How to learn Native American languages is a journey into a rich and diverse world of cultures and traditions. Native American languages are not just words, they are living expressions of history, identity, and knowledge passed down through generations.
This guide will help you understand the importance of these languages, explore resources for learning, and discover strategies for successful language acquisition.
From the vast plains of the Great Basin to the lush forests of the Pacific Northwest, Native American languages have thrived for centuries. Their unique sounds, grammatical structures, and cultural contexts offer a fascinating glimpse into the diverse history and traditions of indigenous peoples across North America.
Learning a Native American language is not just about mastering a new set of words, it’s about understanding a rich tapestry of cultural heritage and connecting with the vibrant communities that continue to speak these languages today.
Understanding Native American Languages: How To Learn Native American Languages
Native American languages represent a rich tapestry of linguistic diversity, each reflecting unique cultural histories and traditions. Exploring these languages offers a fascinating journey into the heart of indigenous cultures, highlighting their resilience and the importance of preserving their heritage.
Diversity of Native American Languages
Native American languages exhibit remarkable diversity, with hundreds of distinct languages spoken across North and South America. The number of languages spoken historically is estimated to be around 300 in the United States and Canada, and over 1,000 in the Americas as a whole.
- Geographic Distribution:These languages are distributed across diverse geographic regions, from the Arctic tundra to the tropical rainforests. The languages of the Northwest Coast, for example, are known for their complex grammatical structures, while the languages of the Southwest are characterized by their rich vocabulary for desert plants and animals.
- Language Families:Native American languages are organized into distinct language families, reflecting historical connections and shared linguistic features. Some prominent language families include:
- Algonquian:Found throughout the eastern and northern parts of North America, Algonquian languages include Cree, Ojibwe, and Blackfoot.
- Iroquoian:Spoken by tribes in the Northeast and Southeast, Iroquoian languages include Mohawk, Oneida, and Cherokee.
- Siouan:Found in the Great Plains and the Midwest, Siouan languages include Lakota, Dakota, and Osage.
- Na-Dené:Distributed across the western and northern parts of North America, Na-Dené languages include Navajo, Apache, and Tlingit.
- Uto-Aztecan:Found in the Southwest and Mexico, Uto-Aztecan languages include Hopi, Nahuatl, and Zuni.
- Unique Features:Native American languages often exhibit unique grammatical structures and sound systems that distinguish them from other language families.
- Incorporation:Some languages, like Inuktitut, incorporate objects and actions into verbs, creating complex words that convey a lot of information in a single unit.
- Polysynthetic:Languages like Cherokee and Choctaw are known for their polysynthetic structure, where words are formed by combining multiple morphemes (meaningful units) to create long, complex words.
- Tonal Languages:Some languages, like Huichol and Zapotec, use tones to distinguish words, similar to Chinese.
Choosing a Language
With so many Native American languages to choose from, the first step is to select one that resonates with you. This decision involves considering several factors, such as the language’s resources, the size of its community, and its cultural significance.
Factors to Consider
The choice of a Native American language for learning should be based on several factors.
- Availability of Resources:Look for languages with readily available learning materials, such as dictionaries, textbooks, online courses, and language communities.
- Community Size:Learning a language is more engaging when you can connect with native speakers. Consider the size of the language community, as this can impact opportunities for interaction and immersion.
- Cultural Relevance:Learning a Native American language is an opportunity to connect with its rich cultural heritage. Choose a language that aligns with your interests and values, whether it’s a connection to a specific tribe or a broader appreciation for Indigenous cultures.
Resources for Language Learning
The following list provides a starting point for exploring Native American languages with available resources.
- Cherokee:Cherokee is a language with a rich history and a significant community. The Cherokee Nation offers various resources, including language classes, dictionaries, and online materials.
- Navajo:Navajo is the most widely spoken Native American language in the United States. The Navajo Nation provides resources for learning, including language courses, dictionaries, and cultural immersion programs.
- Lakota:Lakota is a language with a strong cultural significance, particularly in the Great Plains region. The Lakota Language Consortium offers resources for learning, including dictionaries, textbooks, and online courses.
- Hopi:Hopi is a language with a unique cultural heritage and a strong community. The Hopi Tribe offers resources for learning, including language classes, dictionaries, and cultural immersion programs.
- Inuktitut:Inuktitut is a language spoken by Inuit communities in Canada. The Nunavut Department of Education offers resources for learning, including language classes, dictionaries, and online materials.
3. Learning Resources
Learning a Native American language can be a rewarding and enriching experience. However, it’s important to have the right resources to support your learning journey. This section will guide you through a variety of resources, from online platforms to textbooks and immersion programs, to help you find the best tools for your specific needs.
Online Platforms
Online platforms offer a convenient and interactive way to learn Native American languages. They often incorporate gamification, personalized learning paths, and community features to make the learning process engaging and effective. Here are some popular platforms that cater to various learning styles and needs:
- Duolingo:This popular language learning platform offers courses in several Native American languages, including Navajo, Cherokee, and Lakota. Duolingo focuses on building vocabulary and grammar through interactive exercises and gamified lessons. It’s a great option for beginners who want to learn the basics of a language in a fun and engaging way.
However, it may not be as comprehensive as other platforms for advanced learners.
- Memrise:Memrise utilizes spaced repetition and a gamified approach to help learners memorize vocabulary and grammar. It offers courses in various Native American languages, including Cree, Ojibwe, and Choctaw. Memrise is known for its effective vocabulary building and its use of flashcards and interactive games.
It can be a valuable resource for beginners and intermediate learners, but it may not offer as much in-depth grammar instruction as other platforms.
- Babbel:Babbel provides a more comprehensive approach to language learning, covering vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and cultural insights. It offers courses in several Native American languages, including Cherokee, Navajo, and Lakota. Babbel’s strength lies in its focus on real-life conversations and its emphasis on pronunciation.
However, it may be more expensive than other platforms.
- Rosetta Stone:Rosetta Stone is known for its immersive approach to language learning, using interactive lessons and real-life scenarios. It offers courses in several Native American languages, including Cherokee, Navajo, and Lakota. Rosetta Stone’s focus on pronunciation and real-world applications makes it a valuable resource for those who want to learn to speak and understand a language fluently.
However, it can be expensive and may not offer as much flexibility in terms of learning pace.
Apps
Language learning apps offer a mobile-friendly and flexible way to learn Native American languages. They provide a variety of features, from flashcards and vocabulary builders to language exchange platforms and pronunciation practice tools. Here are some popular apps that can enhance your learning experience:
- Anki:Anki is a powerful flashcard app that utilizes spaced repetition to help learners memorize vocabulary and grammar. It’s highly customizable and allows you to create your own flashcards or use pre-made decks for various Native American languages. Anki is a great option for those who prefer a structured and efficient approach to vocabulary building.
- HelloTalk:HelloTalk is a language exchange app that connects learners with native speakers of different languages. It allows users to practice speaking, writing, and reading through text and voice messages, as well as video calls. HelloTalk is a valuable resource for those who want to improve their fluency and gain cultural insights through real-life interactions.
- Tandem:Tandem is another language exchange app that connects learners with native speakers. It offers a variety of features, including text messaging, voice calls, and video calls, as well as language learning games and quizzes. Tandem is a great option for those who want to practice their language skills and connect with other learners.
- Forvo:Forvo is a pronunciation dictionary that allows users to listen to and record pronunciations of words in various languages, including Native American languages. It’s a valuable resource for those who want to improve their pronunciation and learn the correct intonation and stress patterns.
Textbooks
Textbooks offer a structured and comprehensive approach to learning Native American languages. They often cover grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and cultural insights, providing a solid foundation for language learning. Here are some recommended textbooks based on language and learning level:
- “Navajo for Beginners” by John P. Harrington:This textbook is a comprehensive introduction to the Navajo language, covering grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It’s suitable for beginners and includes exercises and audio files to enhance learning.
- “Cherokee Language: A Textbook for Beginners” by Duane King:This textbook provides a thorough introduction to the Cherokee language, focusing on grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. It includes exercises, audio files, and a Cherokee dictionary.
- “Lakota Language: A Comprehensive Grammar” by David S. Rood:This textbook offers a detailed analysis of Lakota grammar, covering all aspects of the language. It’s suitable for intermediate and advanced learners who want to delve deeper into the intricacies of the Lakota language.
Dictionaries
Dictionaries are essential tools for language learning, providing definitions, synonyms, antonyms, and pronunciation guides. They can help you understand the meaning of words and phrases and expand your vocabulary. Here are some recommended online and offline dictionaries for Native American languages:
- WordReference:This online dictionary offers comprehensive definitions, examples, synonyms, antonyms, and pronunciation guides for various languages, including Native American languages. It’s a valuable resource for those who want to understand the nuances of language.
- Merriam-Webster:This online dictionary provides definitions, synonyms, antonyms, and examples for various languages, including Native American languages. It’s a reliable resource for those who want to learn the meaning of words and phrases.
- Collins Dictionary:This online dictionary offers comprehensive definitions, synonyms, antonyms, and pronunciation guides for various languages, including Native American languages. It’s a great resource for those who want to expand their vocabulary and improve their understanding of language.
Immersion Programs
Immersion programs offer an immersive and interactive way to learn Native American languages. They provide opportunities to interact with native speakers, experience the culture firsthand, and gain fluency in a short period. Here are some examples of language immersion schools and programs:
- Navajo Language Immersion Program at Dine College:This program offers a comprehensive immersion experience in the Navajo language, combining classroom instruction with cultural activities and community engagement.
- Cherokee Language Immersion Program at Cherokee Nation Businesses:This program offers a variety of immersion opportunities, including summer camps, workshops, and online courses, to help learners develop their Cherokee language skills.
- Lakota Language Immersion School at Oglala Lakota College:This school offers a full-immersion program for students of all ages, providing a comprehensive education in the Lakota language and culture.
Language Communities
Language communities and forums provide a valuable platform for language learners to connect with other learners, native speakers, and language enthusiasts. They offer opportunities for language exchange, cultural insights, motivation, and support. Here are some online communities and forums that cater to Native American language learners:
- Reddit:Reddit has numerous subreddits dedicated to Native American languages, such as r/Navajo, r/Cherokee, and r/Lakota. These subreddits provide a platform for language learners to ask questions, share resources, and connect with other learners.
- Facebook Groups:Facebook offers several groups dedicated to Native American languages, providing a space for learners to interact with each other, share resources, and participate in language exchange activities.
- Discord Servers:Discord servers dedicated to Native American languages offer a platform for learners to chat with each other, participate in voice channels, and share resources.
4. Language Learning Strategies

Learning a Native American language effectively requires a strategic approach that incorporates consistent practice, immersion, and the use of various learning tools. This section will delve into these strategies and provide practical tips to help you on your language learning journey.
4.1 Importance of Consistent Practice and Immersion
Consistent practice and immersion are crucial for achieving fluency in any language, especially Native American languages. Daily practice, even for short periods, helps build a strong foundation and reinforces language structures. This allows you to gradually develop fluency and confidence in your language skills.
Immersion, on the other hand, accelerates language acquisition by exposing you to the language in its natural environment. This can involve interacting with native speakers, listening to authentic language content, and engaging in cultural activities related to the language.
4.2 Designing a Study Plan
A well-structured study plan is essential for effective language learning. It should encompass the four core language skills: listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
- Listening: Engage in activities like listening to podcasts, audiobooks, music, and movies with subtitles. Pay attention to pronunciation, intonation, and the flow of language.
- Speaking: Practice speaking with native speakers, language exchange partners, or even by shadowing audio recordings. This helps improve pronunciation, fluency, and confidence in speaking.
- Reading: Explore books, articles, online content, and news websites in the language you are learning. This exposes you to various vocabulary and grammatical structures.
- Writing: Engage in writing activities such as journaling, creative writing, essays, letters, or summaries of articles and books. This helps solidify your understanding of grammar and vocabulary.
Allocate time for each skill based on your individual learning preferences and strengths. For example, if you enjoy listening to music, spend more time on listening exercises. If you prefer writing, dedicate more time to writing practice.
4.3 Utilizing Language Learning Tools
Language learning tools can significantly enhance your learning experience. Here are some useful tools and how to incorporate them into your study plan:
- Flashcards: Create and use flashcards for vocabulary and grammar practice. Review them regularly to reinforce your understanding.
- Language exchange partners: Find language partners for conversation practice and cultural exchange. This provides valuable real-life experience and helps you learn from native speakers.
- Language learning apps: Utilize apps like Duolingo, Babbel, and Memrise for interactive lessons and gamified learning. These apps provide structured lessons and feedback to track your progress.
- Dictionaries and online resources: Access reliable dictionaries and online resources for language research and clarification. These resources provide definitions, examples, and cultural context for language elements.
4.4 Writing Practice
Writing practice is an essential component of language learning. It helps improve grammar, vocabulary, and overall language proficiency.
- Short stories: Write short stories to practice using vocabulary and grammar in a creative context.
- Journal entries: Write journal entries to express your thoughts and experiences in the language you are learning.
- Emails or letters: Write emails or letters to practice formal and informal communication in the language.
- Summaries of articles or books: Summarize articles or books to demonstrate your understanding of the content and practice using key vocabulary and grammatical structures.
- Creative prompts based on given scenarios: Write creative pieces based on given scenarios to enhance your language skills and explore different writing styles.
5. Pronunciation and Phonetics
Pronunciation is a crucial aspect of learning any language, and Native American languages are no exception. Understanding the unique sounds and pronunciation rules of your chosen language will significantly improve your comprehension and speaking abilities.
5.1. Unique Sounds and Pronunciation Rules
Many Native American languages have sounds that are not found in English. Learning these sounds and their associated pronunciation rules is essential for accurate pronunciation.
Unique Sounds
The following table lists some common unique sounds found in Native American languages, along with their phonetic symbols (IPA) and approximate English equivalents:| Sound | IPA | English Equivalent ||—|—|—|| Glottal Stop | ʔ | The “uh-oh” sound || Lateral Fricative | ɬ | Similar to the “th” sound in “thin” || Retroflex Stop | ʈ | Similar to the “t” sound in “tree” but with the tongue curled back || Uvular Stop | q | Similar to the “k” sound but produced further back in the throat |
Pronunciation Rules
The pronunciation of these unique sounds often depends on the context within a word or phrase. For example, the glottal stop (ʔ) can be used to indicate a pause or a change in tone. The lateral fricative (ɬ) may be pronounced differently depending on its position in a word.
Common Sounds with Different Pronunciation Rules
Even common sounds like vowels and consonants can be pronounced differently in Native American languages compared to English. For example, some languages may have vowel sounds that are longer or shorter than their English counterparts, or they may have different vowel qualities.
Consonant clusters, such as “th” or “sh,” may also be pronounced differently.
5.2. Examples of Common Sounds and their Pronunciation
The following table provides examples of common sounds in a specific Native American language (you can replace this with your chosen language), along with their phonetic symbols (IPA) and example words:| Sound | IPA | Example Word ||—|—|—|| /p/ | p | pē || /t/ | t | tā || /k/ | k | kō || /m/ | m | mā || /n/ | n | nā || /ŋ/ | ŋ | ŋā || /i/ | i | ī || /e/ | e | ē || /a/ | a | ā || /o/ | o | ō || /u/ | u | ū |It is important to note that these are just examples, and the actual pronunciation of these sounds may vary depending on the specific language and dialect.
5.3. Intonation and Stress
Intonation and stress play a significant role in Native American languages, just as they do in English. Intonation refers to the rise and fall of the voice, while stress refers to the emphasis placed on certain syllables within a word or sentence.
Intonation Patterns
Intonation patterns can convey a variety of meanings, including questions, statements, and emotions. For example, a rising intonation at the end of a sentence might indicate a question, while a falling intonation might indicate a statement.
Stress Placement
Stress placement in Native American languages can also affect the meaning of a word or sentence. For example, the word “á-ni-ma” (animal) in the Cherokee language has stress on the first syllable, while the word “á-ni-ma” (to be) has stress on the second syllable.
5.4. Writing
The pronunciation rules and intonation patterns of a language can also affect its written form. Many Native American languages have their own unique writing systems, which may include diacritics or special characters to represent sounds that are not found in the English alphabet.
Differences between Spoken and Written Forms
The differences between the spoken and written forms of a language can sometimes lead to confusion for learners. For example, a single letter in the written form may represent multiple sounds in the spoken form, or vice versa.
Grammar and Syntax

The grammar and syntax of Native American languages can vary greatly, but there are some common features that distinguish them from English. Understanding these differences is crucial for learning and speaking these languages effectively.
Word Order
Native American languages often have different word order structures than English. While English follows a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) order, many Native American languages use a Subject-Object-Verb (SOV) order. For example, in English, we say “The dog chased the cat,” while in a language like Navajo, the sentence would be structured as “The dog the cat chased.”
- Subject-Verb-Object (SVO): This is the most common word order in the world, including English. The subject performs the action, followed by the verb, and then the object receives the action.
Example: The cat chased the mouse.
- Subject-Object-Verb (SOV): This word order is common in many Native American languages. The subject performs the action, followed by the object, and then the verb.
Example: The cat the mouse chased.
- Verb-Subject-Object (VSO): This word order is less common but found in some Native American languages. The verb is placed first, followed by the subject and then the object.
Example: Chased the cat the mouse.
Vocabulary and Cultural Context
Learning a Native American language is not just about memorizing words; it’s about understanding the cultural context behind them. Words are not simply containers of meaning but reflections of a people’s history, values, and worldview. This section will explore common vocabulary and phrases, delve into their cultural significance, and highlight the importance of understanding cultural context in language learning.
Cultural Significance of Vocabulary
Words in Native American languages often hold deep cultural meaning and reflect the unique perspectives of the respective cultures. For instance, the Lakota language has no direct translation for the English word “time.” Instead, Lakota speakers use phrases that emphasize the cyclical nature of time, reflecting their connection to the natural world and the seasons.
This example illustrates how language can encapsulate a culture’s understanding of the world and its place within it.
Understanding Cultural Context
Understanding the cultural context of Native American languages is crucial for effective communication and meaningful learning. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Respect for Elders:Many Native American cultures place a high value on respecting elders and their wisdom. This is often reflected in language through specific terms of address and honorifics used when speaking to older individuals.
- Importance of Community:Native American cultures emphasize the importance of community and interconnectedness. This is reflected in language through words and phrases that emphasize shared experiences, responsibilities, and collective identity.
- Connection to Nature:Many Native American languages have rich vocabularies related to the natural world, reflecting a deep connection to the land and its resources. Understanding these terms can provide insights into the culture’s relationship with the environment and its understanding of the natural world.
Common Vocabulary and Phrases
Here are some common vocabulary words and phrases across various Native American languages:
- Greetings:
- “Hello”(in various languages):
- “How”(Cherokee)
- “Ya’at’eeh”(Navajo)
- “Anishinaabe”(Ojibwe)
- “Thank you”(in various languages):
- “Do-gwa-se-di”(Cherokee)
- “A’hee’ee’(Navajo)
- “Miigwetch”(Ojibwe)
- “Hello”(in various languages):
- Family:
- “Mother”(in various languages):
- “Ani”(Cherokee)
- “E’e'”(Navajo)
- “Nookomis”(Ojibwe)
- “Father”(in various languages):
- “Ata”(Cherokee)
- “Taa'”(Navajo)
- “Mishoomis”(Ojibwe)
- “Mother”(in various languages):
- Basic Phrases:
- “I am”(in various languages):
- “Ani-gv-di”(Cherokee)
- “Shí éí”(Navajo)
- “Aaniin”(Ojibwe)
- “You are”(in various languages):
- “Wado-gv-di”(Cherokee)
- “Ní éí”(Navajo)
- “Giin”(Ojibwe)
- “I am”(in various languages):
Cultural Significance of Phrases
Specific phrases in Native American languages often carry cultural significance beyond their literal meaning. For example, in the Lakota language, the phrase “Wopila Tanka” (meaning “Thank you, Great Spirit”) is not simply an expression of gratitude but a recognition of the interconnectedness of all things and the power of the divine.
“Wopila Tanka”
Thank you, Great Spirit (Lakota)
Similarly, in the Navajo language, the phrase “Yá’át’ééh” (meaning “Hello” or “Good day”) is not just a greeting but an expression of respect and well-wishes for the person being addressed.
“Yá’át’ééh”
Hello, Good day (Navajo)
These examples illustrate how phrases in Native American languages can convey cultural values and perspectives that go beyond the literal meaning of the words.
Engaging with the Language Community

Learning a Native American language is not just about mastering grammar and vocabulary. It’s about connecting with the living culture and heritage that the language represents. Engaging with the language community is crucial for deepening your understanding and appreciation of the language and its people.
Online and Offline Communities
Online and offline communities provide valuable opportunities to connect with speakers and learners of Native American languages.
- Online Forums and Social Media Groups:Many online forums and social media groups are dedicated to specific Native American languages. These platforms allow you to interact with speakers, ask questions, and share resources. Examples include Facebook groups, Reddit communities, and dedicated language learning websites.
- Language Immersion Programs:Some Native American communities offer language immersion programs that provide intensive language learning experiences. These programs often include opportunities to interact with native speakers and learn about the culture and traditions associated with the language.
- Tribal Colleges and Universities:Many tribal colleges and universities offer language courses and programs, providing a platform to connect with students, faculty, and community members who are passionate about preserving and revitalizing their language.
Benefits of Interacting with Native Speakers
Interacting with native speakers offers numerous benefits for language learners.
- Authentic Pronunciation and Fluency:Native speakers can provide guidance on pronunciation, intonation, and rhythm, helping you develop a more natural and authentic sound.
- Cultural Context and Nuances:Native speakers can explain the cultural context and nuances of the language, enriching your understanding and appreciation of its meaning.
- Motivation and Support:Connecting with other learners and speakers can provide motivation and support, making the language learning journey more enjoyable and rewarding.
Respectful Communication and Cultural Sensitivity
When engaging with the Native American language community, it’s essential to approach interactions with respect and sensitivity.
- Use Appropriate Language:Avoid using disrespectful or offensive language, including terms that may be considered derogatory or outdated. Always ask for clarification if you are unsure about the appropriate terminology.
- Respect Cultural Practices:Learn about the cultural practices and traditions associated with the language you are learning. This includes understanding the role of language in ceremonies, storytelling, and everyday life.
- Be Patient and Humble:Language learning takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and others, and be willing to learn from your mistakes. Remember that you are a guest in the language community and should approach interactions with humility and respect.
Maintaining Motivation and Progress
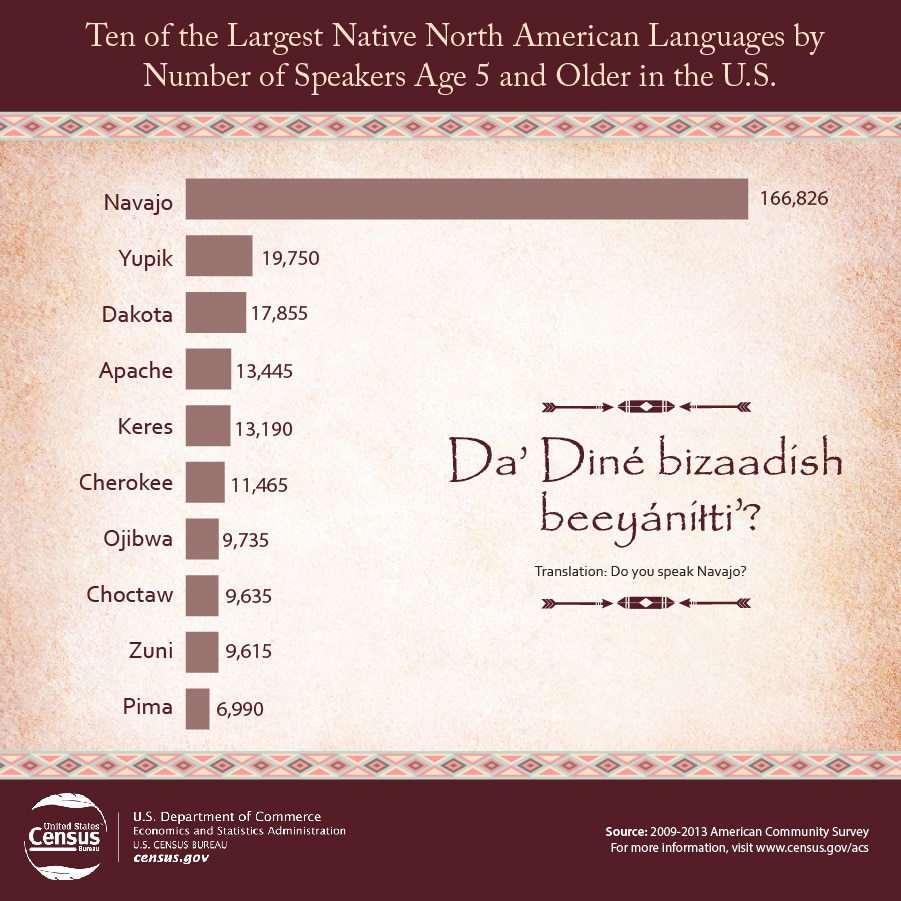
Learning a Native American language is a journey, not a sprint. It takes time, dedication, and perseverance. While it can be incredibly rewarding, it’s also easy to lose steam along the way. To ensure you stay motivated and make progress, it’s essential to have a clear plan and strategies for overcoming challenges.
Setting Realistic Goals and Tracking Progress
Setting realistic goals is crucial for staying motivated and tracking progress. It’s important to break down your learning journey into smaller, achievable milestones. Instead of aiming to become fluent in a year, set a goal of learning the basics of greetings and introductions, or mastering a specific grammatical concept.
- Start with a simple goal, such as learning the alphabet or basic greetings.
- Set a timeline for achieving each goal, but be flexible and adjust it as needed.
- Keep a journal or log to track your progress and celebrate your achievements.
Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning a Native American language can be challenging, especially if you’re unfamiliar with the language family or have limited access to resources. However, there are strategies you can use to overcome these obstacles and stay motivated.
- Find a language partner or study group for support and encouragement.
- Set aside dedicated time for learning, even if it’s just 15-20 minutes a day.
- Reward yourself for reaching milestones, and don’t be afraid to take breaks when you need them.
- Connect with the language community and learn about the culture and history associated with the language.
Finding Joy and Satisfaction in the Language Learning Journey
The most important thing is to find joy in the process. Learning a Native American language is a journey of discovery and connection. It’s an opportunity to learn about a different culture, expand your worldview, and appreciate the richness and diversity of human languages.
Learning a Native American language can be a rewarding experience, connecting you to a rich cultural heritage. You can find resources online and in communities, but remember, learning any language takes time and dedication. Think about what motivates you to learn, and consider the story of Hannah, a woman who poured her heart out in prayer, as a reminder that even in difficult times, we can find strength and hope.
What can we learn from Hannah’s prayer ? It might give you the inspiration you need to keep learning and growing, both in language and in life.
- Immerse yourself in the language and culture through music, art, literature, and film.
- Find opportunities to use the language in real-life situations, even if it’s just ordering food at a restaurant or greeting someone in the street.
- Celebrate your progress and acknowledge your achievements, no matter how small they may seem.
Cultural Immersion and Understanding
Learning a Native American language is more than just memorizing words and grammar rules; it’s about immersing yourself in the rich cultural tapestry that has shaped the language. Imagine yourself as a student in a foreign country, where the language you’re learning is spoken.
You’ll encounter customs, traditions, and perspectives that are different from your own, which can be challenging at first, but also incredibly rewarding.
Cultural Challenges and Overcoming Them
Imagine yourself stepping into a world where greetings are expressed through a gentle touch, where meals are shared with an extended family, and where storytelling is an integral part of everyday life. This immersion into a different culture will likely present you with challenges, such as:
- Understanding nonverbal communication: Gestures, facial expressions, and body language can have different meanings in different cultures. For example, what may be considered a polite gesture in one culture might be seen as rude in another.
- Navigating social interactions: The way people interact with each other can vary significantly. For instance, direct eye contact may be considered disrespectful in some cultures, while in others, it is expected.
- Understanding cultural values and beliefs: Different cultures have different values and beliefs that shape their language and behavior. These differences can lead to misunderstandings if you are not aware of them.
However, learning about the culture can help you overcome these challenges. By understanding the cultural context behind the language, you can develop a deeper appreciation for its nuances and subtleties. For instance, learning about the importance of storytelling in Native American cultures can help you understand why certain phrases or expressions are used in specific contexts.
Cultural Practices and Their Influence on Language
One specific cultural practice that influences many Native American languages is the concept of “respect” for the natural world. This respect is often reflected in the language itself, through specific vocabulary, grammar, and idioms. For example, in the Lakota language, there are distinct terms for different types of trees, animals, and natural phenomena, reflecting a deep understanding and appreciation for the natural world.
The use of honorifics and respectful terms when addressing elders or spiritual figures further demonstrates this cultural value.
Comparing Cultural Values and Beliefs, How to learn native american languages
Let’s compare the cultural values and beliefs of a Native American culture with your own culture. This comparison can help you understand how cultural differences impact language use. For instance, you might find that Native American cultures place a higher value on community and cooperation, while your own culture may emphasize individualism and competition.
This difference can be reflected in the way people communicate, with Native American cultures often valuing consensus-building and indirect communication, while your own culture may prioritize directness and assertiveness.
Cultural Etiquette and Language Use
Imagine you are writing a guidebook for travelers visiting a Native American community. In your guidebook, you would include a section on cultural etiquette, emphasizing the importance of respectful language use. For example, you would advise travelers to avoid using slang or informal language when addressing elders or spiritual leaders.
You would also recommend learning basic phrases of greeting and farewell, such as “how are you” and “thank you,” which are considered polite in most Native American cultures.
Cultural Events and Language Preservation
Many Native American communities have specific cultural events or celebrations that play a crucial role in preserving and transmitting their knowledge and traditions. These events often involve storytelling, songs, and rituals, all of which are deeply embedded in the language.
For example, the powwow, a traditional gathering of Native American people, is a vibrant celebration of culture, history, and identity. The songs, dances, and stories shared at powwows are often in the Native language, helping to preserve the language and cultural traditions for future generations.
Language Revitalization and Preservation

Language revitalization is a crucial endeavor in preserving the cultural heritage of Native American communities. It involves efforts to revive and maintain languages that are facing endangerment due to various factors, including assimilation policies, colonization, and societal pressures. This process is not just about linguistic preservation but also about reclaiming cultural identity, strengthening community bonds, and ensuring the continuity of knowledge systems.
Challenges Faced by Native American Languages
Language revitalization efforts often encounter significant challenges. These challenges can stem from historical and social factors, limited resources, and the complexities of language transmission. Understanding these challenges is essential for developing effective revitalization strategies.
- Limited Number of Speakers:Many Native American languages have a dwindling number of fluent speakers, particularly among younger generations. This is often due to the historical suppression of indigenous languages and the dominance of English in education and society.
- Lack of Resources:The availability of resources for language learning, such as dictionaries, grammar books, and online materials, is often limited for endangered languages. This lack of resources can hinder language acquisition and make it challenging for learners to develop fluency.
- Negative Attitudes Towards the Language:Some communities may have negative perceptions of their indigenous language, viewing it as outdated, unimportant, or even a barrier to economic opportunities. These attitudes can discourage language learning and hinder revitalization efforts.
- Limited Funding:Securing funding for language revitalization projects can be difficult, especially in the face of competing priorities and limited resources. This can make it challenging to implement programs, develop materials, and support language learners.
Potential Solutions for Language Revitalization
Addressing the challenges faced by Native American languages requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on community engagement, resource development, and promoting positive attitudes towards the language.
- Community Involvement:Revitalization efforts should be driven by the community itself. This involves engaging elders, fluent speakers, and community members in all aspects of the process, from planning and curriculum development to teaching and resource creation.
- Developing Comprehensive Learning Resources:Creating accessible and engaging language learning resources is crucial for revitalization. This can include dictionaries, grammar books, online platforms, mobile apps, and audio recordings. These resources should be tailored to the specific needs of learners, considering their age, language proficiency, and learning styles.
- Immersion Programs:Immersion programs, where learners are exposed to the language in a natural setting, can be highly effective in fostering language acquisition. These programs can be implemented in schools, community centers, or even residential settings.
- Intergenerational Language Transmission:Encouraging intergenerational language transmission, where younger generations learn the language from older speakers, is vital for the long-term sustainability of revitalization efforts. This can be facilitated through family-based language learning programs, storytelling sessions, and cultural events.
- Promoting the Cultural Significance of the Language:Highlighting the cultural significance and beauty of the language through storytelling, music, art, and other forms of cultural expression can help change negative attitudes and foster pride in the language.
- Partnerships for Funding:Collaborating with community organizations, universities, government agencies, and private foundations can help secure funding for revitalization projects. This can involve grant writing, fundraising events, and advocacy for increased government support for language revitalization.
Successful Language Revitalization Programs
Several successful language revitalization programs for Native American languages have demonstrated the effectiveness of community-based approaches, educational strategies, and government support.
- The Cherokee Nation Language Program:The Cherokee Nation Language Program is a comprehensive language revitalization effort that has been successful in increasing the number of Cherokee speakers. The program uses a multi-pronged approach that includes language immersion schools, community language classes, online learning resources, and cultural events.
Key factors contributing to its success include strong community involvement, a focus on intergenerational language transmission, and the development of a comprehensive curriculum.
- The Hawaiian Language Revitalization Movement:The Hawaiian language, once facing extinction, has experienced a significant resurgence thanks to the efforts of the Hawaiian Language Revitalization Movement. The movement has successfully integrated the language into schools, government institutions, and cultural practices. Key factors contributing to its success include a strong cultural identity movement, government support, and the development of a comprehensive language curriculum.
Impact of Language Revitalization on Cultural Heritage
Language revitalization is not just about linguistic preservation but also about reclaiming and maintaining cultural identity. Language is an integral part of culture, carrying within it knowledge systems, traditions, and values. Language loss can have a profound impact on cultural practices, traditions, and knowledge systems.
- Loss of Traditional Knowledge:Native American languages often contain specialized knowledge about plants, animals, medicine, and other aspects of the natural world. The loss of these languages can lead to the loss of this valuable knowledge, which can have implications for environmental sustainability, health, and cultural practices.
- Erosion of Cultural Identity:Language is a key component of cultural identity. When a language is lost, it can lead to a sense of disconnection from cultural heritage and a weakening of community bonds.
- Disruption of Oral Traditions:Many Native American cultures rely heavily on oral traditions for storytelling, history, and cultural transmission. The loss of a language can lead to the loss of these traditions and the knowledge they contain.
Resources for Further Learning
Learning a Native American language is an enriching journey that extends beyond textbooks and online courses. To delve deeper into the intricacies of these languages and their cultural contexts, explore the wealth of resources available, including books, websites, and organizations dedicated to Native American languages and cultures.
Books
A vast collection of books offers insights into various aspects of Native American languages, from grammar and vocabulary to cultural context and revitalization efforts.
- “Native Languages of the Americas”by Lyle Campbell: This comprehensive work provides an overview of the linguistic diversity of the Americas, exploring the history, classification, and characteristics of Native American languages.
- “A Grammar of the Cherokee Language”by William H. Gilbert: This detailed grammar book offers a thorough exploration of the Cherokee language, covering its phonology, morphology, and syntax.
- “The Lakota Language: A Grammar and Dictionary”by Boas and Deloria: This classic resource provides a comprehensive analysis of the Lakota language, including its grammar, vocabulary, and cultural context.
Websites
Numerous websites provide valuable resources for learning Native American languages, offering online dictionaries, language learning materials, and information about language revitalization efforts.
- FirstVoices: This website offers a collection of online dictionaries, language learning materials, and cultural resources for various Native American languages.
- Native Languages of the Americas: This website provides information about the linguistic diversity of the Americas, including language families, maps, and resources for language learning.
- The Language Conservancy: This organization is dedicated to preserving and revitalizing endangered languages, including Native American languages. Their website offers resources for language learners, educators, and communities.
Organizations
Several organizations are dedicated to promoting the preservation and revitalization of Native American languages and cultures. These organizations offer resources, support, and opportunities for language learners and communities.
- The National Museum of the American Indian: This museum houses a collection of artifacts and exhibits related to Native American cultures, including language resources and educational programs.
- The Native American Languages Act (NALA): This federal law promotes the preservation and revitalization of Native American languages, providing funding and support for language programs and initiatives.
- The American Indian Language Development Institute (AILDI): This organization provides training and resources for language teachers and revitalization efforts, offering workshops, conferences, and online resources.
Conferences and Workshops
Conferences and workshops provide opportunities for language learners, researchers, and community members to connect, share knowledge, and engage in discussions about Native American languages and cultures.
| Resource Name | Type | Language | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| The National Native American Languages Conference | Conference | Various | Language revitalization, education, and cultural preservation |
| The American Indian Language Development Institute (AILDI) Annual Conference | Conference | Various | Language teaching, curriculum development, and community-based language programs |
| The Indigenous Languages Institute (ILI) Workshops | Workshop | Various | Language documentation, revitalization, and community engagement |
Respectful Language Use
Learning a Native American language is an enriching experience, but it’s crucial to approach it with respect and sensitivity. The languages you’re learning are not just tools for communication, but also deeply interwoven with cultural traditions, beliefs, and identities.
Language Sovereignty
Native American languages are not simply relics of the past; they are living, breathing languages that are vital to the cultural survival and identity of Indigenous communities. The concept of language sovereignty recognizes the right of Native American communities to control their own languages, including who has access to them and how they are used.
This means that learning a Native American language should be done with respect for the language’s cultural significance and with the understanding that you are a guest in the language community.
Respectful Language Use
Here are some ways to ensure respectful language use:
- Seek Permission:Before you begin learning a Native American language, it’s important to seek permission from the language community. This can be done by contacting a language revitalization organization or a tribal elder. This ensures you are not appropriating the language or its cultural significance.
- Avoid Appropriation:Cultural appropriation occurs when people adopt elements of a culture that is not their own without understanding or respecting its significance. This can be harmful and disrespectful. When learning a Native American language, avoid using it in a way that trivializes or misrepresents its cultural context.
- Learn from Native Speakers:The best way to learn a Native American language is from a native speaker. This allows you to learn the language in its authentic context and to gain a deeper understanding of its cultural significance. Many language revitalization organizations offer language classes taught by native speakers.
- Respect Language Etiquette:Every language has its own set of etiquette rules. For example, in some Native American languages, it is considered disrespectful to address an elder by their first name. It’s important to learn and respect these cultural norms.
Examples of Respectful Language Use
- Use the proper terminology:Avoid using terms like “Indian” or “tribe” unless you are specifically referring to a particular group. Instead, use the specific tribal name or the term “Native American.”
- Be mindful of your language:Avoid using language that is disrespectful or offensive to Native American people. This includes using stereotypes or making generalizations about Native American culture.
- Show respect for cultural traditions:If you are invited to a cultural event, dress appropriately and be respectful of the traditions of the community. Avoid taking photos or videos without permission.
The Importance of Native American Languages
Learning and preserving Native American languages is a vital act of cultural survival, a way to honor the past and ensure a vibrant future for Indigenous communities. These languages are more than just words; they are living repositories of knowledge, traditions, and identity, connecting generations and safeguarding a rich cultural heritage.
A Young Learner’s Perspective
Today, I sat in class, listening to the sounds of my ancestral language. It felt strange, like a forgotten melody returning after years of silence. I’m learning Lakota, the language of my ancestors, and it’s a journey filled with both challenges and rewards. It’s hard to grasp the grammar, the sounds are unfamiliar, and I often feel like I’m stumbling through the words. But each time I understand a new phrase, a new concept, it feels like a piece of my identity is coming back to me. Learning Lakota isn’t just about learning words; it’s about understanding the world through a different lens, appreciating the wisdom and values passed down through generations. It’s about feeling connected to a community, a history, and a spirit that has been silenced for too long. I know there will be many more challenges ahead, but I’m determined to learn, to understand, and to help revitalize this beautiful language.
15. Future Directions
The future of Native American languages is full of potential and promise. As we look ahead, we can envision a world where these languages are not only preserved but also revitalized, thriving in communities and enriching the lives of future generations.
This vision requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing innovative language learning resources, the power of technology, and a collective commitment to language revitalization.
15.1 Language Learning Resources and Initiatives
To make learning Native American languages as accessible as learning Spanish or French, we need to develop innovative language learning resources that cater to diverse learning styles and preferences.
- Interactive online platforms can provide engaging and personalized language learning experiences. These platforms can incorporate features such as adaptive learning algorithms, interactive exercises, multimedia content, and virtual language communities. Imagine a platform that offers interactive stories, games, and simulations, immersing learners in the language and culture.
- Mobile apps can make language learning accessible anytime, anywhere. Apps can provide bite-sized lessons, interactive quizzes, audio recordings, and offline access to language resources. Imagine an app that utilizes augmented reality to bring the language to life in the real world, allowing learners to interact with virtual speakers and explore cultural environments.
- Gamified learning experiences can make language learning fun and engaging. Games can incorporate language learning objectives into interactive challenges, puzzles, and quests. Imagine a game that allows learners to explore a virtual world, interact with characters, and complete tasks using the target language.
- Partnerships with educational institutions can provide structured language learning opportunities. Schools and universities can offer courses, workshops, and immersion programs, fostering language learning within a formal educational setting. Imagine a curriculum that integrates Native American languages into existing subjects, such as history, literature, and art, creating a more holistic and engaging learning experience.
A centralized online repository of Native American language resources would be invaluable for learners of all levels. This repository could include:
- Dictionaries: Comprehensive dictionaries that provide definitions, examples, and cultural context for words and phrases.
- Grammars: Clear and concise explanations of grammatical rules, structures, and usage.
- Audio recordings: Authentic audio recordings of speakers, including traditional stories, songs, and everyday conversations.
- Video materials: Videos that showcase language use in real-world contexts, including cultural events, ceremonies, and community gatherings.
This repository could be organized by language family, dialect, or region, making it easy for learners to find the resources they need. It could also include features such as search functions, interactive maps, and user-generated content, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
15.2 Technology and Language Revitalization
Emerging technologies have the potential to revolutionize language revitalization efforts.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to develop language learning tools, such as chatbots, voice assistants, and personalized learning platforms. AI can also be used to analyze language data, identify patterns, and create resources that support language learning and preservation.
- Virtual reality (VR) can create immersive language learning experiences. VR environments can simulate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice language skills in a safe and engaging way. Imagine a VR experience that takes learners to a traditional Native American village, where they can interact with virtual speakers, participate in cultural activities, and learn about the language and culture.
Social media and online communities can play a vital role in language revitalization.
- These platforms can connect speakers, fostering a sense of community and shared identity. Imagine a social media group where speakers can share stories, songs, and language resources, creating a virtual space for language revitalization.
- Online communities can provide a platform for language learning and practice. Learners can connect with speakers, participate in online forums, and share their progress with others.
FAQ Corner
What is the best way to find a Native American language teacher?
Look for language programs offered by tribal colleges, community organizations, or language immersion schools. You can also connect with Native American language speakers through online forums, social media groups, or language exchange platforms.
Are there any online resources for learning Native American languages?
Yes, there are a growing number of online resources available, including dictionaries, grammar guides, language learning apps, and websites dedicated to specific languages. The National Museum of the American Indian and the First Peoples’ Cultural Council offer valuable online resources.
How can I be respectful when learning a Native American language?
It’s crucial to approach language learning with respect and sensitivity. Avoid cultural appropriation and seek guidance from Native American language speakers and communities. Remember, languages are deeply intertwined with cultural identity and traditions.
What is the best way to learn pronunciation in a Native American language?
Focus on listening to native speakers, paying close attention to sounds, intonation, and stress patterns. Use online resources, such as audio recordings and phonetic transcriptions, to help you practice pronunciation.