. While there will be moments of frustration and challenges, the key to success lies in finding the fun in the process.
The Power of Enjoyment in Guitar Learning
When you enjoy the journey of learning guitar, you’re more likely to stick with it. The feeling of accomplishment and the satisfaction of mastering a new skill are powerful motivators.
- Choose Songs You Love:Start by learning songs that you genuinely enjoy listening to. This will make practice more engaging and rewarding.
- Experiment with Different Styles:Don’t limit yourself to one genre. Explore different styles of music to discover what resonates with you.
- Find a Supportive Learning Environment:Surround yourself with people who encourage your guitar journey. This could be a teacher, a friend, or an online community.
- Set Realistic Goals:Don’t get discouraged if you don’t become a virtuoso overnight. Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps.
- Celebrate Small Victories:Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small it may seem. Every step forward is a reason to be proud.
“I remember when I first started learning guitar, I struggled with fingerpicking. It felt impossible at first, but I kept practicing and eventually, I was able to play a beautiful melody. The feeling of accomplishment was amazing!”
Staying Motivated and Consistent with Practice
Consistency is key to progress in guitar learning. Even when you face challenges, it’s crucial to maintain a regular practice routine.
- The Power of Consistency:Regular practice, even for short periods, helps build muscle memory and strengthens your skills.
- Tangible Improvements:You’ll notice significant improvements in your playing over time as you consistently practice.
- Overcoming Obstacles:Time constraints, frustration, and lack of motivation are common obstacles. But with a plan and a positive attitude, you can overcome them.
- Strategies for Staying Motivated:
- Set Achievable Goals:Break down your goals into smaller, manageable steps to track your progress and stay motivated.
- Find a Practice Buddy:Having a friend to practice with can provide support, accountability, and a sense of camaraderie.
- Use Positive Reinforcement:Reward yourself for reaching milestones and celebrate your successes.
Guitar Learning for Different Age Groups
Learning guitar can be a rewarding experience for people of all ages, but the approach to teaching and learning may vary depending on the age group. Understanding the unique needs and characteristics of each age group can make the learning process more effective and enjoyable.
Teaching Guitar to Young Children
Teaching guitar to young children requires a playful and engaging approach. Children are naturally curious and eager to learn, but they also have short attention spans. It’s important to keep lessons fun and interactive, using age-appropriate techniques and activities.
- Colorful Instruments:Using colorful guitars or smaller-sized instruments can make learning more appealing to young children. The bright colors and smaller size can be more engaging and easier for them to handle.
- Simplified Chord Diagrams:Instead of traditional chord diagrams, use simplified versions with pictures or symbols that are easier for children to understand.
- Playful Games:Incorporate games and activities into lessons to make learning fun and interactive. For example, you can use flashcards with chord shapes or play games that involve identifying different notes on the guitar.
Methods for Teaching Guitar to Young Children
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Lessons | Structured learning, personalized attention | Can be expensive, may not be engaging for all children |
| Online Courses | Flexible scheduling, affordable | Lack of personalized feedback, potential technical issues |
| Group Classes | Social interaction, lower cost per student | Less personalized attention, may not cater to individual learning styles |
Teaching Guitar to Teenagers, Is it easy to learn guitar
Teenagers are often more motivated by the prospect of playing their favorite songs or impressing their friends than by traditional musical theory. It’s important to cater to their interests and encourage them to explore different genres and styles of music.
“Teenagers are often more motivated by the prospect of playing their favorite songs or impressing their friends than by traditional musical theory.”
- Choose Their Own Music:Encourage teenagers to choose songs they want to learn. This will help them stay motivated and engaged in the learning process.
- Learn Popular Songs:Learning popular songs can be a fun and rewarding experience for teenagers. It can also help them develop their skills and learn new techniques.
- Develop Their Own Playing Style:Encourage teenagers to experiment with different playing styles and develop their own unique sound. This will help them express their individuality and creativity through music.
Teaching Guitar to Adults
Adults often have more limited time and may have pre-existing musical knowledge. It’s important to set realistic goals, utilize efficient practice methods, and tailor lessons to individual needs and interests.
- Set Realistic Goals:Adults should set realistic goals for their guitar learning. It’s important to start with achievable goals and gradually work towards more challenging ones.
- Utilize Efficient Practice Methods:Adults can benefit from using efficient practice methods, such as focused practice sessions and spaced repetition.
- Tailor Lessons to Individual Needs:Lessons should be tailored to the individual needs and interests of the adult learner. This may involve focusing on specific genres, techniques, or musical styles.
Tips for Adults Learning Guitar
- Overcoming Time Constraints:Break down practice into shorter sessions throughout the day.
- Dealing with Frustration:Remember that learning guitar takes time and patience. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks.
- Maintaining Motivation:Set achievable goals, find a practice buddy, and celebrate your progress.
The Value of Guitar Skills Beyond Music
Learning guitar isn’t just about playing melodies and chords; it’s a journey that enriches various aspects of your life, from cognitive function to social connections. The act of learning and playing guitar can unlock a world of benefits that extend far beyond the musical realm.
Cognitive Benefits
Learning guitar can positively impact your cognitive function, sharpening your mind in multiple ways. Playing guitar involves engaging multiple parts of the brain simultaneously, enhancing cognitive skills such as:
- Memory:Learning guitar requires memorizing chords, scales, and song arrangements, which strengthens your short-term and long-term memory. As you progress, you’ll find it easier to retain information in other areas of your life.
- Problem-solving:Decoding guitar tabs, figuring out chord progressions, and improvising melodies all require problem-solving skills. Guitar playing challenges your brain to think critically and creatively, improving your ability to tackle challenges in other aspects of your life.
- Hand-eye coordination:The coordination required to play guitar, from finger placement to strumming, improves hand-eye coordination. This benefit extends beyond music, enhancing your performance in activities like sports, typing, and even surgery.
- Focus and concentration:Playing guitar demands focus and concentration, helping you develop the ability to block out distractions and maintain attention. This skill is invaluable in various settings, from studying to work to personal projects.
The Guitar Learning Journey: A Personal Perspective

Picking up a guitar was one of the best decisions I ever made. The journey, though challenging at times, has been incredibly rewarding. From fumbling with my first chords to jamming with friends, I’ve learned a lot about myself and the power of music.
In this article, I’ll share my personal perspective on the guitar learning journey, outlining the stages of learning, key skills, common challenges, and practical tips for each stage.
The Beginner Stage: Embracing the Basics
The beginner stage is all about building a solid foundation. It’s like learning the alphabet before you can write a novel. This stage is crucial because it sets the groundwork for everything that comes later.
- Key Skills:
- Basic chords (C, G, D, A, E)
- Strumming patterns
- Basic picking techniques
- Challenges:
- Finger pain and fatigue
- Difficulty memorizing chords
- Frustration with slow progress
- Tips:
- Practice regularly, even for short bursts.
- Use a chord chart or app for reference.
- Focus on accuracy over speed initially.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help from a teacher or online resources.
Remember, it’s a marathon, not a sprint. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see immediate results. Keep practicing, and you’ll start to see progress. I remember when I first started, I struggled to hold down even the simplest chords. My fingers would ache, and I felt like giving up.
But I persevered, and slowly but surely, my fingers became stronger, and I started to get a grasp of the basics.
The Intermediate Stage: Expanding Your Horizons
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you’re ready to move on to the intermediate stage. This is where things start to get really exciting, as you begin to explore more advanced techniques and musical styles.
- Key Skills:
- Advanced chords (barre chords, 7th chords)
- Fingerstyle techniques
- Basic scales and melodies
- Challenges:
- Mastering barre chords
- Developing finger dexterity
- Transitioning between chords smoothly
- Tips:
- Practice regularly, focusing on technique and accuracy.
- Use a metronome to improve timing and rhythm.
- Break down complex techniques into smaller, manageable steps.
- Explore different musical styles and genres.
This stage was a real turning point for me. I started learning barre chords, which opened up a whole new world of possibilities. It was challenging, but I found that breaking down the techniques into smaller steps made it much easier to manage.
I also started experimenting with different musical styles, which helped me develop my own unique sound.
The Advanced Stage: Unleashing Your Creativity
The advanced stage is where you truly become a guitarist. This is where you start to develop your own style, explore improvisation, and delve deeper into music theory.
- Key Skills:
- Improvisation and soloing
- Advanced fingerstyle techniques
- Music theory knowledge
- Challenges:
- Developing musical ear and improvisation skills
- Mastering complex chord progressions and voicings
- Maintaining motivation and staying creative
- Tips:
- Listen to and analyze music from your favorite artists.
- Practice regularly and focus on improving your weaknesses.
- Explore different musical genres and styles.
- Consider taking lessons from a professional or joining a band.
The advanced stage is all about pushing your boundaries and exploring new musical territories. It’s a constant journey of learning and growth. I’m still learning new things every day, and I’m always striving to improve my skills.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Learning guitar is a rewarding journey, but it’s often clouded by misconceptions that can discourage aspiring musicians. Let’s dispel some of these myths and reveal the truth about guitar learning.
Natural Talent is Required
The idea that you need natural talent to play guitar is a common myth. While some people may have a predisposition for music, it’s not a prerequisite for learning. Numerous studies have shown that practice and dedication are far more important than innate talent.
Anyone can learn to play guitar, regardless of their musical background, as long as they’re willing to put in the effort.
Learning Guitar is Too Difficult
Another misconception is that learning guitar is too difficult. While it takes time and effort, it’s not impossible. Many resources and learning methods are available to help you progress at your own pace. Breaking down the learning process into manageable steps and celebrating small victories can make the journey more enjoyable and less daunting.
You Need to Start Young
It’s a myth that you need to start learning guitar at a young age to be successful. While starting young can offer advantages, it’s never too late to pick up an instrument. Many adults have successfully learned to play guitar later in life.
The key is to have a positive attitude, set realistic goals, and enjoy the process.
The Impact of Guitar Learning on Mental Health

Learning to play the guitar can have a profound impact on your mental well-being. Beyond the joy of creating music, the act of playing can significantly reduce stress, boost mood, and enhance overall well-being. This section explores the various ways guitar playing can contribute to a healthier and happier you.
Stress Reduction
Playing the guitar can effectively reduce stress by activating the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation. When you focus on playing, your brain shifts away from anxious thoughts and worries, allowing your body to enter a state of calm. The rhythmic nature of music, particularly slow tempos and gentle melodies, can also have a calming effect on the mind and body.
Mood Improvement
Playing the guitar can boost your mood by triggering the release of endorphins, hormones associated with pleasure and well-being. The act of creating music, whether through improvisation or playing a familiar piece, can be a source of joy and satisfaction, leading to a sense of accomplishment and increased happiness.
Furthermore, learning a new skill like guitar can significantly boost self-esteem and confidence, contributing to an overall improvement in mood. The sense of achievement that comes with mastering new chords, techniques, and songs can positively impact your self-perception and enhance your overall sense of well-being.
Overall Well-Being
Playing the guitar can contribute to overall well-being by fostering social connections and a sense of purpose. Joining a band or playing with friends can provide opportunities for social interaction and a sense of belonging. The shared experience of making music can strengthen bonds and create lasting friendships.
Beyond social benefits, playing guitar can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment, contributing to increased life satisfaction. The dedication and effort required to learn and improve can instill a sense of purpose and accomplishment, leading to a more fulfilling life.
Therapeutic Benefits of Music Making
Music making, including guitar playing, has significant therapeutic benefits, particularly in promoting relaxation and self-expression.
Relaxation
Slow tempos, gentle melodies, and harmonic progressions can induce relaxation and reduce anxiety. The rhythmic patterns and soothing sounds can create a sense of calm and tranquility, helping to alleviate stress and promote a sense of peace.
Self-Expression
Music provides a safe and creative outlet for emotions, allowing individuals to express themselves freely. Guitar playing, especially improvisation, can foster creativity and self-discovery. It allows individuals to explore their emotions and express themselves in a non-verbal and often cathartic way.
Emotional Regulation
Music can help individuals to identify, process, and manage their emotions. Upbeat music can boost energy and improve mood, while calming music can soothe anxiety and promote relaxation. By listening to or playing different types of music, individuals can learn to regulate their emotions and navigate challenging situations more effectively.
Guitar Learning as a Lifelong Pursuit
The journey of learning guitar can be more than just acquiring a skill; it can blossom into a lifelong passion, a source of continuous joy and self-expression. As you progress, the guitar becomes an intimate companion, a canvas for your musical ideas, and a gateway to a world of creativity and fulfillment.
The Benefits of Continuous Learning
The beauty of guitar learning lies in its constant evolution. It’s a journey that never truly ends, offering endless opportunities for growth and exploration. Continuous learning keeps your mind sharp, your fingers agile, and your musical vocabulary expanding. It allows you to delve deeper into different genres, styles, and techniques, constantly challenging yourself to reach new heights.
The Guitar Community
The guitar community is a vibrant and welcoming space where individuals from all walks of life come together to share their passion for music. It’s a place where beginners can find encouragement, seasoned players can connect with like-minded individuals, and everyone can learn and grow together.
Inclusivity and Camaraderie
The guitar community embraces a spirit of inclusivity, welcoming players of all skill levels, musical styles, and backgrounds. Whether you’re a seasoned shredder or just starting to learn the basics, you’ll find a welcoming environment where everyone is encouraged to share their love for the instrument.
This sense of camaraderie is fostered through shared experiences, mutual support, and a common love for music.
Collaboration, Mentorship, and Shared Experiences
The guitar community offers numerous opportunities for collaboration, mentorship, and shared experiences.
- Online platforms like YouTube and social media have revolutionized the way guitarists connect and learn from each other. These platforms provide a space for sharing tutorials, performances, and creative projects, fostering a sense of community and collaboration.
- Guitar teachers, workshops, and jam sessions play a vital role in providing mentorship and fostering a sense of shared experience. These gatherings allow guitarists to learn from experienced players, develop their skills, and connect with others who share their passion.
Online Forums, Social Media Groups, and Live Performances
Online forums and social media groups serve as platforms for sharing knowledge, advice, and encouragement. They provide a space for guitarists to ask questions, share their progress, and connect with others who are on a similar journey.
- Attending live performances, festivals, and concerts creates a shared sense of community and inspires guitarists. These events offer a chance to witness the talent and passion of fellow guitarists, fostering a sense of belonging and motivating individuals to continue their own musical pursuits.
The Journey of Guitar Mastery
The path to guitar mastery is a captivating adventure, filled with both exhilarating triumphs and humbling challenges. It’s a journey that demands unwavering dedication, a relentless pursuit of improvement, and a deep-seated love for the instrument. While the allure of effortlessly playing intricate melodies and solos is enticing, the reality is that guitar mastery is a lifelong pursuit, requiring consistent effort and a willingness to embrace the process of continuous growth.
The Importance of Consistent Practice
Consistent practice is the cornerstone of guitar mastery. It’s not about spending hours on end mindlessly strumming; it’s about focused, deliberate practice that targets specific areas for improvement. Here’s a breakdown of different practice techniques and their benefits:
| Practice Technique | Benefits | Recommended Time Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Slow and Accurate Practice | Develops precision, improves technique, and strengthens muscle memory. | 20-30 minutes per day |
| Repetition and Memorization | Builds muscle memory, enhances speed and fluency, and improves accuracy. | 15-20 minutes per day |
| Scales and Exercises | Improves finger dexterity, expands technical abilities, and strengthens musical foundations. | 10-15 minutes per day |
| Improvisation and Creativity | Encourages exploration, fosters musical expression, and develops musical intuition. | 15-20 minutes per day |
| Song Learning | Expands musical knowledge, improves rhythm and timing, and builds repertoire. | 30-45 minutes per day |
A perfect example of the power of consistent practice is the legendary guitarist, Eric Clapton. He started playing guitar at a young age and dedicated himself to practicing for hours every day. This unwavering commitment to his craft allowed him to develop his signature blues style, refine his technique, and ultimately achieve legendary status.
Exploration and Experimentation
“The more you explore, the more you discover. Don’t be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and try new things.”
Steve Vai
Exploring different genres, techniques, and musical styles is crucial for expanding your musical horizons and becoming a well-rounded guitarist. For instance, renowned guitarist, Carlos Santana, initially gained fame for his fiery Latin-infused rock music. However, he later ventured into jazz, blues, and world music, demonstrating his versatility and expanding his musical palette.
This exploration allowed him to discover new sounds, refine his technique, and ultimately become one of the most influential guitarists of all time.
The Love for the Instrument
The journey to guitar mastery is not merely about technical proficiency; it’s about developing a deep and profound connection with the instrument. Passion and dedication are essential ingredients in this process. The guitar becomes an extension of oneself, a conduit for emotions, and a source of inspiration.Many guitarists find solace, joy, and fulfillment in playing their instruments.
They pour their heart and soul into their music, expressing themselves through the strings and creating something truly unique. This love for the instrument fuels their motivation, drives their practice, and ultimately shapes their musical journey.
Renowned Guitarists as Inspiration
The world of music is filled with inspiring guitarists who have dedicated their lives to honing their craft and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible on the instrument. Their journeys serve as a testament to the power of passion, dedication, and continuous growth.
Here are a few notable examples:
- Jimi Hendrix: Known for his innovative use of effects, psychedelic soundscapes, and electrifying performances, Hendrix revolutionized rock guitar playing. He pushed the limits of the instrument and inspired countless musicians with his virtuosity and musical vision.
- B.B. King: The “King of the Blues,” B.B. King, was renowned for his soulful vocals, masterful guitar technique, and captivating stage presence. His influence on blues guitar is immeasurable, and his music continues to inspire generations of musicians.
- Eddie Van Halen: A pioneer of rock guitar, Eddie Van Halen revolutionized the instrument with his innovative techniques, including two-handed tapping and harmonic tapping. His virtuosity and musical creativity made him a legendary figure in the world of rock.
- Stevie Ray Vaughan: A master of blues guitar, Stevie Ray Vaughan possessed a fiery intensity and raw emotion that captivated audiences worldwide. His signature tone, lightning-fast solos, and blues-infused rock made him one of the most influential blues guitarists of his generation.
These guitarists, along with countless others, serve as inspiration to aspiring musicians. Their dedication, talent, and relentless pursuit of excellence demonstrate that guitar mastery is not an end goal, but rather a continuous journey of growth, exploration, and artistic expression.
Question Bank
How long does it take to learn guitar?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on your natural aptitude, practice habits, and goals. Some people see progress quickly, while others take more time. The key is to be patient, consistent, and enjoy the process.
Do I need to be musically talented to learn guitar?
Absolutely not! Musical talent is helpful, but it’s not a requirement. Anyone can learn guitar with dedication and practice. Focus on enjoying the journey, and you’ll be surprised at how far you can go.
What’s the best way to practice guitar?
Short, focused practice sessions are more effective than long, unproductive ones. Aim for 15-30 minutes daily, focusing on technique and accuracy. Break down complex skills into smaller steps, and celebrate your progress along the way.
What if I get frustrated?
Frustration is a natural part of the learning process. Take breaks when needed, focus on small victories, and remember that every mistake is an opportunity to learn. Don’t give up!