How to learn native american language – Learning a Native American language is a journey of discovery, not just of a new way to speak, but of a rich tapestry of culture, history, and identity. It’s a chance to connect with the stories, traditions, and perspectives of Indigenous peoples across North America.
But where do you begin?
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of how to learn Native American languages, from understanding their diversity and significance to choosing a language, exploring learning strategies, and immersing yourself in cultural contexts. It’s a path filled with challenges, but also immense rewards, offering a unique opportunity to learn, grow, and contribute to the preservation of these vital languages.
Understanding Native American Languages
Native American languages represent a rich tapestry of linguistic diversity, with a fascinating history and profound cultural significance. Exploring these languages offers a unique window into the history, beliefs, and traditions of Indigenous communities across North and South America.
Diversity of Native American Languages
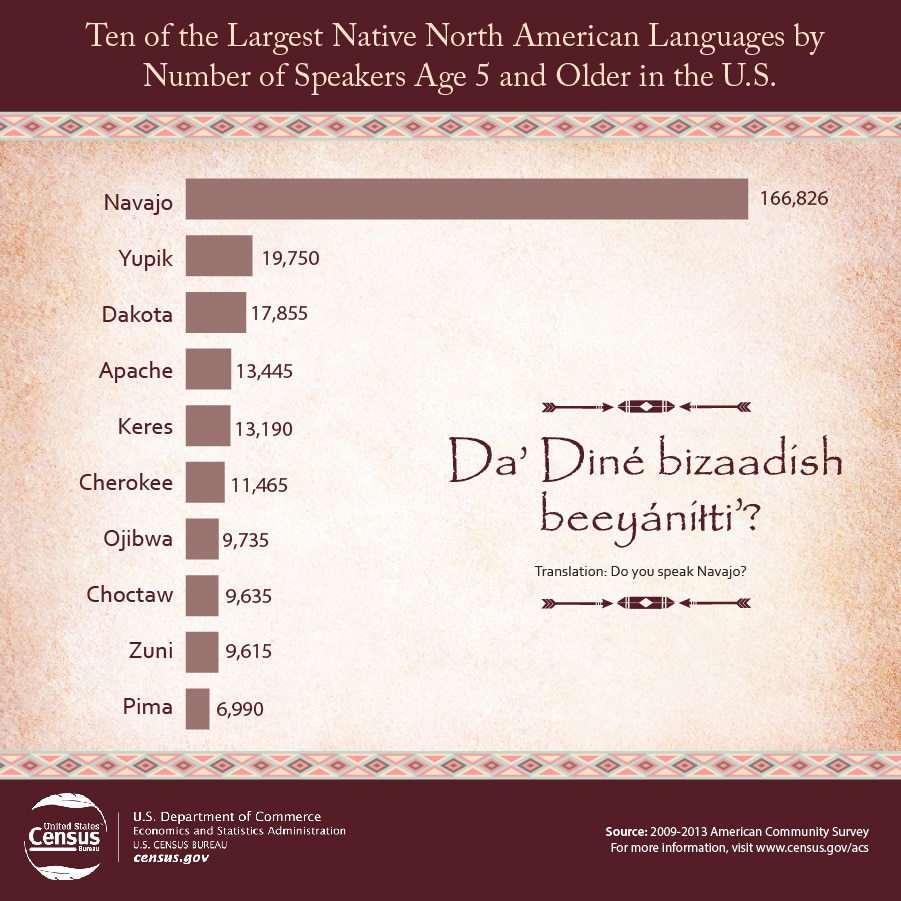
Native American languages are remarkably diverse, with hundreds of distinct languages spoken across the Americas. Understanding this diversity requires examining the various language families and their geographic distribution.
- Language Families: Native American languages are grouped into distinct language families, reflecting shared ancestry and historical connections. Some of the major language families include:
- Algonquian: This family is widely distributed across eastern and central North America, with languages like Ojibwe, Cree, and Blackfoot.
It encompasses approximately 40 languages.
- Athabaskan: The Athabaskan family extends from Alaska to the southwestern United States, with languages like Navajo, Apache, and Dene. It comprises around 50 languages.
- Iroquoian: The Iroquoian family is found primarily in the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada, with languages like Mohawk, Oneida, and Cherokee. It includes approximately 10 languages.
- Siouan: The Siouan family is distributed across the central and eastern United States, with languages like Lakota, Dakota, and Osage. It encompasses about 15 languages.
- Uto-Aztecan: The Uto-Aztecan family is found in the southwestern United States and Mexico, with languages like Nahuatl, Hopi, and Shoshone. It includes over 100 languages.
- Salishan: The Salishan family is primarily located in the Pacific Northwest, with languages like Salish, Squamish, and Coeur d’Alene. It encompasses approximately 20 languages.
- Tupi: The Tupi family is found in South America, particularly in Brazil, with languages like Tupi, Guarani, and Nheengatu. It includes over 50 languages.
- Quechuan: The Quechuan family is widespread in the Andes region of South America, with languages like Quechua, Aymara, and Jaqaru. It encompasses over 40 languages.
- Algonquian: This family is widely distributed across eastern and central North America, with languages like Ojibwe, Cree, and Blackfoot.
- Geographic Distribution: The geographic distribution of Native American languages is a testament to the diverse migrations and historical interactions of Indigenous peoples.
- Areas of high linguistic diversity: The Pacific Northwest, the Southwest, and the Eastern Woodlands of North America are known for their high concentration of distinct languages.
- Areas with fewer languages: The Great Plains, the Arctic, and parts of South America have fewer languages, reflecting factors like historical migrations, contact with other cultures, and environmental conditions.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Native American languages hold immense historical and cultural significance, serving as repositories of knowledge, traditions, and identity.
- Oral Traditions and Storytelling: Oral traditions have been central to Native American cultures for millennia, with language serving as the primary vehicle for preserving stories, myths, and historical knowledge.
- Storytelling: Language plays a vital role in storytelling, with narratives often reflecting cultural values, beliefs, and ancestral wisdom.
Stories are passed down through generations, shaping cultural identity and providing insights into the natural world and human relationships.
- Mythology: Myths and legends are often encoded in language, providing explanations for natural phenomena, social structures, and spiritual beliefs. These narratives are often rich in symbolism and metaphors, offering profound insights into the worldview of Indigenous communities.
- Storytelling: Language plays a vital role in storytelling, with narratives often reflecting cultural values, beliefs, and ancestral wisdom.
- Language Revitalization and Preservation: Many Native American languages face significant challenges due to colonization, assimilation, and language shift.
- Challenges: The decline of Native American languages is a result of historical and ongoing pressures, including forced assimilation policies, language suppression, and the dominance of European languages.
These factors have led to a significant reduction in the number of speakers of many Native American languages.
- Revitalization Efforts: Communities across the Americas are working to revitalize and preserve their languages through various initiatives.
- Language Immersion Programs: These programs provide immersive language learning experiences for children and adults, fostering fluency and cultural understanding.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Community-led efforts, such as language classes, cultural events, and storytelling sessions, are essential for revitalizing languages and promoting cultural continuity.
- Digital Resources: Online dictionaries, language learning apps, and digital archives are providing new avenues for language preservation and access.
- Challenges: The decline of Native American languages is a result of historical and ongoing pressures, including forced assimilation policies, language suppression, and the dominance of European languages.
Examples of Native American Languages and Unique Features
Exploring specific Native American languages reveals the remarkable diversity and unique features of these linguistic systems.
- Navajo (Diné bizaad):
- Language Family: Athabaskan
- Geographic Distribution: Southwestern United States (Arizona, New Mexico, Utah)
- Unique Features: Navajo has a complex grammar with a rich system of prefixes and suffixes, allowing for nuanced expression. It also features a distinctive sound system with a wide range of consonant and vowel sounds. The language has a written form, developed during World War II for use in military communications.
- Example: “Yá’át’éeh!” (Hello!)
Navajo is the most spoken Native American language in the United States, with a rich oral tradition and a strong cultural identity. It played a significant role in the success of the Navajo Code Talkers during World War II, demonstrating its unique features and importance in wartime communication.
- Cherokee (Tsalagi Gawonihisdi):
- Language Family: Iroquoian
- Geographic Distribution: Southeastern United States (North Carolina, Oklahoma)
- Unique Features: Cherokee is known for its unique syllabary, a writing system developed by Sequoyah in the early 19th century. The syllabary consists of 85 symbols, each representing a syllable, making it a relatively easy system to learn. The language also features a complex grammatical structure, with a system of prefixes and suffixes.
- Example: “Aniyvitsa!” (Thank you!)
Cherokee has a rich history and cultural significance, with a strong connection to the Cherokee Nation. The development of the Cherokee syllabary was a significant achievement in language preservation, allowing for the documentation and transmission of Cherokee language and culture.
- Inuktitut:
- Language Family: Inuit-Unangan
- Geographic Distribution: Arctic regions of Canada, Greenland, and Alaska
- Unique Features: Inuktitut is a polysynthetic language, meaning that it uses complex words formed by combining multiple morphemes (meaningful units). It also features a rich system of suffixes and a distinctive sound system, with a large number of consonant sounds.
Learning a Native American language can be a rewarding but challenging journey. It’s similar to learning any new language, requiring dedication and immersion. You might wonder, how does that compare to learning an instrument like the banjo? Well, how difficult is it to learn the banjo depends on your natural aptitude and commitment to practice.
Just like with languages, the key to mastering the banjo is consistent effort and a passion for the craft.
- Example: “Nunavut” (Our Land)
Inuktitut is a vital language for the Inuit people, reflecting their deep connection to the Arctic environment and their unique cultural traditions. It is spoken in various dialects across the Arctic, with efforts underway to preserve and revitalize the language in the face of language shift.
Finding Learning Resources
Learning a Native American language can be an enriching experience, but finding the right resources is crucial. There are various online platforms, apps, and institutions dedicated to language preservation and revitalization.
Online Resources
Online resources offer a convenient and accessible way to learn Native American languages. Here are some reputable websites:
- FirstVoices:This website provides a wealth of information about Indigenous languages, including dictionaries, language learning materials, and resources for educators. It’s a collaborative project that includes contributions from various Indigenous communities.
- Native Languages of the Americas:This website offers a comprehensive database of Native American languages, including information on language families, language revitalization efforts, and resources for learners.
- University of California Berkeley Language Archives:This archive houses a vast collection of recordings, texts, and other materials related to Native American languages, making it a valuable resource for researchers and language learners.
Language Learning Apps and Software
There are also several language learning apps and software programs specifically designed for Native American languages.
- Duolingo:This popular language learning app offers courses for several Native American languages, including Navajo, Cherokee, and Hawaiian.
- Memrise:This app uses flashcards and spaced repetition to help users learn vocabulary and grammar. It offers courses for a few Native American languages, such as Cherokee and Lakota.
Organizations and Institutions
Many organizations and institutions offer Native American language classes, workshops, and other learning opportunities.
- Native American Language Immersion Schools:These schools provide immersive language learning experiences for students of all ages. They often use traditional teaching methods and emphasize cultural immersion.
- Tribal Colleges and Universities:Many tribal colleges and universities offer Native American language courses and programs, providing access to local knowledge and expertise.
- Language Revitalization Organizations:These organizations work to preserve and revitalize Native American languages through various initiatives, including language classes, workshops, and community outreach programs.
Choosing a Language to Learn
Selecting a Native American language to learn is a rewarding journey that opens doors to rich cultures and unique perspectives. Many factors influence this choice, from personal interests to language availability and learning goals.
Factors to Consider
It’s important to consider various factors when selecting a Native American language to learn. These include:
- Personal Interests:What aspects of Native American culture or history pique your interest? For example, if you’re fascinated by the art and traditions of the Navajo people, learning Navajo might be a good choice.
- Language Availability:Not all Native American languages have readily available learning resources. Research the availability of language courses, dictionaries, and other materials before making your decision.
- Learning Goals:Are you aiming for fluency, basic communication, or a deeper understanding of the language and its cultural context? Your goals will influence the amount of time and effort you’re willing to invest.
Benefits of Learning a Specific Language
Learning a specific Native American language offers numerous benefits:
- Cultural Immersion:Language learning provides a window into the cultural values, beliefs, and traditions of the people who speak it.
- Preservation of Indigenous Languages:Many Native American languages are endangered, and learning them helps preserve their cultural heritage.
- Career Advancement:Learning a Native American language can open doors to career opportunities in education, cultural preservation, and government.
Choosing a Language Based on Difficulty and Resources
The difficulty of learning a Native American language varies depending on its structure, grammar, and availability of resources.
- Language Structure:Languages with complex grammar or sounds that are unfamiliar to English speakers may be more challenging to learn.
- Availability of Resources:Languages with abundant learning materials, such as textbooks, online courses, and language communities, will be easier to learn.
Learning Strategies
Learning a Native American language can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to a rich cultural heritage and a unique way of understanding the world. To successfully embark on this journey, it’s crucial to explore different learning strategies that cater to your individual needs and preferences.
Here’s a breakdown of effective approaches to help you learn and master a Native American language.
Immersion
Immersion programs offer an unparalleled opportunity to immerse yourself in the language and culture of a Native American community. This approach provides a dynamic and engaging environment for language acquisition.
- Immersion programs provide an opportunity to learn the language in its natural context, surrounded by native speakers. This constant exposure to the language fosters fluency and cultural understanding.
- These programs often involve living within the community, participating in daily activities, and interacting with local residents. This creates a rich and authentic learning experience that goes beyond traditional classroom settings.
Examples of immersion programs include:
- The Navajo Language Immersion Programat the University of New Mexico offers a comprehensive program that combines classroom instruction with community-based learning experiences.
- The Lakota Language Immersion Schoolin Kyle, South Dakota, provides a full-immersion education for children from kindergarten to high school.
Challenges and considerations for immersion programs:
- The availability of immersion programs varies depending on the language and location. It’s essential to research and identify programs that align with your language goals and personal circumstances.
- Participating in an immersion program can require significant time commitment and financial resources. It’s crucial to factor in travel expenses, accommodation costs, and program fees.
- Immersion programs often involve a high level of cultural immersion, which may require adapting to new customs and traditions. It’s important to approach this experience with an open mind and a willingness to learn.
Language Exchange Programs
Language exchange programs offer a structured and interactive approach to learning a Native American language. These programs connect learners with native speakers for mutual language practice and cultural exchange.
- Language exchange programs provide a valuable opportunity to practice speaking and listening skills in a real-world setting. This interaction with native speakers enhances fluency and improves pronunciation.
- These programs often involve online platforms or in-person meetups, providing flexibility and convenience for learners. This allows you to connect with language partners from different locations and backgrounds.
Examples of language exchange platforms:
- HelloTalkis a popular app that connects language learners with native speakers for text and voice chat.
- Tandemis another app that facilitates language exchange through messaging, video calls, and voice recordings.
- Meetupis a website that organizes in-person language exchange groups in various cities around the world.
Tips for finding a language exchange partner:
- Be clear about your language goals and learning level when searching for a partner.
- Look for partners who are enthusiastic about language learning and willing to share their cultural knowledge.
- Set regular practice sessions and stick to a schedule to maintain consistency.
- Be patient and understanding as you both learn and improve your language skills.
Self-Study
Self-study offers a flexible and independent approach to learning a Native American language. This method allows you to learn at your own pace and on your own terms.
- Self-study provides the flexibility to learn at your own pace and according to your individual learning style.
- This approach allows you to focus on specific areas of the language that you find challenging or interesting.
Resources for self-study:
- Textbooks: Many textbooks are available for learning Native American languages, covering grammar, vocabulary, and cultural context.
- Online courses: Online platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer courses on various Native American languages, providing structured learning materials and interactive exercises.
- Apps: Language learning apps like Duolingo, Memrise, and Babbel offer interactive lessons and vocabulary building exercises.
- Dictionaries: Native American language dictionaries provide definitions, pronunciations, and examples of usage for words and phrases.
Guidance for creating a self-study plan:
- Set realistic goals for your learning journey, starting with small and achievable milestones.
- Develop a consistent study schedule and stick to it as much as possible.
- Incorporate regular practice and review sessions into your plan to reinforce your learning.
- Find ways to make learning enjoyable and engaging to stay motivated.
Pronunciation
Accurate pronunciation is crucial for effective communication in any language, especially in Native American languages, which often have unique sounds and intonation patterns.
- Native American languages often have sounds that don’t exist in English, requiring learners to develop new pronunciation skills.
- Intonation patterns can also vary significantly between Native American languages and English, impacting the meaning and understanding of spoken language.
Tips for mastering pronunciation:
- Pay close attention to the sounds and intonation patterns of the language you’re learning.
- Practice mimicking native speakers by listening to audio recordings and videos.
- Use pronunciation guides and dictionaries to understand the correct pronunciation of words and phrases.
- Seek feedback from native speakers or language tutors to identify and correct pronunciation errors.
Resources for pronunciation practice:
- Audio recordings: Listen to audio recordings of native speakers to familiarize yourself with the sounds and intonation patterns of the language.
- Pronunciation guides: Many online resources and textbooks provide pronunciation guides for Native American languages.
- Language tutors: Consider hiring a language tutor who can provide personalized pronunciation guidance and feedback.
Grammar
Native American languages often have unique grammatical features that differ significantly from English. Understanding these grammatical structures is essential for building fluency and comprehension.
- Native American languages often have complex verb morphology, with verbs incorporating information about tense, aspect, mood, and person.
- Word order can vary significantly from English, with some languages placing the verb at the end of the sentence.
- Many Native American languages have noun classes, categorizing nouns based on gender, animacy, or other features.
Strategies for learning grammar:
- Start with the basic grammatical structures and gradually work your way up to more complex concepts.
- Use grammatical exercises and practice drills to reinforce your understanding of rules.
- Read authentic texts and analyze the grammatical patterns used in them.
Resources for grammar practice:
- Textbooks: Textbooks often provide detailed explanations of grammatical rules and examples of usage.
- Online exercises: Many websites offer online grammar exercises and quizzes to test your understanding.
- Language learning software: Some language learning software programs incorporate grammar lessons and exercises.
Vocabulary
Building a strong vocabulary is essential for effective communication in any language. Expanding your vocabulary in a Native American language allows you to express yourself more fully and understand a wider range of concepts.
- Native American languages often have unique vocabulary that reflects their cultural values and worldview.
- Learning new words helps you understand the nuances of the language and appreciate the richness of its cultural heritage.
Strategies for learning vocabulary:
- Use flashcards to memorize new words and their definitions.
- Create vocabulary lists based on themes or topics relevant to your interests.
- Immerse yourself in authentic materials, such as books, articles, and websites, to encounter new words in context.
Resources for expanding vocabulary:
- Dictionaries: Native American language dictionaries provide definitions, pronunciations, and examples of usage for words and phrases.
- Online glossaries: Many websites offer online glossaries of Native American language vocabulary.
- Language learning apps: Some language learning apps include vocabulary building exercises and games.
Speaking Practice
Regular speaking practice is crucial for developing fluency and confidence in a Native American language. This involves actively using the language in real-world settings.
- Speaking practice allows you to put your language skills into action and receive feedback from native speakers.
- This experience helps you identify areas where you need to improve and develop strategies for overcoming speaking challenges.
Tips for overcoming speaking anxiety:
- Start with short conversations and gradually increase the complexity of your interactions.
- Practice speaking with friends, family members, or language partners who are supportive and encouraging.
- Focus on communicating your ideas clearly and effectively, rather than striving for perfect grammar or pronunciation.
Opportunities for speaking practice:
- Language exchange programs: Language exchange programs provide a structured environment for practicing speaking with native speakers.
- Online conversation groups: Many online platforms offer conversation groups where learners can practice speaking with other language enthusiasts.
- Community events: Participate in community events where you can interact with native speakers and practice your language skills in a social setting.
Reading Practice
Reading authentic materials in a Native American language is an excellent way to improve your vocabulary, comprehension, and cultural understanding. This approach exposes you to the language in its natural context.
- Reading authentic materials helps you learn new vocabulary, understand grammatical structures, and gain insights into the culture and history of the language.
- This practice also improves your reading comprehension skills, enabling you to understand and interpret complex texts.
Resources for finding reading materials:
- Books: Many books have been translated into Native American languages, offering a wide range of genres and reading levels.
- Articles: Online publications and newspapers often publish articles in Native American languages, providing current events and cultural insights.
- Websites: Numerous websites dedicated to Native American languages offer online articles, stories, and other reading materials.
- Traditional stories: Traditional stories and myths are a rich source of cultural knowledge and language learning.
Tips for improving reading comprehension:
- Start with short and simple texts and gradually work your way up to more challenging materials.
- Use a dictionary to look up unfamiliar words and phrases.
- Practice summarizing what you’ve read to test your comprehension.
Writing Practice
Writing in a Native American language is a valuable way to develop fluency, express your creativity, and deepen your cultural understanding. This practice allows you to translate your thoughts and ideas into the language.
- Writing in a Native American language helps you solidify your grammar and vocabulary knowledge.
- This practice also encourages you to think in the language, fostering a deeper understanding of its cultural nuances.
Tips for practicing writing:
- Start with simple writing tasks, such as journaling or writing letters to friends.
- Create short stories or poems to express your creativity and explore different aspects of the language.
- Seek feedback from native speakers or language tutors to improve your writing skills.
Resources for learning writing conventions:
- Textbooks: Textbooks often provide guidance on writing conventions and grammar rules in specific Native American languages.
- Online resources: Many websites offer resources on writing in Native American languages, including grammar guides and style tips.
Cultural Immersion

Learning a Native American language goes beyond memorizing words and grammar. It’s about understanding the cultural context that shaped the language and continues to influence its use today. Cultural immersion is vital for gaining a deeper appreciation and comprehension of the language, its nuances, and its significance within the community.
Connecting with Native American Communities
Connecting with Native American communities is crucial for cultural immersion. It allows you to learn firsthand about their traditions, customs, and values, which are deeply intertwined with their language.
- Attend cultural events:Participate in powwows, storytelling sessions, and traditional ceremonies to experience the language in its natural setting and observe how it’s used in different contexts.
- Engage with Native American organizations:Many organizations offer workshops, classes, and cultural programs that provide opportunities to learn about the language and culture.
- Seek out mentors:Find Native American language speakers who are willing to share their knowledge and insights.
- Respect cultural protocols:It’s important to approach cultural immersion with respect and sensitivity. Learn about the appropriate protocols for interacting with Native American communities and avoid cultural appropriation.
Experiencing Native American Culture
Immersion in Native American culture can take many forms.
- Visit museums and cultural centers:Explore exhibits and artifacts that showcase the history, art, and traditions of different Native American tribes.
- Read Native American literature:Immerse yourself in stories, poems, and essays written by Native American authors, which provide valuable insights into their cultural perspectives.
- Watch Native American films and documentaries:Films and documentaries offer a window into the lives and experiences of Native American people, showcasing their resilience, creativity, and cultural heritage.
- Travel to Native American lands:Visiting tribal lands and communities allows you to witness firsthand the cultural practices and traditions that are still alive and thriving.
6. Language Revitalization Efforts

Native American language revitalization efforts are crucial for preserving the rich cultural heritage and linguistic diversity of Indigenous communities. These efforts face numerous challenges, but there are also organizations and initiatives working tirelessly to ensure the survival of these languages.
Challenges Facing Native American Language Revitalization Efforts
The revitalization of Native American languages is a complex and challenging endeavor, facing a multitude of obstacles that threaten the survival of these languages.
- Cultural barriers: Changing cultural practices and assimilation have significantly impacted language transmission. As younger generations adopt dominant cultural norms and practices, the use of Native American languages in everyday life diminishes, leading to a decline in fluency and a disconnect between generations.
- Economic factors: Limited resources and lack of funding pose significant challenges to language revitalization programs. The development and implementation of effective language programs require financial support for teacher training, curriculum development, community outreach, and technological infrastructure.
- Political obstacles: Political barriers, such as government policies that do not adequately support language revitalization efforts, can hinder progress. A lack of recognition and support from policymakers can make it difficult to secure funding and implement effective programs.
- Lack of speakers: The dwindling number of fluent speakers poses a major challenge to language revitalization. As the number of fluent speakers decreases, it becomes increasingly difficult to find qualified teachers and mentors, and the knowledge base of the language is at risk of being lost.
- Intergenerational knowledge gaps: The disconnect between generations, particularly in the transmission of language skills, poses a significant challenge. Older generations may not be able to effectively teach younger generations due to differences in learning styles and cultural contexts.
- Technological challenges: The use of technology to support language revitalization presents both opportunities and challenges. Developing language learning resources and platforms that are culturally appropriate and accessible to diverse learners requires expertise and resources.
Organizations and Initiatives Working to Preserve and Revive Native American Languages
Several organizations and initiatives are dedicated to preserving and reviving Native American languages. These organizations play a vital role in promoting language revitalization through various programs and activities.
- The First Nations Language Conservancy (FNLC): The FNLC is a non-profit organization dedicated to preserving and revitalizing Indigenous languages in North America. Their mission is to support language communities in their efforts to document, teach, and use their languages. The FNLC provides resources, training, and technical assistance to language programs across the continent.
- The National Museum of the American Indian (NMAI): The NMAI is a Smithsonian Institution museum dedicated to promoting understanding and appreciation of Native American cultures and histories. The museum offers a variety of programs and resources related to Native American languages, including exhibits, educational workshops, and online resources.
- The Native American Languages Act (NALA): Passed in 1990, the NALA is a federal law that recognizes the importance of Native American languages and supports efforts to revitalize them. The law encourages federal agencies to provide resources and assistance to Native American language programs.
The Role of Language Learning in Supporting Native American Language Revitalization
Language learning is a crucial component of Native American language revitalization. Immersion programs, community-based learning initiatives, online resources, and language documentation efforts all contribute to the survival and growth of these languages.
- Importance of immersion programs: Immersion programs provide learners with an opportunity to experience the language in a natural and immersive environment. This intensive exposure to the language helps students develop fluency and cultural understanding.
- Value of community-based learning: Community-based learning initiatives promote language revitalization by fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members. These programs often involve elders and fluent speakers, who share their knowledge and traditions with younger generations.
- Impact of online language resources: Online platforms and resources provide learners with access to language learning materials, community forums, and cultural information. These resources can be particularly valuable for learners who live in areas where traditional language classes are not available.
- Benefits of language documentation and preservation: Efforts to document and preserve languages are essential for their revitalization. These efforts involve recording and transcribing language materials, creating dictionaries and grammars, and developing language learning resources.
The Importance of Respect: Native American Languages and Cultures
Respecting Native American languages and cultures is crucial for fostering understanding, promoting inclusivity, and acknowledging the rich history and diversity of Indigenous peoples. It involves recognizing the unique identities and traditions of each Nation and tribe, and using language that reflects this respect.
Respectful Language Use
Using respectful language when discussing Native American cultures and languages is essential for avoiding harmful stereotypes and promoting accurate representation. Instead of using broad generalizations or outdated terms, it’s important to be specific and use language that reflects the diversity of Native American communities.
“Instead of using the term ‘Indian,’ it’s important to use the specific tribal affiliation or Nation name when referring to a person or group. For example, instead of ‘Indian languages,’ it’s more respectful to say ‘Native American languages’ or even more specific, ‘Cherokee language.'”
Here are some additional examples of respectful language choices:
- Instead of: “Native American tribes” Use: “Cherokee Nation,” “Navajo Nation,” “Hopi Tribe” (use the specific name of the tribe or Nation)
- Instead of: “Indian culture” Use: “Indigenous cultures” or “Native American cultures” (use more inclusive and accurate terminology)
- Instead of: “Native American traditions” Use: “Ancestral traditions” or “Cultural practices” (avoid generalizations and use specific terms)
Ethical Considerations of Learning Native American Languages
Learning a Native American language is a privilege that comes with ethical responsibilities. It’s important to approach this journey with respect, sensitivity, and a commitment to cultural preservation. Here are some key ethical considerations to keep in mind:
| Ethical Considerations | Examples |
|---|---|
| Respect for Cultural Sensitivity: | Using language in a way that honors the cultural context and avoids appropriating or misrepresenting the language. For example, understanding the appropriate use of ceremonial language and respecting the role of elders in language transmission. |
| Respect for Indigenous Knowledge Systems: | Recognizing that Native American languages are deeply intertwined with traditional knowledge, beliefs, and practices. For example, understanding the connection between language and storytelling, oral history, and environmental knowledge. |
| Respect for Language Revitalization Efforts: | Supporting and collaborating with language revitalization programs, respecting the efforts of Indigenous communities to preserve their languages. For example, participating in language immersion programs, contributing to language dictionaries, or supporting language learning resources. |
| Respect for Intellectual Property Rights: | Acknowledging and respecting the intellectual property rights associated with Native American languages, including traditional songs, stories, and ceremonies. For example, obtaining permission before recording or sharing language materials and respecting the cultural context of language use. |
Guidelines for Respectful Communication with Native American Speakers
Effective communication with Native American speakers requires sensitivity, cultural awareness, and a willingness to learn. Here are some guidelines for respectful communication and interaction:
- Ask for permission before recording or filming:Always seek permission before recording or filming conversations or ceremonies. Respect the privacy and cultural sensitivities of Native American speakers.
- Be mindful of cultural differences in communication styles:Recognize that communication styles can vary across cultures. For example, some Native American cultures value directness and brevity, while others prioritize politeness and indirect communication.
- Avoid interrupting or speaking over others:Allow speakers to finish their thoughts and demonstrate respect for their time. Active listening is essential for meaningful communication.
- Be open to learning and understanding:Show a genuine interest in learning about Native American cultures and languages. Ask questions respectfully and be open to new perspectives.
- Acknowledge and respect the role of elders and knowledge holders:Recognize the importance of elders and knowledge holders in Native American communities. Seek their guidance and respect their expertise.
Writing a Reflection
Respecting Native American languages and cultures is not just about using the right words or phrases. It’s about acknowledging the history, resilience, and ongoing struggles of Indigenous peoples. It’s about recognizing the interconnectedness of language, culture, and identity. For example, during my research, I learned about the devastating impact of language suppression policies on Native American communities.
The forced assimilation and boarding school system aimed to eradicate Indigenous languages and cultures, resulting in significant language loss. Understanding this history helps us appreciate the importance of language revitalization efforts and the need to support Indigenous communities in reclaiming their linguistic heritage.
Respecting Native American languages and cultures is not just a matter of politeness; it’s a matter of justice and equality. By recognizing the unique identities and traditions of Indigenous peoples, we can create a more inclusive and respectful society.
Language Learning Resources: How To Learn Native American Language
Learning a Native American language can be a rewarding experience, but finding the right resources is crucial. Thankfully, there are various online platforms and materials available to support your language journey. This section explores some valuable resources to help you embark on your learning adventure.
Online Resources for Learning Native American Languages
The internet offers a wealth of resources for learning Native American languages. These resources include language learning apps, websites, and dictionaries, each offering unique features and benefits. The following table provides an overview of some popular online resources:
| Resource | Features | Target Language(s) | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duolingo | Interactive lessons, gamified learning, progress tracking, free and paid tiers | Various Native American languages, including Cherokee, Navajo, and Lakota | Free with premium options |
| Memrise | Flashcard-based learning, spaced repetition, language courses, free and paid tiers | Limited Native American languages, including Navajo and Cherokee | Free with premium options |
| Navajo Language Project | Comprehensive language learning platform, online courses, dictionaries, cultural resources | Navajo | Free |
| Cherokee Nation Language Program | Language courses, dictionaries, cultural resources, online and in-person classes | Cherokee | Free |
| FirstVoices | Online dictionaries, language learning materials, community resources, various Native American languages | Wide range of Native American languages | Free |
| Native Languages of the Americas | Online dictionary, language learning resources, cultural information, various Native American languages | Wide range of Native American languages | Free |
Language Learning Techniques
Learning a Native American language requires dedication and strategic approaches. There are several effective language learning techniques that can help you acquire proficiency in these languages.
Flashcards
Flashcards are a valuable tool for memorizing vocabulary, grammar rules, and cultural concepts. Create flashcards with the Native American word or phrase on one side and its English translation on the other. You can use physical flashcards or digital apps.
- Regular Review:Regularly review your flashcards, focusing on words or concepts you find challenging. This spaced repetition technique helps reinforce memory.
- Active Recall:Instead of simply reading the flashcards, try to recall the information from memory before flipping the card. This active recall method strengthens your understanding.
- Categorization:Organize your flashcards into categories based on themes or topics. This helps you understand the relationships between different words and concepts.
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition is a scientifically proven technique that optimizes memory retention. This method involves reviewing information at increasing intervals, gradually spacing out the reviews as you become more familiar with the material.
- Digital Apps:Several digital spaced repetition apps, such as Anki and Memrise, can help you create and manage flashcards with spaced repetition algorithms.
- Customized Intervals:Experiment with different intervals to find what works best for your learning style and memory. Adjust the spacing based on your individual progress.
- Regular Practice:Consistent practice is crucial for effective spaced repetition. Set aside dedicated time for reviewing your flashcards and incorporating new vocabulary and grammar.
Language Exchange, How to learn native american language
Language exchange involves connecting with a native speaker of the language you’re learning and practicing conversation with them.
- Online Platforms:Several online platforms, such as HelloTalk and Tandem, facilitate language exchange partnerships. You can connect with native speakers and practice speaking, listening, and writing in a real-world setting.
- Local Communities:Explore local Native American communities or organizations for language exchange opportunities. You might find language classes, workshops, or events where you can interact with native speakers.
- Cultural Immersion:Participating in cultural events, festivals, or ceremonies can provide valuable opportunities for language immersion and interaction with native speakers.
Immersion Techniques
Immersion involves surrounding yourself with the language you’re learning as much as possible. This creates a constant exposure to the language, aiding in natural acquisition.
- Language Learning Resources:Utilize online resources, such as podcasts, audiobooks, and videos, in the Native American language you’re learning. These resources provide authentic language exposure and cultural context.
- Native American Media:Explore Native American films, television shows, music, and literature. These media sources offer cultural insights and opportunities to hear the language spoken naturally.
- Language Partners:Connect with native speakers for conversation practice and cultural exchange. This provides valuable opportunities to learn about the language and culture from a native perspective.
Personalized Learning Plan
Developing a personalized learning plan that incorporates these techniques can enhance your learning journey.
- Set Realistic Goals:Start with achievable goals and gradually increase the complexity of your learning as you progress.
- Regular Practice:Dedicate consistent time to language learning, even if it’s just for a few minutes each day.
- Track Your Progress:Monitor your progress and make adjustments to your learning plan as needed. Celebrate your achievements and stay motivated.
10. Cultural Context
Understanding the cultural context of Native American languages is essential for appreciating their richness and significance. These languages are deeply intertwined with the traditions, beliefs, and values of their respective cultures, shaping how people interact with the world around them.
Storytelling
Storytelling is a central element of many Native American cultures, serving as a means of preserving history, transmitting knowledge, and fostering a sense of community. It’s a powerful tool for teaching moral lessons, sharing cultural values, and connecting generations.
Here’s a lesson plan designed to help students understand the cultural significance of storytelling in the [Name of specific Native American language] language:
- Traditional Stories:
- Story 1:[Name of story], a traditional [Name of specific Native American language] tale, recounts the origin of [briefly describe the origin story]. This story emphasizes the importance of [cultural value 1] and [cultural value 2].
- Story 2:[Name of story], another traditional story, highlights the significance of [briefly describe the theme]. This story teaches valuable lessons about [cultural value 3] and [cultural value 4].
- Storytelling Techniques:
- Stories in [Name of specific Native American language] are often told orally, passed down through generations.
- These stories often feature specific language features like [describe specific language features, such as repetition, metaphors, or use of proverbs].
- Non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions, gestures, and vocal inflections, play a crucial role in storytelling.
- Activities:
- Role-playing:Students can act out scenes from the stories, paying attention to the use of language and non-verbal cues.
- Story Creation:Students can create their own stories inspired by the themes and values presented in the traditional tales.
- Visual Representations:Students can create visual representations of the stories, such as drawings, collages, or short animations, to understand the visual elements and symbolism.
Language and Identity
[Name of specific Native American language] is more than just a language; it’s a vital part of the cultural identity of its speakers. The language carries within it the history, traditions, and values of the community, acting as a bridge between past and present.
- Historical Context:
- The [Name of specific Native American language] community has faced significant challenges in preserving its language.
- Historical events like [briefly describe historical events that led to language loss, such as colonization or assimilation policies].
- However, in recent years, there has been a growing movement to revitalize the language.
- Cultural Significance:
- Language plays a crucial role in preserving cultural traditions, values, and beliefs.
- It allows for the transmission of knowledge, stories, and cultural practices across generations.
- Speaking [Name of specific Native American language] connects individuals to their heritage and fosters a sense of belonging.
- Personal Experiences:
- [Share a personal anecdote or interview a speaker of the [Name of specific Native American language] to illustrate the connection between language and identity.]
Specific Cultural Terms
| Word/Phrase | English Translation | Cultural Significance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Word/Phrase 1] | [English Translation 1] | [Explain the cultural context and meaning of the word/phrase, including its historical roots, traditional uses, and any associated rituals or practices.] | [Provide a short example of how the word/phrase is used in a sentence or conversation.] |
| [Word/Phrase 2] | [English Translation 2] | [Explain the cultural context and meaning of the word/phrase, including its historical roots, traditional uses, and any associated rituals or practices.] | [Provide a short example of how the word/phrase is used in a sentence or conversation.] |
| [Word/Phrase 3] | [English Translation 3] | [Explain the cultural context and meaning of the word/phrase, including its historical roots, traditional uses, and any associated rituals or practices.] | [Provide a short example of how the word/phrase is used in a sentence or conversation.] |
Language Learning Journey: Embracing the Challenge of Native American Languages
Embarking on the journey of learning a Native American language is an adventure filled with unique challenges and profound rewards. It’s a journey that requires dedication, patience, and a willingness to immerse yourself in a rich cultural tapestry.
Challenges and Rewards
Learning a Native American language presents challenges that may differ from those encountered while learning more widely spoken languages. The availability of resources, the complexity of grammar, and the cultural context can all pose unique hurdles. However, the rewards are equally profound.
Mastering a Native American language opens doors to a deeper understanding of a vibrant culture, connects you to a rich history, and fosters personal growth.
- Limited Resources:Access to learning materials, such as textbooks, dictionaries, and online courses, may be limited for some Native American languages. This can make it challenging to find comprehensive and reliable resources.
- Complex Grammar:Many Native American languages have complex grammatical structures, with intricate verb conjugations, noun classes, and unique sentence formations. This can be challenging for learners accustomed to simpler grammatical systems.
- Cultural Context:Understanding the cultural context is crucial for mastering a Native American language. This includes learning about traditional beliefs, customs, and values that are interwoven with the language.
- Language Revitalization Efforts:Learning a Native American language can contribute to the ongoing efforts of language revitalization. This is a rewarding aspect, as it allows learners to play a role in preserving and promoting endangered languages.
- Personal Growth:Learning a Native American language can foster personal growth by expanding your understanding of different perspectives, enhancing your cognitive abilities, and deepening your appreciation for diversity.
Patience, Persistence, and Growth Mindset
Patience, persistence, and a growth mindset are essential for success in learning a Native American language. These qualities help overcome challenges and foster a positive learning experience.
- Patience:Learning a new language takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and embrace the process of gradual learning.
- Persistence:Don’t give up easily. Set realistic goals and consistently practice, even when faced with obstacles.
- Growth Mindset:View mistakes as opportunities for learning. Embrace challenges as opportunities to grow and develop your language skills.
Inspiring Stories
Many individuals have successfully learned Native American languages, overcoming challenges and embracing the journey. Their stories inspire others to embark on their own language learning adventures.
“Learning Lakota has been a transformative experience. It’s not just about learning a language, it’s about connecting with my heritage and understanding the values and traditions of my ancestors.”
[Name of individual]
This individual’s journey exemplifies the power of dedication and the profound impact that learning a Native American language can have on one’s life.
Connecting with Native American Communities
Connecting with Native American communities is an invaluable step in your language learning journey. It provides a deeper understanding of the language’s cultural context, offers opportunities to practice your skills, and fosters meaningful relationships with members of the community.
Finding and Connecting with Native American Communities
The first step is to identify Native American communities in your area or online. You can start by searching for tribal websites, community organizations, or cultural centers.
- Tribal Websites:Many tribes have websites that provide information about their language, culture, and events.
- Community Organizations:Organizations like the Native American Rights Fund (NARF) or the National Congress of American Indians (NCAI) can offer resources and connections to local communities.
- Cultural Centers:Cultural centers often host language classes, workshops, and events that provide opportunities to learn and connect with the community.
Benefits of Interacting with Native Speakers and Participating in Cultural Events
Direct interaction with native speakers is essential for language acquisition. It provides a natural learning environment where you can hear the language spoken authentically and receive feedback on your pronunciation and grammar.
- Authentic Language Exposure:Engaging with native speakers provides you with the opportunity to hear the language spoken in its natural context, including nuances of pronunciation, intonation, and regional dialects.
- Cultural Immersion:Participating in cultural events like powwows, ceremonies, or storytelling sessions offers insights into the language’s role in the community and its cultural significance.
- Building Relationships:Building relationships with members of the community can provide invaluable support and guidance on your language learning journey.
Respectful Engagement with Native American Communities
Respectful engagement is paramount when connecting with Native American communities. It involves recognizing the cultural significance of the language and respecting the traditions and customs of the community.
“Always remember that you are a guest in their community and their culture.”
- Seeking Permission:Before attending events or engaging with community members, seek permission and guidance from tribal leaders or elders.
- Learning Cultural Norms:Familiarize yourself with the community’s cultural norms and protocols, such as appropriate dress, greetings, and ways of interacting.
- Openness to Learning:Approach your interactions with a willingness to learn from the community’s experiences and perspectives.
Resources for Further Learning
Your journey into the world of Native American languages and cultures is just beginning. To deepen your understanding and continue your learning, it’s essential to explore a variety of resources, engage with experts, and connect with online communities. This section will guide you to valuable materials that can enhance your knowledge and inspire you to continue on your path.
Curated Reading List
Books, articles, and documentaries offer diverse perspectives and in-depth insights into Native American languages and cultures. They provide valuable historical context, cultural understanding, and contemporary perspectives on language revitalization efforts.
- Books:
- The Lakota Language: A Grammarby E. Paul Foster: This book provides a comprehensive grammar of the Lakota language, including its structure, phonology, morphology, and syntax. It’s an excellent resource for those interested in a deep dive into the language.
- Anishinaabe Language and Culture: A Guide for Beginnersby David S. Wilkins: This book offers a practical introduction to the Anishinaabe language and culture, covering basic grammar, vocabulary, and cultural practices. It’s a great starting point for those new to the language.
- Native American Languages: A Historical and Comparative Perspectiveby Geoffrey Pullum: This book provides an overview of the history, classification, and evolution of Native American languages, offering insights into their diversity and relationships.
- The Cherokee Nation: A Historyby Gary E. Clayton: This book tells the story of the Cherokee Nation, from its origins to the present day, highlighting its cultural traditions, language, and resilience.
- Voices from the Past: Native American Oral Historiesby Robert M. Slaughter: This collection of oral histories provides a rich and intimate glimpse into the lives, experiences, and perspectives of Native Americans from various tribes and regions.
- Articles:
- Language Revitalization in the Twenty-First Century: A Critical Reviewby Teresa L. McLaughlin: This article explores the challenges and opportunities for language revitalization efforts in the contemporary context, examining the role of technology, community engagement, and educational initiatives.
- The Role of Indigenous Knowledge in Environmental Sustainabilityby Leanne Betts: This article highlights the importance of Indigenous knowledge systems in addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable practices. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of language, culture, and the natural world.
- The Power of Indigenous Storytelling: A Tool for Language Revitalizationby Mary Ann Riley: This article examines the role of storytelling in preserving and revitalizing Native American languages. It explores how storytelling connects language to cultural identity and fosters intergenerational knowledge transmission.
- Documentaries:
- The Last Speakers: This documentary follows the journeys of several Native American language speakers who are working to preserve their languages and cultures. It highlights the challenges they face and the importance of their efforts.
- The Language Keepers: This documentary focuses on the work of Native American language teachers and revitalization programs. It explores the impact of language loss and the efforts to revitalize languages and cultural traditions.
Engaging with Experts and Organizations
Connecting with experts and organizations involved in Native American language and culture can provide invaluable opportunities for learning, research, and support.
- Research Opportunities:
- National Museum of the American Indian: This museum offers research opportunities, internships, and fellowships focused on Native American history, art, culture, and language. It provides access to extensive collections and resources.
- Smithsonian Institution: The Smithsonian Institution, through its various museums and research centers, offers research opportunities related to Native American languages, cultures, and history. It provides access to a wealth of knowledge and resources.
- American Indian Language Development Institute: This organization provides resources, training, and support for language revitalization efforts, offering opportunities for research and collaboration.
- Support for Learners:
- First Voices Language Conservancy: This organization offers language learning resources, online dictionaries, and community support for individuals interested in learning Native American languages. It provides a platform for language learners to connect with speakers and experts.
- Native Language Immersion School Network: This network connects and supports Native language immersion schools across the United States. It provides resources, training, and networking opportunities for educators and learners.
- Indigenous Language Institute: This organization offers language learning programs, workshops, and resources for individuals interested in learning Native American languages. It provides a supportive and culturally sensitive learning environment.
Online Communities and Resources
Online communities and resources provide valuable platforms for language learning, cultural exchange, and connection with Native American speakers and experts.
- Websites:
- Native Languages of the Americas: This website provides a comprehensive resource for information on Native American languages, including dictionaries, language learning materials, and cultural resources. It offers a wealth of knowledge and tools for learners.
- FirstVoices: This website offers a collection of online dictionaries, language learning materials, and cultural resources for various Native American languages. It provides a platform for language learners to access authentic resources and connect with speakers.
- The Indigenous Language Institute: This website provides language learning resources, workshops, and online communities for individuals interested in learning Native American languages. It offers a supportive and culturally sensitive learning environment.
- Online Communities:
- Native American Language Learning Facebook Group: This Facebook group provides a platform for language learners to connect with speakers, share resources, and discuss language learning experiences. It offers a supportive and welcoming community for learners.
- Indigenous Language Institute Forum: This forum provides a space for language learners to ask questions, share resources, and engage in discussions related to Native American languages and cultures. It offers a valuable platform for learning and connection.
Writing
The preservation of Native American languages and cultures is a vital task in the 21st century. These languages represent a rich tapestry of knowledge, history, and cultural identity, and their loss would be an immense tragedy. Technology can play a crucial role in revitalization efforts, providing platforms for language learning, documentation, and community engagement.
Intergenerational knowledge transmission is essential for ensuring the survival of these languages and cultures. By embracing the challenges and opportunities of the digital age, we can contribute to the preservation of this invaluable heritage for future generations.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the best way to learn a Native American language?
The best approach depends on your learning style and resources. Consider immersion programs, language exchange partners, self-study materials, or online courses. The key is to find a method that engages you and provides regular practice.
Are there any Native American languages that are easier to learn than others?
The difficulty of learning a language varies based on your native language and the language’s complexity. However, many Native American languages have unique structures and sounds that may present challenges. It’s important to be prepared for the learning curve and to embrace the process.
How can I find a Native American language teacher or tutor?
You can search for Native American language instructors at universities, community colleges, or cultural centers. Some organizations dedicated to language revitalization may also offer tutoring or mentorship programs.
Is it okay to learn a Native American language if I’m not Native American?
Learning a Native American language can be a wonderful way to connect with Indigenous cultures and contribute to their preservation. However, it’s crucial to approach this learning journey with respect, cultural sensitivity, and a commitment to ethical language use.