Is Hindi difficult to learn sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Learning Hindi, the official language of India, can be an exciting journey, opening doors to a vibrant culture, rich history, and diverse population.
But many wonder, “Is Hindi difficult to learn?” The answer, like most things in life, is complex.
Hindi, a member of the Indo-Aryan language family, boasts a fascinating history and intricate grammar. While it shares some similarities with English, there are also unique aspects that may present challenges for learners. From mastering the Devanagari script to navigating the nuances of verb conjugation, the learning process can be both rewarding and demanding.
But with dedication and the right approach, mastering Hindi is within reach for anyone who is willing to put in the effort.
Hindi Language Basics
Hindi, a language spoken by millions worldwide, boasts a rich history and a fascinating evolution. Understanding its origins, development, and geographical spread sheds light on its cultural significance and linguistic intricacies.
Origins and History
Hindi, an Indo-Aryan language, traces its roots back to Sanskrit, the ancient language of India. Over centuries, Sanskrit evolved into various regional dialects, with Hindi emerging as a prominent descendant. Its development was influenced by numerous historical events and figures, shaping its standardization and official recognition.
- The influence of Persian and Arabic on Hindi vocabulary and grammar is evident. During the Mughal period, Persian became the language of administration, leaving a lasting impact on Hindi. Words like “dastoor” (custom), “zameen” (land), and “tareekh” (history) are borrowed from Persian.
Arabic also contributed to Hindi vocabulary, with words like “kitab” (book) and “ilm” (knowledge) becoming common.
Geographical Distribution
Hindi is primarily spoken in India, with its speakers concentrated in the northern and central regions. It is also spoken in other countries like Nepal, Mauritius, Fiji, and South Africa, due to historical migrations and cultural connections.
- According to estimates, there are over 600 million Hindi speakers globally, making it one of the most spoken languages in the world. Its widespread use is attributed to factors such as its official status in India, its role in Bollywood films, and its presence in various media outlets.
Dialects
Hindi, like many languages, exhibits regional variations known as dialects. These dialects differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammatical features.
- The term “Hindustani” encompasses both Hindi and Urdu, which share a common origin and linguistic features. Hindustani evolved from the Khariboli dialect of Hindi, spoken in Delhi and its surrounding regions. While Hindi primarily uses the Devanagari script, Urdu utilizes the Perso-Arabic script.
Writing
Hindi is written in the Devanagari script, a system of writing that originated in ancient India. This script, characterized by its unique consonant and vowel symbols, is used to write various languages, including Sanskrit, Marathi, and Nepali.
- The Devanagari script is known for its phonetic nature, where each symbol represents a distinct sound. This makes it relatively easy to learn for those familiar with other Indic scripts. Learning to write basic Hindi words and phrases in Devanagari involves understanding the pronunciation of consonants, vowels, and the diacritics used to modify sounds.
Pronunciation and Sounds
Hindi pronunciation can be a bit tricky for English speakers, as it has some unique sounds and pronunciation rules. But don’t worry, with a little practice, you’ll be able to pronounce Hindi words with confidence.
Vowel Sounds
Hindi has 11 vowel sounds, compared to English’s 14. Some of these sounds are similar to English, while others are quite different.
- Short Vowels:
- a(as in “father”) – Phonetic symbol: /ə/
- i(as in “machine”) – Phonetic symbol: /i/
- u(as in “flute”) – Phonetic symbol: /u/
- e(as in “bed”) – Phonetic symbol: /e/
- o(as in “hot”) – Phonetic symbol: /o/
- Long Vowels:
- ā(as in “father” but longer) – Phonetic symbol: /ɑː/
- ī(as in “machine” but longer) – Phonetic symbol: /iː/
- ū(as in “flute” but longer) – Phonetic symbol: /uː/
- ē(as in “say” but shorter) – Phonetic symbol: /eː/
- ō(as in “go” but shorter) – Phonetic symbol: /oː/
Consonant Sounds, Is hindi difficult to learn
Hindi has 33 consonant sounds, compared to English’s 24. Some of these sounds are similar to English, while others are quite different.
- Stops:
- k(as in “kite”) – Phonetic symbol: /k/
- kh(as in “loch” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /kʰ/
- g(as in “gate”) – Phonetic symbol: /ɡ/
- gh(as in “loch” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /ɡʰ/
- ṅ(nasalized “ng” as in “singer”) – Phonetic symbol: /ŋ/
- c(as in “chair”) – Phonetic symbol: /tʃ/
- ch(as in “chair” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /tʃʰ/
- j(as in “joy”) – Phonetic symbol: /dʒ/
- jh(as in “joy” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /dʒʰ/
- ñ(nasalized “ny” as in “canyon”) – Phonetic symbol: /ɲ/
- ṭ(retroflex “t” as in “tea” but with tongue curled back) – Phonetic symbol: /ʈ/
- ṭh(retroflex “t” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /ʈʰ/
- ḍ(retroflex “d” as in “day” but with tongue curled back) – Phonetic symbol: /ɖ/
- ḍh(retroflex “d” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /ɖʰ/
- ṇ(nasalized “n” with tongue curled back) – Phonetic symbol: /ɳ/
- t(as in “tea”) – Phonetic symbol: /t/
- th(as in “tea” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /tʰ/
- d(as in “day”) – Phonetic symbol: /d/
- dh(as in “day” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /dʰ/
- n(as in “no”) – Phonetic symbol: /n/
- p(as in “pen”) – Phonetic symbol: /p/
- ph(as in “pen” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /pʰ/
- b(as in “bat”) – Phonetic symbol: /b/
- bh(as in “bat” but aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /bʰ/
- m(as in “man”) – Phonetic symbol: /m/
- Fricatives:
- f(as in “fan”) – Phonetic symbol: /f/
- v(as in “van”) – Phonetic symbol: /v/
- ś(as in “ship” but with tongue curled back) – Phonetic symbol: /ʃ/
- ṣ(as in “ship” but with tongue curled back and aspirated) – Phonetic symbol: /ʃʰ/
- s(as in “sun”) – Phonetic symbol: /s/
- h(as in “hat”) – Phonetic symbol: /h/
- Approximants:
- y(as in “yes”) – Phonetic symbol: /j/
- r(as in “run”) – Phonetic symbol: /r/
- l(as in “love”) – Phonetic symbol: /l/
- w(as in “wet”) – Phonetic symbol: /w/
Aspirated Consonants
One of the most distinctive features of Hindi pronunciation is the use of aspirated consonants. Aspirated consonants are pronounced with a puff of air after the sound is made. For example, the Hindi consonant “kh” is aspirated, while the consonant “k” is not.
Aspirated consonants are marked with an “h” in Hindi script.
“kh” is aspirated, while “k” is not.
Retroflex Consonants
Another important feature of Hindi pronunciation is the use of retroflex consonants. Retroflex consonants are pronounced with the tongue curled back towards the roof of the mouth. For example, the Hindi consonant “ṭ” is retroflex, while the consonant “t” is not.
Retroflex consonants are marked with a dot under the consonant in Hindi script.
“ṭ” is retroflex, while “t” is not.
Nasalized Consonants
Hindi also has nasalized consonants, which are pronounced with the air flowing through the nose. For example, the Hindi consonant “ṅ” is nasalized, while the consonant “n” is not. Nasalized consonants are marked with a tilde over the consonant in Hindi script.
“ṅ” is nasalized, while “n” is not.
3. Script and Writing System
The Hindi language is written using the Devanagari script, a sophisticated and elegant system that has been used for centuries to represent various languages of India. Understanding the Devanagari script is crucial for learning Hindi as it forms the foundation for reading and writing.
3.1 Devanagari Script for Hindi
The Devanagari script is one of the most widely used writing systems in India. It’s used for writing Hindi, Sanskrit, Marathi, Nepali, and several other languages.The Devanagari script originated from the ancient Brahmi script, which is believed to have been developed in India around the 3rd century BCE.
Over centuries, the Brahmi script evolved into various regional scripts, with Devanagari emerging as a prominent script in North India.Devanagari is known for its unique characteristics:
- Consonant-vowel combinations:The script utilizes a system of combining consonants and vowels, where vowels are typically written as small marks above or below the consonants.
- Syllabic structure:Each Devanagari letter represents a syllable, combining a consonant and a vowel sound.
- Clarity and precision:The script is highly phonetic, meaning each letter represents a specific sound, making it relatively easy to learn pronunciation.
- Aesthetic appeal:The Devanagari script is considered visually appealing, with its flowing curves and elegant structure.
Devanagari shares similarities with other Indian scripts, such as the Bengali, Gujarati, and Tamil scripts, as they all originated from the same ancient Brahmi script. However, Devanagari distinguishes itself with its distinct consonant shapes and the way vowels are combined with consonants.
3.2 Structure and Components of Devanagari Letters
Devanagari letters are formed using a combination of consonants, vowels, and matras. The basic structure of a Devanagari letter consists of a consonant base and a vowel mark.
- Consonants:Consonants form the base of a letter. They are written as distinct symbols, each representing a specific consonant sound. For example, the consonant “क” (ka) is written as a simple curved line.
- Vowels:Vowels are written as small marks, called matras, above or below the consonants. The vowel “अ” (a) is considered the inherent vowel and is not written explicitly. Other vowels, like “इ” (i), “उ” (u), “ए” (e), and “ओ” (o), are represented by matras.
For example, to write “कि” (ki), the vowel “इ” (i) matra is placed above the consonant “क” (ka).
- Matras:Matras are small marks that represent vowels. They are placed above or below the consonant base to indicate the vowel sound. For instance, the matra for “इ” (i) is a small horizontal line above the consonant, while the matra for “उ” (u) is a small curved line below the consonant.
Different components combine to form various letters. For example, the letter “का” (ka) is formed by combining the consonant “क” (ka) with the inherent vowel “अ” (a). The letter “कि” (ki) is formed by combining the consonant “क” (ka) with the vowel “इ” (i) matra.
3.3 Writing Basic Hindi Words and Phrases
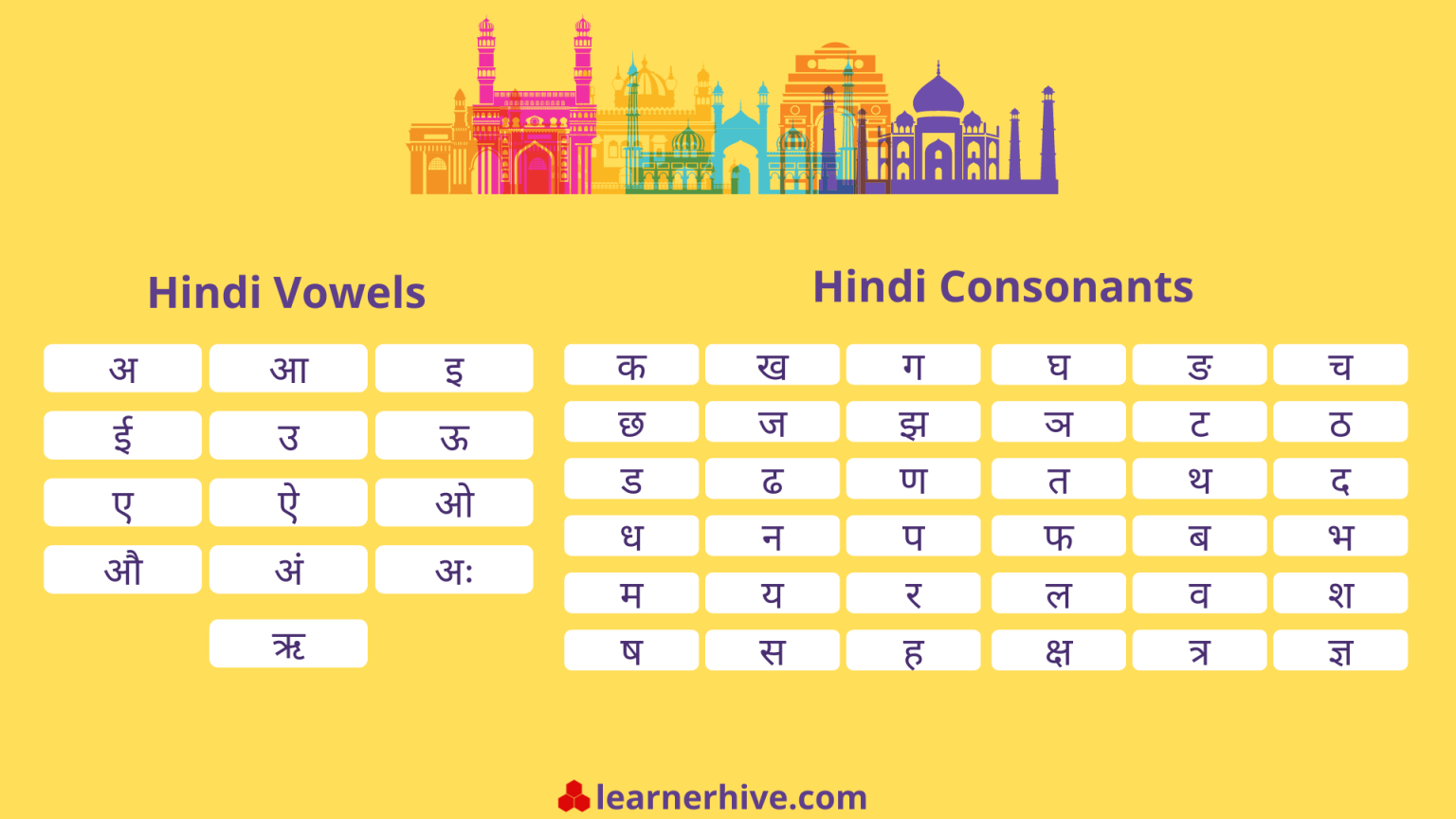
Here is a table showing the Devanagari script for the Hindi alphabet, including vowels, consonants, and matras:
| Letter | Pronunciation | Devanagari |
|---|---|---|
| अ | a | अ |
| आ | aa | आ |
| इ | i | इ |
| ई | ee | ई |
| उ | u | उ |
| ऊ | oo | ऊ |
| ऋ | ri | ऋ |
| ए | e | ए |
| ऐ | ai | ऐ |
| ओ | o | ओ |
| औ | au | औ |
| क | ka | क |
| ख | kha | ख |
| ग | ga | ग |
| घ | gha | घ |
| ङ | nga | ङ |
| च | cha | च |
| छ | chha | छ |
| ज | ja | ज |
| झ | jha | झ |
| ञ | nya | ञ |
| ट | ta | ट |
| ठ | tha | ठ |
| ड | da | ड |
| ढ | dha | ढ |
| ण | na | ण |
| त | ta | त |
| थ | tha | थ |
| द | da | द |
| ध | dha | ध |
| न | na | न |
| प | pa | प |
| फ | pha | फ |
| ब | ba | ब |
| भ | bha | भ |
| म | ma | म |
| य | ya | य |
| र | ra | र |
| ल | la | ल |
| व | va | व |
| श | sha | श |
| ष | sha | ष |
| स | sa | स |
| ह | ha | ह |
Here are some simple Hindi words written in Devanagari:
- नमस्ते (namaste) – Hello
- आपका नाम क्या है? (aapka naam kya hai?) – What is your name?
- धन्यवाद (dhanyavaad) – Thank you
- कृपया (kripya) – Please
Here are some simple Hindi phrases written in Devanagari:
- मैं हिंदी सीख रहा हूँ। (main hindi sikh raha hoon) – I am learning Hindi.
- आप कैसे हैं? (aap kaise hain?) – How are you?
- मैं ठीक हूँ। (main theek hoon) – I am fine.
3.4 Writing Practice
Here are some simple Hindi words and phrases to practice writing in Devanagari:
- नमस्ते (namaste)
- आपका नाम क्या है? (aapka naam kya hai?)
- धन्यवाद (dhanyavaad)
- कृपया (kripya)
- मैं हिंदी सीख रहा हूँ। (main hindi sikh raha hoon)
- आप कैसे हैं? (aap kaise hain?)
- मैं ठीक हूँ। (main theek hoon)
Try writing these words and phrases in Devanagari. You can compare your writing with the examples provided. If you have access to a Hindi tutor or language learning resources, you can get feedback on your writing practice.
3.5 Resources for Learning Devanagari Script
There are many resources available for learning the Devanagari script. Here are some suggestions:
- Online Resources:
- Websites:Websites like HindiPod101, Learn Hindi with Fun, and Memrise offer interactive lessons and exercises for learning Devanagari.
- Videos:YouTube channels like “Hindi With Anjali” and “Learn Hindi with Shruti” provide comprehensive tutorials on Devanagari.
- Apps:Mobile apps like “Duolingo” and “Babbel” include Devanagari script learning modules in their Hindi courses.
- Books:Books like “Teach Yourself Hindi” and “Hindi for Beginners” provide detailed explanations of the Devanagari script and its application in writing Hindi words and phrases.
Hindi Grammar Deep Dive

Now that you’ve got a handle on the basics of Hindi pronunciation and writing, let’s dive into the heart of the language: grammar. Understanding Hindi grammar will unlock the door to forming your own sentences and understanding the nuances of spoken and written Hindi.
Sentence Structure
Hindi sentence structure is different from English, and this can be a bit tricky at first. In Hindi, the typical word order is Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). This means the subject comes first, followed by the object, and then the verb. For example:
English
“I eat apples.”
Hindi
“मैं सेब खाता हूँ” (main seb khāta hūn) Here, “मैं” (main) is the subject, “सेब” (seb) is the object, and “खाता हूँ” (khāta hūn) is the verb. Here are some examples of different sentence types in Hindi:* Declarative:“वह घर जाता है” (vah ghar jāta hai)”He goes home.”
Interrogative
“क्या तुम खाना खा रहे हो?” (kyā tum khānā khā rahe ho?)
- “Are you eating food?”
- “Give me water.”
Imperative
“मुझे पानी दो” (mujhe pānī do)
Particles and conjunctions play a crucial role in forming complex sentences. They help connect clauses and express relationships between different parts of the sentence. For example:* “और” (aur)
- “and”
- “लेकिन” (lekin)
- “but”
- “क्योंकि” (kyonki)
- “because”
Case Markers
Case markers are grammatical particles that indicate the function of a noun or pronoun in a sentence. They tell us whether a noun is the subject, object, or something else. Hindi has a system of case markers that are added to the end of nouns and pronouns.Here are some common case markers in Hindi:* Nominative:“ने” (ne)used for the subject of a transitive verb (a verb that takes a direct object)
Accusative
“को” (ko)
- used for the direct object of a transitive verb
- used for the indirect object of a verb
- used to indicate the instrument or means by which something is done
- used to indicate the source or point of origin
Dative
“को” (ko)
Instrumental
“से” (se)
Ablative
“से” (se)
Here are some examples:* “राम ने किताब पढ़ी”(Rām ne kitāb paṛhī)
- “Ram read the book.” (“ने” marks Ram as the subject)
- “मैंने उसे एक पेन दिया”(maine use ek pen diyā)
- “I gave him a pen.” (“को” marks “use” as the indirect object)
- “वह कार से गया”(vah kār se gayā)
- “He went by car.” (“से” marks “car” as the instrument)
Verb Conjugation
Hindi verbs are conjugated to indicate tense, mood, and aspect. This means the verb form changes depending on the time of the action, the speaker’s attitude towards the action, and whether the action is completed or ongoing.Here’s a basic breakdown of verb conjugation in Hindi:* Present Tense:“मैं खाता हूँ” (main khāta hūn)”I eat”
Past Tense
“मैंने खाया” (maine khāyā)
- “I ate”
- “I will eat”
Future Tense
“मैं खाऊँगा” (main khāūngā)
The rules for forming different verb forms are complex and depend on the verb’s root, the subject’s gender and number, and other factors.
Comparative Analysis
While Hindi and English share some grammatical similarities, there are also significant differences that can be challenging for English speakers. Similarities:* Both languages have a subject-verb-object (SVO) word order in declarative sentences.
Both languages use articles (a, an, the) and prepositions (in, on, at).
Differences:* Hindi uses case markers to indicate the function of nouns and pronouns, while English uses prepositions.
- Hindi verb conjugation is more complex than English, with more tenses and aspects.
- Hindi has a system of honorifics, which are used to show respect for the person being addressed, while English does not.
Learning Hindi grammar can be challenging, but it’s also rewarding. By understanding the core concepts, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of the language.
Writing
मैं सुबह जल्दी उठता हूँ। मैं नाश्ता करता हूँ और फिर काम पर जाता हूँ। दोपहर में मैं खाना खाता हूँ और फिर काम पर वापस जाता हूँ। शाम को मैं घर आता हूँ और टीवी देखता हूँ। फिर मैं सो जाता हूँ।
This paragraph describes a typical daily routine, using the grammatical elements we’ve discussed. You can see the use of case markers, verb conjugation, and different sentence types.
5. Vocabulary and Common Phrases
Learning essential Hindi vocabulary is crucial for effective communication. This section will introduce you to some of the most frequently used Hindi words and phrases, categorized for easy learning and recall. These words and phrases will be helpful for navigating daily situations in India, from greetings and introductions to shopping and dining.
Greetings and Introductions
This section covers essential greetings and introductions used in Hindi.
- Namaste(नमस्ते) – Hello, greetings (formal and informal)
- Aap kaise hain?(आप कैसे हैं?) – How are you? (formal)
- Tum kaise ho?(तुम कैसे हो?) – How are you? (informal)
- Main theek hoon(मैं ठीक हूँ) – I am fine.
- Mera naam [your name] hai(मेरा नाम [आपका नाम] है) – My name is [your name].
- Aap ka naam kya hai?(आपका नाम क्या है?) – What is your name? (formal)
- Tumhara naam kya hai?(तुम्हारा नाम क्या है?) – What is your name? (informal)
Food and Drink
This section provides basic vocabulary for discussing food and drink in Hindi.
- Khaana(खाना) – Food
- Pani(पानी) – Water
- Chai(चाय) – Tea
- Coffee(कॉफ़ी) – Coffee
- Roti(रोटी) – Bread (flatbread)
- Dal(दाल) – Lentil soup
- Sabzi(सब्ज़ी) – Vegetables
- Aam(आम) – Mango
- Kela(केला) – Banana
- Biryani(बिर्यानी) – Rice dish with meat or vegetables
Shopping and Markets
This section focuses on vocabulary used in shopping and markets.
- Dukaan(दुकान) – Shop
- Bazaar(बाज़ार) – Market
- Kitna?(कितना?) – How much?
- Zyaada(ज़्यादा) – More
- Kam(कम) – Less
- Theek hai(ठीक है) – Okay
- Mujhe yeh chahiye(मुझे ये चाहिए) – I want this
Travel and Transportation
This section introduces vocabulary related to travel and transportation.
- Bus(बस) – Bus
- Train(ट्रेन) – Train
- Taxi(टैक्सी) – Taxi
- Airport(एयरपोर्ट) – Airport
- Station(स्टेशन) – Station
- Kahan jaana hai?(कहाँ जाना है?) – Where do you want to go?
- Mujhe [location] jaana hai(मुझे [स्थान] जाना है) – I want to go to [location].
Family and Relationships
This section covers vocabulary related to family and relationships.
- Maa(माँ) – Mother
- Papa(पापा) – Father
- Bhai(भाई) – Brother
- Behen(बहन) – Sister
- Pati(पति) – Husband
- Patni(पत्नी) – Wife
- Dost(दोस्त) – Friend
Health and Well-being
This section provides vocabulary related to health and well-being.
- Achchha(अच्छा) – Good
- Bura(बुरा) – Bad
- Beemar(बीमार) – Sick
- Dard(दर्द) – Pain
- Doctor(डॉक्टर) – Doctor
- Hospital(हॉस्पिटल) – Hospital
Time and Dates
This section covers vocabulary related to time and dates.
- Aaj(आज) – Today
- Kal(कल) – Tomorrow
- Parson(परसों) – Day after tomorrow
- Subah(सुबह) – Morning
- Dopahar(दोपहर) – Afternoon
- Shaam(शाम) – Evening
- Raat(रात) – Night
Numbers and Counting
This section introduces basic numbers and counting in Hindi.
| Hindi | English | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Ek | One | Mujhe ek chai chahiye (मुझे एक चाय चाहिए)
|
| Do | Two | Do roti dena (दो रोटी देना)
|
| Teen | Three | Main teen din ke liye aaya hoon (मैं तीन दिन के लिए आया हूँ)
|
| Chaar | Four | Chaar log hain (चार लोग हैं)
|
| Paanch | Five | Paanch rupay dena (पाँच रुपए देना)
|
| Chhe | Six | Chhe ghanta baad aana (छह घंटा बाद आना) Learning Hindi can seem daunting at first, with its unique script and grammar. But just like learning to ski, which can be tough at first but gets easier with practice ( how hard is it to learn to ski ), Hindi becomes more manageable with consistent effort. The key is to start with the basics, gradually build your vocabulary, and practice speaking as much as possible. You’ll be surprised how quickly you can start communicating in Hindi!
|
| Saat | Seven | Saat din mein (सात दिन में)
|
| Aath | Eight | Aath baje (आठ बजे)
|
| Nau | Nine | Nau saal (नौ साल)
|
| Das | Ten | Das rupiya (दस रुपया)
|
Colors and Shapes
This section introduces basic colors and shapes in Hindi.
| Hindi | English | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Laal | Red | Laal gaadi (लाल गाड़ी)
|
| Peela | Yellow | Peela banana (पीला केला)
|
| Hara | Green | Hara ghaas (हरा घास)
|
| Neela | Blue | Neela aasmaan (नीला आसमान)
|
| Kala | Black | Kala kapda (काला कपड़ा)
|
| Safed | White | Safed dudh (सफ़ेद दूध)
|
| Gola | Round | Gola aam (गोला आम)
|
| Chaukor | Square | Chaukor table (चौकोर टेबल)
|
| Lamba | Long | Lamba raasta (लंबा रास्ता)
|
Basic Verbs and Adjectives
This section introduces basic verbs and adjectives in Hindi.
- Aana(आना) – To come
- Jaana(जाना) – To go
- Khaana(खाना) – To eat
- Pina(पीना) – To drink
- Bolna(बोलना) – To speak
- Suno(सुनो) – Listen
- Dekho(देखो) – Look
- Achchha(अच्छा) – Good
- Bura(बुरा) – Bad
- Chota(छोटा) – Small
- Bada(बड़ा) – Big
Learning Resources and Methods: Is Hindi Difficult To Learn

Learning Hindi can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to a rich culture and diverse language. You have several options for learning Hindi, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right resources and methods depends on your learning style, time commitment, and goals.
Online Learning Platforms
Online learning platforms provide a convenient and flexible way to learn Hindi. They offer structured courses, interactive exercises, and personalized feedback. Popular platforms include:
- Duolingo:A gamified approach to language learning with interactive lessons and progress tracking. It focuses on vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, with a fun and engaging interface. Duolingo is a great starting point for beginners, but may not provide in-depth grammar or cultural insights.
- Memrise:Another gamified platform that uses flashcards and spaced repetition techniques to help you memorize vocabulary. Memrise offers a variety of courses, including Hindi, and provides a strong foundation for building vocabulary.
- Babbel:A language learning app with a focus on real-life conversations. Babbel provides interactive lessons, audio exercises, and cultural insights. It is a good option for those who want to learn Hindi for practical purposes.
- italki:A platform that connects learners with native Hindi speakers for one-on-one lessons. It allows for personalized learning and provides opportunities to practice speaking and listening skills. italki is suitable for those who want to focus on fluency and communication.
Textbooks
Textbooks offer a comprehensive and structured approach to learning Hindi. They cover grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation in detail, providing a solid foundation for language learning.
- Hindi for Everyone:A beginner-friendly textbook that covers basic grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It includes exercises, dialogues, and cultural insights.
- A Textbook of Hindi:A more advanced textbook that covers a wider range of grammar topics and vocabulary. It is suitable for those who have a basic understanding of Hindi.
- Teach Yourself Hindi:A comprehensive textbook that covers all aspects of Hindi language learning, from basic grammar to advanced topics. It is suitable for learners of all levels.
Language Exchange Programs
Language exchange programs provide an opportunity to practice Hindi with native speakers. They involve pairing learners of different languages to exchange conversation and language skills.
- HelloTalk:A language exchange app that connects learners from around the world. It allows for text and voice messaging, as well as video calls. HelloTalk is a great way to practice speaking and listening skills with native speakers.
- Tandem:Another language exchange app that connects learners based on their interests and language goals. It provides a platform for language practice, cultural exchange, and making new friends.
- Meetup:A website and app that connects people with shared interests. You can find local Hindi language exchange groups and meet native speakers for conversation practice.
Effective Learning Strategies
- Set Realistic Goals:Start with small, achievable goals and gradually increase the difficulty. Don’t try to learn everything at once.
- Practice Regularly:Consistency is key to language learning. Aim to practice Hindi for at least 30 minutes each day.
- Immerse Yourself:Surround yourself with Hindi language and culture. Watch Hindi movies, listen to Hindi music, and read Hindi books or articles.
- Find a Language Buddy:Practice speaking Hindi with a native speaker or another learner. This will help you improve your fluency and confidence.
- Use Flashcards:Create flashcards to help you memorize vocabulary and grammar rules. You can use online tools or create your own physical flashcards.
- Record Yourself:Record yourself speaking Hindi and listen back to identify areas for improvement. This will help you improve your pronunciation and fluency.
7. Cultural Context and Importance
Hindi, the official language of India alongside English, is deeply intertwined with the country’s rich and diverse culture. It is not merely a language but a powerful symbol of Indian identity, history, and heritage.
7.1 Cultural Significance of Hindi in India
Hindi’s roots in India can be traced back to Sanskrit, the ancient language of the Indian subcontinent. Over centuries, Sanskrit evolved into various Indo-Aryan languages, with Hindi emerging as one of the prominent descendants. The influence of Sanskrit is evident in Hindi’s vocabulary, grammar, and literature.
Hindi has played a significant role in shaping Indian culture and identity. It has served as a unifying force across diverse regions and communities, fostering a sense of shared heritage and cultural understanding. The language has been instrumental in the preservation and transmission of Indian traditions, values, and beliefs.Hindi permeates various aspects of Indian life, including religion, literature, music, and cinema.
In the realm of religion, Hindi is the language of worship for millions of Hindus, with sacred texts like the Bhagavad Gita and Ramayana being written in this language. Hindi literature boasts a rich tradition, with renowned authors like Premchand, Munshi Premchand, and Harivansh Rai Bachchan leaving an enduring mark on Indian literature.
Hindi music, with its diverse genres like classical, folk, and film music, has captivated generations of Indians. From the soulful melodies of Lata Mangeshkar to the energetic rhythms of Bollywood music, Hindi music has played a vital role in shaping Indian cultural expression.
Bollywood, the Hindi film industry, has become a global phenomenon, with its stories, songs, and dances captivating audiences worldwide. Hindi cinema reflects Indian culture, societal values, and aspirations, serving as a powerful medium of storytelling and entertainment.
7.2 Cultural Significance of Hindi Beyond India
Hindi has transcended geographical boundaries through migration and cultural exchange, establishing a presence in various parts of the world. Large Hindi-speaking communities have emerged in countries like the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United Arab Emirates. These communities have preserved and celebrated their cultural heritage through language, festivals, and traditions.The influence of Hindi language and culture can be observed in global arts and entertainment.
Bollywood music and films have gained immense popularity worldwide, with a dedicated fanbase in countries like China, Japan, and Latin America. Hindi music has inspired fusion genres and collaborations with international artists, demonstrating the language’s global reach.
7.3 Understanding Hindi for Enhanced Cultural Appreciation
Learning Hindi can provide valuable insights into Indian values, beliefs, and traditions. By understanding the language, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the nuances of Indian culture, including its social customs, religious practices, and philosophical perspectives.Knowledge of Hindi facilitates communication and interaction with people from India and the Indian diaspora.
It allows for a more meaningful and authentic exchange of ideas and experiences, fostering a sense of connection and understanding. Learning Hindi enriches one’s appreciation of Indian art, literature, music, and cinema. By understanding the language, one can access the rich tapestry of Indian creative expression, appreciating the depth and complexity of its storytelling, musical traditions, and artistic innovations.
7.4 Examples of Hindi Literature, Music, and Films
Hindi literature boasts a rich heritage with works that have shaped Indian culture and identity. Here are three prominent examples:
- “Godan” by Premchand:This novel is considered a masterpiece of Hindi literature, depicting the struggles and hardships of rural India. It explores themes of poverty, social injustice, and the resilience of the human spirit.
- “Gaban” by Munshi Premchand:This novel examines the themes of greed, corruption, and social decay. It is a powerful commentary on the moral decline of society, exposing the hypocrisy and double standards prevalent in the early 20th century.
- “Madhushala” by Harivansh Rai Bachchan:This collection of poems explores themes of love, life, and death. The poet’s philosophical musings and evocative imagery have made it a beloved work in Hindi literature.
Hindi music is diverse and vibrant, with a range of genres that have captivated generations of Indians. Here are some examples:
- Classical Music:This genre is characterized by its intricate melodies, rhythmic patterns, and devotional themes. It is a highly respected and influential tradition in Indian music.
- Folk Music:This genre is rooted in the diverse cultures and traditions of India’s various regions. It reflects the daily lives, beliefs, and aspirations of different communities.
- Film Music:This genre is closely associated with Bollywood cinema and has become an integral part of Indian popular culture. It features a wide range of styles, from romantic ballads to energetic dance numbers.
Hindi cinema, or Bollywood, has a global reach, with its films captivating audiences worldwide. Here are three influential Hindi films:
- “Mother India” (1957):This epic drama is considered one of the greatest Indian films ever made. It tells the story of a strong and resilient woman who fights for her family and community against injustice.
- “Sholay” (1975):This action-adventure film is a cult classic in Indian cinema. Its iconic characters, memorable dialogues, and thrilling storyline have made it an enduring favorite.
- “Lagaan” (2001):This historical drama is set during the British Raj and tells the story of a group of villagers who challenge their colonial rulers to a cricket match. It explores themes of freedom, unity, and the power of the human spirit.
Challenges and Difficulties in Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi, like any language, comes with its own set of challenges. While the journey can be rewarding, understanding these hurdles can help you prepare and navigate them effectively.
Pronunciation Challenges
Pronunciation is a major hurdle for many Hindi learners, especially those whose native languages lack similar sounds.
- Retroflex Consonants:Hindi has a set of retroflex consonants (ṭ, ṭh, ḍ, ḍh, ṇ) that are produced by curling the tongue back towards the roof of the mouth. These sounds are often difficult for speakers of English, Spanish, or French, who may substitute them with similar-sounding sounds.
For instance, the word “ṭhānḍā” (cold) might be pronounced as “than-da” by someone unfamiliar with the retroflex ṭh sound.
- Vowel Length:Hindi distinguishes between short and long vowels, which can significantly alter the meaning of a word. For example, “jana” (to go) is different from “jānā” (to know). Learners often struggle with correctly identifying and producing these vowel lengths.
- Aspirated Consonants:Hindi has aspirated consonants (kh, gh, ch, jh, ṭh, ḍh, ph, bh) that are pronounced with a puff of air after the consonant sound. These sounds are often confused with their unaspirated counterparts, leading to mispronunciation. For example, “khaana” (to eat) is different from “kaana” (deaf).
Strategies:
- Phonetic Transcription:Using phonetic transcriptions, which represent sounds with symbols, can be incredibly helpful in understanding and practicing Hindi pronunciation.
- Native Speaker Interaction:Engaging with native Hindi speakers, either in person or online, provides valuable opportunities for listening to and imitating correct pronunciation.
- Pronunciation Guides:Online resources like pronunciation guides and videos can offer detailed explanations and demonstrations of specific sounds, helping you break down the complexities of Hindi pronunciation.
Grammar Challenges
While Hindi grammar shares some similarities with English, it also presents its own set of unique challenges.
- Verb Conjugation:Hindi verbs conjugate based on tense, person, and gender. This system can be quite complex for learners, especially as it differs significantly from the simpler verb conjugation systems in many European languages. For example, the verb “karna” (to do) can be conjugated as “karta hu” (I do), “karti hai” (she does), or “karte hain” (they do).
- Gender Agreement:Nouns in Hindi are categorized as masculine or feminine, and adjectives, pronouns, and verbs must agree in gender with the noun they modify. This can be challenging, especially for learners who are not used to grammatical gender. For example, the word “kitab” (book) is feminine, so you would use the feminine form of the adjective “achchhi” (good) to say “achchhi kitab” (good book).
- Case Marking:Hindi uses case marking, which means that nouns and pronouns change form depending on their function in a sentence. This can be confusing for learners who are accustomed to using prepositions to indicate case. For example, the word “ghar” (house) can be “ghar mein” (in the house) or “ghar se” (from the house) depending on its role in the sentence.
Strategies:
- Grammar Rules:Studying Hindi grammar rules, focusing on verb conjugation, gender agreement, and case marking, is crucial for understanding the structure of the language.
- Sentence Formation:Practicing sentence formation, using different grammatical structures, helps solidify your understanding of these concepts.
- Flashcards:Creating and using flashcards for memorizing verb conjugations, gender-specific words, and case markers can be an effective way to reinforce grammar concepts.
Vocabulary Challenges
Building a strong Hindi vocabulary is essential for effective communication. However, the vastness of the Hindi vocabulary and its differences from other languages can present challenges.
- Vast Vocabulary:Hindi has a vast vocabulary, encompassing a wide range of words and expressions. This can be daunting for learners, especially those who are starting from scratch.
- Cognates:While some Hindi words share cognates (words with a common origin) with English, these often have slightly different meanings or are used in different contexts. For example, the Hindi word “samay” (time) is similar to the English word “time,” but it can also mean “occasion” or “opportunity.”
- Loanwords:Hindi has borrowed words from other languages, including English, Persian, and Arabic. This can add another layer of complexity to vocabulary acquisition, as learners may need to be aware of the origins and specific meanings of these loanwords.
Strategies:
- Dictionaries:Using Hindi-English dictionaries is essential for learning new words and understanding their meanings and usage.
- Hindi Literature:Reading Hindi literature, such as novels, short stories, and poetry, can expose you to a wide range of vocabulary and help you learn words in context.
- Hindi Movies:Watching Hindi movies can be a fun and engaging way to expand your vocabulary, as you hear words used naturally in everyday conversations.
- Vocabulary Lists:Creating and practicing with vocabulary lists, focusing on common words and phrases, can help you build a solid foundation in Hindi vocabulary.
Benefits of Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi offers a wealth of personal and professional advantages, opening doors to a rich cultural experience and a wider world of opportunities. Beyond its linguistic beauty, Hindi serves as a bridge to connect with India’s vibrant heritage, diverse communities, and growing economy.
Education
Learning Hindi can be immensely beneficial for students pursuing studies related to Indian history, literature, and culture. By understanding the language, students can access original sources, gain deeper insights into Indian thought and philosophy, and appreciate the nuances of Indian art and literature.
The growing demand for Hindi language teachers and translators in educational institutions reflects the increasing importance of Hindi in academia.
Business
India’s rapidly expanding economy presents significant opportunities for businesses worldwide. Fluency in Hindi can be a valuable asset for professionals seeking to establish connections, navigate business transactions, and build relationships with Indian companies and individuals. Many multinational corporations are recognizing the strategic importance of Hindi and are actively seeking employees with Hindi language skills.
Travel
Learning Hindi can transform your travel experience in India, allowing for deeper cultural immersion and meaningful interactions with locals. Being able to navigate, communicate, and engage in everyday conversations in Hindi can enrich your understanding of the country’s traditions, customs, and way of life.
It can also help you overcome language barriers, connect with people on a personal level, and discover hidden gems that may not be accessible to non-Hindi speakers.
Motivation and Perseverance

Learning a new language, especially one as complex and nuanced as Hindi, requires a significant investment of time, effort, and dedication. While the initial excitement and enthusiasm are crucial, it’s the sustained motivation and unwavering perseverance that truly pave the way to fluency.
The journey of language learning is often punctuated by challenges, plateaus, and moments of doubt. It’s during these times that the importance of motivation and perseverance shines through. These two qualities act as the driving force, pushing you to overcome obstacles and continue progressing towards your goal.
Staying Motivated and Overcoming Learning Plateaus
Maintaining motivation in language learning is essential. Here are some tips to keep your spirits high and your progress steady:
- Set Realistic Goals:Don’t aim for fluency overnight. Break down your learning goals into smaller, achievable milestones. This creates a sense of accomplishment and keeps you motivated.
- Find a Learning Buddy:Learning with a friend or group can be incredibly motivating. You can hold each other accountable, share tips, and celebrate successes together.
- Make it Fun:Incorporate activities you enjoy into your learning routine. Watch Hindi movies, listen to music, read books, or engage in conversations with native speakers. The more enjoyable the process, the more likely you are to stick with it.
- Embrace Mistakes:Mistakes are a natural part of learning. Don’t let them discourage you. View them as opportunities for growth and learning. Remember that even native speakers make mistakes!
- Celebrate Milestones:Acknowledge your progress, no matter how small. Treat yourself to something special when you reach a milestone, whether it’s completing a chapter in your textbook or having a successful conversation with a native speaker.
Stories of Successful Hindi Learners
Many individuals have successfully learned Hindi, drawing inspiration from their personal experiences and overcoming challenges along the way. These stories serve as a testament to the power of motivation and perseverance.
“I started learning Hindi because I was fascinated by Indian culture. At first, it was difficult, but I found a great online community of Hindi learners who supported me. I also made an effort to connect with native speakers and practice speaking whenever possible. It took time, but I eventually reached a level of fluency that allowed me to communicate comfortably.”
Sarah, a successful Hindi learner.
“Learning Hindi was a journey of self-discovery. I realized that the key to success was consistency. I made it a habit to study for at least 30 minutes every day, even if it was just reviewing vocabulary or listening to a podcast. This consistent effort helped me build a strong foundation and eventually led to fluency.”
John, a successful Hindi learner.
Hindi in the Digital Age
The digital age has revolutionized the way we learn languages, and Hindi is no exception. The vast array of online resources, interactive apps, and social media platforms offer a unique and engaging learning experience, making it easier than ever to acquire fluency in this beautiful language.
Online Resources and Apps for Hindi Learning
The internet provides a wealth of resources for learning Hindi, from comprehensive online courses to interactive apps that cater to different learning styles.
- Online Courses:Platforms like Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise offer structured courses with interactive lessons, vocabulary building exercises, and pronunciation practice. These platforms are designed to be user-friendly and adaptable to individual learning paces.
- Language Learning Apps:Dedicated Hindi learning apps like HindiPod101 and Learn Hindi provide a range of features, including audio lessons, vocabulary flashcards, and grammar exercises. These apps often incorporate gamification elements to make learning fun and engaging.
- Language Exchange Platforms:Platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem connect language learners with native speakers for conversation practice. This allows you to immerse yourself in real-life conversations and gain valuable insights into the nuances of the language.
Social Media for Hindi Language Acquisition
Social media platforms have become an invaluable tool for language learners. Engaging with Hindi content on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram allows you to immerse yourself in the language and culture.
- Following Hindi-Speaking Accounts:Connecting with accounts that post regularly in Hindi exposes you to authentic language usage, current trends, and cultural references. This can help you develop your understanding of the language in a natural context.
- Joining Hindi Language Groups:Participating in online communities dedicated to Hindi language learning allows you to connect with other learners, share tips, and ask questions. This collaborative environment can provide valuable support and motivation.
- Watching Hindi Movies and TV Shows:Streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime offer a wide selection of Hindi movies and TV shows with subtitles. Watching these programs can be an enjoyable way to improve your listening comprehension and vocabulary.
Digital Tools for Enhancing Hindi Learning
Technology offers a range of tools to enhance your Hindi learning experience.
- Online Dictionaries and Translators:Websites like Google Translate and Collins Dictionary provide instant translations and definitions, allowing you to quickly understand unfamiliar words and phrases.
- Speech Recognition Software:Apps like Google Assistant and Siri can help you practice your pronunciation by recognizing your spoken Hindi and providing feedback. This can be a valuable tool for improving your fluency.
- Text-to-Speech Software:Programs like NaturalReader and Voice Dream Reader can convert written Hindi text into spoken audio, allowing you to listen to the language and improve your pronunciation and comprehension.
Hindi for Specific Purposes
Learning Hindi for a specific purpose can make the journey more focused and rewarding. Whether you’re aiming to conduct business in India, pursue higher education in a Hindi-speaking institution, or simply navigate your travels, tailoring your learning approach can significantly enhance your experience.
Hindi for Business
Learning Hindi for business purposes requires a strong foundation in professional vocabulary, business etiquette, and cultural nuances. This involves understanding key industry terms, financial concepts, and the art of negotiation.
- Specialized Vocabulary:Familiarize yourself with industry-specific terms relevant to your field, such as finance, technology, or marketing. Resources like online dictionaries and business glossaries can be helpful.
- Business Etiquette:Understanding cultural norms in business communication is crucial. For instance, greetings, addressing colleagues, and negotiation styles may differ from what you’re accustomed to.
- Business Resources:Consider exploring business-oriented Hindi learning materials like textbooks, online courses, or language exchange programs focused on business communication.
Hindi for Education
Learning Hindi for academic purposes demands a comprehensive understanding of grammar, vocabulary, and academic writing styles. This allows you to engage with scholarly materials, participate in discussions, and conduct research effectively.
- Academic Vocabulary:Expand your vocabulary beyond everyday language to include terms related to your field of study. Academic dictionaries and specialized textbooks can provide valuable insights.
- Academic Writing:Learn the conventions of academic writing in Hindi, including citation styles, referencing, and formal language.
- Educational Resources:Explore academic resources like textbooks, journals, and online platforms dedicated to Hindi language learning for students.
Hindi for Travel
Learning Hindi for travel purposes focuses on practical communication skills needed for everyday interactions. This includes navigating transportation, ordering food, asking for directions, and engaging in basic conversations.
- Essential Phrases:Master common phrases related to travel, such as greetings, asking for directions, ordering food, and basic questions.
- Travel Resources:Utilize travel-specific language guides, apps, and phrasebooks designed for travelers.
- Immersion:If possible, immerse yourself in the language by interacting with locals, attending cultural events, or joining language exchange programs.
Hindi for Beginners
Starting your Hindi learning journey can be exciting and rewarding. This section provides a structured approach for beginners to navigate the basics of Hindi.
Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Here’s a table outlining a step-by-step guide for beginners learning Hindi:| Step | Description ||—|—|| 1. Learn the Hindi Alphabet | Start by mastering the Devanagari script, the writing system for Hindi. Learn the vowels, consonants, and basic pronunciation rules.
|| 2. Focus on Pronunciation | Hindi has unique sounds that may be unfamiliar to English speakers. Practice these sounds consistently to improve your fluency. || 3. Build Basic Vocabulary | Start with common greetings, numbers, days of the week, and essential verbs like “to be,” “to have,” and “to do.” || 4.
Learn Basic Grammar | Understand the basic sentence structure, including subject-verb-object order and the use of articles and prepositions. || 5. Practice Speaking and Listening | Engage in conversation with native speakers or language partners, even if it’s just a few basic phrases.
|| 6. Immerse Yourself in the Language | Expose yourself to Hindi through movies, music, books, and podcasts. This helps you learn naturally and develop an ear for the language. |
Basic Hindi Phrases and Sentences
Here are some basic Hindi phrases and sentences to help you get started:
- Namaste(Hello/Good day)
- Aap kaise hain?(How are you?)
- Main theek hoon.(I am fine.)
- Shukriya(Thank you)
- Kya aap Hindi bolte hain?(Do you speak Hindi?)
- Mujhe Hindi seekhna chahta hoon.(I want to learn Hindi.)
Importance of Consistent Practice and Immersion
Consistent practice and immersion are crucial for language learning success. Dedicate a specific time each day to study Hindi, even if it’s just for 15-20 minutes. Surround yourself with the language as much as possible by listening to Hindi music, watching Hindi movies, or reading Hindi books.
The more you practice and immerse yourself in the language, the faster you’ll learn and improve your fluency.
Hindi for Intermediate Learners
You’ve mastered the basics of Hindi, and now you’re ready to dive deeper into the language and take your skills to the next level. This is where the real fun begins! As an intermediate learner, you’ll be able to understand more complex grammar concepts, expand your vocabulary, and start engaging in meaningful conversations with native speakers.
Learning Plan for Intermediate Learners
A structured learning plan can help you stay on track and make steady progress. Here’s a sample plan that you can adapt to your individual needs and preferences:
Module 1: Grammar Deep Dive
This module focuses on solidifying your understanding of Hindi grammar and building a solid foundation for more complex concepts.
- Learning Objectives:
- Master the use of past perfect, future perfect, and conditional tenses.
- Learn to form and use relative clauses, noun clauses, and adverbial clauses.
- Understand the difference between active and passive voice.
- Explore the use of indicative, imperative, and subjunctive mood.
- Activities and Resources:
- Grammar:
- Practice exercises: Work through grammar exercises that focus on the specific grammar points covered in this module. You can find these in textbooks, online resources, or create your own.
- Online quizzes and games: Test your understanding of grammar concepts with interactive quizzes and games. Websites like Quizlet and Memrise offer a variety of resources.
- Grammar books and websites: Refer to grammar books specifically designed for intermediate learners. Websites like Hindipod101 and Learn Hindi provide comprehensive grammar explanations and exercises.
- Vocabulary:
- Flashcards and vocabulary lists: Create flashcards or use online vocabulary lists to learn new words related to specific topics.
- Word games and puzzles: Engage in word games like crossword puzzles and word searches to reinforce your vocabulary.
- Reading materials: Read articles, short stories, or novels that use the vocabulary you are learning.
- Listening:
- Hindi podcasts and audiobooks: Listen to Hindi podcasts and audiobooks that are designed for intermediate learners. These resources often use clear pronunciation and introduce new vocabulary.
- Hindi music and movies: Listen to Hindi music and watch Hindi movies to improve your listening comprehension and exposure to natural language.
- Listening comprehension exercises: Complete listening comprehension exercises to test your ability to understand spoken Hindi.
- Speaking:
- Conversation practice with native speakers or language partners: Find a language partner or join an online conversation group to practice speaking Hindi with native speakers.
- Role-playing activities: Engage in role-playing activities to practice common conversations in different scenarios.
- Pronunciation exercises: Work on improving your pronunciation by focusing on specific sounds and intonation patterns.
- Reading:
- Hindi newspapers and magazines: Read Hindi newspapers and magazines to gain exposure to current events and everyday language.
- Short stories and novels: Read short stories and novels that are written for intermediate learners. This will help you build your vocabulary and improve your reading comprehension.
- Reading comprehension exercises: Complete reading comprehension exercises to test your understanding of written Hindi.
- Writing:
- Writing exercises on various topics: Write about different topics using the grammar and vocabulary you are learning.
- Creative writing prompts: Use creative writing prompts to stimulate your imagination and practice your writing skills.
- Grammar and vocabulary checks: Use grammar and vocabulary checkers to ensure that your writing is accurate.
Module 2: Advanced Grammar
This module delves into more advanced grammar concepts that will help you express yourself more precisely and confidently.
- Learning Objectives:
- Master the use of complex sentence structures, including relative clauses, noun clauses, and adverbial clauses.
- Learn to use the passive voice effectively.
- Understand the nuances of different moods, such as indicative, imperative, and subjunctive.
- Activities and Resources:
- Grammar:
- Practice exercises: Work through exercises that focus on forming and using complex sentences with different types of clauses.
- Online resources: Explore websites like Hindipod101 and Learn Hindi for detailed explanations and exercises on advanced grammar concepts.
- Grammar books: Consult grammar books specifically designed for intermediate or advanced learners.
- Vocabulary:
- Vocabulary lists and flashcards: Create or use vocabulary lists and flashcards to learn new words related to specific topics, such as business, technology, culture, or travel.
- Reading materials: Read articles, books, and websites that focus on your areas of interest.
- Word games and puzzles: Engage in word games and puzzles to reinforce your vocabulary.
- Listening:
- Hindi podcasts: Listen to Hindi podcasts that discuss topics related to your interests.
- Audiobooks: Listen to audiobooks in Hindi, focusing on genres you enjoy.
- Hindi news channels: Watch Hindi news channels to improve your listening comprehension and stay informed about current events.
- Speaking:
- Language exchange platforms: Join online language exchange platforms like HelloTalk or Tandem to connect with native Hindi speakers.
- Online conversation groups: Participate in online conversation groups where you can practice speaking Hindi with other learners.
- Pronunciation exercises: Continue working on your pronunciation through dedicated exercises and apps like Forvo.
- Reading:
- Hindi newspapers and magazines: Read Hindi newspapers and magazines to expand your vocabulary and stay updated on current events.
- Short stories and novels: Read short stories and novels in Hindi that are written for intermediate or advanced learners.
- Online libraries: Explore online libraries like the Internet Archive for access to a wide range of Hindi books and articles.
- Writing:
- Writing exercises: Write essays, stories, or articles on topics that interest you.
- Online writing platforms: Utilize online writing platforms like Grammarly or ProWritingAid to improve your grammar and style.
- Grammar and vocabulary checkers: Use grammar and vocabulary checkers to ensure the accuracy of your writing.
Module 3: Advanced Vocabulary
This module expands your vocabulary beyond basic terms, allowing you to express yourself more precisely and engage in more complex conversations.
- Learning Objectives:
- Expand your vocabulary related to specific topics like business, finance, science, technology, culture, society, travel, and tourism.
- Learn synonyms and antonyms for commonly used words.
- Develop an understanding of idioms and proverbs.
- Activities and Resources:
- Vocabulary:
- Vocabulary lists and flashcards: Create or use vocabulary lists and flashcards for specific topics, such as business terms, scientific concepts, or cultural expressions.
- Reading materials: Read articles, books, and websites related to your areas of interest to encounter new vocabulary.
- Word games and puzzles: Engage in word games and puzzles to reinforce your vocabulary.
- Listening:
- Hindi podcasts: Listen to Hindi podcasts that focus on specific topics, such as business, technology, or culture.
- Audiobooks: Listen to audiobooks related to your areas of interest.
- Hindi news channels: Watch Hindi news channels to expand your vocabulary and learn new terms related to current events.
- Speaking:
- Language exchange platforms: Join language exchange platforms to practice speaking about specific topics with native speakers.
- Online conversation groups: Participate in online conversation groups that focus on specific areas of interest.
- Role-playing activities: Engage in role-playing activities to practice conversations in different scenarios.
- Reading:
- Hindi newspapers and magazines: Read Hindi newspapers and magazines to expand your vocabulary and learn about current events.
- Books and articles: Read books and articles related to your areas of interest.
- Online libraries: Explore online libraries for access to a wide range of Hindi books and articles.
- Writing:
- Writing exercises: Write essays, stories, or articles on topics that require using your expanded vocabulary.
- Online writing platforms: Utilize online writing platforms to improve your grammar and style.
- Grammar and vocabulary checkers: Use grammar and vocabulary checkers to ensure the accuracy of your writing.
Hindi for Advanced Learners
You’ve tackled the basics, explored the grammar, and built a solid vocabulary. Now, it’s time to delve deeper into the nuances of Hindi and elevate your language skills to new heights. This journey of continuous learning and development will open doors to a richer understanding of the language, culture, and society.
Strategies for Achieving Fluency and Proficiency
Reaching fluency and proficiency in Hindi requires dedication and strategic approaches. Here are some key strategies to help you on your journey:
- Immersion and Exposure:Surround yourself with the language as much as possible. Watch Hindi movies and TV shows, listen to Hindi music, and engage in conversations with native speakers. The more you expose yourself to the language, the more natural it will become.
- Focus on Reading and Writing:Reading Hindi literature, newspapers, and articles will expand your vocabulary and expose you to different writing styles. Practice writing regularly, whether it’s journaling, composing emails, or even creating short stories.
- Active Listening:Pay close attention to the nuances of pronunciation, intonation, and word choice in spoken Hindi. Try to understand the context and meaning behind the words, not just their literal translation.
- Engage in Conversations:Practice speaking Hindi with native speakers or other learners. Join online forums, language exchange programs, or local Hindi groups to create opportunities for conversation.
- Utilize Language Learning Apps and Resources:Numerous apps and websites offer advanced Hindi learning materials, including grammar exercises, vocabulary building, and interactive lessons.
Exploring Hindi Literature, Culture, and Society
Hindi literature is rich and diverse, encompassing a wide range of genres, from poetry and prose to drama and fiction. Exploring this literary landscape will deepen your understanding of Hindi culture and society.
- Classic Hindi Literature:Start with works by renowned authors such as Premchand, Rabindranath Tagore, and Munshi Premchand. Their writings offer insights into historical contexts, social issues, and the human experience.
- Contemporary Hindi Literature:Discover contemporary Hindi writers who are exploring new themes and perspectives. These authors often reflect on modern-day issues, societal changes, and the complexities of life in India.
- Hindi Cinema:Hindi films offer a unique window into Indian culture, values, and storytelling traditions. Watching films with subtitles can help you improve your listening comprehension and vocabulary.
- Cultural Events and Festivals:Attend cultural events, festivals, and workshops related to Hindi language and culture. These events provide opportunities to immerse yourself in the language and interact with native speakers.
Key Questions Answered
Is Hindi similar to Sanskrit?
Hindi evolved from Sanskrit, but it has simplified grammar and borrowed words from other languages. While you might find some cognates (similar words), they are not always directly interchangeable.
How long does it take to learn Hindi?
Learning any language takes time and dedication. The pace depends on your commitment, learning style, and exposure to the language. Some reach basic fluency in a few months, while others may take a year or more.
Are there good online resources for learning Hindi?
Yes, there are excellent online resources, including apps, websites, and language exchange platforms. Some popular options include Duolingo, Memrise, and HelloTalk.
Is it necessary to learn the Devanagari script to learn Hindi?
While it’s not absolutely necessary to learn the script initially, it’s highly recommended. Knowing the script will enhance your understanding of the language and make it easier to read and write.
What are some tips for staying motivated while learning Hindi?
Set realistic goals, find a learning partner or group, immerse yourself in Hindi media (movies, music, podcasts), and celebrate your progress. Remember, consistency is key!