Is Hindi a hard language to learn? The answer, like many things in life, is not so simple. While some find Hindi’s unique sounds and grammar challenging, others discover a surprising ease in its rhythmic flow and logical structure.
Learning any language involves effort, but the journey of mastering Hindi can be a rewarding adventure, opening doors to a vibrant culture, rich literature, and a global community.
Hindi, an Indo-Aryan language spoken by millions across India and the world, boasts a fascinating history and diverse linguistic features. The Devanagari script, with its elegant curves and clear pronunciation, might seem intimidating at first, but with practice, you’ll find it quite intuitive.
The grammatical structure, while different from English, follows a logical pattern once you understand the key concepts. With dedicated study and a willingness to embrace the cultural nuances, learning Hindi can be a truly enriching experience.
Hindi Script and Pronunciation
Hindi uses the Devanagari script, a beautiful and complex writing system that’s used for many other languages in India, including Sanskrit, Marathi, and Nepali. Understanding Devanagari is crucial for learning Hindi, as it’s the foundation for reading and writing the language.
Devanagari Script
The Devanagari script is a syllabic script, meaning each character represents a syllable, typically a consonant followed by a vowel. The script is written from left to right, and it’s known for its unique structure, with a horizontal line at the top called a “matra” that connects the characters.
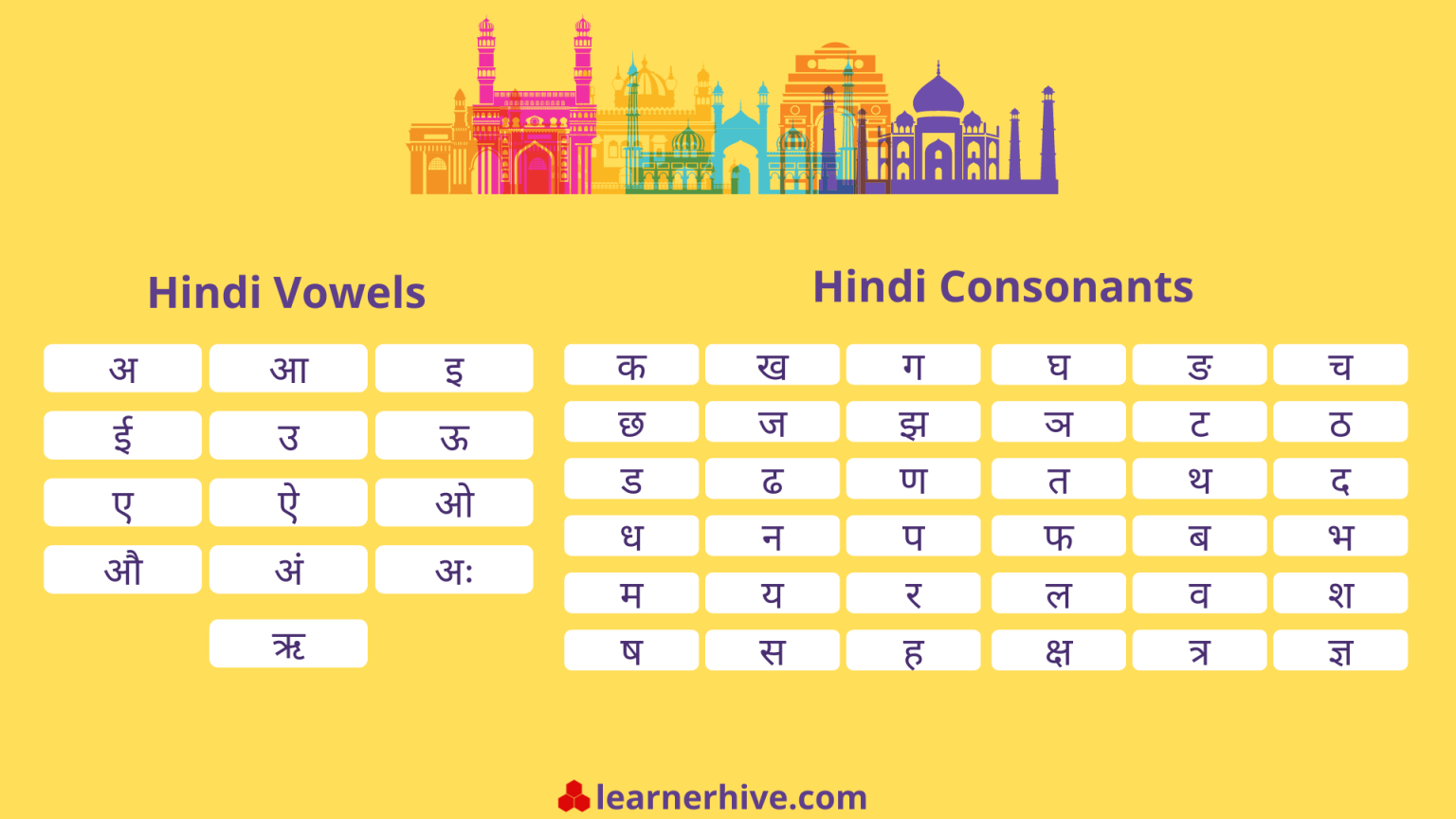
The script has 14 vowels and 33 consonants, each with a unique form. The consonants are arranged in a specific order, making it easier to learn the script. Vowels are represented by diacritics, which are added to the consonant to indicate the vowel sound.
Hindi Pronunciation Rules
Understanding Hindi pronunciation rules is essential for accurate communication. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
Vowels
Hindi has 11 basic vowel sounds, and they are pronounced similarly to their English counterparts:
- a: as in “father” (अ)
- i: as in “machine” (इ)
- u: as in “flute” (उ)
- e: as in “bed” (ए)
- ai: as in “my” (ऐ)
- o: as in “go” (ओ)
- au: as in “cow” (औ)
- ri: as in “tree” (ऋ)
- ee: as in “see” (ई)
- oo: as in “food” (ऊ)
Consonants
Hindi has 33 consonants, and many of them are pronounced similarly to their English counterparts. However, some have unique sounds that require practice to master:
- k: as in “kite” (क)
- kh: as in “loch” (ख)
- g: as in “gate” (ग)
- gh: as in “ghost” (घ)
- ṅ: as in “sing” (ङ)
- ch: as in “chair” (च)
- chh: as in “church” (छ)
- j: as in “jump” (ज)
- jh: as in “judge” (झ)
- ñ: as in “canyon” (ञ)
- ṭ: as in “tub” (ट)
- ṭh: as in “thin” (ठ)
- ḍ: as in “drum” (ड)
- ḍh: as in “that” (ढ)
- ṇ: as in “sun” (ण)
- t: as in “tea” (त)
- th: as in “thin” (थ)
- d: as in “day” (द)
- dh: as in “this” (ध)
- n: as in “nose” (न)
- p: as in “pen” (प)
- ph: as in “phone” (फ)
- b: as in “bat” (ब)
- bh: as in “breath” (भ)
- m: as in “moon” (म)
- y: as in “yes” (य)
- r: as in “run” (र)
- l: as in “light” (ल)
- v: as in “voice” (व)
- ś: as in “ship” (श)
- ṣ: as in “she” (ष)
- s: as in “sun” (स)
- h: as in “hat” (ह)
Diacritics
Diacritics are small marks added to consonants to indicate vowel sounds. They are crucial for accurate pronunciation and understanding the meaning of words. Here are some common diacritics:
- ā: long “a” sound, as in “father” (आ)
- ī: long “i” sound, as in “machine” (ई)
- ū: long “u” sound, as in “flute” (ऊ)
- ṛ: retroflex “r” sound (ऋ)
- e: as in “bed” (ए)
- ai: as in “my” (ऐ)
- o: as in “go” (ओ)
- au: as in “cow” (औ)
Examples of Common Hindi Sounds
Here are some examples of common Hindi sounds and their pronunciation compared to English:
- ka: pronounced like “ka” in “car” (क)
- kha: pronounced like “kha” in “khan” (ख)
- ga: pronounced like “ga” in “gate” (ग)
- gha: pronounced like “gha” in “ghost” (घ)
- nga: pronounced like “nga” in “sing” (ङ)
- cha: pronounced like “cha” in “chair” (च)
- chha: pronounced like “chha” in “church” (छ)
- ja: pronounced like “ja” in “jump” (ज)
- jha: pronounced like “jha” in “judge” (झ)
- nya: pronounced like “nya” in “canyon” (ञ)
Grammar and Syntax
Now that you’ve got a handle on the Hindi script and pronunciation, let’s dive into the structure of the language. Grammar is the backbone of any language, and Hindi is no exception. Understanding the basic rules of grammar will help you construct sentences and communicate effectively.
Sentence Structure and Word Order
Hindi sentence structure is generally Subject-Verb-Object (SVO), just like English. This means the subject of the sentence comes first, followed by the verb, and then the object. Here are some examples:
- Simple sentence:
राम खाना खाता है।(Ram khānā khātā hai.) (Ram eats food.)
- Compound sentence:
राम खाना खाता है और सीता फल खाती है।(Ram khānā khātā hai aur Sītā phal khātī hai.) (Ram eats food and Sita eats fruit.)
- Complex sentence:
जब राम खाना खाता है, तब सीता फल खाती है।(Jab Rām khānā khātā hai, tab Sītā phal khātī hai.) (When Ram eats food, then Sita eats fruit.)
Conjunctions like “और” (aur) – and, “जब” (jab) – when, “तब” (tab) – then, and other grammatical elements help connect clauses within a sentence. Just like in English, the order of words in Hindi can change the meaning of a sentence.
For example, “राम सीता को देखता है” (Rām Sītā ko dekhta hai) means “Ram sees Sita,” while “सीता को राम देखता है” (Sītā ko Rām dekhta hai) means “Ram sees Sita.”
Comparing Hindi and English Grammar
While Hindi and English share some similarities in sentence structure, there are also significant differences. Here’s a table comparing and contrasting the grammatical structures of the two languages:
| Feature | Hindi | English |
|---|---|---|
| Word Order | Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) | Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) |
| Verb Conjugation | Highly conjugated; verbs change based on tense, person, and number | Less conjugated; verbs change mainly based on tense |
| Articles | No definite or indefinite articles (like “the” or “a”) | Uses definite and indefinite articles |
| Prepositions | Uses prepositions, but often in different ways than English | Uses prepositions extensively |
| Gender | Nouns and pronouns have grammatical gender | No grammatical gender for nouns and pronouns |
For example, the verb “to eat” in Hindi changes based on the tense, person, and number. In English, the verb “to eat” only changes based on tense. Also, Hindi does not use articles like “the” or “a” before nouns.
This can be a bit tricky for English speakers to get used to.
Tenses, Verb Conjugations, and Case Markers
Hindi verbs are conjugated based on tense, person, and number. There are three main tenses in Hindi: present, past, and future. Each tense has different forms of the verb.
- Present tense:
राम खाना खाता है।(Rām khānā khātā hai.) (Ram eats food.)
- Past tense:
राम खाना खाया।(Rām khānā khāyā.) (Ram ate food.)
- Future tense:
राम खाना खाएगा।(Rām khānā khāegā.) (Ram will eat food.)
Case markers are another important aspect of Hindi grammar. They are suffixes added to nouns and pronouns to indicate their grammatical function in a sentence. For example, the accusative case marker “को” (ko) is used for the direct object of a verb.
Here’s an example:
राम ने सीता को देखा। (Rām ne Sītā ko dekhā.) (Ram saw Sita.)
In this sentence, “सीता” (Sītā) is the direct object of the verb “देखा” (dekhā) – saw. The accusative case marker “को” (ko) is added to “सीता” (Sītā) to indicate its function as the direct object.
Writing a Sample Sentence
Let’s write a Hindi sentence using the elements you provided:
छात्र ने किताब पढ़ी। (Chātr ne kitāb paṛhī.) (The student read the book.)
In this sentence, “छात्र” (chātr) – student is the subject, “पढ़ी” (paṛhī) – read is the verb in the past tense, “किताब” (kitāb) – book is the object, and “ने” (ne) is the case marker indicating the subject, and “को” (ko) is the case marker indicating the object.
Vocabulary and Word Formation
Building a strong vocabulary is essential for fluency in any language, and Hindi is no exception. Hindi vocabulary draws heavily from Sanskrit, a rich and ancient language, resulting in a diverse range of words and phrases. Understanding how words are formed will help you grasp the nuances of Hindi and effectively communicate your thoughts.
Common Hindi Words and Phrases
This section will provide a list of common Hindi words and phrases categorized by topic, aiding in your understanding of everyday communication.
- Greetings:
- Namaste (नमस्ते) – Hello, Greetings
- Shubh prabhat (शुभ प्रभात) – Good morning
- Shubh ratri (शुभ रात्रि) – Good night
- Kaise ho (कैसे हो) – How are you?
- Main theek hoon (मैं ठीक हूँ) – I am fine
- Daily Life:
- Khaana (खाना) – Food
- Paani (पानी) – Water
- Ghar (घर) – Home
- Dost (दोस्त) – Friend
- Kaam (काम) – Work
- Travel:
- Sadaak (सड़क) – Road
- Garee (गाड़ी) – Vehicle
- Station (स्टेशन) – Station
- Hawaai jahaz (हवाई जहाज) – Airplane
- Kahan ja rahe ho (कहाँ जा रहे हो) – Where are you going?
Common Hindi Root Words and Their Derivatives
Hindi vocabulary is built upon a foundation of root words, which are the basic units of meaning. Understanding these root words will help you decipher the meaning of unfamiliar words and phrases.
- Root Word: Jan(जान) – meaning ‘to know’
- Jaanana(जानना) – to know
- Jaankari(जानकारी) – information
- Jaanwar(जानवर) – animal (literally ‘knowing creature’)
- Root Word: Kar(कर)
meaning ‘to do’
- Karna(करना) – to do
- Kaam(काम) – work
- Karta(कर्ता) – doer
- Root Word: Ghar(घर)
meaning ‘home’
- Gharana(घराना) – family
- Ghari(घड़ी) – clock (literally ‘home of time’)
- Gharwal(घरवाल) – family member
Word Formation in Hindi
Hindi word formation is a complex process involving prefixes, suffixes, and compound words. Understanding these mechanisms will allow you to create new words and phrases, expanding your vocabulary.
- Prefixes: Prefixes are added to the beginning of a word to modify its meaning.
- An(अन) – meaning ‘not’
Anjaan(अनजान) – unknown (not known)
- A(अ) – meaning ‘without’
Agyaan(अज्ञान) – ignorance (without knowledge)
- Su(सु) – meaning ‘good’
Sundar(सुंदर) – beautiful (good looking)
- An(अन) – meaning ‘not’
- Suffixes: Suffixes are added to the end of a word to modify its meaning.
- -wala(-वाला) – meaning ‘one who has’
Kitabwala(किताबवाला) – bookseller (one who has books)
- -ni(-नी) – feminine ending
Ladka(लड़का) – boy Ladki(लड़की) – girl
- -ta(-ता) – meaning ‘state of being’
Garma(गरमा) – hot Garmi(गर्मी) – heat
- -wala(-वाला) – meaning ‘one who has’
- Compound Words: Compound words are formed by combining two or more words.
- Doodh(दूध) – milk + pati(पति) – husband = Doodhpati(दूधपति) – milkman
- Saaf(साफ़) – clean + sutta(सुत्त) – cigarette = Saafsutta(साफ़सुत्त) – clean cigarette
- Jal(जल) – water + pradesh(प्रदेश) – region = Jalpradesh(जलप्रदेश) – water region
4. Cultural Context and Usage
The Hindi language is deeply intertwined with Indian culture, and understanding its cultural context is essential for effective communication. This section explores the various cultural nuances that influence Hindi communication, from idiomatic expressions to regional variations.
4.1 Understanding Cultural Nuances in Hindi Communication
Cultural context plays a significant role in shaping the meaning and interpretation of Hindi language. It influences how words are used, the tone of voice employed, and the gestures that accompany communication. For example, the same word can have different meanings depending on the social context and the relationship between the speakers.Here are some specific situations where understanding cultural context is crucial for effective communication:* Formal vs. Informal Communication:In formal settings, such as business meetings or academic discussions, Hindi speakers use a more formal register, with a greater emphasis on politeness and respect.
In informal settings, such as conversations with friends or family, the language becomes more casual and relaxed.
Addressing People
The way people are addressed in Hindi depends on their age, social status, and relationship to the speaker. For example, using the honorific “ji” after a person’s name indicates respect and formality.
Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication, such as gestures and body language, plays a crucial role in Hindi culture. For instance, a slight nod of the head can indicate agreement, while a shake of the head can mean disagreement. It’s important to be aware of these subtle cues to avoid misinterpretations.
4.2 Exploring Idiomatic Expressions and Cultural References
Hindi is rich in idiomatic expressions, which are phrases that have a figurative meaning different from the literal meaning of the words. These expressions often reflect cultural beliefs, values, and experiences.Here are five common idiomatic expressions in Hindi and their cultural significance:
- “Aankhon mein dhool jhaankna” (To throw dust in someone’s eyes):This idiom means to deceive or mislead someone. It reflects the cultural understanding that appearances can be deceiving, and it’s important to look beyond the surface.
- “Hathi ke paon mein bhi lakdi hoti hai” (Even an elephant has a stick in its foot):This idiom means that everyone has their weaknesses, even the most powerful. It emphasizes the importance of humility and recognizing that no one is perfect.
- “Ek haath se tali nahi bajti” (You can’t clap with one hand):This idiom emphasizes the importance of cooperation and collaboration. It suggests that achieving a goal requires the effort of multiple individuals.
- “Dil mein aag lagna” (To have fire in one’s heart):This idiom means to be passionate or enthusiastic about something. It reflects the cultural value of passion and dedication.
- “Saam, daam, dand, bhed” (Policy of conciliation, inducement, punishment, and division):This phrase refers to the four strategies for achieving a political objective. It highlights the cultural understanding of power dynamics and the importance of strategic thinking.
These expressions are frequently used in everyday conversation, adding color and depth to the language. They also provide insights into the cultural values and beliefs of Hindi speakers.
4.3 Delving into Dialects and Regional Variations, Is hindi a hard language to learn
Hindi has several major dialects, each with its unique linguistic features and geographical distribution. These dialects differ in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar, reflecting the diverse cultural influences across different regions of India.Here are three major dialects of Hindi:
- Khariboli:This is the standard dialect of Hindi, spoken in the northern and central regions of India. It is the basis for the Hindi language taught in schools and used in media and literature.
- Braj Bhasha:This dialect is spoken in the Braj region of Uttar Pradesh, known for its lyrical and poetic quality.
It is often used in religious literature and classical music.
- Awadhi:This dialect is spoken in the Awadh region of Uttar Pradesh. It is characterized by its distinctive pronunciation and vocabulary, with influences from Persian and Arabic.
These regional variations influence communication within Hindi-speaking communities. While speakers of different dialects can often understand each other, there may be differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar that can lead to misunderstandings.
4.4 Writing a Short Story Reflecting Cultural Context
The story is about a young man named Raj who visits his grandmother in a village in Uttar Pradesh. Raj, having grown up in a city, struggles to understand the local dialect and the cultural nuances of village life. Raj arrived at his grandmother’s village, eager to reconnect with his roots. He was greeted with warm smiles and traditional sweets, but the village dialect felt like a foreign language to him. His grandmother, noticing his confusion, chuckled and said, “Beta, ‘aankhon mein dhool jhaankna’ hai yeh sab! (Son, they’re all trying to throw dust in your eyes!)”Raj was perplexed. He didn’t understand the idiom. His grandmother explained that the villagers often exaggerated their stories and used colorful language, a trait she attributed to their love for storytelling and their strong connection to their cultural heritage. Over the next few days, Raj learned to appreciate the village’s unique charm. He saw how the villagers, despite their differences, came together to celebrate festivals and help each other in times of need. He learned the importance of community and the deep-rooted cultural values that shaped their lives.Raj realized that the Hindi language, with its diverse dialects and cultural nuances, was a tapestry woven with the threads of history, tradition, and shared experiences. It was a language that spoke not only through words but also through gestures, expressions, and the collective memory of a people.
Learning Resources and Strategies
Learning Hindi can be an enriching experience, and having the right resources and strategies can make the journey more enjoyable and effective. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of learning resources, including textbooks, online courses, and language exchange platforms, and explore effective strategies for mastering Hindi.
Available Resources
Finding the right resources is crucial for a successful learning experience. There are numerous options available, each catering to different learning styles and preferences.
- Textbooks: Textbooks provide a structured and comprehensive approach to learning Hindi. They cover grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, often with exercises and practice materials. Popular options include “Hindi for Everyone” by A.K. Jain and “Teach Yourself Hindi” by Rupert Snell.
- Online Courses: Online platforms like Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise offer interactive and engaging Hindi courses. They provide bite-sized lessons, gamified learning experiences, and often incorporate audio and video elements for pronunciation practice.
- Language Exchange Platforms: Platforms like HelloTalk and Tandem connect language learners with native speakers for conversation practice. This allows you to immerse yourself in real-world language use, improve your pronunciation, and gain cultural insights.
Effective Learning Strategies
Learning a new language requires dedication and a structured approach. The following strategies can help you learn Hindi effectively:
- Set Clear Goals: Define your learning objectives, whether it’s conversational fluency, reading comprehension, or writing skills. This helps you stay motivated and track your progress.
- Practice Regularly: Consistency is key. Dedicate a specific time each day or week to practice Hindi, even if it’s just for a short period. Regular practice helps reinforce learning and build fluency.
- Seek Feedback: Get feedback from native speakers or language tutors to identify areas for improvement. This could involve speaking practice, writing exercises, or reviewing your grammar.
- Immerse Yourself: Surround yourself with Hindi as much as possible. Listen to Hindi music, watch Hindi movies, and read Hindi books or articles. This helps you become familiar with the language and culture.
- Utilize Technology: Take advantage of language learning apps, online dictionaries, and translation tools. These resources can be invaluable for vocabulary building, pronunciation practice, and understanding complex grammar concepts.
Improving Hindi Skills
Each aspect of language learning requires specific strategies for improvement.
Pronunciation
- Listen Carefully: Pay close attention to the pronunciation of Hindi sounds, especially those that differ from your native language. Listen to native speakers, watch Hindi videos, and use online pronunciation resources.
- Practice with a Mirror: Observe your mouth movements and tongue placement while speaking Hindi. This helps you identify and correct any pronunciation errors.
- Record Yourself: Record your voice while speaking Hindi and listen back to identify areas for improvement. This allows you to hear your pronunciation objectively and focus on specific sounds.
Vocabulary
- Focus on Common Words: Start by learning the most frequently used Hindi words. This provides a solid foundation for communication and understanding basic conversations.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with Hindi words and their English translations. Regularly review these flashcards to reinforce your vocabulary.
- Learn Word Roots: Understanding common word roots can help you decipher new words and expand your vocabulary more efficiently. For example, knowing the root “jan” (meaning “birth”) can help you understand words like “janam” (birth) and “janmadin” (birthday).
Grammar
- Start with the Basics: Begin with the fundamental grammar concepts, such as noun genders, verb conjugations, and sentence structure. This provides a framework for understanding more complex grammatical rules.
- Practice with Exercises: Utilize grammar exercises in textbooks or online resources to reinforce your understanding of grammatical rules. These exercises often involve sentence formation, translation, and verb conjugation.
- Seek Help from a Tutor: If you’re struggling with grammar, consider seeking guidance from a Hindi tutor. They can provide personalized explanations and address specific areas of difficulty.
Hindi for Specific Purposes

Learning Hindi for specific purposes can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to new opportunities and cultural connections. Whether you’re aiming to conduct business, explore India, or delve into academic research, mastering Hindi can provide you with a distinct advantage.
Challenges and Opportunities of Learning Hindi for Specific Purposes
The challenges and opportunities of learning Hindi for specific purposes vary depending on your goals. For instance, business professionals may need to focus on financial terminology and negotiation skills, while travelers may prioritize basic conversational phrases and understanding local customs.
- Business:The growing Indian economy presents significant business opportunities. Learning Hindi can help you establish stronger relationships with clients and partners, navigate cultural nuances, and gain a competitive edge in the market. For example, understanding Hindi financial terminology can be crucial for investment negotiations, and knowing how to address clients respectfully can foster trust and rapport.
- Travel:Hindi is the most widely spoken language in India, making it essential for travelers seeking authentic experiences. Learning basic phrases and understanding local customs can enhance your journey, allowing you to connect with locals, navigate everyday situations, and enjoy a deeper cultural immersion.
- Academic Research:Hindi is a rich language with a vast literary tradition. For scholars researching Indian history, culture, or literature, proficiency in Hindi can provide access to primary sources, unlock deeper understanding, and contribute to groundbreaking research.
Examples of Hindi Language Skills in Professional Settings
Hindi language skills can be applied in various professional settings, opening doors to exciting career opportunities.
- Translation and Interpretation:The demand for Hindi translators and interpreters is increasing as India’s global presence expands. Professionals in this field bridge communication gaps between Hindi speakers and those who do not, facilitating business transactions, legal proceedings, and cultural exchanges.
- Tourism and Hospitality:In India’s thriving tourism industry, Hindi language skills are highly valued. Hotel staff, tour guides, and travel agents who can communicate effectively with Hindi-speaking tourists can provide exceptional service, enhancing visitor experiences and fostering positive perceptions of India.
- Education and Research:Educators and researchers who specialize in Indian studies often require proficiency in Hindi to access and analyze primary sources, conduct fieldwork, and collaborate with local scholars.
The Role of Hindi in the Global Context
Hindi’s role in the global context is steadily growing. As India’s influence expands, Hindi is gaining recognition as a language of international communication and diplomacy.
- International Business and Trade:India’s growing economy and its increasing involvement in global trade have led to a surge in demand for Hindi language skills in international business. Companies seeking to expand their operations in India or engage with Indian businesses need professionals who can communicate effectively in Hindi.
- Cultural Exchange and Diplomacy:Hindi plays a significant role in promoting cultural exchange and diplomacy between India and other countries. The language serves as a bridge for understanding Indian culture, history, and values, fostering stronger relationships and promoting mutual respect.
Comparison with Other Languages: Is Hindi A Hard Language To Learn
Comparing Hindi to other languages helps us understand its unique features and challenges. This section examines how Hindi’s difficulty level stacks up against other Indo-European languages and explores its relationship with other South Asian languages.
Comparison with Indo-European Languages
Hindi, as an Indo-European language, shares a common ancestor with English, French, and Spanish. However, its specific features and evolution create unique challenges for learners.
- Pronunciation:Hindi’s pronunciation system, with its distinct sounds and tonal variations, can be challenging for speakers of English, French, or Spanish. For instance, Hindi uses retroflex consonants (like ‘ṭ’ and ‘ḍ’), which are not present in these languages.
- Grammar:Hindi’s grammar is more complex than English, with a more elaborate system of verb conjugations and noun declensions. While French and Spanish also have complex grammar, the structures differ significantly from Hindi.
- Vocabulary:While Hindi shares some cognates (words with common origins) with other Indo-European languages, its vocabulary has been influenced by Sanskrit and Persian, resulting in a distinct set of words.
Comparison with South Asian Languages
Hindi’s close relationship with other South Asian languages like Urdu, Bengali, and Marathi creates both similarities and differences in learning.
- Shared Roots:These languages share a common linguistic ancestry, resulting in shared vocabulary and grammatical structures. For instance, Hindi and Urdu share a large portion of their vocabulary and have similar grammatical systems.
- Distinct Features:Despite their shared roots, these languages have evolved with distinct influences, leading to differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. For example, Bengali has a more complex vowel system than Hindi, while Marathi has a distinct writing system.
- Impact of Language Family:The Indo-Aryan language family, to which Hindi and these other languages belong, has a significant impact on their structures and features. These languages share a common set of grammatical rules and vocabulary, making them relatively easier to learn for speakers of other Indo-Aryan languages.
Impact of Linguistic Features
Linguistic features play a crucial role in determining the difficulty of learning a language.
- Writing System:Hindi’s Devanagari script, while initially challenging, is phonetic, meaning that each letter represents a single sound. This makes it easier to learn than languages with more complex writing systems, such as Arabic or Chinese.
- Grammatical Complexity:Hindi’s grammatical complexity, with its extensive verb conjugations and noun declensions, can be a significant challenge for learners. However, this complexity is often mitigated by the fact that Hindi is a relatively regular language, with consistent patterns in its grammar.
- Vocabulary Acquisition:Acquiring vocabulary in Hindi can be challenging, as it has a large and diverse vocabulary influenced by Sanskrit, Persian, and English. However, learners can leverage cognates and common roots with other Indo-Aryan languages to facilitate vocabulary acquisition.
8. Personal Experiences and Perspectives on Learning Hindi
Learning a new language can be an enriching experience, and Hindi is no exception. It’s a beautiful and complex language with a rich cultural heritage. While it can be challenging at times, the rewards of fluency are immense.
Personal Anecdote: Conquering the Verb Conjugations
One of the biggest hurdles I faced was mastering Hindi verb conjugations. The sheer number of tenses and the subtle variations in their forms felt overwhelming at first. I remember struggling to distinguish between the past perfect and the pluperfect tenses, which seemed to have very similar meanings.
I spent countless hours poring over grammar books and practicing conjugations, but it took time for the patterns to solidify in my mind. What helped me overcome this challenge was breaking down the process into smaller, manageable steps.
I started by focusing on the most common tenses and gradually expanded my knowledge base. I also found that using flashcards and creating sentence examples helped me to internalize the different forms. This experience taught me the importance of patience and perseverance in language learning.
It also highlighted the value of a systematic approach, rather than trying to learn everything at once.
Factors Affecting Learning Difficulty
The difficulty of learning Hindi can vary greatly depending on several factors.
- Language Background:Speakers of Indo-European languages, particularly those with a Romance or Slavic background, may find some aspects of Hindi grammar more familiar than others. For example, the use of genders and declensions in Hindi shares similarities with these languages.
However, languages with different grammatical structures, like Chinese or Japanese, may present more significant challenges.
- Learning Style:Some individuals thrive on structured learning, while others prefer more immersive methods. Those who enjoy rote memorization may find Hindi vocabulary relatively easy to acquire, while those who prefer contextual learning might benefit more from immersion in Hindi media or interacting with native speakers.
- Motivation and Commitment:The level of dedication and motivation plays a crucial role in language acquisition. If you are genuinely interested in Hindi and its culture, you are more likely to persevere through the challenges and achieve fluency.
Tips for Success in Learning Hindi
If you’re starting your Hindi learning journey, here are a few tips that I’ve found helpful:
- Start with the Basics:Don’t try to learn everything at once. Focus on mastering the fundamentals, including the Devanagari script, basic grammar, and common vocabulary. A solid foundation will make it easier to build upon as you progress.
- Immerse Yourself:Expose yourself to Hindi as much as possible. Listen to Hindi music, watch movies and TV shows, read books and articles, and engage in conversations with native speakers. Immersion is a powerful tool for accelerating language acquisition.
- Find a Learning Partner or Tutor:Learning a language with someone else can be incredibly motivating and helpful. You can practice speaking, share your struggles, and celebrate your successes together. A tutor can provide personalized guidance and feedback, ensuring that you are on the right track.
Comparing Hindi Learning with Another Language
| Feature | Hindi | Spanish ||—|—|—|| Difficulty Level | Moderate to Difficult | Moderate || Key Challenges | Devanagari script, verb conjugations, gendered nouns | Pronunciation, verb conjugations, subjunctive mood || Rewarding Aspects | Rich cultural heritage, access to a vast body of literature and music, rewarding conversations with native speakers | Wide global usage, beautiful literature and music, easy to find learning resources || Unique Insights | The Devanagari script is fascinating and unique, and mastering it opens up a whole new world of literature and culture | Spanish is a very expressive language with a rich history, and its usage in many parts of the world makes it a valuable asset |
9. Motivations and Benefits of Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi offers a wealth of personal and professional benefits, opening doors to cultural immersion, career advancement, and enriched communication skills. Whether you’re driven by a passion for Indian culture, a desire to connect with loved ones, or a quest for new opportunities, learning Hindi can be a transformative journey.
Personal Interest
Learning Hindi can be deeply rewarding for individuals with a personal interest in Indian culture, literature, or family connections.
- Passion for Indian Culture:Imagine yourself captivated by the vibrant colors and intricate storytelling of Bollywood films. You’re drawn to the rich history and diverse culture of India. Learning Hindi can help you explore these interests further, allowing you to understand the nuances of Indian music, dance, and literature, experiencing the culture through its authentic expression.
- Love for Hindi Literature:For book lovers, Hindi literature offers a treasure trove of stories, poems, and essays that have shaped Indian culture and thought. Learning Hindi opens the door to experiencing these works in their original language, gaining a deeper appreciation for the beauty and depth of their expression.
- Connecting with Family and Friends:If you have family or friends who speak Hindi, learning the language can strengthen your bonds and deepen your connections. Imagine sharing stories, celebrating traditions, and engaging in meaningful conversations with your loved ones in their native tongue.
Career Goals
In today’s globalized world, proficiency in Hindi can be a valuable asset for individuals seeking career advancement in various fields.
- Tourism:With India becoming a popular tourist destination, Hindi language skills can be a significant advantage for tour guides, hospitality professionals, and travel agents. It allows you to communicate effectively with Indian tourists and provide a more personalized and culturally sensitive experience.
- International Business:India is a major player in the global economy, and businesses operating in India or seeking to expand their reach to the Indian market often require employees with Hindi proficiency. Fluency in Hindi can open doors to new opportunities, allowing you to negotiate deals, build relationships with clients, and navigate the business landscape effectively.
- Healthcare:As the Indian population continues to grow, healthcare professionals with Hindi language skills are in high demand. Fluency in Hindi allows medical professionals to build rapport with patients, provide culturally sensitive care, and improve patient satisfaction.
- Education:Teachers and educators who speak Hindi can connect with a wider range of students, provide culturally relevant instruction, and create a more inclusive learning environment.
Cultural Appreciation
Beyond practical benefits, learning Hindi offers a unique opportunity to deepen your understanding and appreciation of Indian culture.
- Diverse Perspectives:Learning Hindi allows you to engage with diverse perspectives, understanding the values, beliefs, and social norms of Hindi-speaking communities. It helps you break down cultural barriers and foster empathy and respect for different ways of life.
- Cultural Nuances:Hindi is a rich and expressive language that reflects the complexities of Indian culture. By learning Hindi, you gain access to a deeper understanding of cultural nuances, including social etiquette, religious beliefs, and traditional practices.
- Richness of Indian Traditions:Learning Hindi provides a window into the world of Indian music, dance, literature, and art. You can appreciate the richness of Indian traditions and customs, from the vibrant colors of Holi to the soulful melodies of classical music.
Communication Skills
Learning Hindi can significantly enhance your communication skills, enabling you to connect with a broader range of people and build relationships based on mutual understanding.
- Connecting with a Wider Audience:Hindi is spoken by over 600 million people worldwide, making it one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. Learning Hindi opens up opportunities to connect with a vast and diverse community, from friends and family to colleagues and business partners.
- Building Relationships:The ability to communicate in Hindi can foster deeper relationships, building trust and understanding between individuals from different cultures. Imagine being able to engage in meaningful conversations with Hindi speakers, understanding their perspectives, and sharing your own experiences.
- Understanding Diverse Viewpoints:Learning Hindi provides a unique perspective on the world, allowing you to understand diverse viewpoints and appreciate the richness of different cultures. It helps you develop empathy and tolerance, fostering a more inclusive and understanding world.
Cultural Understanding
Learning Hindi offers a valuable opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of the values, beliefs, and social norms of Hindi-speaking communities.
- Insights into Indian Society:Through learning Hindi, you gain insights into the social structures, family dynamics, and cultural practices of Indian society. You can understand the importance of family and community, the role of tradition and modernity, and the complexities of Indian social life.
- Appreciation of Indian Values:Learning Hindi allows you to appreciate the values that shape Indian culture, such as hospitality, respect for elders, and the pursuit of knowledge. You can gain a deeper understanding of the Indian worldview and its impact on everyday life.
- Understanding Indian Etiquette:Learning Hindi provides insights into the nuances of Indian etiquette, from greeting customs to dining practices. This understanding helps you navigate social situations with confidence and respect, fostering positive interactions with Hindi speakers.
New Opportunities
Learning Hindi can open doors to a world of new opportunities, from travel and study abroad to research and business ventures.
- Travel:Imagine the possibilities of traveling through India, engaging in conversations with locals, and experiencing the country’s vibrant culture firsthand. Learning Hindi can enhance your travel experience, allowing you to connect with people on a deeper level and gain a more authentic understanding of the country.
- Study Abroad:Learning Hindi can be a valuable asset for students seeking to study abroad in India. It allows you to engage with academic communities, immerse yourself in the culture, and build lasting relationships with Indian peers and professors.
- Research:For researchers interested in India, fluency in Hindi can be essential for accessing primary sources, conducting interviews, and collaborating with Indian scholars. It allows you to delve deeper into your research topics and gain a more nuanced understanding of the subject matter.
- Business Ventures:Learning Hindi can be a strategic advantage for entrepreneurs seeking to expand their business into India. It allows you to communicate effectively with clients, negotiate deals, and navigate the business landscape with confidence.
Success Stories
Many individuals have successfully learned Hindi and have benefited greatly from their language skills.
- Cultural Immersion:A student who learned Hindi while studying abroad in India found it opened doors to new friendships, cultural immersion, and a deeper understanding of the country. He was able to engage in meaningful conversations with locals, participate in cultural events, and experience the country’s rich traditions firsthand.
- Career Advancement:A professional who learned Hindi to advance his career in international business found that his language skills gave him a competitive edge. He was able to build relationships with clients in India, negotiate deals effectively, and expand his company’s reach in the Indian market.
- Personal Fulfillment:An individual who learned Hindi for personal fulfillment found that it enriched his life in unexpected ways. He was able to connect with his family’s heritage, appreciate the beauty of Hindi literature, and enjoy the rich cultural experiences that Hindi opened up to him.
10. Historical and Linguistic Background
The Hindi language, spoken by millions across India and the world, has a rich and fascinating history. Its journey from ancient roots to modern prominence is a testament to cultural influences, linguistic evolution, and the enduring power of language.
Origins
Hindi’s origins can be traced back to the ancient Indo-Aryan languages that entered the Indian subcontinent around 1500 BCE. These languages, which evolved from Proto-Indo-European, eventually gave rise to various dialects in the northern and central regions of India. Hindi itself emerged from the Apabhramsha languages, which were the vernacular forms of Sanskrit, the classical language of ancient India.
Evolution
Hindi’s evolution is marked by a series of key milestones and influences. During the medieval period, the Delhi Sultanate (1206-1526 CE) and the Mughal Empire (1526-1857 CE) played a significant role in shaping the language. The influence of Persian, the language of the ruling class, is evident in Hindi vocabulary, particularly in terms of administrative, military, and cultural terms.
The 19th century saw the rise of a standardized form of Hindi, known as “Hindustani,” which was heavily influenced by both Persian and Sanskrit. This standardized form became the basis for modern Hindi, which was officially recognized as one of the official languages of India after independence in 1947.
Standardization
The standardization of Hindi was a complex process involving various factors, including political, cultural, and linguistic considerations. The efforts of scholars and reformers in the 19th and early 20th centuries led to the development of a standardized form of Hindi based on the Khariboli dialect, spoken in and around Delhi.
This standardized form, known as “Standard Hindi,” is based on the Devanagari script and incorporates elements of both Persian and Sanskrit.
Sanskrit Influence
Sanskrit, the classical language of ancient India, has had a profound influence on Hindi. Sanskrit is considered the “mother” of many Indo-Aryan languages, including Hindi, and its influence is evident in Hindi vocabulary, grammar, and syntax. Many Sanskrit words are directly incorporated into Hindi, often with slight modifications in pronunciation or spelling.
For example, the Hindi word “vidyarthi” (student) is derived from the Sanskrit word “vidyarthi.” Sanskrit also influences Hindi grammar, particularly in terms of verb conjugations and noun declensions. For example, the Hindi verb “karna” (to do) has a similar conjugation pattern to the Sanskrit verb “kṛ.”
Cultural Role
Hindi plays a central role in Indian culture, serving as a language of literature, music, film, and everyday life. Hindi literature is a rich and diverse tradition, spanning centuries and encompassing various genres, from poetry and prose to drama and storytelling.
Some of the most famous Hindi writers include Premchand, Munshi Premchand, and Harivansh Rai Bachchan. Hindi music, known as “filmi music” or “Bollywood music,” is an integral part of Indian cinema and popular culture. Hindi film songs often reflect the social, cultural, and emotional realities of Indian society.Hindi cinema, or Bollywood, is the largest film industry in the world, producing hundreds of films annually.
Hindi films are popular not only in India but also in the diaspora communities around the world.
Societal Role
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in India, serving as a lingua franca for communication across various regions and communities. It is used in education, government, and the media, and is increasingly used in business and technology.Hindi’s role in Indian society is multifaceted.
It serves as a unifying force, bringing together people from diverse linguistic backgrounds. However, it also faces challenges in a multilingual country like India, where other languages, such as Bengali, Marathi, and Tamil, have their own significant cultural and societal roles.
11. Hindi Literature and Art
Hindi literature and art have played a pivotal role in shaping Indian cultural identity and promoting understanding across borders. This section delves into the rich tapestry of Hindi literature, exploring its diverse genres and influential figures, and then examines the profound impact of Hindi language and culture on various art forms, including music, dance, and cinema.
Poetry
Hindi poetry is a vibrant and diverse tradition, encompassing a wide range of themes and styles. From the devotional verses of medieval saints to the modern explorations of social and political realities, Hindi poetry has captured the essence of human experience.
- Five Renowned Hindi Poets and their Major Works:
- Mirabai (15th-16th Century): A prominent Bhakti poet, known for her devotional songs dedicated to Lord Krishna. Her most famous works include “Padavali” and “Bhajan”.
- Tulsidas (16th Century): A revered poet who wrote “Ramcharitmanas”, an epic poem narrating the life and teachings of Lord Rama. This work is considered one of the most significant literary creations in Hindi literature.
- Kabir (15th-16th Century): A Sufi mystic and poet known for his simple yet profound verses that challenged social norms and emphasized spiritual unity. His major works include “Kabir Granthavali” and “Bijak”.
- Surdas (16th Century): A blind poet known for his devotional poetry dedicated to Lord Krishna. His “Sur Sagar” is a collection of poems that explore the themes of love, devotion, and divine grace.
- Premchand (19th-20th Century): A modern Hindi writer known for his social realism and poignant portrayal of rural life. His poetry, though less famous than his prose, reflects his keen observation of social injustices and human struggles.
- Key Themes in Hindi Poetry:
- Love: Love, in its various forms, is a recurring theme in Hindi poetry. From the romantic love of Mirabai’s devotional songs to the spiritual love of Sufi poets like Kabir, love has been a source of inspiration and expression.
- Spirituality: Hindi poetry is deeply rooted in spirituality, reflecting the influence of Hinduism, Islam, and other religious traditions. Poets like Tulsidas and Kabir explored the nature of God, the path to salvation, and the significance of spiritual enlightenment.
- Social Commentary: Many Hindi poets have used their art to address social issues, such as poverty, inequality, and injustice. Premchand’s poetry, for example, reflects his concern for the plight of the underprivileged and the need for social reform.
- National Identity: With the rise of nationalism in the 20th century, Hindi poetry began to explore themes of national identity, patriotism, and the struggle for freedom. Poets like Harivansh Rai Bachchan and Maithili Sharan Gupt contributed significantly to this literary movement.
- Impact of Poetic Forms:
- Doha: A two-line verse form with a specific rhyme scheme, often used to express wisdom, moral teachings, and philosophical ideas. It is a popular form in Hindi poetry, particularly in devotional and didactic works.
- Couplet: A two-line verse form, similar to doha, but with a more flexible structure and rhyme scheme. Couplets are commonly used in love poems, ballads, and narrative poems.
- Ghazal: A form of poetry originating in Arabic literature, adopted into Hindi literature. Ghazal typically consists of couplets with a specific rhyme scheme and a recurring refrain. It is often used to express love, longing, and philosophical reflections.
Prose
Hindi prose has evolved significantly over the centuries, reflecting the changing social, political, and cultural landscape of India. From the early works of social reformists to the contemporary explorations of complex human relationships and social realities, Hindi prose has captured the complexities of modern life.
- Prominent Hindi Novelists and their Notable Works:
- Premchand (19th-20th Century): A pioneer of modern Hindi literature, known for his realistic portrayal of rural life and social issues. His most famous novels include “Gaban” (1931), “Godan” (1936), and “Karmabhoomi” (1937).
- Munshi Premchand (19th-20th Century): Another prominent writer who explored the lives of ordinary people and the complexities of human relationships. His works, including “Rangbhumi” (1925) and “Nirmala” (1927), are known for their social commentary and psychological depth.
- Shrilal Shukla (20th-21st Century): A contemporary novelist known for his satirical and often humorous take on social and political realities. His most famous novel, “Raag Darbari” (1968), is a sharp critique of the Indian bureaucracy and its impact on society.
- Evolution of Hindi Prose:
- Early 20th Century:The early 20th century witnessed the emergence of modern Hindi prose, influenced by the social reform movements and the growing awareness of national identity. Writers like Premchand and Munshi Premchand played a pivotal role in establishing Hindi as a language of literary expression.
- Mid-20th Century:The mid-20th century saw the rise of various literary movements, including the “Progressive Writers Movement” and the “Navya-Katha” (New Story) movement. These movements focused on exploring themes of social realism, political awareness, and psychological complexities.
- Present Day:Contemporary Hindi prose continues to evolve, reflecting the diverse realities of modern India. Writers are exploring new themes, experimenting with different styles, and pushing the boundaries of literary expression.
- Social Realism and Political Themes in Contemporary Hindi Novels:
- Contemporary Hindi novels often address issues of social injustice, political corruption, and economic inequality. Writers like Chetan Bhagat, Arundhati Roy, and Shrilal Shukla have used their works to raise awareness about these pressing social concerns.
- The influence of global events and changing social dynamics has also impacted contemporary Hindi fiction. Writers are exploring themes of globalization, migration, and the impact of technology on society.
- Contemporary Hindi novels are characterized by their use of realism, social commentary, and a focus on the human condition. They often explore the complexities of human relationships, the struggles of ordinary people, and the search for meaning in a rapidly changing world.
Drama
Hindi drama has a rich history, drawing inspiration from traditional Indian theatre forms and evolving into a powerful medium for social commentary and cultural expression.
- Influential Hindi Playwrights and their Famous Plays:
- Mohan Rakesh (20th Century): A prominent playwright known for his insightful social commentary and exploration of human relationships. His most famous plays include “Ashadh Ka Ek Din” (1958) and “Lehron Ke Rajhans” (1960).
- Girish Karnad (20th-21st Century): A celebrated playwright and actor known for his innovative use of language and his exploration of themes related to identity, culture, and social change. His most famous plays include “Tughlaq” (1964) and “Hayavadana” (1971).
- Influence of Traditional Indian Theatre Forms:
- Natak: A traditional Indian theatre form, often featuring elaborate costumes, music, and dance. Natak has influenced Hindi drama in terms of its storytelling techniques, use of symbolism, and emphasis on the role of music and dance.
- Nautanki: A popular folk theatre form from Uttar Pradesh, known for its lively performances and use of songs, dialogues, and humor. Nautanki has influenced Hindi drama in terms of its storytelling style, use of colloquial language, and emphasis on audience engagement.
- Role of Hindi Drama in Addressing Social Issues:
- Hindi drama has played a crucial role in addressing social issues, raising awareness about injustice, inequality, and the need for social reform. Playwrights like Mohan Rakesh and Girish Karnad have used their works to critique social structures and challenge conventional norms.
- Hindi drama has also been instrumental in promoting cultural awareness and understanding. Playwrights have explored diverse cultural traditions, historical events, and social realities, contributing to a broader understanding of Indian society.
- The use of humor, satire, and emotional depth in Hindi drama has made it a powerful tool for social commentary and cultural engagement.
Music
Hindi language and culture have had a profound impact on Indian classical music, as well as on the evolution of Hindi film music.
- Impact on Indian Classical Music:
- Hindi language has been used in the lyrics of classical compositions, adding a layer of emotional depth and cultural context. Many ragas, like “Bhairavi” and “Todi”, are associated with specific themes and moods that resonate with Hindi literature and culture.
- Classical music compositions often draw inspiration from Hindi mythology, epics, and literary works, enriching the musical experience with cultural and historical references.
- Evolution of Hindi Film Music:
- Early Days of Cinema:The early days of Hindi cinema saw the emergence of a distinct style of film music, characterized by its use of traditional Indian instruments and melodies. This music often reflected the cultural influences of the time, drawing inspiration from folk songs, classical ragas, and devotional hymns.
- Golden Age of Hindi Cinema:The golden age of Hindi cinema (1950s-1970s) saw the rise of legendary music directors like Naushad, O.P. Nayyar, and Shankar-Jaikishan, who introduced a new wave of popular music that combined traditional elements with Western influences. This era witnessed the emergence of iconic songs that continue to be popular today.
- Modern Hindi Film Music:Modern Hindi film music has evolved further, incorporating contemporary musical styles, electronic sounds, and global influences. While retaining its traditional roots, Hindi film music has adapted to changing tastes and trends, reflecting the diverse cultural landscape of modern India.
- Role of Lyrics and Music in Shaping Cultural Identity:
- Hindi film music has played a significant role in shaping the cultural identity of Hindi cinema. The lyrics of songs often reflect the themes, emotions, and social realities depicted in the films, providing a deeper understanding of the characters and their experiences.
- The use of specific musical styles and instruments, combined with the evocative power of Hindi lyrics, has created a unique and memorable soundscape that has become synonymous with Hindi cinema.
Dance
Hindi language and culture have influenced traditional Indian dance forms, inspiring the emergence of contemporary dance forms that celebrate the richness of Hindi literature and mythology.
- Influence on Traditional Dance Forms:
- Kathak: A North Indian classical dance form, often associated with storytelling and the use of rhythmic footwork. Kathak draws heavily on Hindi literature, particularly epics like the Ramayana and Mahabharata, for its themes and narratives.
- Bharatanatyam: A South Indian classical dance form, known for its intricate movements, graceful gestures, and expressive storytelling. Bharatanatyam, while originating in the South, has also been influenced by Hindi literature and mythology, particularly in its use of Sanskrit verses and themes.
- Contemporary Dance Forms Inspired by Hindi Literature and Mythology:
- Contemporary dance choreographers have drawn inspiration from Hindi literature and mythology, creating innovative dance works that blend traditional elements with modern sensibilities.
- These contemporary dance forms often explore themes of love, loss, social commentary, and spiritual awakening, drawing from the rich tapestry of Hindi literature and mythology.
- Role of Dance in Expressing Emotions and Narratives:
- Dance has always played a significant role in expressing emotions and narratives in Hindi culture. From the devotional dances of the Bhakti saints to the elaborate dance sequences in Hindi films, dance has been a powerful medium for storytelling and emotional expression.
- Contemporary dance forms continue to explore the expressive potential of dance, using movement, gesture, and music to convey complex emotions and narratives rooted in Hindi culture.
Cinema
Hindi language and culture have played a pivotal role in shaping the narrative and themes of Bollywood films, making Hindi cinema a global phenomenon.
- Influence on Bollywood Films:
- Narrative and Themes:Bollywood films often draw inspiration from Hindi literature, mythology, and folklore, creating stories that resonate with Indian audiences. Themes of love, family, social issues, and cultural values are prominent in Bollywood films, reflecting the values and beliefs of Hindi culture.
- Music and Dance:Hindi film music and dance are integral parts of Bollywood films, playing a crucial role in storytelling, emotional expression, and audience engagement. The use of Hindi lyrics, melodies, and dance styles creates a unique and memorable cinematic experience.
- Impact on Global Audiences:
- Bollywood films have gained immense popularity worldwide, captivating audiences with their colorful visuals, dramatic storytelling, and infectious music. This global appeal has contributed to the spread of Hindi language and culture, introducing audiences to Indian traditions and values.
- The success of Bollywood films has also led to the emergence of a global Indian diaspora, connecting people from different cultures and backgrounds through a shared love of Hindi cinema.
- Influence on Global Music Industry:
- Hindi film music has had a significant influence on the global music industry, inspiring musicians and composers worldwide. The popularity of Bollywood songs has led to collaborations between Indian and international artists, promoting cultural exchange and musical innovation.
- The use of Hindi lyrics and melodies in global music has also contributed to the growing appreciation for Indian culture and music around the world.
Cultural Exchange and Understanding
Hindi literature and art have played a crucial role in promoting cultural exchange and understanding between India and other nations.
- Role in Promoting Cultural Exchange:
- Hindi literature and art have served as bridges between cultures, fostering dialogue and understanding through the sharing of stories, ideas, and artistic expressions.
- Translations of Hindi literary works into other languages have introduced global audiences to the richness and diversity of Indian culture, promoting cultural exchange and appreciation.
- International film festivals, music concerts, and dance performances featuring Hindi artists have also contributed to cultural exchange, bringing Indian art forms to a global audience.
- Bridging Cultural Gaps:
- Hindi language and culture have been used to bridge cultural gaps and foster dialogue, promoting understanding and tolerance between different communities.
- The universal themes of love, loss, joy, and sorrow explored in Hindi literature and art resonate with people from diverse backgrounds, fostering a sense of shared humanity and cultural connection.
- International Collaborations and Events:
- International collaborations between Hindi and foreign artists have resulted in the creation of innovative and cross-cultural artistic works, enriching both cultures and promoting mutual understanding.
- Events like the “World Hindi Conference” and the “International Film Festival of India” have brought together artists, scholars, and enthusiasts from around the world, celebrating Hindi language and culture and promoting cultural exchange.
Hindi in the Digital Age
The digital revolution has profoundly impacted the learning and use of Hindi, creating new avenues for language acquisition and fostering a vibrant online community. Technology has made it easier than ever before to learn Hindi, connect with native speakers, and access a wealth of digital resources.
Online Resources and Platforms for Hindi Learners
The internet offers a wide range of resources and platforms designed specifically for Hindi learners. These resources cater to different learning styles and levels, providing interactive exercises, engaging content, and personalized learning paths.
- Language Learning Apps:Popular apps like Duolingo, Memrise, and Babbel offer structured Hindi courses with interactive lessons, vocabulary building exercises, and pronunciation practice. These apps leverage gamification techniques to make learning fun and engaging.
- Online Courses and Websites:Websites like italki, Verbling, and HelloTalk provide opportunities to connect with native Hindi speakers for personalized lessons, language exchange, and conversation practice. Online courses offered by platforms like Coursera and edX offer comprehensive Hindi learning programs, covering grammar, vocabulary, and cultural aspects.
- Digital Dictionaries and Translators:Online dictionaries like Shabdkosh and Google Translate are invaluable tools for Hindi learners, providing instant translations, word definitions, and pronunciation guides. These resources are particularly helpful for understanding unfamiliar words and phrases encountered in digital content.
Hindi in Digital Media
Hindi is increasingly present in digital media, reflecting its growing global reach and popularity. Social media platforms, websites, and mobile applications have embraced Hindi, making it accessible to a wider audience.
- Social Media:Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have large Hindi-speaking communities, where users share information, engage in discussions, and consume content in Hindi. This online presence fosters a sense of community and allows Hindi learners to interact with native speakers in a casual and informal setting.
- Websites and Mobile Applications:Many websites and mobile applications offer Hindi language support, including news portals, e-commerce platforms, and entertainment streaming services. This growing accessibility allows Hindi speakers to access information and services in their native language, further promoting its use in the digital sphere.
- Digital Content Creation:Hindi is increasingly used in digital content creation, including movies, TV shows, music, and podcasts. This trend reflects the growing demand for Hindi content and its appeal to a wider audience. Online platforms like YouTube and Spotify have become hubs for Hindi language content, showcasing the diversity and creativity of Hindi creators.
13. Future of Hindi Language

Hindi, the official language of India, is experiencing a surge in popularity both domestically and internationally. Its future looks promising, driven by several factors that are propelling it towards a more prominent global role.
Current Status of Hindi
Hindi is currently the fourth most spoken language in the world, with over 600 million speakers. It is the primary language in India’s northern and central regions and is widely understood throughout the country. Hindi is also spoken by significant communities in countries like Nepal, Mauritius, Fiji, and South Africa.
- Number of speakers:Hindi is spoken by over 600 million people worldwide, making it the fourth most spoken language globally.
- Geographic distribution:Hindi is primarily spoken in northern and central India, but its influence extends to neighboring countries like Nepal, Mauritius, Fiji, and South Africa.
- Use in education, media, and government:Hindi is the official language of India and is widely used in education, media, and government. It is also the medium of instruction in many schools and universities.
- Presence in the digital world:Hindi has a growing presence in the digital world, with a significant number of websites, social media platforms, and online content available in the language.
Factors Influencing the Growth of Hindi
The growth of Hindi is being driven by several factors, including:
- Economic factors:India’s rapid economic growth is making Hindi a more important language for international business and trade.
- Political factors:India’s growing role in global affairs is increasing the importance of Hindi in international diplomacy.
- Cultural factors:The increasing popularity of Indian culture, cinema, and music is helping to spread Hindi to a wider audience.
- Technological factors:Technology is playing a crucial role in promoting the use of Hindi online and in communication.
Predictions for the Future of Hindi
Hindi is poised to play an increasingly significant role in the 21st century. Here are some predictions for its future:
- Global communication:Hindi is likely to become a more important language in international business and diplomacy, particularly in regions with strong economic ties to India.
- Education:Hindi is expected to be more widely taught and studied in schools and universities worldwide, as demand for language skills in India and other Hindi-speaking regions grows.
- Technology:Hindi is likely to become a dominant language in the digital world, including AI and machine learning, as technology companies seek to expand their reach in India and other Hindi-speaking markets.
- Culture:Hindi is expected to continue to spread through popular culture, music, and cinema, further enhancing its global reach and influence.
Misconceptions about Hindi

Hindi, a vibrant and widely spoken language, often faces misconceptions that deter potential learners. This article aims to debunk these myths and reveal the rewarding aspects of learning Hindi.
The Difficulty of Learning Hindi
It’s a common belief that Hindi is an incredibly difficult language for English speakers to learn. However, this misconception stems from a lack of understanding of the language’s structure and the benefits it offers.
- “Hindi is too difficult for English speakers.”This statement is often based on the perception of Hindi’s unfamiliar script and complex grammar. However, studies have shown that Hindi is actually easier to learn than some other languages, such as Mandarin Chinese, for English speakers. The reason for this is the shared Indo-European roots of English and Hindi, leading to a significant number of cognates, words with similar origins and meanings.
For example, “father” in English is “pita” in Hindi, and “mother” is “maa”.
- “The writing system is too complex.”While the Devanagari script may appear daunting at first, it is actually quite logical and phonetic. Each letter represents a specific sound, and the script is written from left to right. This makes it relatively straightforward to learn compared to languages with more complex writing systems.
The Devanagari script is also highly efficient, with each symbol representing a distinct sound, unlike some alphabets with multiple pronunciations for the same letter.
- “There are too many dialects.”While Hindi has various dialects, the standard Hindi spoken in the media and used in education is widely understood across the country. This standard Hindi provides a common ground for communication and learning, making it easier to navigate the language landscape.
The Benefits of Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi offers a wealth of opportunities and rewards that extend beyond simply acquiring linguistic skills.
- “Hindi is a gateway to a rich culture and diverse population.”India, the second-most populous country in the world, boasts a rich cultural heritage, vibrant traditions, and a diverse population. Learning Hindi allows you to engage with this culture, understand its nuances, and connect with its people on a deeper level.
You can enjoy the vast array of Bollywood films, experience the vibrant festivals like Diwali and Holi, and immerse yourself in the diverse culinary traditions of India.
- “Learning Hindi opens up career opportunities in India and beyond.”India’s economy is rapidly growing, making it a hub for business and investment. Proficiency in Hindi provides a significant advantage in securing jobs in various sectors, including IT, finance, tourism, and education. Even beyond India, Hindi is spoken in many other countries, including Nepal, Mauritius, Fiji, and Suriname, opening doors to global opportunities.
Whether Hindi is hard to learn depends on your background and how you approach it. Just like in the workplace, where understanding different learning styles is key to success ( how to accommodate different learning styles in the workplace ), tailoring your Hindi learning strategy to your strengths will make the journey smoother.
If you’re a visual learner, focus on flashcards and movies. If you’re an auditory learner, dive into podcasts and music. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to learning a new language, just like there’s no single way to learn effectively in the workplace.
- “Hindi is a valuable asset in the globalized world.”In today’s interconnected world, multilingualism is highly valued. Learning Hindi adds a valuable skill to your resume, making you a more competitive candidate in the global job market. The language’s growing influence in the digital age, with its increasing presence on social media and online platforms, further enhances its value.
Tips for Success in Learning Hindi
Learning Hindi can be an exciting and rewarding journey, but it’s also a process that requires dedication and a strategic approach. Whether you’re a beginner or have some prior experience, these tips can help you achieve fluency and unlock the beauty of this vibrant language.
Consistency is Key
Consistency is crucial for mastering any language. Set aside a dedicated time each day or week to practice Hindi, even if it’s just for 15-30 minutes. Regular exposure will help you build a solid foundation and gradually improve your skills.
Immerse Yourself in the Language
Surround yourself with Hindi as much as possible. Watch Hindi movies and TV shows, listen to Hindi music, read Hindi books and articles, and try to find opportunities to converse with native speakers. Immersion helps you learn naturally and develop a better understanding of the language’s nuances.
Embrace a Positive Learning Attitude
Learning a new language can be challenging at times, but it’s important to maintain a positive attitude. Celebrate your successes, no matter how small, and don’t be discouraged by setbacks. Remember that everyone learns at their own pace, and every step forward is a valuable achievement.
Utilize a Variety of Learning Resources
There are countless resources available to help you learn Hindi, from textbooks and online courses to language exchange partners and apps. Explore different options and find the ones that best suit your learning style and preferences.
Focus on Active Learning
Don’t just passively absorb information; actively engage with the language. Practice speaking and writing Hindi as much as possible. Try to have conversations with native speakers, even if they are brief and simple at first.
Embrace Mistakes as Learning Opportunities
Mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. Don’t be afraid to make them; instead, view them as opportunities for growth. Pay attention to your mistakes, understand why they happened, and correct them for future reference.
Find a Learning Buddy
Learning with a friend or partner can provide motivation, accountability, and a chance to practice your Hindi skills in a supportive environment. You can also help each other with challenging concepts and provide feedback on your progress.
Set Realistic Goals
Don’t try to learn everything at once. Set achievable goals for yourself and gradually increase the difficulty as you progress. Celebrate your milestones and acknowledge your progress along the way.
Don’t Be Afraid to Ask for Help
If you’re struggling with a particular aspect of Hindi, don’t hesitate to ask for help. There are many resources available, including teachers, tutors, and online forums. Don’t be afraid to reach out and seek guidance.
Stay Motivated
Learning a new language can be a long journey, so it’s essential to stay motivated. Remind yourself why you started learning Hindi in the first place. Think about the benefits of fluency, the cultural experiences you’ll gain, and the new connections you’ll make.
Don’t Give Up
There will be times when you feel frustrated or discouraged. Don’t give up on your Hindi learning journey. Take a break if you need to, but don’t abandon your goals. Persistence and dedication will ultimately lead you to success.
FAQ Section
Is Hindi a tonal language?
No, Hindi is not a tonal language. While some sounds might seem similar, the meaning doesn’t change based on the tone of the word.
How many dialects of Hindi are there?
There are many regional variations of Hindi, but Standard Hindi, used in media and education, is widely understood.
What are some good resources for learning Hindi?
There are many excellent resources available, including textbooks, online courses, language exchange platforms, and even apps. Start by exploring what best suits your learning style.