How many lessons to learn to drive? This is a question that many aspiring drivers ask themselves, and the answer can vary depending on a number of factors. From the structure of driving school programs to individual learning needs, there’s a lot to consider.
This guide will explore the key aspects of learning to drive, providing insights into the process and what you can expect along the way.
Driving School Programs
Driving schools are essential for learning the rules of the road and developing safe driving habits. They offer structured programs that combine classroom instruction with practical driving lessons.
Structure of Driving School Programs
Driving school programs typically follow a structured curriculum that includes both theoretical and practical components. The classroom portion covers traffic laws, road signs, vehicle operation, and defensive driving techniques. Practical driving lessons provide hands-on experience behind the wheel, supervised by a certified instructor.
Average Number of Lessons in Basic Driving Courses
The average number of driving lessons included in basic driving courses varies depending on the country and the specific program. In the United States, a typical basic driving course might consist of around 30 hours of classroom instruction and 15-20 hours of behind-the-wheel training.
However, this can range from 15 to 35 hours, depending on the state and the individual student’s needs.
Duration of Driving Lessons Across Different Countries
The duration of driving lessons can vary significantly across different countries. In some countries, like the United Kingdom, driving lessons are typically shorter and more frequent, with students taking several 1-hour lessons per week. In other countries, like Germany, driving lessons are longer, with students taking fewer but longer sessions.
Factors Influencing the Number of Lessons Needed
Several factors can influence the number of driving lessons a student requires to become proficient. These include:
- Age:Younger learners may require more lessons as they have less experience with driving and may need more time to develop the necessary skills.
- Prior Experience:Students who have prior driving experience, such as from driving go-karts or motorcycles, may need fewer lessons than those with no prior experience.
- Learning Pace:Some students learn more quickly than others, and they may need fewer lessons to reach proficiency. Similarly, students who struggle with certain aspects of driving may need additional lessons to master those skills.
Individual Learning Needs
Learning to drive is a complex process that involves acquiring various skills and knowledge. While driving schools offer structured programs, individual learning needs can vary significantly. Recognizing and addressing these differences is crucial for a successful and safe driving experience.
Factors Affecting Learning Speed
Each individual learns at their own pace, influenced by various factors. Some of the key factors that can affect learning speed include:
- Prior Experience:Individuals with prior experience in operating vehicles or similar machinery may learn faster than those with no prior exposure. For example, someone who has operated a tractor or a forklift might grasp driving concepts more quickly.
- Cognitive Abilities:Cognitive abilities, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills, play a crucial role in learning to drive. Individuals with strong cognitive abilities may pick up driving skills more readily.
- Physical Abilities:Physical abilities, such as hand-eye coordination, reaction time, and physical strength, also influence learning. Individuals with good physical coordination and reaction time may find it easier to master driving skills.
- Learning Style:Individuals have different learning styles. Some learn best through visual aids, others through hands-on experience, and others through verbal explanations. Tailoring the learning approach to an individual’s learning style can significantly impact their learning speed.
- Motivation and Attitude:A positive attitude and strong motivation to learn can significantly enhance learning speed. Individuals who are genuinely interested in learning to drive and are committed to the process tend to progress faster.
Self-Assessment and Lesson Requirements
Self-assessment is an essential tool for determining the number of lessons required to learn to drive effectively. It involves honestly evaluating your current driving skills and identifying areas that need improvement.
- Identify Your Strengths and Weaknesses:Begin by assessing your existing driving skills. Are you comfortable with basic maneuvers like steering, braking, and accelerating? Do you have any specific areas where you feel less confident, such as parallel parking or driving on highways?
- Consider Your Learning Goals:Determine your driving goals. Are you aiming to obtain a driver’s license as quickly as possible, or do you want to develop a comprehensive understanding of driving techniques and road safety? Your goals will influence the number of lessons you need.
- Seek Feedback from Others:Ask for feedback from experienced drivers or driving instructors. They can provide valuable insights into your strengths and weaknesses, helping you identify areas that require more practice.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Learning Plan
Regularly tracking your progress is crucial for identifying areas where you are excelling and areas that need further attention. This helps you adjust your learning plan accordingly.
Figuring out how many driving lessons you need is like choosing between Mandarin and Cantonese – it depends on your goals! If you want to be fluent in driving, you’ll need more lessons than if you just want to get around town.
But before you get behind the wheel, you might want to check out should i learn mandarin or cantonese to see which language might be more useful for your future travels. Just like with driving, the more time you invest, the better your results will be!
- Keep a Driving Journal:Maintain a driving journal to record your progress. Note down the skills you practice, any challenges you encounter, and your observations about your performance. This will help you identify areas for improvement.
- Seek Feedback from Instructors:During your lessons, actively seek feedback from your driving instructor. Ask them to identify areas where you can improve and provide specific suggestions for practice.
- Practice Regularly:Consistent practice is essential for mastering driving skills. Schedule regular practice sessions, even if they are short, to reinforce what you have learned and build confidence.
Role of Practice and Repetition
Practice and repetition are essential for mastering driving skills. Repetition helps you develop muscle memory and automaticity, making driving more intuitive and less demanding.
“Practice makes perfect.”
- Focus on Specific Skills:Break down driving skills into smaller, manageable components. For example, practice parallel parking in a safe and controlled environment before attempting it on the road.
- Gradually Increase Complexity:Start with basic skills and gradually introduce more complex maneuvers as you gain proficiency. This allows you to build confidence and avoid overwhelming yourself.
- Practice in Different Environments:Practice driving in various environments, such as city streets, highways, and rural roads. This will help you adapt to different driving conditions and build your overall driving skills.
3. Driving Test Requirements

The driving test is the final hurdle to obtaining your driver’s license. It’s a comprehensive assessment of your driving skills and knowledge, designed to ensure you are safe and responsible behind the wheel. Understanding the requirements, procedures, and potential consequences of the driving test is crucial for your success.
Driving Test Types and Assessment
Driving tests vary depending on the jurisdiction and vehicle type. However, common types include:
- Practical Driving Test:This is the most common type of driving test, where you demonstrate your driving skills in a real-world setting. The test typically involves a series of maneuvers, such as parallel parking, reversing, and turning, as well as navigating different road conditions, such as traffic, intersections, and highways.
- Written Test:This test assesses your understanding of traffic laws, road signs, and vehicle safety. It is often a multiple-choice exam covering various aspects of road rules and regulations.
- Hazard Perception Test:This test assesses your ability to identify potential hazards on the road and react appropriately. It typically involves viewing a series of video clips of driving scenarios and identifying potential risks.
- Theory Test:This test, similar to the written test, evaluates your knowledge of traffic rules, road signs, and safe driving practices. It might include multiple-choice questions, true/false statements, and scenario-based questions.
The specific skills and knowledge assessed in each test vary depending on the jurisdiction. For example, in some countries, the practical driving test might include a specific test for driving a motorcycle, while in others, it might be a single test for all types of vehicles.
Comparative Analysis of Driving Test Requirements
Here is a table comparing the passing criteria and minimum requirements for driving tests across different countries:
| Country/Jurisdiction | Minimum Age Requirement | Practical Driving Test Duration | Number of Attempts Allowed | Passing Score Percentage | Specific Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States (varies by state) | 16-18 years | 30-60 minutes | Unlimited | 70-80% | Vision test, written test, behind-the-wheel test, driver’s education completion |
| Canada (varies by province) | 16-17 years | 30-60 minutes | Unlimited | 70-80% | Vision test, written test, behind-the-wheel test, driver’s education completion |
| United Kingdom | 17 years | 40 minutes | Unlimited | 80% | Vision test, theory test, practical driving test |
| Australia (varies by state) | 16-18 years | 30-60 minutes | Unlimited | 70-80% | Vision test, written test, hazard perception test, practical driving test |
| Germany | 18 years | 45 minutes | Unlimited | 70% | Vision test, written test, first aid course, practical driving test |
Consequences of Failure and Retake Procedures
Failing a driving test can be disappointing, but it’s important to remember that it’s not the end of the road. You can retake the test after a waiting period, typically a few weeks. However, there might be fees associated with retaking the test.
In some jurisdictions, failing the driving test might also affect your insurance premiums or driving privileges. Retaking the driving test usually involves booking a new appointment through the relevant authority. You might need to provide additional documentation, such as proof of further driving lessons or training.
4. Driving Laws and Regulations
Understanding the rules of the road is essential for safe and legal driving. Failing to do so can lead to accidents, fines, or even legal repercussions. This section will delve into the importance of understanding local traffic laws, provide a comprehensive overview of common driving rules, and explore the consequences of violating them.
Importance of Understanding Local Traffic Laws
Knowing and adhering to local traffic laws is crucial for safe and legal driving. Failing to understand local driving laws can result in accidents, fines, or even legal repercussions. For instance, driving on the wrong side of the road in a new country could lead to a head-on collision.
Similarly, exceeding the speed limit in a school zone could result in a hefty fine and points on your driving record. Understanding local driving laws is especially important when:* Driving in a new country:Driving regulations can vary significantly from one country to another.
Driving in a rural area
Rural areas may have different speed limits, right-of-way rules, and other regulations compared to urban areas.
Driving during specific weather conditions
Weather conditions like rain, snow, or fog can affect visibility and road conditions, requiring drivers to adjust their driving habits accordingly.
Comprehensive Overview of Common Driving Rules
Here is a comprehensive overview of common driving rules and regulations:* Speed limits:Speed limits vary based on the type of road and location. For example, highways generally have higher speed limits than residential streets. It is important to always be aware of the posted speed limit and to drive within the legal limit.
Right-of-way rules
Right-of-way rules dictate who has the priority at intersections and other situations. For example, vehicles approaching from the right generally have the right-of-way at an intersection, but there are exceptions to this rule.
Lane changes, passing, and overtaking
Lane changes, passing, and overtaking should be done safely and legally. Drivers must signal their intentions and ensure there is enough space to maneuver safely.
Parking, stopping, and turning
Rules for parking, stopping, and turning vary depending on the location. Drivers should always be aware of the signage and markings indicating where they are allowed to park, stop, or turn.
Use of headlights, turn signals, and other vehicle lights
Headlights, turn signals, and other vehicle lights are essential for communication and safety. Drivers must use them correctly to signal their intentions and to be visible to other drivers.
Consequences of Violating Traffic Laws
Violating traffic laws can have serious consequences, including:* Fines and penalties:Traffic violations can result in fines ranging from a few dollars to hundreds of dollars, depending on the severity of the violation.
Potential suspension or revocation of driver’s license
Repeat offenders or those who commit serious violations may face suspension or revocation of their driver’s license.
Points on driving record
Traffic violations can result in points being added to a driver’s record. Too many points can lead to increased insurance premiums or even license suspension.
Potential legal consequences
In severe cases, traffic violations can lead to legal consequences, including jail time.
Impact on future employment opportunities
Some employers may conduct background checks that include driving records. A history of traffic violations could negatively impact future employment opportunities.
Table of Key Differences in Driving Laws
| Country | Driving Side of the Road | Minimum Driving Age | Blood Alcohol Content Limit | Seatbelt Laws | Common Traffic Violations & Penalties ||—|—|—|—|—|—|| United States | Right | 16 | 0.08% | Mandatory for all occupants | Speeding (fines and points), driving under the influence (fines, license suspension, jail time), running red lights (fines and points) || United Kingdom | Left | 17 | 0.08% | Mandatory for all occupants | Speeding (fines and points), driving without insurance (fines and points), driving without a license (fines and points) || Japan | Left | 18 | 0.03% | Mandatory for all occupants | Speeding (fines and points), driving under the influence (fines, license suspension, jail time), running red lights (fines and points) || Australia | Left | 17 | 0.05% | Mandatory for all occupants | Speeding (fines and points), driving under the influence (fines, license suspension, jail time), running red lights (fines and points) || India | Left | 18 | 0.03% | Mandatory for front seat occupants | Speeding (fines and points), driving under the influence (fines, license suspension, jail time), running red lights (fines and points) |
Driving Scenario
Imagine you are driving in a foreign country where the driving side of the road is the opposite of what you are used to. You are approaching an intersection with a roundabout. You are unsure of the right-of-way rules in roundabouts in this country.
You remember that in your home country, vehicles entering the roundabout must yield to traffic already circulating in the roundabout. However, you are not sure if this rule applies in this country. You decide to proceed cautiously, slowing down and carefully observing the traffic flow in the roundabout before entering.
You also make sure to signal your intentions clearly. By carefully observing the traffic flow and applying your knowledge of general driving rules, you are able to navigate the roundabout safely and legally.
5. Driving Skills and Techniques
Mastering driving skills and techniques is crucial for becoming a safe and responsible driver. This section will delve into the core skills, common driving maneuvers, and defensive driving practices that will equip you with the knowledge and abilities necessary to navigate the roads confidently.
5.1 Core Driving Skills and Techniques
Developing core driving skills and techniques is fundamental for safe driving. These skills enable you to control the vehicle, understand your surroundings, and make informed decisions in various driving situations.
- Vehicle Control:This encompasses the ability to steer, brake, and accelerate the vehicle effectively. Steering involves maintaining a steady course, while braking allows you to slow down or stop the vehicle. Acceleration, on the other hand, enables you to increase speed and maintain a desired pace.
The interplay between these three skills is essential for navigating various driving conditions, such as merging onto highways, navigating curves, and responding to unexpected situations.
- Situational Awareness:Situational awareness involves constantly observing and understanding your surroundings. This includes being aware of other vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, road signs, traffic signals, and weather conditions. Maintaining a clear view of your surroundings allows you to anticipate potential hazards and react appropriately.
- Decision Making:Decision-making is a critical aspect of safe driving. It involves analyzing the driving situation, identifying potential hazards, and choosing the appropriate course of action. Factors like speed, distance, road conditions, and other vehicles’ behavior play a role in making informed decisions.
For example, you might need to adjust your speed or change lanes based on the presence of a hazard or approaching traffic.
5.2 Detailed Driving Maneuvers
Performing common driving maneuvers safely and efficiently is crucial for navigating roads and parking spaces. Here are detailed instructions for parallel parking, reversing, and merging:
Parallel Parking
Parallel parking is a common maneuver that requires precision and careful execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Find a Suitable Spot:Choose a parking space that is at least 1.5 times the length of your vehicle. Ensure there is enough space in front and behind the space to maneuver.
- Align the Vehicle:Position your vehicle parallel to the parked car in front of the space, leaving a gap of about 2-3 feet between the vehicles. Keep a safe distance from the curb.
- Signal and Check Mirrors:Signal your intention to park and check your rearview mirrors and side mirrors to ensure no oncoming traffic or pedestrians.
- Back into the Space:Slowly back into the space, turning the steering wheel fully in the direction of the curb. Continue backing until your vehicle is at a 45-degree angle to the curb.
- Straighten the Wheel:Straighten the steering wheel and continue backing until your vehicle is parallel to the curb.
- Adjust Steering:Turn the steering wheel in the opposite direction of the curb to align the vehicle with the space.
- Final Adjustments:Make minor adjustments to the steering wheel and vehicle position until your vehicle is centered in the space. Ensure your vehicle is close enough to the curb without touching it.
Reversing
Reversing requires careful attention and precise control. Here’s a guide to safe reversing:
- Check Surroundings:Before reversing, check your rearview mirrors and side mirrors for pedestrians, other vehicles, and obstacles.
- Use Mirrors:Use your mirrors to guide your reversing movement. Check your rearview mirror for a clear view behind the vehicle and your side mirrors to check for any blind spots.
- Turn the Steering Wheel:When reversing in a straight line, keep the steering wheel straight. When reversing around corners, turn the steering wheel in the direction you want to go.
- Slow and Steady:Reverse slowly and steadily, making small adjustments to the steering wheel as needed.
- Stop and Check:If you need to stop while reversing, put the vehicle in park and check your surroundings again before continuing.
Merging
Merging onto a highway or busy road requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a guide to safe merging:
- Signal and Check Blind Spots:Signal your intention to merge and check your blind spots to ensure no other vehicles are in your way.
- Accelerate Gradually:Increase your speed gradually to match the flow of traffic on the highway or busy road.
- Find a Gap:Look for a safe gap in traffic to merge into. Ensure there is enough space between vehicles to avoid collisions.
- Merge Smoothly:Merge smoothly into the traffic flow, maintaining a safe distance from other vehicles.
- Maintain Speed:Once you have merged, maintain a safe speed and follow the flow of traffic.
5.3 Driving Skills Checklist
Mastering a comprehensive set of driving skills is essential for obtaining a driver’s license and becoming a safe driver. Here’s a checklist of essential skills to be mastered:
- Basic Vehicle Control:
- Steering: Maintaining a steady course, turning smoothly, and making adjustments to correct direction.
- Braking: Applying brakes effectively to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Acceleration: Increasing speed gradually and smoothly.
- Parking: Parallel parking, perpendicular parking, and backing into a parking space.
- Road Rules and Regulations:
- Traffic Signs: Understanding and obeying all traffic signs, including stop signs, yield signs, speed limit signs, and warning signs.
- Traffic Signals: Understanding and obeying all traffic signals, including red lights, yellow lights, and green lights.
- Right-of-Way: Understanding and yielding right-of-way to pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles according to traffic laws.
- Safe Driving Practices:
- Defensive Driving Techniques: Maintaining a safe following distance, scanning the road ahead, anticipating potential hazards, and adjusting driving behavior accordingly.
- Maintaining a Safe Following Distance: Calculating a safe following distance based on speed and road conditions.
- Avoiding Distractions: Minimizing distractions like cell phones, music, and passengers.
- Emergency Procedures:
- Flat Tires: Knowing how to change a flat tire safely.
- Engine Failure: Knowing how to handle engine failure and safely pull over to the side of the road.
- Accidents: Knowing how to respond to accidents, including calling emergency services and providing assistance.
5.4 Defensive Driving Techniques
Defensive driving techniques are crucial for preventing accidents and staying safe on the road. These techniques involve anticipating potential hazards, maintaining a safe following distance, and adjusting driving behavior to avoid dangerous situations.
- Maintaining a Safe Following Distance:The “3-second rule” is a widely used guideline for maintaining a safe following distance. This rule suggests that you should be able to count to three seconds after the vehicle in front of you passes a fixed object.
Adjust the following distance based on speed and road conditions.
- Scanning the Road:Continuously scan the road ahead, sides, and rear for potential hazards. Look for pedestrians, cyclists, other vehicles, road signs, and potential obstacles.
- Anticipating Potential Problems:Identify potential hazards like slippery roads, blind spots, or aggressive drivers. Adjust your driving behavior accordingly to avoid potential collisions.
- Maintaining a Safe Speed:Adapt your speed to road conditions and traffic flow. Drive slower in areas with reduced visibility, curves, or heavy traffic.
- Avoiding Distractions:Minimize distractions like cell phones, music, and passengers. Focus on the road and your surroundings.
Driving Experience and Confidence
Driving experience is crucial for developing strong driving skills and gaining confidence behind the wheel. As you gain more experience, you’ll become more comfortable with different driving situations and learn to anticipate potential hazards.
Benefits of Practicing Driving in Various Conditions
The more you practice driving in different environments, the more adaptable and skilled you’ll become. Driving in various weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or fog, helps you learn how to adjust your driving speed and techniques to maintain control.
Similarly, practicing on different road types, including highways, city streets, and rural roads, will enhance your ability to navigate different driving scenarios.
Building Confidence Behind the Wheel
Building confidence is essential for enjoying a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Here are some tips to help you gain confidence:
- Start Slowly:Begin by practicing in familiar areas and gradually work your way up to more challenging environments.
- Focus on the Basics:Mastering the fundamentals of driving, such as steering, braking, and accelerating, will provide a strong foundation for your confidence.
- Practice Regularly:The more you drive, the more comfortable you’ll become with the experience. Make a point to drive regularly to maintain your skills and confidence.
- Take a Defensive Driving Course:These courses teach valuable techniques for anticipating potential hazards and avoiding accidents. They can also help you build confidence by providing a structured learning environment.
- Identify and Address Anxieties:If you experience anxiety while driving, try to identify the specific triggers and develop strategies to address them. For example, if you’re anxious about driving on highways, start by practicing on less busy roads and gradually increase the level of traffic.
Recommended Resources for New Drivers
There are many resources available to help new drivers enhance their skills and knowledge. Here are some examples:
- Driving Schools:These schools offer structured training programs that cover all aspects of driving, from the basics to advanced techniques.
- Online Courses:Several online platforms provide interactive courses and simulations that can help you learn about driving rules, techniques, and safety procedures.
- Driving Organizations:Organizations like the AAA (American Automobile Association) offer resources, tips, and advice for drivers of all experience levels.
- Driving Books and Manuals:A wide range of books and manuals are available to provide detailed information on driving techniques, rules, and safety practices.
Driving Costs and Budget: How Many Lessons To Learn To Drive
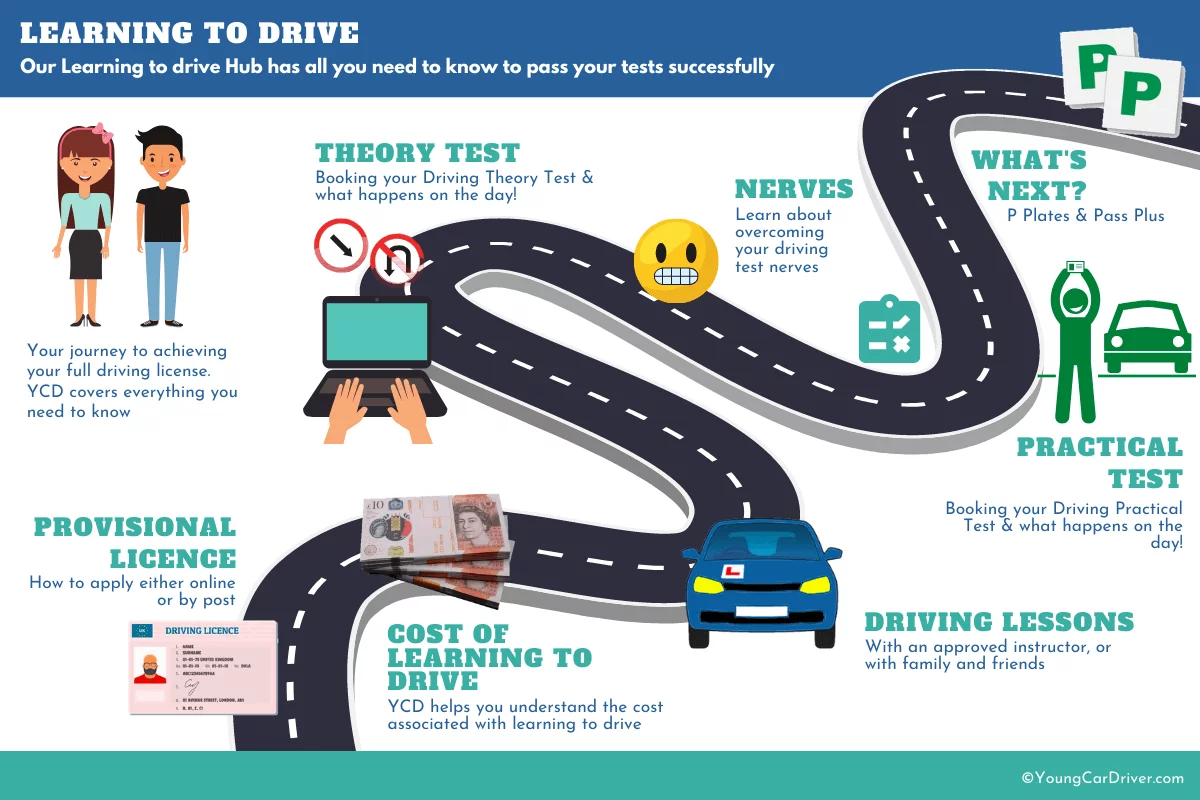
Getting your driver’s license is a significant step towards independence and mobility. However, driving comes with its own set of costs, and it’s essential to plan and budget accordingly. This guide will provide an overview of the various expenses associated with driving, from lessons to ongoing costs, and offer strategies for saving money.
Driving Lessons
Driving lessons are an essential investment for new drivers. They provide the knowledge, skills, and experience needed to become safe and confident behind the wheel. Here’s a breakdown of the costs involved:
- Lesson Fees:The cost of driving lessons varies depending on location, instructor experience, and the type of lesson. Private lessons are typically more expensive than group lessons. On average, driving lessons can range from $30 to $70 per hour.
- Vehicle Rentals:Many driving schools offer vehicle rental options for practice sessions. Rental costs can vary based on the type of vehicle and the duration of the rental. Expect to pay around $30 to $50 per hour for a vehicle rental.
- Materials:You’ll need essential materials for driving lessons, including a driver’s manual, practice tests, and potentially a driving simulator. The cost of these materials can range from $20 to $50.
Budgeting and Saving Money
Creating a budget for driving lessons can help you manage your expenses effectively. Here are some tips for budgeting and saving money:
- Realistic Budget:Consider your financial situation and set a realistic budget for driving lessons. Factor in the cost of lessons, vehicle rentals, materials, and any additional expenses.
- Tracking Expenses:Track your driving lesson expenses to monitor your progress and identify areas where you can save. Utilize budgeting tools or spreadsheets to keep track of your spending.
- Group Lessons:Group lessons are often more affordable than private lessons. They provide an opportunity to learn from other students and share the cost of instruction.
- Negotiating Fees:Don’t hesitate to negotiate fees with driving instructors, especially if you’re taking multiple lessons or have a referral.
- Practice with Family or Friends:Practice driving with a family member or friend who has experience. This can help you gain confidence and reduce the number of paid lessons needed.
- Online Courses:Online driving courses can supplement traditional lessons and offer a more affordable way to learn about traffic laws and driving techniques.
Financial Assistance Programs
Financial assistance programs are available to help individuals afford driving education. Here’s a look at some options:
- State and Local Programs:Many states and local governments offer financial assistance programs for driving education. These programs may have eligibility requirements and application procedures. For example, some programs may provide assistance to low-income families or individuals with disabilities.
- Federal Programs:Federal programs, such as scholarships and grants, may also provide financial assistance for driving education. Check with the Department of Education or other relevant government agencies for more information.
Ongoing Costs of Driving
Once you have your driver’s license, you’ll face ongoing expenses associated with driving. These include:
- Insurance:Car insurance is a mandatory expense for all drivers. The cost of insurance varies depending on factors such as age, driving record, vehicle type, and location.
- Fuel:The cost of fuel fluctuates, but it’s a significant expense for drivers. You can reduce fuel consumption by practicing efficient driving habits, such as maintaining a consistent speed and avoiding aggressive acceleration and braking.
- Vehicle Maintenance:Regular vehicle maintenance, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and inspections, is essential for safe driving. It’s important to budget for these expenses and address any unexpected maintenance costs promptly.
Driving Safety and Responsibility
Driving is a privilege and a responsibility. It’s important to drive safely and responsibly to protect yourself, your passengers, and other road users. Reckless driving not only puts you at risk but also endangers others.
Consequences of Reckless Driving and Traffic Violations
Reckless driving and traffic violations can have serious consequences, including:
- Fines and penalties:Traffic violations can result in fines, points on your driving record, and even license suspension.
- Increased insurance premiums:Insurance companies consider your driving record when determining your premiums. A history of traffic violations can lead to higher premiums.
- Accidents and injuries:Reckless driving is a major cause of accidents, resulting in injuries, property damage, and even fatalities.
- Criminal charges:In some cases, reckless driving or traffic violations that result in serious accidents can lead to criminal charges.
Preventing Accidents and Promoting Road Safety
Driving safely is a continuous process. Here are some tips to help you prevent accidents and promote road safety:
- Be alert and focused:Avoid distractions like cell phones, texting, or eating while driving.
- Obey traffic laws:Follow speed limits, traffic signals, and road signs.
- Maintain a safe following distance:Allow enough space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you. This gives you time to react in case of an emergency.
- Drive defensively:Be aware of your surroundings and anticipate potential hazards.
- Avoid driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs:Never drive if you have been drinking or using drugs.
- Get enough rest:Fatigue can impair your driving ability. Avoid driving if you are tired.
- Regularly maintain your vehicle:Ensure your vehicle is in good working order, including brakes, tires, and lights.
- Be courteous to other drivers:Be patient and understanding, especially during rush hour or in heavy traffic.
Common Causes of Driving Accidents
Traffic accidents are often caused by preventable factors. Here is a table highlighting some common causes and how to avoid them:
| Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|
| Speeding | Obey speed limits and adjust your speed for road conditions. |
| Distracted driving | Avoid using cell phones, texting, or eating while driving. |
| Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs | Never drive if you have been drinking or using drugs. |
| Drowsy driving | Get enough rest before driving and avoid driving if you are tired. |
| Aggressive driving | Be patient and avoid tailgating, speeding, and other aggressive behaviors. |
| Failure to yield | Yield to pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles as required by traffic laws. |
| Improper lane changes | Signal your intentions clearly and check your mirrors before changing lanes. |
9. Alternative Learning Methods

Learning to drive doesn’t always have to involve traditional in-person classes. The modern world offers various alternative methods that cater to different learning styles and preferences. These options provide flexibility, convenience, and cost-effectiveness while offering a unique approach to mastering the art of driving.
A. Online Driving Courses, How many lessons to learn to drive
Online driving courses have gained popularity in recent years, offering a convenient and flexible alternative to traditional in-person classes. These courses cover theoretical knowledge, traffic laws, and road signs, providing a solid foundation for driving. The availability of online driving courses varies depending on the region.
Many countries, including the United States, Canada, and Australia, offer accredited online driving courses that meet local requirements.Online courses can be effective for acquiring theoretical knowledge, as they provide interactive modules, videos, and quizzes. However, they lack the practical experience of in-person classes, limiting the development of essential driving skills like handling emergencies and maneuvering in traffic.
The individualized learning pace offered by online courses is a significant advantage, allowing students to progress at their own speed and revisit topics as needed. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for individuals with busy schedules or specific learning needs.Online driving courses are generally more cost-effective than traditional in-person classes.
The reduced overhead costs associated with online platforms allow providers to offer courses at lower prices.Here are some examples of reputable online driving course providers:* Driver’s Ed Online:This provider offers a comprehensive online driving course that meets the requirements of most states in the United States.
Aceable
This platform provides interactive online driving courses, including defensive driving and motorcycle safety training.
Drive Right
This provider offers online driving courses in multiple states, including interactive simulations and real-world driving scenarios.
B. Driving Simulators
Driving simulators have become increasingly sophisticated, offering realistic driving experiences without the risks associated with real-world driving. These simulators can be found in various forms, ranging from home simulators to professional simulators used in driving schools.Home simulators are typically less expensive and offer a basic driving experience.
They are often used for recreational purposes or to familiarize oneself with the basics of driving. Professional simulators, on the other hand, are highly advanced and provide a more realistic driving experience. These simulators are used in driving schools to train students in various driving scenarios, including adverse weather conditions and night driving.Driving simulators play a crucial role in developing driving skills by providing a risk-free environment for practicing maneuvers such as parallel parking and reversing.
They also expose students to a wide range of driving scenarios, helping them develop reaction time and decision-making abilities. However, it’s important to remember that driving simulators cannot fully replicate real-world driving experiences. They lack the sensory input and unpredictability of real-world driving, which can limit the effectiveness of training.
C. Self-Study Methods
Self-study methods for driving education offer flexibility and convenience, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule. They are also a cost-effective option, as they eliminate the expenses associated with formal courses or simulators.Self-study methods typically involve reading driving manuals, watching instructional videos, and practicing driving with a licensed driver.
However, these methods have limitations, including the lack of practical experience and feedback. Without proper guidance, individuals may develop incorrect driving habits or fail to grasp complex skills.Self-study methods also increase the risk of misinformation or incomplete understanding. Without a qualified instructor to provide accurate information and address any questions, learners may rely on unreliable sources or miss crucial details.
D. Comparison of Learning Methods
Here is a table comparing the advantages and disadvantages of online courses, driving simulators, and self-study methods:
| Learning Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability for Different Learners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Courses | Convenient, flexible, cost-effective, individualized learning pace | Lack of practical experience, limited development of driving skills | Suitable for learners who prioritize convenience and cost-effectiveness, but require additional practical training. |
| Driving Simulators | Risk-free environment for practicing maneuvers, exposure to various driving scenarios, development of reaction time and decision-making abilities | Cannot fully replicate real-world driving experiences, limited practical application | Suitable for learners who want to develop basic driving skills and gain experience in different driving scenarios. |
| Self-Study Methods | Flexible, convenient, cost-effective, personalized learning pace | Lack of practical experience and feedback, potential for misinformation, difficulty in mastering complex skills | Suitable for learners who are self-motivated and have access to a licensed driver for practical training. |
Driving for Specific Purposes
Driving isn’t just about getting from point A to point B. There are many different situations and purposes that require specific driving skills, knowledge, and qualifications. This section will explore the unique requirements for driving in various contexts, from commercial driving to navigating rural roads.
Specialized Driving Courses
Specialized driving courses cater to specific needs and enhance driving skills for various purposes. These courses are designed to equip drivers with the knowledge and practical skills necessary for specific situations, such as driving in adverse weather conditions, operating heavy vehicles, or navigating challenging terrains.
Examples of specialized driving courses include:
- Defensive driving courses: These courses focus on safe driving techniques and strategies to avoid accidents, emphasizing awareness, anticipation, and responsible driving practices.
- Commercial driver’s license (CDL) training: This comprehensive training program prepares individuals for operating commercial vehicles, covering regulations, safety protocols, vehicle inspection, and maneuvering techniques.
- Off-road driving courses: These courses provide instruction and practice in navigating challenging terrain, such as dirt roads, rocky trails, and steep inclines, focusing on vehicle control, recovery techniques, and safety precautions.
Licensing and Certification Requirements
Driving for specific purposes often necessitates obtaining the appropriate license and certifications to operate vehicles legally and safely. These requirements ensure drivers have the necessary training, knowledge, and experience to handle specific tasks.
- Commercial driver’s license (CDL): A CDL is required for operating commercial vehicles, such as trucks, buses, and tractor-trailers. The CDL licensing process involves passing written, physical, and driving tests to demonstrate proficiency in handling large vehicles and adhering to safety regulations.
- Specialized endorsements: Some CDLs require specific endorsements, such as a hazardous materials endorsement (H) for transporting hazardous substances or a passenger endorsement (P) for operating passenger buses. These endorsements require additional training and testing to ensure drivers are qualified to handle specific types of cargo or passengers.
- State-specific requirements: Licensing and certification requirements can vary by state. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific regulations of the state where you intend to operate a vehicle for a particular purpose.
Licensing and Training Requirements for Different Types of Driving
| Type of Driving | Licensing Requirements | Training Requirements ||—|—|—|| Commercial Driving | Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) with appropriate endorsements | CDL training program, including written, physical, and driving tests || Rural Driving | Standard driver’s license | Basic driver education, defensive driving courses, and experience driving in rural areas || Off-Road Driving | May require specific licensing depending on the vehicle and terrain | Off-road driving courses, specialized training in vehicle recovery techniques, and experience in challenging terrain || Driving with Disabilities | Adaptive driving training and assessments, potential need for specialized driving aids or modifications | Adaptive driving programs designed for individuals with disabilities, including vehicle modifications and training on assistive devices || Driving in Adverse Conditions | Standard driver’s license | Defensive driving courses, specialized training in handling vehicles in adverse weather conditions (e.g., snow, ice, rain) |
Driving and Technology
The way we drive has been significantly impacted by technological advancements. From navigation systems to driver-assistance features, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing safety, convenience, and efficiency on the road.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS features are designed to assist drivers in various aspects of driving, making the experience safer and more comfortable. These systems use sensors, cameras, and software to monitor the surroundings and intervene when necessary.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC):ACC automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe distance from the vehicle ahead. It uses sensors to detect the distance and speed of the car in front and automatically accelerates or decelerates to maintain the set distance.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW):LDW alerts the driver if the vehicle drifts out of its lane without signaling. It uses cameras or sensors to monitor lane markings and issues warnings through visual or auditory alerts.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB):AEB automatically applies the brakes to avoid or mitigate a collision. It uses sensors to detect potential collisions and automatically applies the brakes if the driver fails to react in time.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM):BSM uses sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots and alerts the driver through visual or auditory signals. This helps drivers change lanes safely and avoid collisions.
- Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA):RCTA alerts the driver to vehicles approaching from the sides when reversing. It uses sensors to detect approaching vehicles and warns the driver through visual or auditory signals.
GPS Navigation and Mobile Apps
GPS navigation systems and mobile apps have revolutionized how we navigate. These tools provide real-time directions, traffic updates, and alternative routes, making it easier to find our way around.
- Real-Time Navigation:GPS navigation systems and mobile apps use satellite data to determine the vehicle’s location and provide turn-by-turn directions. They also consider real-time traffic conditions and suggest alternative routes to avoid delays.
- Traffic Updates:Many navigation apps provide real-time traffic updates, allowing drivers to avoid congested areas and plan their routes accordingly. This can save time and reduce stress.
- Point of Interest (POI) Search:GPS navigation systems and mobile apps allow users to search for specific points of interest, such as restaurants, gas stations, and hotels. This can be helpful when planning a trip or finding nearby amenities.
- Parking Assistance:Some navigation apps offer parking assistance features, such as finding available parking spots and providing directions to parking garages.
Benefits and Risks of Using Technology While Driving
While technology can enhance driving, it also presents potential risks if not used responsibly.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced safety: ADAS features can help prevent accidents by detecting potential hazards and assisting the driver in avoiding them.
- Increased convenience: Navigation systems and mobile apps make driving easier and more efficient.
- Improved driving experience: Technology can make driving more enjoyable by providing entertainment options and information.
- Risks:
- Distracted driving: Using smartphones, tablets, or other devices while driving can lead to distracted driving, which is a major cause of accidents.
- Overreliance on technology: Drivers should not become overly reliant on ADAS features and should always maintain situational awareness.
- Privacy concerns: Some navigation apps collect data about driving habits, which can raise privacy concerns.
Safe and Responsible Use of Technology While Driving
To maximize the benefits of technology while minimizing the risks, it’s essential to use it safely and responsibly.
- Avoid using smartphones while driving:This includes texting, calling, browsing the internet, or using social media. Even hands-free devices can be distracting, so it’s best to avoid using them while driving.
- Use ADAS features appropriately:ADAS features are designed to assist drivers, not replace them. Drivers should always maintain situational awareness and be prepared to intervene if necessary.
- Stay focused on the road:It’s crucial to focus on driving and avoid distractions, such as adjusting the radio, eating, or talking to passengers.
- Pull over to use technology:If you need to use your phone or other devices, pull over to a safe location and park your vehicle.
- Keep your car’s software up to date:Software updates can improve the performance and safety of ADAS features.
Driving and Environmental Considerations
Driving is an integral part of modern life, providing us with freedom and convenience. However, it comes with a significant environmental cost. Understanding the environmental impact of driving and exploring ways to mitigate it is crucial for creating a sustainable future.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change
Driving contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2). The combustion of fossil fuels in internal combustion engines releases CO2 into the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing global warming. This rise in global temperatures leads to a range of adverse effects, including extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems.
The transportation sector is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for nearly 28% of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2021.
Air Pollution and Human Health
In addition to climate change, driving also contributes to air pollution, which has detrimental effects on human health. Exhaust fumes from vehicles release harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and ground-level ozone. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and even cancer.
Exposure to air pollution from traffic can lead to increased asthma attacks, reduced lung function, and premature death.
Driving and Health Considerations
Driving is a complex activity that requires a combination of physical and mental abilities. It’s essential to be aware of how health factors can impact driving safety and to take steps to maintain your fitness for safe driving. This section will delve into the crucial aspects of driving and health, examining the physical and mental requirements for safe driving, exploring common health conditions that may affect driving ability, emphasizing the importance of regular health checkups, and providing tips for maintaining physical and mental fitness for safe driving.
Physical Requirements for Safe Driving
Safe driving requires specific physical abilities. These abilities allow drivers to perform essential tasks such as steering, braking, accelerating, and reacting to unexpected situations. Here’s a table outlining common physical requirements for driving, their importance, and potential implications if compromised:
| Physical Requirement | Importance | Potential Implications if Compromised |
|---|---|---|
| Vision | Essential for perceiving road conditions, traffic signals, and other vehicles | Impaired vision can lead to difficulty judging distances, recognizing traffic signals, and reacting to hazards |
| Hearing | Crucial for detecting approaching vehicles, sirens, and other auditory cues | Hearing impairment can hinder awareness of surrounding traffic and emergency vehicles |
| Mobility | Needed for operating vehicle controls, such as steering wheel, pedals, and gear shift | Limited mobility can make it difficult to control the vehicle effectively and safely |
| Reaction Time | Important for responding quickly to changing road conditions and potential hazards | Slower reaction time can increase the risk of accidents, as it takes longer to react to dangers |
| Strength and Endurance | Necessary for sustained driving, especially during long journeys | Weakness or fatigue can impair the ability to maintain control of the vehicle and increase the risk of errors |
Mental Requirements for Safe Driving
Driving demands significant mental focus and cognitive skills. Attention, memory, decision-making, and emotional control all play critical roles in safe driving. These mental abilities allow drivers to process information, make quick judgments, and respond appropriately to dynamic road conditions.
“Driving is a complex task that requires constant attention and quick decision-making. Even momentary lapses in concentration can lead to dangerous situations.”
Source
[Insert relevant source here]
Driving Restrictions and Limitations
Certain health conditions can affect driving ability and may necessitate restrictions or limitations. These restrictions are put in place to ensure the safety of the driver and others on the road. Here’s a table summarizing common health conditions affecting driving, associated restrictions, and resources for drivers seeking further information:
| Health Condition | Associated Restrictions | Resources for Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | May require a medical certificate from a neurologist, potential driving restrictions based on seizure frequency and type | National Epilepsy Foundation, Epilepsy Foundation |
| Diabetes | May require regular blood sugar monitoring, potential restrictions on driving hours or vehicle type | American Diabetes Association, Diabetes.org |
| Heart Conditions | May require a medical evaluation and potential driving restrictions based on the severity of the condition | American Heart Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) |
| Vision Impairment | May require corrective lenses, potential restrictions on night driving or driving in certain conditions | American Academy of Ophthalmology, National Eye Institute |
| Hearing Impairment | May require a hearing evaluation, potential restrictions on driving in certain environments or conditions | American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders |
Importance of Regular Health Checkups
Regular health checkups are crucial for drivers of all ages. These checkups help identify potential health issues that could impact driving ability, allowing for early intervention and management. Early detection and treatment can help drivers maintain their safety and the safety of others on the road.
“Early detection and management of health conditions can help drivers maintain their safety and the safety of others on the road.”
Source
[Insert relevant source here]
Maintaining Physical and Mental Fitness for Safe Driving
Drivers can take proactive steps to maintain their physical and mental fitness for safe driving. These steps contribute to overall well-being and enhance driving performance. Here are some recommendations for drivers to enhance their physical and mental fitness:
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health, stamina, and reaction time. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Balanced diet: Consume a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein to maintain energy levels and cognitive function.
- Stress reduction techniques: Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to reduce anxiety and improve focus.
- Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to ensure alertness and cognitive sharpness while driving.
- Avoiding alcohol and drugs while driving: Alcohol and drugs impair judgment, reaction time, and coordination, making driving extremely dangerous.
- Regular breaks during long drives: Take breaks every 2-3 hours during long drives to stretch, walk around, and rest your eyes to prevent fatigue.
Driving and Social Responsibility
Driving is not just about getting from point A to point B; it’s about sharing the road with others and ensuring everyone’s safety. Being a responsible driver means understanding the impact of your actions on pedestrians, cyclists, and other drivers.
Impact on Pedestrians and Cyclists
Pedestrians and cyclists are particularly vulnerable on the road, and drivers have a responsibility to prioritize their safety. They are often at a disadvantage, especially in areas with limited visibility or inadequate infrastructure. Drivers must be extra cautious when approaching crosswalks, intersections, and areas where pedestrians and cyclists might be present.
Driving Etiquette
Driving etiquette plays a crucial role in fostering a safe and harmonious driving environment. It involves adhering to common courtesy and respecting the rules of the road.
“Driving etiquette is about creating a more positive and predictable driving environment for everyone.”
Tips for Being a Courteous and Responsible Driver
- Yield to pedestrians and cyclists:Always stop for pedestrians in crosswalks, even if they are not actively crossing. Give cyclists plenty of space when passing them, especially on narrow roads.
- Avoid aggressive driving:Road rage and aggressive driving can lead to accidents. Maintain a calm and controlled demeanor while driving, even in stressful situations.
- Use turn signals:Signaling your intentions clearly helps other drivers anticipate your movements and react accordingly.
- Be aware of your surroundings:Pay attention to your surroundings and be prepared to react to unexpected situations.
- Avoid distractions:Avoid using cell phones, texting, or other distractions while driving. These actions can impair your judgment and reaction time.
- Respect the speed limit:Adhering to speed limits ensures a safe and controlled flow of traffic.
- Be patient:Practice patience and understanding on the road. Everyone makes mistakes, and it’s important to be forgiving.
15. Driving and Future Trends
The future of driving is undergoing a dramatic transformation, with autonomous vehicles and connected car technologies poised to revolutionize how we travel. These advancements present both exciting opportunities and significant challenges, requiring careful consideration of their impact on driving education, regulations, and society as a whole.
Autonomous Vehicles and Driving Education
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles will undoubtedly necessitate changes in driving education. Traditional driving schools may need to adapt their curriculum to prepare drivers for a future where human control is less prevalent. This could involve incorporating lessons on:
- Understanding autonomous vehicle technology:Drivers should be familiar with the capabilities and limitations of self-driving systems, including how they perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and interact with other vehicles and pedestrians.
- Human-machine interaction:Learning to effectively interact with autonomous vehicle systems, including how to monitor their performance, intervene when necessary, and understand the nuances of shared control scenarios.
- Ethical considerations:Exploring the ethical dilemmas posed by autonomous vehicles, such as how they should make decisions in complex or unexpected situations, and understanding the legal and societal implications of their actions.
- Emergency preparedness:Drivers should be prepared to take control of the vehicle in case of system failure or unexpected events, ensuring they are able to safely maneuver the vehicle in manual mode.
- Autonomous vehicle regulations:Understanding the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding autonomous vehicles, including licensing requirements, insurance policies, and liability frameworks.
Connected Car Technologies: Benefits and Challenges
Connected car technologies offer a range of benefits, but they also present challenges that need to be addressed. Here’s a table comparing the advantages and disadvantages:
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Enhanced safety through features like lane departure warnings, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking. | Privacy concerns related to the collection and use of personal data by connected car systems. |
| Improved traffic flow through real-time information sharing and coordination between vehicles. | Potential for cybersecurity vulnerabilities that could compromise vehicle control or data security. |
| Increased convenience through features like remote vehicle access, navigation assistance, and personalized entertainment systems. | The need for robust infrastructure and widespread adoption to fully realize the benefits of connected car technologies. |
| Reduced fuel consumption and emissions through optimized driving strategies and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication. | The potential for distractions and driver complacency as reliance on connected car features increases. |
| Improved accessibility for individuals with disabilities through features like automated parking and adaptive driving modes. | The need for clear legal and ethical frameworks to address issues related to liability and data ownership. |
Vision for the Future of Driving in a Major City
As a transportation planner, my vision for the future of driving in a major city is one that embraces the transformative potential of autonomous vehicles and connected car technologies to create a more sustainable, efficient, and equitable transportation system.
- Autonomous Vehicle Integration:Autonomous vehicles will play a significant role in my vision, operating alongside human-driven vehicles to provide a range of transportation options. Dedicated lanes and infrastructure will be developed to facilitate smooth and efficient autonomous vehicle operations, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow.
- Connected Car Network:Connected car technologies will be seamlessly integrated into the city’s transportation network, enabling vehicles to communicate with each other, traffic signals, and infrastructure. This real-time data exchange will optimize traffic flow, reduce accidents, and enhance the driving experience.
- Safety and Accessibility:Safety is paramount in my vision. Autonomous vehicles will be designed with advanced safety features and redundancy systems to minimize the risk of accidents. Furthermore, accessibility for individuals with disabilities will be a key focus, with autonomous vehicles providing transportation options that are inclusive and empowering.
- Environmental Sustainability:Reducing the environmental impact of transportation is a critical aspect of my vision. Autonomous vehicles will be optimized for fuel efficiency and emissions reduction, while the city will promote the use of electric vehicles and alternative fuels. Smart traffic management systems will be implemented to minimize congestion and reduce unnecessary idling, further decreasing emissions.
Quick FAQs
How long does it typically take to learn to drive?
The average duration of driving lessons varies, but it often takes around 30 to 40 hours of instruction to become proficient. However, individual learning needs and the specific requirements in your area can influence this timeframe.
Are there any resources available to help me practice driving?
Yes, there are several resources available to help you practice driving. You can practice with a family member or friend who holds a valid driver’s license, use driving simulators, or take advantage of online driving courses. These resources can provide valuable experience and feedback.
What are some tips for finding affordable driving lessons?
To find affordable driving lessons, consider taking group lessons, negotiating fees with instructors, looking for discounts or promotions, and exploring alternative learning methods like online courses or driving simulators. Practicing with a family member or friend can also help reduce the cost of lessons.