Is Hindi hard to learn for English speakers? This question often pops up for those curious about diving into the world of India’s official language. While Hindi might seem daunting at first, it’s not as impenetrable as some might think.
The key lies in understanding its unique linguistic structure and embracing the cultural context that shapes its use.
Hindi, with its roots in the Indo-Aryan language family, boasts a rich history and a vast number of speakers, making it a valuable asset for anyone interested in exploring India’s vibrant culture and growing economy. But how challenging is it for English speakers to master this language?
Let’s delve into the complexities and explore the paths to fluency.
Hindi Language Analysis: A Challenge for English Speakers

Hindi, an Indo-Aryan language spoken by over 600 million people globally, is the official language of India and a prominent language in several other countries. Its significance for English speakers extends beyond its sheer number of speakers, as it offers a gateway to understanding a rich cultural heritage and a burgeoning economy.
However, the question of Hindi’s difficulty for English speakers remains a topic of debate.
Linguistic Comparisons
This section explores the key differences and similarities between Hindi and English grammar and phonology, providing a foundation for understanding the challenges and opportunities for English speakers learning Hindi.
Grammar
The following table highlights some key differences in grammar between Hindi and English:
| Feature | Hindi | English |
|---|---|---|
| Verb Conjugation | Highly complex, with different forms based on tense, person, and number. | Relatively simpler, with fewer forms and a more consistent system. |
| Noun Declension | Nouns change form based on case and number. | Nouns generally remain unchanged, with exceptions for plurals and possessives. |
| Word Order | Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) in most cases. | Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) |
| Articles | Does not use definite or indefinite articles like “the” or “a”. | Uses articles extensively to specify definiteness or indefiniteness. |
Phonology
Hindi and English have distinct phonological systems, with differences in vowel and consonant sounds and intonation patterns. * Vowels:Hindi has a wider range of vowel sounds than English, including retroflex vowels that do not exist in English.
Consonants
Hindi has a larger inventory of consonants, including retroflex consonants and aspirated consonants.
Intonation
Hindi intonation patterns differ significantly from English, with a more melodic and rising-falling intonation.
Vocabulary Acquisition
This section explores the extent to which English vocabulary can aid in learning Hindi, considering cognates, borrowed words, and the presence of common roots.
Learning Hindi can be a challenge for English speakers, especially with the Devanagari script and unfamiliar sounds. It’s a bit like figuring out how hard is to learn Java, how hard is to learn java , where you need to grasp the syntax and logic.
But with dedication and practice, both languages can be mastered, opening up new worlds of communication and opportunity.
Cognates
Cognates are words that share a common origin and often have similar meanings. English speakers can leverage cognates to accelerate their Hindi vocabulary acquisition. * Examples:“Doctor” (English) and “Daktar” (Hindi), “Telephone” (English) and “Telefon” (Hindi).
Challenges
Some cognates have different meanings or are used in different contexts in Hindi, requiring careful attention to their specific usage.
Cultural Context
Cultural context and social norms in India can significantly influence the learning and use of Hindi for English speakers. * Example:In Hindi, it is customary to use honorifics when addressing elders or people in positions of authority.
Learning Resources, Is hindi hard to learn for english speakers
This section evaluates the availability and effectiveness of online and offline resources for learning Hindi, including language learning apps, textbooks, and immersion programs.* Online Resources:There are numerous online resources available for learning Hindi, including language learning apps like Duolingo and Babbel, online courses, and websites with interactive exercises and vocabulary lists.
Offline Resources
Textbooks, dictionaries, and language exchange programs offer valuable offline resources for learning Hindi.
Immersion Programs
Immersion programs provide a more intensive and comprehensive learning experience, allowing students to practice Hindi in real-life situations.
Linguistic Similarities and Differences
While Hindi and English might seem worlds apart at first glance, they share some interesting similarities in their grammar structures, which can be both helpful and challenging for English speakers learning Hindi. Understanding these similarities and differences is crucial for navigating the intricacies of Hindi grammar.
Word Order and Sentence Structure
The basic word order in both Hindi and English is Subject-Verb-Object (SVO). This similarity can be a comforting starting point for English speakers, making it easier to grasp the fundamental sentence structure. For example, “The boy eats the apple” in English translates to “लड़का सेब खाता है” (ladka seb khāta hai) in Hindi.
However, Hindi also allows for variations in word order for emphasis or stylistic purposes, which can add complexity.
Verb Conjugation
One of the key differences lies in verb conjugation. English verbs change relatively little, mainly with tense and number. Hindi verbs, however, undergo significant conjugation based on tense, person, gender, and number. This adds a layer of complexity, requiring learners to master a wider range of verb forms.
For instance, the verb “to eat” (khānā) in Hindi can have numerous forms depending on the context:
- Present tense: “I eat” – मैं खाता हूँ (main khāta hūn), “He eats” – वह खाता है (vah khāta hai)
- Past tense: “I ate” – मैंने खाया (maine khāyā), “She ate” – उसने खाया (usne khāyā)
Gender and Number Agreement
Hindi employs grammatical gender for nouns, adjectives, and pronouns, which is absent in English. This means that every noun is classified as masculine, feminine, or neuter, and the adjectives and pronouns modifying it must agree in gender. This can be challenging for English speakers, who are accustomed to gender-neutral language.
For example, “the book” (kitab) is feminine in Hindi, so the adjective describing it must also be feminine: “the red book” (laal kitab).
Case System
Hindi utilizes a case system, which indicates the grammatical function of a noun or pronoun within a sentence. English, on the other hand, relies on prepositions and word order to convey these functions. Hindi has six cases: nominative, accusative, instrumental, dative, ablative, and vocative.
This system can be initially confusing for English speakers, but understanding the nuances of case helps to build a deeper understanding of Hindi grammar.
Article System
English employs definite and indefinite articles (“the” and “a/an”), while Hindi does not. This absence of articles can be confusing for English speakers, who may feel the need to insert them in Hindi sentences. However, the context and word order in Hindi usually make the meaning clear without the need for articles.
Prepositions
Prepositions in Hindi can be tricky for English speakers as they often differ in meaning and usage. For example, the English preposition “on” can be translated into several different prepositions in Hindi, depending on the context. Mastering the use of prepositions requires careful observation and practice.
Conclusion
While Hindi and English share some similarities in sentence structure, the differences in verb conjugation, gender agreement, case system, and articles present challenges for English speakers. However, with dedicated effort and a structured approach, learning Hindi can be an enriching experience, opening doors to a vibrant culture and language.
Pronunciation and Phonetics
Hindi pronunciation presents both challenges and opportunities for English speakers. While some sounds are similar to English, others are quite different, requiring specific attention and practice. Understanding the nuances of Hindi phonetics is crucial for achieving clear and accurate pronunciation.
Key Sounds and Pronunciation Rules
Hindi has a rich phonetic system with sounds that do not exist in English. These differences can lead to difficulties for English speakers, but they also offer opportunities to expand their phonetic repertoire.
- Vowel Sounds:Hindi has a wider range of vowel sounds than English. For instance, the short “i” sound in Hindi, as in “kitāb” (book), is different from the short “i” sound in English “kit”. Similarly, the long “i” sound in Hindi, as in “nīla” (blue), is distinct from the long “i” sound in English “feel”.
- Consonant Sounds:Hindi has several consonant sounds that are not found in English, such as the retroflex consonants, which are pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth. Examples include “ṭ” (as in “ṭāṅg” – leg) and “ḍ” (as in “ḍāktar” – doctor).
Another challenge is the aspirated consonants, which are pronounced with a puff of air. Examples include “kh” (as in “khaana” – food) and “gh” (as in “ghara” – house).
- Tonal Variations:While Hindi is not a tonal language like Mandarin, there are subtle tonal variations that can affect meaning. These variations are often subtle and may not be immediately apparent to English speakers. For instance, the word “kāl” can mean “time” or “black” depending on the tone used.
Common Hindi Sounds and English Equivalents
The following table highlights common Hindi sounds and their English equivalents, emphasizing areas where English speakers might find difficulty.
| Hindi Sound | English Equivalent | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| अ (a) | “a” in “father” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| इ (i) | “i” in “kit” | Shorter than the English “i” sound |
| ई (ī) | “ee” in “see” | Longer than the English “ee” sound |
| उ (u) | “oo” in “book” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| ऊ (ū) | “oo” in “moon” | Longer than the English “oo” sound |
| ऋ (ṛ) | No direct equivalent | Pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth, similar to the sound in “bird” |
| ए (e) | “a” in “say” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| ऐ (ai) | “ai” in “say” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| ओ (o) | “o” in “go” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| औ (au) | “ow” in “cow” | Similar to the English sound, but slightly shorter |
| क (k) | “k” in “kit” | Similar to the English sound |
| ख (kh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “k” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| ग (g) | “g” in “go” | Similar to the English sound |
| घ (gh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “g” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| ङ (ṅ) | No direct equivalent | Pronounced with the back of the tongue against the soft palate, similar to the “ng” sound in “sing” |
| च (c) | “ch” in “chair” | Similar to the English sound |
| छ (chh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “ch” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| ज (j) | “j” in “jump” | Similar to the English sound |
| झ (jh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “j” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| ञ (ñ) | No direct equivalent | Pronounced with the tongue tip against the alveolar ridge, similar to the “ny” sound in “canyon” |
| ट (ṭ) | No direct equivalent | Retroflex “t” sound, pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth |
| ठ (ṭh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated retroflex “t” sound, pronounced with a puff of air and the tongue curled back |
| ड (ḍ) | No direct equivalent | Retroflex “d” sound, pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth |
| ढ (ḍh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated retroflex “d” sound, pronounced with a puff of air and the tongue curled back |
| ण (ṇ) | No direct equivalent | Pronounced with the tongue tip against the alveolar ridge, similar to the “n” sound in “sun” but with the tongue curled back |
| त (t) | “t” in “tea” | Similar to the English sound |
| थ (th) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “t” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| द (d) | “d” in “day” | Similar to the English sound |
| ध (dh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “d” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| न (n) | “n” in “no” | Similar to the English sound |
| प (p) | “p” in “pen” | Similar to the English sound |
| फ (ph) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “p” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| ब (b) | “b” in “bat” | Similar to the English sound |
| भ (bh) | No direct equivalent | Aspirated “b” sound, pronounced with a puff of air |
| म (m) | “m” in “man” | Similar to the English sound |
| य (y) | “y” in “yes” | Similar to the English sound |
| र (r) | “r” in “run” | Similar to the English sound, but often pronounced with the tongue tip touching the alveolar ridge |
| ल (l) | “l” in “love” | Similar to the English sound |
| व (v) | “w” in “water” | Similar to the English sound |
| श (ś) | “sh” in “ship” | Similar to the English sound |
| ष (ṣ) | No direct equivalent | Retroflex “sh” sound, pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth |
| स (s) | “s” in “sun” | Similar to the English sound |
| ह (h) | “h” in “hat” | Similar to the English sound |
Vocabulary Acquisition

Learning Hindi vocabulary can be both challenging and rewarding for English speakers. While there are some similarities between the two languages, there are also significant differences that can make vocabulary acquisition a bit tricky. Understanding the extent to which English vocabulary can be leveraged in learning Hindi, along with effective strategies for acquiring Hindi vocabulary, will help you navigate this process successfully.
English Vocabulary and its Leverage in Learning Hindi
English speakers can leverage their existing vocabulary to some extent when learning Hindi. Both languages share a significant number of cognates, words that have a common origin and share similar meanings. These cognates often have similar spellings and pronunciations, making them relatively easy to learn.
For example, the Hindi word “kitab” (book) is a cognate of the English word “kitab” (book). However, it is important to note that not all cognates are directly equivalent. Some cognates may have slightly different meanings or nuances in Hindi.
For instance, the Hindi word “kala” (black) is a cognate of the English word “color” but has a more specific meaning in Hindi. Furthermore, English speakers should be aware that many Hindi words have no direct equivalents in English.
These words often reflect unique cultural contexts or concepts that are not readily translated. In such cases, it is essential to learn the Hindi word and its associated meaning independently.
Strategies for Acquiring Hindi Vocabulary
Several strategies can help English speakers acquire Hindi vocabulary effectively.
- Focus on High-Frequency Words:Start by learning the most frequently used Hindi words. These words will form the foundation of your vocabulary and allow you to communicate effectively in a variety of situations. Many resources are available to help you identify and learn high-frequency words.
- Utilize Contextual Learning:Learning words in context is a highly effective strategy. This involves encountering words in natural settings, such as reading Hindi books, watching Hindi movies, or listening to Hindi music. By observing how words are used in different contexts, you can gain a deeper understanding of their meaning and usage.
- Employ Flashcards:Flashcards are a traditional but effective tool for vocabulary acquisition. Write the Hindi word on one side of the card and its English translation on the other. Regularly reviewing these flashcards will help you memorize new words and reinforce your learning.
- Use Vocabulary Lists and Apps:Many online resources and mobile apps offer pre-made vocabulary lists and quizzes. These resources can help you focus on specific themes or topics, such as daily life, travel, or business. They can also provide interactive exercises and games to make learning more engaging.
- Practice Active Recall:Instead of simply reading or memorizing words, actively recall them. Try to define the word without looking at the answer. This technique forces your brain to work harder and improves retention.
- Record and Review:Record yourself speaking Hindi and listen back to your recordings. Pay attention to your pronunciation and vocabulary usage. This can help you identify areas where you need to improve.
- Immerse Yourself in Hindi Culture:Immerse yourself in Hindi culture by attending cultural events, interacting with native Hindi speakers, and exploring Hindi literature and art. This exposure will help you develop a deeper understanding of the language and its nuances.
Writing System and Script
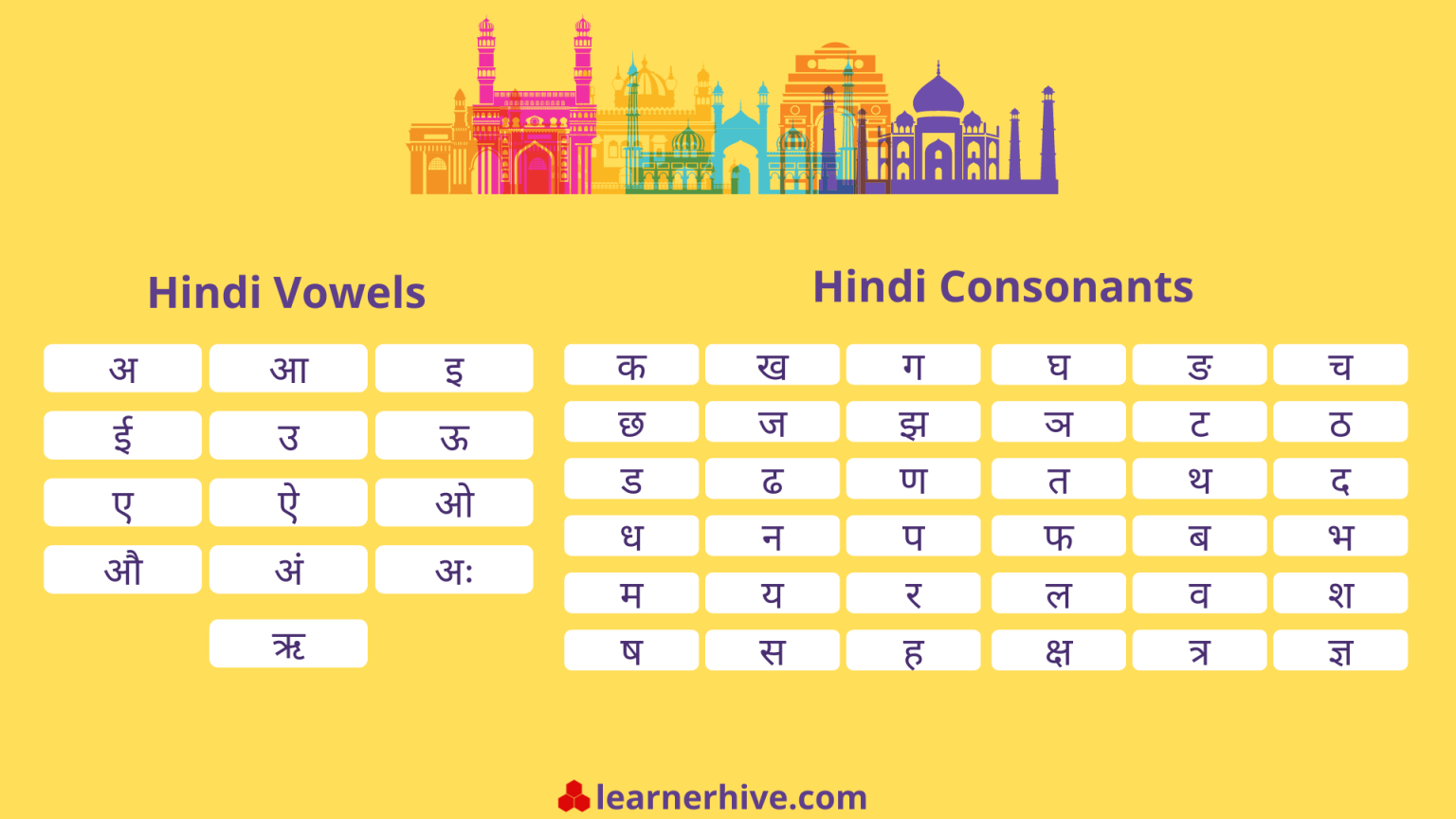
The Devanagari script is the primary writing system for Hindi and other Indian languages. It is a complex script with a rich history, originating from ancient Indian scripts. This section will delve into the structure and key features of Devanagari, comparing it to the Roman alphabet and exploring the challenges and strategies for learning it.
Devanagari Script: Structure and Key Features
Devanagari is a syllabic script, meaning that each character represents a syllable, typically consisting of a consonant and a vowel. The basic structure of the script is composed of consonant forms, which are written as base characters, and vowel forms, which are either added as diacritics (marks) to the consonant or written as independent characters.
- Consonants:Devanagari has 33 consonant characters, each representing a distinct sound. These consonants are written as base characters, with the majority having a vertical stroke on the right side.
- Vowels:Devanagari has 11 vowel characters, representing the different vowel sounds in the language. Some vowels are written as diacritics, called “matras,” attached to the consonant base. Others are written as independent characters.
- Diacritics and Matras:Diacritics, or matras, are small marks added to the consonant base to indicate the vowel sound. For example, the matra for “a” is a small horizontal line placed above the consonant.
- Conjunct Consonants:Devanagari uses a system of conjunct consonants, where two or more consonants are combined into a single character. This is achieved by writing the second consonant as a diacritic attached to the first consonant.
Similarities and Differences with the Roman Alphabet
Devanagari and the Roman alphabet share some similarities, but they also have significant differences. Both are alphabetical scripts, meaning they use a set of characters to represent sounds. However, the directionality of the two scripts is different. Devanagari is written from left to right, while the Roman alphabet is written from left to right.
- Directionality:Devanagari is written from left to right, similar to the Roman alphabet.
- Structure:Devanagari is a syllabic script, while the Roman alphabet is primarily an alphabetic script, with each letter representing a single sound.
- Sound Representation:Devanagari uses a system of diacritics and matras to represent vowel sounds, while the Roman alphabet uses separate letters for vowels.
- Correspondences:While there are no direct one-to-one correspondences between Devanagari and Roman letters, some similarities exist. For example, the Devanagari character for “k” is similar in shape to the Roman letter “k.”
Challenges and Strategies for Learning Devanagari
Learning Devanagari can be challenging for English speakers due to the unfamiliar script and the presence of diacritics and matras. However, with practice and the right strategies, it is achievable.
- Challenges:
- Unfamiliar script: The Devanagari script is significantly different from the Roman alphabet, requiring learners to memorize new characters and their corresponding sounds.
- Diacritics and matras: The use of diacritics and matras to represent vowel sounds can be confusing, as they are not present in the Roman alphabet.
- Conjunct consonants: Learning to recognize and write conjunct consonants can be challenging, as they involve combining multiple consonants into a single character.
- Strategies:
- Focus on specific sounds:Break down the Devanagari characters into their individual sounds and practice pronouncing them.
- Practice letter recognition:Use flashcards or other visual aids to practice recognizing the Devanagari characters.
- Use mnemonics:Create mnemonics or associations to help remember the characters and their corresponding sounds.
- Immerse yourself in the language:Surround yourself with Hindi language materials, such as books, movies, and music, to expose yourself to the script and sounds.
Table of Devanagari-Roman Equivalents
| Devanagari | Roman | English |
|---|---|---|
| अ | a | a |
| आ | ā | a (long) |
| इ | i | i |
| ई | ī | i (long) |
| उ | u | u |
| ऊ | ū | u (long) |
| ऋ | ṛ | r (short) |
| ऌ | ṝ | r (long) |
| ॡ | ḷ | l (short) |
| ॡ | ḹ | l (long) |
| ए | e | e |
| ऐ | ai | ai |
| ओ | o | o |
| औ | au | au |
| क | k | k |
| ख | kh | kh |
| ग | g | g |
| घ | gh | gh |
| ङ | ṅ | ng |
| च | c | ch |
| छ | chh | chh |
| ज | j | j |
| झ | jh | jh |
| ञ | ñ | ny |
| ट | ṭ | t (retroflex) |
| ठ | ṭh | th (retroflex) |
| ड | ḍ | d (retroflex) |
| ढ | ḍh | dh (retroflex) |
| ण | ṇ | n (retroflex) |
| त | t | t |
| थ | th | th |
| द | d | d |
| ध | dh | dh |
| न | n | n |
| प | p | p |
| फ | ph | ph |
| ब | b | b |
| भ | bh | bh |
| म | m | m |
| य | y | y |
| र | r | r |
| ल | l | l |
| व | v | v |
| श | ś | sh |
| ष | ṣ | s (retroflex) |
| स | s | s |
| ह | h | h |
Cultural Context and Communication: Is Hindi Hard To Learn For English Speakers
Beyond the linguistic intricacies, understanding Indian culture is crucial for effective communication in Hindi. Cultural nuances and social norms significantly influence language use and etiquette, shaping how people interact and interpret messages. This understanding is particularly important for English speakers who might otherwise miss subtle cues and social implications.
Cultural Factors Influencing Hindi Communication
Understanding the cultural context surrounding Hindi is essential for navigating social interactions effectively. Here are key cultural factors that influence language use and etiquette in Hindi, and their relevance for English speakers:
- Respect and Hierarchy:Indian culture emphasizes respect for elders and authority figures. This is reflected in Hindi through the use of honorifics, which are specific terms of address used to show deference. For example, using “aap” instead of “tum” when addressing someone older or of higher status is crucial.
English speakers need to be mindful of these distinctions to avoid disrespecting others.
- Non-Verbal Communication:Non-verbal cues play a significant role in Hindi communication. Body language, gestures, and facial expressions can convey emotions and intentions that may not be explicitly stated. For instance, a slight nod of the head might indicate agreement, while a raised eyebrow could signal disapproval.
English speakers need to be aware of these nuances to avoid misinterpretations.
- Social Context:The social context of a conversation influences the language used in Hindi. For example, the language used in a formal setting, such as a business meeting, will differ from that used in a casual setting, such as a conversation with friends.
English speakers need to adjust their language accordingly to avoid sounding inappropriate.
- Politeness and Indirectness:Hindi communication often emphasizes politeness and indirectness. Instead of directly stating their opinions or requests, people may use subtle hints or euphemisms. For example, instead of saying “no,” someone might say “maybe later” or “I’ll try.” English speakers need to be sensitive to these indirect communication styles to avoid misunderstandings.
Learning Resources and Strategies
Embarking on your Hindi learning journey requires access to reliable resources and the implementation of effective learning strategies. This section explores various tools and techniques to help you navigate the path to Hindi fluency.
Textbooks
Textbooks provide a structured foundation for learning Hindi, offering comprehensive grammar explanations, vocabulary lists, and practice exercises.
- Hindi Made Easy: A Complete Course for Beginnersby Rupert Snell: This textbook is ideal for beginners, covering the basics of Hindi grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary. It employs a conversational approach and includes audio recordings for pronunciation practice. It is widely available online and in bookstores.
- Teach Yourself Complete Hindiby Anna Suvorova: This comprehensive textbook caters to both beginners and intermediate learners. It features clear explanations of grammar, extensive vocabulary lists, and practical exercises. The book also includes audio recordings and a glossary of key terms. It is available online and in bookstores.
- A Comprehensive Grammar of the Hindi Languageby John R. Platt: This advanced textbook delves into the intricacies of Hindi grammar, providing a detailed analysis of its structure and nuances. It is suitable for learners with a strong foundation in Hindi and aims to enhance their understanding of the language’s complexities.
It is available online and in academic bookstores.
- Hindi for Everyone: A Practical Guide to Speaking and Understanding Hindiby David Harper: This textbook emphasizes practical application, focusing on conversational Hindi. It covers essential grammar, vocabulary, and cultural insights. It is available online and in bookstores.
- Modern Hindi Grammarby M.S. Bhatia: This textbook offers a comprehensive and up-to-date guide to Hindi grammar. It is suitable for advanced learners and researchers. It is available online and in academic bookstores.
Online Platforms
Online platforms offer interactive and engaging learning experiences, providing flexibility and accessibility.
- Duolingo:This popular language learning app offers a gamified approach to learning Hindi. It features interactive lessons, quizzes, and progress tracking. Duolingo is free to use, with optional premium features for additional content and features. It is suitable for beginners and intermediate learners.
- Memrise:This app utilizes spaced repetition techniques to enhance vocabulary acquisition. It offers a wide range of courses, including Hindi. Memrise is free to use, with optional premium features for additional courses and features. It is suitable for all levels.
- Babbel:This platform offers structured courses with a focus on conversational Hindi. It features interactive lessons, audio recordings, and progress tracking. Babbel offers a free trial and subscription plans for continued access. It is suitable for beginners and intermediate learners.
Language Exchange Programs
Language exchange programs connect language learners with native speakers for mutual practice and cultural exchange.
- HelloTalk:This app connects language learners with native speakers worldwide for text and voice chat, audio and video calls, and translation assistance. It is free to use, with optional premium features for additional features. It is suitable for all levels.
- Tandem:This app pairs language learners based on their interests and language goals. It offers text and voice chat, audio and video calls, and language exchange activities. It is free to use, with optional premium features for additional features. It is suitable for all levels.
Cultural Immersion Experiences
Cultural immersion experiences provide firsthand exposure to Hindi culture, enhancing language learning and cultural understanding.
- Volunteer Programs in India:Volunteer programs offer opportunities to immerse oneself in Indian culture, interact with local communities, and learn Hindi through real-life experiences. Programs vary in duration and focus, offering opportunities in education, healthcare, and community development. They are available through organizations like GoAbroad and Volunteer World.
- Hindi Language Courses in India:Intensive Hindi language courses in India provide immersive learning experiences. These courses combine classroom instruction with cultural activities, excursions, and opportunities to interact with local communities. They are offered by universities and language schools across India.
Learning Strategies
Developing a personalized learning plan is crucial for effective Hindi acquisition.
- Vocabulary Acquisition:
- Create flashcards for new vocabulary words, including their Hindi pronunciation, English translation, and example sentences.
- Use vocabulary lists from textbooks or online resources.
- Engage in active recall by testing yourself regularly on learned vocabulary.
- Immerse yourself in Hindi media, such as movies, TV shows, and music, to encounter new vocabulary in context.
- Grammar Mastery:
- Study Hindi grammar rules systematically, focusing on verb conjugations, noun declensions, and sentence structure.
- Practice grammar exercises in textbooks or online platforms.
- Identify common grammar patterns and apply them in your own writing and speaking.
- Seek clarification from language tutors or online resources when encountering difficulties.
- Pronunciation Practice:
- Listen to audio recordings of native Hindi speakers, paying attention to pronunciation and intonation.
- Use pronunciation guides to learn the correct pronunciation of Hindi sounds.
- Practice pronunciation with a language exchange partner or tutor.
- Record yourself speaking Hindi and listen back to identify areas for improvement.
- Cultural Understanding:
- Learn about Indian culture, customs, and traditions.
- Engage in conversations with native Hindi speakers to gain insights into cultural nuances.
- Watch Hindi movies and TV shows to experience cultural perspectives.
- Read books and articles about Indian history and society.
Consistent Practice, Immersion, and Personalized Learning
Consistent practice, immersion, and personalized learning are key to achieving fluency in Hindi.
- Consistent Practice:
- Dedicate a specific time each day for Hindi study, even if it’s just for 30 minutes.
- Set realistic goals and track your progress to stay motivated.
- Use a variety of learning materials and activities to keep your learning engaging.
- Review previously learned material regularly to reinforce your knowledge.
- Immersion:
- Surround yourself with Hindi language and culture. Listen to Hindi music, watch Hindi movies, and read Hindi books and articles.
- Find a Hindi-speaking community online or in your local area.
- Create a Hindi-speaking environment at home by labeling objects, using Hindi flashcards, and speaking Hindi whenever possible.
- Immerse yourself in Hindi media, such as movies, TV shows, and music, to experience the language in a natural context.
- Personalized Learning:
- Identify your individual strengths and weaknesses in Hindi.
- Set realistic goals based on your learning style and available time.
- Adapt your learning methods to suit your needs and preferences.
- Seek feedback from language tutors or language exchange partners to identify areas for improvement.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges

Learning any new language comes with its own set of challenges, and Hindi is no exception. While it’s true that Hindi shares some similarities with English, it also presents unique hurdles for English speakers. Understanding these challenges and debunking common misconceptions can help you approach Hindi learning with a more realistic and effective mindset.
Debunking Misconceptions
Many people believe that learning Hindi is incredibly difficult, but this is often based on misconceptions rather than actual experience. Here are three common misconceptions and their debunking statements:
- Misconception:Hindi is too difficult for English speakers because it uses a completely different writing system.
- Debunking:While the Devanagari script used for Hindi might look unfamiliar, it’s actually quite logical and phonetic. The script’s structure makes it relatively easy to learn pronunciation and connect letters to sounds. Many English speakers find the Devanagari script easier to learn than the Roman alphabet because it’s designed for consistent pronunciation.
The script also has a clear one-to-one correspondence between letters and sounds, unlike English, where the same letter can have multiple pronunciations.
- Misconception:Hindi grammar is overly complex and confusing for English speakers.
- Debunking:While Hindi grammar has its own rules, it’s not inherently more complex than English grammar. English has its own set of intricate grammatical structures, including irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. Hindi grammar is actually more consistent in some aspects, like verb conjugation, making it easier to grasp once you understand the basic principles.
- Misconception:Hindi is only spoken in India, so it’s not a useful language to learn.
- Debunking:Hindi is spoken by millions of people worldwide, not just in India. It’s the official language of India and is also widely spoken in other countries like Nepal, Fiji, and Mauritius. Learning Hindi can open doors to a wider range of cultural experiences and professional opportunities.
Addressing Specific Challenges
Here are the top three challenges that English speakers typically face when learning Hindi:
| Challenge | Difficulties | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation and Phonetics | Hindi has a wider range of sounds than English, including retroflex consonants (sounds made with the tongue curled back) and aspirated consonants (sounds with a puff of air). |
|
| Vocabulary Acquisition | Hindi vocabulary is vast and often lacks direct translations for many English words. Many words are derived from Sanskrit, which can make them unfamiliar to English speakers. |
|
| Grammar and Sentence Structure | Hindi sentence structure differs from English. Word order, verb conjugation, and the use of grammatical particles can be challenging for English speakers. |
|
English speakers learning Hindi often struggle with the complexities of pronunciation, vocabulary acquisition, and grammar. For example, the retroflex consonants like “ṭ” and “ḍ” are difficult to pronounce for English speakers because they don’t exist in the English language.
Additionally, Hindi has a wide range of verb conjugations that depend on factors like tense, mood, and gender, which can be challenging to master. Vocabulary acquisition can also be a hurdle, as many Hindi words have no direct English equivalents.
Learning how to express concepts like “respect” or “gratitude” in Hindi requires understanding cultural nuances and finding the appropriate vocabulary.
Cultural Understanding
Cultural understanding plays a crucial role in overcoming language learning challenges. Hindi is not just a language; it’s deeply intertwined with Indian culture. Learning Hindi involves understanding the social norms, customs, and values that shape communication. For example, the use of honorifics in Hindi is essential for showing respect to elders and authority figures.
Learning these cultural nuances can help you navigate conversations more effectively and build stronger relationships with Hindi speakers.
Resources and Tools
Several resources and tools can help English speakers overcome specific challenges they might face while learning Hindi. Here are a few examples:
- Duolingo:This popular language learning app offers a gamified approach to learning Hindi, focusing on vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation.
- Memrise:Memrise uses flashcards and spaced repetition techniques to help you memorize new vocabulary effectively.
- HindiPod101:This website and app provide a wide range of Hindi learning resources, including audio lessons, video tutorials, and cultural insights.
- Forvo:This website allows you to listen to native speakers pronounce Hindi words and phrases, which can help you improve your pronunciation.
Motivation and Perseverance: Mastering Hindi
Learning any new language, especially one as different from English as Hindi, can be challenging. But with the right motivation and a persistent attitude, achieving fluency is within reach.
Understanding the Challenges
Hindi presents a unique set of challenges for English speakers. The pronunciation system is different, with sounds not found in English, like the retroflex consonants. The grammar, with its focus on verb conjugations and case endings, can be complex.
And understanding the cultural nuances embedded in the language takes time and immersion.
The Power of Motivation
Motivation is the fuel that drives you through these challenges. It’s the reason you pick up your Hindi textbook after a long day, the reason you watch Bollywood movies, and the reason you try to converse with native speakers, even if it’s just a few words at first.
- Personal Goals:Maybe you want to connect with your heritage, travel to India, or pursue a career in a Hindi-speaking environment. These personal goals provide a powerful reason to push through the difficulties.
- Cultural Immersion:Engaging with Hindi culture through music, literature, and art can spark a love for the language and make the learning process more enjoyable.
- Passion for the Language:Some people are simply drawn to the beauty and complexity of Hindi. The challenge of mastering such a rich and nuanced language can be intrinsically motivating.
The Importance of Perseverance
Learning Hindi, like any skill, requires consistent effort. There will be times when you hit plateaus, feel frustrated, or even want to give up. But it’s during these moments that perseverance is key.
- Setting Realistic Goals:Don’t try to learn everything at once. Break down your learning into manageable chunks and celebrate each small victory.
- Finding a Learning Partner:Learning with a friend or group can provide support, motivation, and a space for practicing your skills.
- Staying Engaged:Find ways to make your learning fun and engaging. Listen to Hindi music, read stories, or watch movies. The more you immerse yourself in the language, the easier it will be to stay motivated.
Inspirational Stories
Many English speakers have successfully learned Hindi. Their stories are inspiring examples of how motivation and perseverance can overcome any challenge.
- The Business Executive:John, a business executive, learned Hindi to expand his company’s operations into India. He found that immersing himself in the culture, through movies, music, and even cooking classes, made the learning process more enjoyable.
- The Student:Sarah, a college student, was inspired to learn Hindi after studying abroad in India. She found that connecting with local people through conversations, even if they were simple at first, helped her progress quickly.
A Personal Journey
As a recent learner of Hindi, I can relate to the challenges and the joys of this journey. My initial motivation stemmed from a fascination with Indian culture and a desire to understand the stories and songs I heard.
The pronunciation was initially daunting, but I found that breaking down sounds into smaller components and practicing regularly helped. Grammar was another hurdle, but I discovered that using flashcards and creating sentence structures in my head made it more accessible.
The most rewarding moments came when I could have simple conversations with Hindi speakers, even if they were just about the weather or my favorite food. These small victories fueled my motivation to keep learning.
Unlocking a World of Opportunities: The Benefits of Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi, the official language of India and one of the most spoken languages globally, offers a plethora of personal, professional, and cultural advantages. It’s a gateway to a rich and diverse culture, a valuable asset in the global job market, and a key to unlocking a world of new experiences and connections.
Personal Benefits
Learning Hindi can significantly enrich your life, opening doors to new experiences and perspectives. It allows you to connect with a vibrant culture, enhance your travel experiences, and even boost your cognitive abilities.
- Expand Your Cultural Horizons: India boasts a rich tapestry of history, literature, and traditions. Learning Hindi provides a deeper understanding of these aspects, allowing you to appreciate the nuances of Indian culture. You can delve into the works of renowned poets like Kabir and Rumi, explore the fascinating epics of the Mahabharata and Ramayana, and gain insights into the diverse religious and philosophical traditions of India.
- Enhance Travel Experiences: Knowing Hindi can transform your travel experiences in India. It allows you to communicate with locals, engage in meaningful conversations, and gain a more authentic understanding of the country. You can navigate markets, order food, and explore hidden gems with ease, making your journey more enjoyable and enriching.
- Boost Cognitive Abilities: Learning a new language, especially one as complex as Hindi, can have significant cognitive benefits. It improves memory, problem-solving skills, multitasking abilities, and even enhances creativity. Studies have shown that bilingual individuals have better cognitive flexibility and are better at adapting to new situations.
Professional Benefits
In today’s globalized world, learning Hindi can give you a significant edge in the job market. It opens doors to new career opportunities, makes you a more competitive candidate, and enhances your communication skills.
- Increase Career Opportunities: The demand for Hindi speakers is steadily growing across various fields, including business, tourism, technology, and education. With the increasing economic and cultural ties between India and the rest of the world, proficiency in Hindi is becoming a valuable asset.
- Gain a Competitive Edge: In a globalized job market, learning Hindi can set you apart from the competition. It demonstrates your commitment to cultural understanding, adaptability, and a willingness to learn new skills.
- Improve Communication Skills: Learning Hindi can improve your overall communication skills. It teaches you to think differently, express yourself more clearly, and understand diverse perspectives. This can make it easier to interact with people from various backgrounds and cultures, both personally and professionally.
Cultural Advantages
Learning Hindi connects you to a global community, fosters cultural exchange, and deepens your understanding of Indian culture. It allows you to appreciate the beauty of the language and its rich literary heritage.
- Connect with a Global Community: Hindi is spoken by over 600 million people worldwide, making it one of the most widely spoken languages globally. Learning Hindi opens doors to a vast network of people and cultures, allowing you to build relationships and foster cultural exchange.
- Develop a Deeper Understanding of Indian Culture: Learning Hindi provides insights into Indian values, customs, and social dynamics. It allows you to understand the nuances of Indian culture, appreciate its rich history, and connect with its people on a deeper level.
- Appreciate the Beauty of the Language: Hindi is a beautiful and expressive language with a rich literary heritage. Its poetry, music, and storytelling traditions are renowned for their elegance and depth. Learning Hindi allows you to explore this rich cultural heritage and appreciate the beauty of the language.
Conclusion
Learning Hindi as an English speaker presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. While the language may seem daunting at first, with dedication and the right approach, mastering Hindi can be an enriching and rewarding experience.
Key Findings and Takeaways
This analysis has highlighted several key aspects of Hindi language learning for English speakers.
- Linguistic Similarities and Differences:While Hindi and English share some common roots, their grammatical structures and vocabulary differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective learning.
- Pronunciation and Phonetics:The Hindi sound system poses a challenge for English speakers, particularly with unfamiliar vowels and consonants. Practice and exposure to native pronunciation are essential for achieving fluency.
- Vocabulary Acquisition:Building a strong vocabulary is essential for effective communication. Learning Hindi vocabulary requires a combination of memorization, context-based learning, and immersion in the language.
- Writing System and Script:The Devanagari script, used for writing Hindi, presents a unique challenge for English speakers accustomed to the Roman alphabet. Mastering the script requires dedicated practice and familiarity with its structure.
- Cultural Context and Communication:Hindi is deeply intertwined with Indian culture, and understanding cultural nuances is essential for effective communication. Immersing oneself in Indian culture can enhance language learning and understanding.
- Learning Resources and Strategies:Numerous resources are available to support Hindi language learning, including online courses, textbooks, language exchange programs, and immersion experiences. Choosing the right resources and strategies is crucial for individual learning success.
- Common Misconceptions and Challenges:Overcoming common misconceptions about Hindi, such as its perceived difficulty or the lack of learning resources, is essential for maintaining motivation and perseverance.
- Motivation and Perseverance:Learning Hindi requires sustained effort and motivation. Setting realistic goals, finding a learning community, and celebrating milestones can help maintain momentum and foster a positive learning experience.
- Unlocking a World of Opportunities:Learning Hindi offers numerous benefits, including enhanced cultural understanding, increased career opportunities, and access to a rich literary and artistic heritage. It opens doors to a world of possibilities and enriches one’s life in profound ways.
Common Queries
Is Hindi a tonal language?
No, Hindi is not a tonal language. While it has stress patterns, the meaning of a word doesn’t change based on the pitch of your voice.
How long does it take to learn Hindi?
The time it takes to learn Hindi varies greatly depending on your dedication, learning style, and exposure to the language. Some might achieve conversational fluency in a few months, while others may take longer. Consistent practice is key!
Is there a lot of slang in Hindi?
Yes, Hindi has a wide range of slang words and phrases, just like any language. Learning some common slang can make your interactions more natural and authentic.