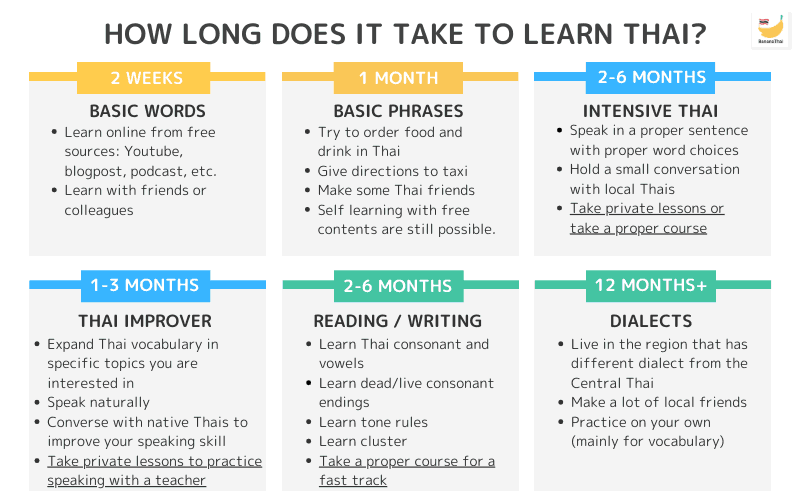
How long does it take to learn Thai? It’s a question that pops up for anyone considering diving into this fascinating language. While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, understanding the factors that influence learning time can help you set realistic goals and create a personalized learning plan.
Think of it as a journey, not a race. You’ll encounter unique challenges, discover hidden joys, and ultimately, develop a deeper appreciation for Thai culture.
From the intricacies of the Thai alphabet and the melodious tones to the rich cultural nuances that shape everyday conversation, learning Thai is an enriching experience. Whether you’re motivated by a passion for travel, a desire to connect with Thai friends, or simply a thirst for linguistic exploration, this guide will provide you with the insights and strategies you need to embark on your Thai language journey.
Factors Influencing Learning Time

The journey to fluency in Thai, like any language, is influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these factors can help you estimate your learning time and tailor your approach for maximum effectiveness.
Prior Language Learning Experience
Prior experience with other languages can significantly impact your Thai learning journey. If you’ve already learned Romance languages like Spanish or French, you might find certain aspects of Thai easier to grasp. This is because Romance languages share some grammatical structures and vocabulary with Thai, such as the use of articles and verb conjugations.
However, the tonal nature of Thai, a feature absent in Romance languages, will likely require dedicated attention.
Native Language Similarities or Differences
Your native language plays a crucial role in shaping your Thai learning experience. Speakers of tonal languages like Mandarin Chinese, Japanese, and Korean often have an advantage in acquiring Thai’s tonal system. These languages share a similar emphasis on pitch and intonation, which can make the transition smoother.
However, the writing systems of these languages differ significantly from Thai, requiring a new learning curve.
Individual Learning Style and Motivation
Learning styles and motivation are critical factors in language acquisition. Visual learners may find success with Thai language learning apps and videos, while auditory learners might prefer podcasts and music. Kinesthetic learners might benefit from hands-on activities like role-playing and language exchange.
Intrinsic motivation, driven by personal interest and enjoyment, can fuel consistent learning, while extrinsic motivation, such as career goals or travel plans, can provide external impetus.
Available Resources
Access to diverse learning resources can significantly impact your Thai language proficiency. Online courses offer flexibility and structure, while textbooks provide a comprehensive foundation. Language exchange partners offer valuable opportunities for real-time practice and cultural immersion. Immersive language programs, such as studying abroad in Thailand, provide an unparalleled learning experience by immersing you in the language and culture.
Basic Thai Language Acquisition
Learning Thai can be a rewarding journey, and mastering the basics is crucial for effective communication. This section explores the time needed to learn the Thai alphabet and pronunciation, provides essential vocabulary and phrases, and Artikels a plan for acquiring fundamental grammar structures.
Thai Alphabet and Pronunciation
The Thai alphabet, known as “Thai script,” consists of 44 consonants and 32 vowels. It is a tonal language, meaning the tone of a word can change its meaning. Mastering the alphabet and pronunciation takes time and dedication.
- Consonants:It is recommended to spend approximately 2-3 weeks on learning the consonants. This includes understanding their shapes, pronunciation, and how they are written.
- Vowels:Mastering vowels requires about 2-4 weeks, as they are more complex than consonants and have different pronunciations depending on their position in a word.
- Tones:Understanding the five tones of Thai takes approximately 2-3 weeks. Mastering the tones is essential for accurate pronunciation and comprehension.
Essential Thai Phrases and Vocabulary
Basic Thai phrases and vocabulary are essential for starting conversations and navigating everyday situations.
- Greetings:
- “S̄awasdī” (สวัสดี) – Hello
- “S̄awasdī khrap” (สวัสดีครับ) – Hello (male)
- “S̄awasdī kha” (สวัสดีค่ะ) – Hello (female)
- “Lā khon” (ลาก่อน) – Goodbye
- Common Phrases:
- “Khǒp khun” (ขอบคุณ) – Thank you
- “Khǒp khun khrap” (ขอบคุณครับ) – Thank you (male)
- “Khǒp khun kha” (ขอบคุณค่ะ) – Thank you (female)
- “Māi pen rai” (ไม่เป็นไร) – You’re welcome/Don’t worry
- “Khǒ thǒng” (ขอโทษ) – Excuse me/I’m sorry
- Numbers:
- “Nʉ̄ng” (หนึ่ง) – One
- “Sǒng” (สอง) – Two
- “Sā̄m” (สาม) – Three
- “Sǐ̄” (สี่) – Four
- “Hā̄” (ห้า) – Five
Basic Thai Grammar Structures
Acquiring basic grammar structures is crucial for understanding and forming sentences in Thai.
- Verb Conjugations:Thai verbs are not conjugated for tense or person. However, they can change based on aspect (whether an action is completed, ongoing, or habitual).
- Sentence Formation:The basic word order in Thai is Subject-Verb-Object (SVO).
- Example:“Khǒm kīn nām” (ฉันกินน้ำ) – I drink water.
- Particles:Thai particles are small words that add grammatical information to a sentence. For example, the particle “khrap” (ครับ) is used by males at the end of a sentence to show politeness.
Building Basic Vocabulary
Building a basic vocabulary is essential for everyday conversations.
- Start with Common Nouns:Focus on learning common nouns like “khǒm” (ฉัน) – I, “khun” (คุณ) – you, “nām” (น้ำ) – water, “kān” (ข้าว) – rice, “bāan” (บ้าน) – house.
- Expand to Verbs and Adjectives:Gradually expand your vocabulary to include verbs like “kīn” (กิน) – eat, “dʉ̄” (ดู) – watch, “lāy” (ไป) – go, and adjectives like “dī” (ดี) – good, “rɔ̄i” (ร้อน) – hot, “yen” (เย็น) – cold.
- Use Flashcards and Repetition:Flashcards and repetition are effective ways to memorize new vocabulary.
Intermediate Thai Language Proficiency: How Long Does It Take To Learn Thai

Reaching intermediate proficiency in Thai signifies a significant milestone in your language learning journey. At this level, you can confidently engage in conversations, understand basic cultural nuances, and even begin to write simple texts. This stage is crucial for deepening your understanding of the language and culture, paving the way for more advanced learning.
Time Needed for Fluency in Reading and Writing
To achieve fluency in reading and writing Thai, with a dedicated study time of 10 hours per week, it typically takes around 12-18 months. This estimate assumes you have a solid foundation in the Thai alphabet and pronunciation, access to comprehensive learning materials, and consistent practice.
Conversational Topics and Cultural Nuances
At an intermediate level, you’ll be able to engage in conversations about various topics, but cultural nuances are essential for smooth communication.
| Topic | Cultural Nuances | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Food | Thai cuisine is deeply rooted in tradition and regional variations. Be mindful of dietary restrictions and avoid direct criticism of food, even if you don’t enjoy it. | When offered a dish, politely accept even if you are unsure about it. A simple “Thank you, I’ll try it” conveys appreciation and respect. |
| Family | Family plays a crucial role in Thai society. Respect for elders is paramount, and showing interest in their lives is appreciated. | Ask about family members, their occupations, and their well-being. Refrain from asking personal questions about finances or relationships. |
| Travel | Thai people are proud of their country and are often eager to share their culture with visitors. Show interest in local customs and traditions, and be respectful of religious sites. | When visiting temples, dress modestly and remove shoes before entering. Ask permission before taking photos of people. |
| Politics | Politics is a sensitive topic in Thailand. It’s best to avoid expressing strong opinions or engaging in debates. | Stick to neutral topics and refrain from making generalizations about the country or its government. |
| Religion | Buddhism is the dominant religion in Thailand. Respect religious beliefs and practices, and avoid making disrespectful comments. | When visiting temples, observe the rituals and avoid disturbing the monks during meditation. |
Key Grammar Concepts and Vocabulary Expansions
Mastering key grammar concepts and expanding your vocabulary are crucial for achieving intermediate proficiency.
| Grammar Concept | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Tense and Aspect | Thai uses different particles to express tense and aspect, which can be challenging for learners. | “กำลัง” (gamlang) indicates an ongoing action (present continuous), “แล้ว” (laew) indicates a completed action (past tense), and “จะ” (ja) indicates future tense. |
| Particles and Prepositions | Particles like “ก็” (gor) and “นะ” (na) are used to express different nuances in Thai. | “ก็” can express agreement, while “นะ” can soften a statement or express surprise. |
| Formal and Informal Speech | Thai language has different levels of formality depending on the context and the relationship between speakers. | “คุณ” (khun) is used for formal address, while “พี่” (pii) or “น้อง” (nong) are used for older and younger siblings, respectively. |
Strategies for Improving Listening Comprehension and Spoken Fluency
Improving listening comprehension and spoken fluency requires consistent practice and strategic approaches.
“Engage in active listening by focusing on the speaker’s tone, body language, and context. Utilize shadowing techniques, repeating phrases and sentences to improve pronunciation and intonation.”
Learning Thai can take a while, depending on your dedication and learning style. You’ll likely need to commit some serious time to mastering the unique tones and script. But don’t worry, it’s not all that different from learning other languages, like Portuguese, which also has its own set of challenges.
You can find some useful information about learning Portuguese here , which might give you some insights into how long it might take you to learn Thai as well. The key is to be consistent, stay motivated, and enjoy the process!
“Practice speaking with native speakers or language partners through online platforms or language exchange programs. Record your speech and analyze your pronunciation and fluency.”
Writing Proficiency
Intermediate Thai language learners are expected to be able to write basic texts, such as emails, short essays, and reviews. Here are examples of writing tasks:
Write a personal email to a Thai friend, inviting them to a social gathering.
Use appropriate greetings and closings.
Include details about the event, such as the date, time, and location.
- Use polite language and avoid slang or informal expressions.
- Compose a short essay about a Thai cultural event or tradition.
Research the topic thoroughly and use reliable sources.
Organize your thoughts logically and use transitions effectively.
- Use accurate grammar and vocabulary.
- Write a review of a Thai restaurant or movie.
Provide a clear and concise summary of the experience.
Use descriptive language to convey your impressions.
Offer constructive feedback and avoid being overly critical.
Advanced Thai Language Mastery
Reaching advanced Thai language proficiency signifies a significant milestone in your language journey. This stage involves delving into the intricate nuances of Thai grammar, expanding your vocabulary to encompass sophisticated expressions, and immersing yourself in the rich tapestry of Thai culture.
While the path to mastery is demanding, it rewards you with the ability to communicate effectively in diverse settings, comprehend complex texts, and appreciate the beauty of Thai literature and art.
Time Commitment
Attaining a level of fluency comparable to a native speaker typically requires a substantial time commitment. The estimated time frame can vary significantly based on individual factors such as prior language experience, learning style, and available resources.
- Individuals with prior language learning experience, particularly in tonal languages, might find the transition to advanced Thai easier and require less time.
- A dedicated learning style characterized by consistent practice and active engagement in language learning activities can accelerate progress.
- Access to comprehensive learning materials, including textbooks, online resources, and immersive experiences, plays a crucial role in enhancing learning efficiency.
While precise time estimations are difficult, a general guideline suggests dedicating at least 10-15 hours per week to advanced Thai language learning. This time allocation should be distributed across various aspects of learning, including:
- Reading:Engaging with Thai literature, newspapers, and online articles to expand vocabulary and improve comprehension.
- Writing:Practicing grammar exercises, writing essays, and engaging in online writing communities to refine writing skills.
- Listening:Watching Thai films and television shows, listening to Thai music, and engaging in conversations with native speakers to enhance listening comprehension and improve pronunciation.
- Speaking:Participating in language exchange programs, joining conversation groups, and seeking opportunities to converse with native speakers to develop fluency and improve pronunciation.
- Cultural Immersion:Attending cultural events, exploring Thai cuisine, and immersing oneself in Thai customs and traditions to gain a deeper understanding of the language and culture.
Consistent practice is paramount in achieving fluency. Regularly engaging with the language through various activities like reading, writing, listening, and speaking helps solidify your understanding and promotes faster progress.
Advanced Vocabulary and Idioms
Mastering advanced Thai vocabulary involves expanding your knowledge beyond basic phrases and incorporating words and expressions commonly used in formal settings, literary works, and everyday conversations.
- Formal Settings:Words related to government, law, business, and academia, such as “กฎหมาย” (law), “เศรษฐกิจ” (economy), and “วิทยาศาสตร์” (science), are essential for navigating formal environments.
- Literary Works:Literary vocabulary includes words and phrases that are often found in poetry, novels, and short stories, such as “ความรัก” (love), “ความสุข” (happiness), and “ความทุกข์” (suffering).
- Everyday Conversations:Colloquial expressions and slang terms used in everyday conversations, such as “แบบนี้” (like this), “เฮ้ย” (hey), and “อ่ะ” (well), are essential for understanding informal communication.
Thai idioms are a rich and fascinating aspect of the language, often conveying nuanced meanings that are not readily apparent from their literal translations. Understanding these idioms is crucial for appreciating the depth and subtlety of Thai communication.
- “น้ำขึ้นให้รีบตัก” (nam khun hai riep tak):This idiom literally translates to “When the tide rises, quickly scoop water.” Figuratively, it means to seize opportunities when they arise.
- “ปลูกต้นไม้ไว้ร่มให้ลูกหลาน” (plook dton mai wai rom hai look lan):Literally, “Plant a tree to provide shade for your descendants.” Figuratively, it emphasizes the importance of planning for the future and leaving a legacy for generations to come.
- “ช้างตายทั้งตัวเอาใบบัวมาปิด” (chang dtai thang tua ao bai bhua ma pit):This idiom literally means “A dead elephant is covered with a lotus leaf.” Figuratively, it signifies attempting to conceal a major problem with a superficial solution.
Thai language and culture exhibit regional variations, particularly in vocabulary and idioms. Different regions may have their own unique expressions and ways of speaking.
- Northern Thailand:Northern dialects often feature unique vocabulary and pronunciation, with words like “เฮา” (we) and “เจียงใหม่” (Chiang Mai) being distinct from their Central Thai counterparts.
- Northeastern Thailand:The northeastern dialect, known as Isan, is influenced by Lao language and features words like “บัก” (fruit) and “เฮ็ด” (do) that are not commonly used in Central Thai.
- Southern Thailand:Southern dialects are characterized by distinct pronunciation and vocabulary, with words like “ฮู้” (know) and “กู” (I) being specific to the region.
Mastering Grammar and Literary Nuances
Advanced Thai grammar involves understanding complex grammatical structures, such as the use of particles, honorifics, and verb conjugations. These structures can pose challenges for non-native speakers, but mastering them is essential for accurate and fluent communication.
- Particles:Thai particles, such as “นะ” (na), “ค่ะ” (kha), and “ครับ” (krap), convey subtle nuances of politeness, emphasis, and affirmation. Understanding their usage is crucial for communicating appropriately in different social contexts.
- Honorifics:Thai language uses honorifics to express respect and deference. Using the appropriate honorifics when addressing individuals of higher social standing or authority is essential for maintaining social harmony.
- Verb Conjugations:Thai verbs conjugate to indicate tense, aspect, and mood. Learning the various verb conjugations is essential for constructing grammatically correct sentences.
Thai literature is renowned for its rich use of literary devices, which enhance the beauty and impact of the text. Appreciating these devices requires a deep understanding of the language and culture.
- Metaphors:Thai literature often employs metaphors to convey abstract concepts or emotions through concrete imagery. For example, “หัวใจ” (heart) can be used metaphorically to represent love, courage, or sadness.
- Similes:Similes are used to compare two things using words like “เหมือน” (like) or “ดัง” (as). They provide vivid descriptions and enhance the reader’s understanding.
- Alliteration:Alliteration, the repetition of consonant sounds, is a common literary device in Thai poetry and prose. It creates a sense of rhythm and musicality.
Thai writing exhibits distinct formal and informal styles, with variations in script, punctuation, and vocabulary. Understanding these differences is essential for communicating effectively in different contexts.
- Formal Writing:Formal writing, often used in academic papers, official documents, and literary works, employs a more complex and refined vocabulary and follows strict grammatical rules. It may also utilize the “Khom” script, which is considered more formal than the standard Thai script.
- Informal Writing:Informal writing, used in personal correspondence, social media posts, and everyday communication, is characterized by a more casual tone and may include slang terms and colloquial expressions.
Strategies for Achieving Proficiency, How long does it take to learn thai
Reaching advanced Thai language proficiency requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses various strategies for improving spoken and written skills, as well as deepening your understanding of Thai culture.
- Focus on Spoken Thai:
- Immersion Programs:Participating in immersive language programs in Thailand provides an opportunity to interact with native speakers in real-life situations, enhancing pronunciation, intonation, and fluency.
- Language Exchange Partners:Connecting with native Thai speakers through language exchange programs or online platforms allows for regular conversation practice and feedback on pronunciation and grammar.
- Conversation Practice:Joining conversation groups, attending language meetups, and seeking opportunities to converse with native speakers in informal settings promotes fluency and confidence.
- Develop Written Thai Skills:
- Grammar Exercises:Regularly practicing grammar exercises reinforces grammatical rules and improves accuracy in writing.
- Writing Essays:Writing essays on various topics in Thai helps develop writing skills, expand vocabulary, and improve sentence structure.
- Online Writing Communities:Engaging in online writing communities provides opportunities to practice writing in Thai, receive feedback from other learners, and share your work.
- Embrace Thai Culture:
- Attend Cultural Events:Participating in Thai cultural events, such as festivals, concerts, and traditional performances, provides insights into the cultural context of the language and enhances appreciation for Thai customs.
- Watch Thai Films:Watching Thai films and television shows exposes you to authentic spoken Thai, familiarizes you with cultural references, and enhances listening comprehension.
- Read Thai Literature:Engaging with Thai literature, from classic novels to contemporary works, provides a deeper understanding of the language, culture, and history.
- Constant Exposure:You are constantly surrounded by the language, hearing it spoken in everyday conversations, on the streets, and in the media. This constant exposure accelerates your learning process and helps you internalize the language naturally.
- Authentic Language Use:You encounter the language in its natural form, including colloquialisms, slang, and regional variations. This helps you develop a deeper understanding of the language and its nuances.
- Cultural Immersion:Immersing yourself in Thai culture provides valuable context for understanding the language. You learn about customs, traditions, and social norms, which are essential for effective communication.
- Increased Confidence:Being surrounded by native speakers and having to use the language daily boosts your confidence and fluency. You become more comfortable speaking and understanding Thai in real-life situations.
- Active Listening:Pay attention to how native speakers use the language, their pronunciation, intonation, and grammar.
- Speaking Opportunities:Engage in conversations with locals, even if it’s just a few words at first. Don’t be afraid to make mistakes; it’s part of the learning process.
- Feedback and Correction:Seek feedback from native speakers on your pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary. This helps you identify areas for improvement.
- Language Exchange:Connect with Thai language learners and practice speaking with them. You can help each other learn and improve.
- Language School:Enroll in a Thai language school to receive formal instruction and practice in a structured environment.
- Homestay:Live with a Thai family to experience daily life and interact with native speakers in a comfortable setting.
- Cultural Activities:Participate in cultural events, festivals, and activities to immerse yourself in Thai culture and practice your language skills.
- Volunteer Work:Engage in volunteer work to interact with locals and use your language skills in a meaningful way.
- Explore Local Markets:Visit local markets to practice your bargaining skills and learn everyday vocabulary related to food, clothing, and household items.
- Try Thai Cuisine:Explore different Thai restaurants and street food stalls to expand your vocabulary related to food and flavors.
- Attend Religious Ceremonies:Observe religious ceremonies and learn about the cultural significance of different rituals and practices.
- Connect with Locals:Engage in conversations with locals, ask questions about their culture, and share your own experiences.
- Duolingo: A popular language learning app known for its gamified approach, Duolingo offers a free Thai course with interactive lessons, quizzes, and progress tracking.
- Memrise: Memrise focuses on vocabulary acquisition through flashcards and spaced repetition, helping learners memorize new words and phrases effectively.
- Babbel: Babbel provides comprehensive Thai language courses with structured lessons, interactive exercises, and personalized learning paths.
- Rosetta Stone: Known for its immersive approach, Rosetta Stone offers a Thai language program with interactive lessons, speech recognition technology, and cultural insights.
- HelloTalk: A language exchange app that connects learners with native Thai speakers for conversation practice and cultural immersion.
- Classroom Learning: Traditional classroom settings offer structured lessons, teacher guidance, and opportunities for interactive learning with classmates. However, they can be time-consuming and may not always cater to individual learning paces.
- Self-Study: Self-study allows learners to learn at their own pace and convenience. Online resources, apps, and textbooks provide flexibility and access to a wealth of learning materials. However, self-study requires strong motivation and self-discipline to stay on track.
- Hybrid Approach: Combining classroom learning with self-study can offer the best of both worlds. Learners can attend structured lessons while supplementing their learning with online resources and practice sessions.
- Textbooks: Textbooks provide structured lessons, grammar explanations, vocabulary lists, and exercises to develop language skills. Some popular Thai textbooks include “Thai for Beginners” by John Okell and “Teach Yourself Thai” by Michael Freeman.
- Dictionaries: Dictionaries are essential for understanding the meaning of words and phrases. Online dictionaries like Thai-English Dictionary by Oxford Languages and Thai-English Dictionary by Merriam-Webster provide comprehensive definitions, examples, and pronunciations.
- Online Resources: Websites and blogs dedicated to Thai language learning offer valuable resources, such as grammar guides, vocabulary lists, pronunciation tips, and cultural insights. Examples include ThaiPod101, Learn Thai with ThaiPod101, and Omniglot.
- Beginner: Understand and use basic greetings and phrases. Introduce yourself and ask simple questions. Read and understand short, simple texts.
- Intermediate: Engage in basic conversations about familiar topics. Understand and respond to everyday situations. Read and understand longer texts with some assistance.
- Advanced: Engage in complex conversations on a variety of topics. Understand and respond to nuanced language. Read and understand complex texts with ease.
- Set smaller goals: Break down large goals into smaller, more achievable steps. This will help you feel a sense of accomplishment as you progress. For example, instead of aiming to learn 100 new words a week, start with 20 and gradually increase the number.
- Find a language learning buddy: Having someone to study with can provide motivation, accountability, and a chance to practice your language skills in a supportive environment. You can share your progress, challenges, and celebrate milestones together.
- Celebrate milestones: Reward yourself for achieving your goals, no matter how small they may seem. This will reinforce positive habits and keep you motivated. For example, treat yourself to a delicious meal or watch a movie in Thai after completing a certain number of lessons.
- Wai:The wai is a traditional Thai greeting, a gesture of respect and reverence. It involves placing your palms together in front of your chest and bowing slightly. The level of the wai depends on the age and social status of the person you are greeting.
- Respect for Elders:Thai society places great importance on respect for elders. This is reflected in language use, where different forms of address are used depending on the age and social status of the person you are speaking to.
- Non-Verbal Communication:Body language plays a significant role in Thai communication. For example, pointing with your feet is considered rude, and direct eye contact can be perceived as aggressive.
- Buddhism:Buddhism is the dominant religion in Thailand, and its influence is evident in many aspects of daily life, including language use and social norms. Understanding Buddhist concepts and practices can provide valuable insights into Thai culture.
- Books:There are many excellent books available on Thai culture, history, and language. Some popular choices include “Thailand: A Cultural History” by Michael Smithies and “Thai Culture: The Essential Guide” by Michael Freeman.
- Websites:Websites like the Thai Tourism Authority (TAT) and the Cultural Office of Thailand offer comprehensive information about Thai culture, traditions, and history.
- Documentaries:Documentaries provide a visual and engaging way to learn about Thai culture. You can find documentaries on topics such as Thai history, art, cuisine, and Buddhism.
- Museums:Museums dedicated to Thai art, history, and culture offer a wealth of information and artifacts.
- Enhanced Language Acquisition:Understanding the cultural context behind language use can help you grasp the nuances of the language and communicate more effectively.
- Increased Motivation:Learning about Thai culture can make your language learning journey more engaging and motivating.
- Improved Communication Skills:Cultural immersion helps you understand the social norms and etiquette associated with language use, improving your communication skills.
- Cultural Sensitivity:Learning about Thai culture promotes cultural sensitivity and helps you interact with Thai people with respect and understanding.
- The Spaced Repetition Technique (SRT) is a highly effective method for vocabulary memorization. It involves reviewing vocabulary items at progressively longer intervals, based on your recall ability. For instance, you might review a new word immediately after learning it, then again after 20 minutes, then after 8 hours, and so on.
This spaced repetition schedule helps reinforce the information in your memory, ensuring long-term retention.
- Flashcards are a simple yet powerful tool for vocabulary learning. They allow you to create visual cues for new words, aiding in both memorization and recall.
For effective flashcard use, create a set of cards with the Thai word on one side and its English translation on the other. Review the cards regularly, focusing on words you find challenging. You can also use flashcards to practice pronunciation and spelling.
- Vocabulary mapping is a technique that involves connecting new words to existing knowledge. It helps build a network of related words, making it easier to remember and recall them in context. For example, when learning the Thai word for “fruit” (ผลไม้), you could map it to other related words, such as “apple” (แอปเปิ้ล), “banana” (กล้วย), and “orange” (ส้ม).
This interconnected network strengthens your understanding and retention.
- One effective strategy for mastering Thai grammar is to analyze real-world examples. Start by identifying common sentence structures and patterns in authentic Thai texts, such as books, articles, or dialogues. Breaking down these examples into their constituent parts (subject, verb, object) will reveal the underlying grammatical rules.
- Identifying and analyzing common grammatical errors is essential for improving accuracy. Pay attention to mistakes you make while speaking or writing and try to understand the underlying grammatical rule that was violated. This will help you avoid repeating the same errors in the future.
- Practice is key to solidifying grammatical concepts. Engage in exercises that involve constructing sentences based on given grammatical rules. Error correction drills can also be beneficial, where you identify and correct grammatical mistakes in written or spoken Thai.
- Active listening techniques, such as paraphrasing and summarizing, help you process and internalize information. Paraphrasing involves rephrasing what you hear in your own words, while summarizing involves condensing the main points of a conversation or text. These techniques encourage deeper understanding and retention.
- Speaking practice is essential for developing fluency. Engage in various activities that involve using Thai, such as role-playing, debates, and presentations. These activities provide a platform for practicing pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary in a dynamic and engaging setting.
- Finding language partners or joining online communities can provide opportunities for regular conversation practice.
These platforms allow you to interact with native speakers or other learners, creating a supportive and immersive environment for language development.
- Developing fluency requires a personalized plan that includes a schedule for speaking practice, target language exposure, and regular self-assessment. Allocate specific time slots for speaking practice, whether it’s with a language partner, in a language exchange group, or through self-practice.
Immerse yourself in the target language through movies, music, podcasts, and news sources. Regularly assess your progress and identify areas that need improvement.
- Shadowing and pronunciation exercises play a crucial role in improving fluency and natural language flow. Shadowing involves mimicking native speakers, replicating their intonation, rhythm, and pace.
Pronunciation exercises focus on mastering the sounds and tones of Thai, enhancing your ability to articulate words and phrases clearly.
- Immersing yourself in the target language environment can significantly accelerate fluency development. Watch Thai movies and TV shows, listen to Thai music, and attend cultural events.
This exposure to authentic language and culture helps you internalize the language and develop a deeper understanding of its nuances.
- Keep a Learning Journal:Document your learning experiences, including new vocabulary, grammar rules, and challenges faced. This helps you track your progress and identify areas needing more attention.
- Practice Speaking and Listening:Record yourself speaking Thai and listen back to identify areas for improvement, such as pronunciation or fluency. You can also practice with a language partner or use online resources like language exchange platforms.
- Take Self-Assessments:Numerous online resources and apps offer self-assessment quizzes and tests that can provide insights into your current proficiency level.
- Set Realistic Goals:Break down your learning goals into smaller, achievable milestones. This makes the learning process less daunting and provides a sense of accomplishment as you achieve each milestone.
- Thai Language Proficiency Test (TLPT):This test is designed to assess the language proficiency of non-native speakers. It covers listening, reading, writing, and speaking skills.
- International English Language Testing System (IELTS):While primarily used for English proficiency, IELTS can also be used to assess Thai language skills, particularly for those who wish to study or work in Thailand.
- TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language):Similar to IELTS, TOEFL can also be used to assess Thai language proficiency for certain academic or professional purposes.
- Short-Term Goals:Set achievable goals for each week or month, such as learning a specific number of new vocabulary words, practicing a certain number of hours, or completing a particular grammar lesson.
- Long-Term Goals:Establish long-term goals, such as reaching a specific proficiency level or being able to hold a conversation in Thai. This provides a clear vision for your learning journey.
- Use a Tracker:Utilize a calendar, spreadsheet, or app to track your progress towards your goals. This helps you visualize your achievements and identify areas where you may need to adjust your strategy.
- Focus on Specific Skills:Identify the language skills you need to improve, such as pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, or fluency.
- Seek Feedback:Ask teachers, language partners, or native speakers for feedback on your progress and areas for improvement.
- Analyze Mistakes:When you make mistakes, analyze them to understand why you made them and how to avoid similar errors in the future.
Immersion and Practice
Immersion and consistent practice are crucial for mastering the Thai language. While learning from textbooks and online resources can provide a foundation, nothing compares to the experience of living and interacting in a Thai environment.
Benefits of Immersive Language Learning
Immersive language learning experiences, like living in Thailand, offer several advantages:
Role of Consistent Practice and Interaction
Consistent practice and interaction with native speakers are essential for language acquisition. This means:
Structured Immersion Plan
A structured immersion plan can enhance your learning experience:
Maximizing Language Learning Opportunities
Here are some tips for maximizing language learning opportunities through travel and cultural experiences:
Learning Resources and Tools

Having access to the right resources is crucial for a successful Thai language learning journey. From apps and online platforms to textbooks and dictionaries, there are numerous tools available to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
Popular Thai Language Learning Apps and Online Platforms
Several apps and online platforms are specifically designed to teach Thai. These platforms offer interactive lessons, exercises, and personalized feedback to help learners acquire language skills.
Comparison of Different Language Learning Methods
Choosing the right learning method depends on individual preferences, learning styles, and time constraints.
Effective Learning Materials
A variety of learning materials can enhance your Thai language acquisition journey.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Learning Approaches
Different learning approaches have their own advantages and disadvantages.
| Learning Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Classroom Learning | Structured lessons, teacher guidance, interactive learning, access to classmates for practice | Time-consuming, may not cater to individual learning paces, limited flexibility |
| Self-Study | Flexibility, learn at your own pace, access to a wealth of learning materials | Requires strong motivation and self-discipline, lack of structured guidance, limited opportunities for interactive learning |
| Hybrid Approach | Combines the advantages of classroom learning and self-study, provides flexibility and structure | May require more time and effort to manage both approaches |
7. Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is crucial for successful language learning. It’s like planning a journey—you need a destination and a map to guide you. Without clear goals, you might wander aimlessly, feeling lost and discouraged.
Importance of Setting Achievable Goals
Imagine trying to climb Mount Everest without proper training or preparation. You’d likely face immense challenges and a high chance of failure. Similarly, setting unrealistic goals in language learning can lead to demotivation and frustration. You might feel overwhelmed by the vast amount of material, discouraged by slow progress, or even give up entirely.
Examples of Realistic Milestones for Different Proficiency Levels
To avoid this, break down your language learning journey into smaller, manageable steps. Here are some examples of realistic milestones for different proficiency levels:
Strategies for Staying Motivated and Maintaining Consistency
Staying motivated and consistent is key to achieving your language learning goals. Here are some effective strategies:
Design a Personalized Learning Plan with Specific Goals and Timeframes
A personalized learning plan can help you stay focused and on track. Here’s how to create one:
1. Assess your current proficiency level
Honestly evaluate your current language skills. This will help you set realistic goals and choose appropriate learning materials.
2. Identify your learning style
Do you prefer visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learning? Understanding your learning style will help you select effective learning methods and resources.
3. Determine your available time
How much time can you realistically dedicate to language learning each week? Be honest with yourself and set achievable goals based on your schedule.
4. Set specific goals and timeframes
For example, “I will learn 20 new Thai words each week and practice speaking with my language buddy twice a week for the next month.”
5. Break down your goals into smaller steps
Divide your goals into smaller, manageable tasks. For example, instead of trying to learn all the Thai grammar rules at once, focus on learning one grammatical concept per week.
6. Choose learning resources
Select resources that align with your learning style and goals. This could include textbooks, online courses, language exchange partners, or apps.
7. Track your progress
Regularly monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed. This will help you stay motivated and ensure you’re on the right track.
Importance of Setting Realistic Goals in Language Learning
“Setting realistic goals is like building a sturdy foundation for your language learning journey. It provides a clear path to follow, motivates you to keep going, and ultimately leads to success.”
Setting realistic goals is crucial for successful language learning. It allows you to make steady progress, experience a sense of accomplishment, and maintain motivation. By setting achievable goals, you’ll avoid feeling overwhelmed, discouraged, and frustrated. Instead, you’ll experience the joy of learning, the satisfaction of progress, and the confidence to continue your journey.
Cultural Immersion
Learning Thai is more than just memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules; it’s about understanding the cultural context in which the language is spoken. Immersing yourself in Thai culture can significantly enhance your language learning journey.
Understanding Thai Culture and Customs
Thai culture is rich in traditions and etiquette, and these aspects play a crucial role in daily interactions. Understanding Thai customs can help you navigate social situations with ease, avoid misunderstandings, and build stronger connections with Thai people.
Examples of Cultural Practices and Social Etiquette
Here are some examples of cultural practices and social etiquette relevant to language acquisition:
Resources for Learning About Thai Culture and History
There are numerous resources available to help you learn about Thai culture and history:
Benefits of Integrating Cultural Immersion into Language Learning
Integrating cultural immersion into your language learning can have numerous benefits:
Language Learning Strategies
Mastering the Thai language requires a strategic approach, combining effective learning techniques with consistent practice. This section delves into specific strategies that can accelerate your progress and enhance your overall language acquisition experience.
Vocabulary Memorization
Vocabulary forms the foundation of any language, and Thai is no exception. Mastering a robust vocabulary is essential for comprehension, communication, and fluency. Effective vocabulary memorization techniques can significantly enhance your learning journey.
Grammar Mastery
Thai grammar, while distinct from English, follows a logical structure. Understanding the core principles of Thai grammar is crucial for accurate and fluent communication.
Active Listening and Speaking
Active listening and speaking are integral to language acquisition. They provide opportunities for real-time application of vocabulary and grammar, fostering fluency and confidence.
Fluency Development
Fluency involves speaking smoothly and naturally, without excessive hesitation or grammatical errors. It is a gradual process that requires consistent practice and exposure to the target language.
Thai Language Learning Communities
Connecting with other learners and native speakers is a crucial part of mastering any language, and Thai is no exception. Language learning communities offer a wealth of resources, support, and opportunities to practice your skills in a fun and engaging environment.
Thai Language Learning Communities: An Overview
Here’s a table summarizing some popular online and offline communities dedicated to Thai language learning:
| Community Name | Platform | Target Audience | Key Features | Overall Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thai Language & Culture Forum | Online | Beginners to advanced learners | Discussion forums, language exchange partners, cultural insights | Highly effective for language learning and cultural understanding |
| Thai Language Meetup | Offline | All levels | Regular gatherings, language exchange events, social activities | Excellent for practicing conversational skills and building relationships |
| HelloTalk | Online | All levels | Language exchange app, voice and text messaging, cultural insights | Highly effective for practicing speaking and writing skills |
| Tandem | Online | All levels | Language exchange app, voice and text messaging, cultural insights | Highly effective for practicing speaking and writing skills |
| italki | Online | All levels | Language lessons, language exchange partners, cultural insights | Highly effective for structured language learning and personalized instruction |
“Connecting with other learners and native speakers is a powerful tool for language acquisition. It provides a real-world context for practicing your skills, receiving feedback, and gaining cultural insights.”
Benefits of Connecting with Other Learners and Native Speakers
Engaging with other learners and native speakers offers a multitude of benefits for Thai language acquisition. It fosters a sense of community, provides opportunities for authentic language practice, and facilitates cultural immersion.* Improved Motivation:Connecting with others who share your language learning goals can boost your motivation and keep you on track.
Seeing others progress can inspire you to push yourself further.
Authentic Language Exposure
Interacting with native speakers allows you to hear and experience the language in its natural context. You’ll encounter different accents, slang, and idiomatic expressions, enriching your understanding of the language.
Cultural Immersion
Immersing yourself in the Thai culture through interactions with native speakers provides valuable insights into customs, traditions, and perspectives. This helps you understand the language on a deeper level.
Practice Conversational Skills
Engaging in conversations with other learners and native speakers provides opportunities to practice your speaking and listening skills. You can get feedback on your pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary, improving your fluency and confidence.
Build Confidence
Speaking Thai with others, even if you make mistakes, helps you build confidence in your abilities. It allows you to overcome any hesitation and embrace the learning process.
Tips for Finding Language Exchange Partners and Practicing Conversational Skills
* Utilize Online Platforms:Platforms like HelloTalk, Tandem, and italki connect language learners with native speakers for language exchange. You can find partners who are interested in learning your native language in exchange for helping them with Thai.
Join Local Meetups
Search for Thai language meetups in your area. These gatherings provide a great opportunity to practice conversational skills with other learners and native speakers in a casual and friendly environment.
Participate in Language Exchange Events
Many universities, cultural centers, and language schools organize language exchange events. These events provide a structured setting for practicing your Thai with native speakers.
Look for Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and communities dedicated to Thai language learning offer opportunities to connect with other learners, ask questions, and participate in discussions.
Be Proactive and Open-Minded
Reach out to people, attend events, and participate actively in online communities. The more you engage, the more opportunities you’ll have to practice your Thai and make new connections.
Social Interaction: A Key to Language Acquisition
Social interaction is a cornerstone of language acquisition. It provides a real-world context for applying your knowledge, receiving feedback, and experiencing the language in its natural form. Language learning communities facilitate this process by creating spaces for meaningful interactions, fostering a supportive environment, and providing access to authentic language resources.
Assessment and Progress Tracking
Keeping track of your progress is crucial for staying motivated and understanding your strengths and weaknesses in your Thai learning journey. Regularly assessing your skills helps you identify areas needing improvement and adjust your learning strategy for better results.
Self-Assessment and Monitoring
Regular self-assessment allows you to track your progress and identify areas for improvement. You can use various methods to evaluate your understanding of the language.
Language Proficiency Tests and Assessments
Formal language proficiency tests can provide an objective evaluation of your Thai language skills. These tests are often used for academic or professional purposes.
Setting Milestones and Tracking Achievements
Setting milestones and tracking your achievements is a valuable way to stay motivated and measure your progress.
Evaluating Language Skills and Identifying Areas for Improvement
Regularly evaluate your language skills to identify areas needing improvement. This can be done through self-assessment, feedback from teachers or language partners, and formal assessments.
The Joy of Learning Thai
Learning Thai is an enriching and rewarding experience that goes beyond simply acquiring a new language. It’s a journey of cultural immersion, intellectual stimulation, and personal growth. Embracing the intricacies of the Thai language opens doors to a vibrant world of history, art, and traditions.
Personal and Professional Growth
Learning a new language, particularly one as unique as Thai, expands your horizons and enhances your cognitive abilities. It challenges you to think differently, improve your memory, and develop greater cultural sensitivity. In a globalized world, multilingualism is a valuable asset in both personal and professional life.
It opens doors to new career opportunities, facilitates international travel, and fosters meaningful connections with people from diverse backgrounds.
Cultural and Intellectual Rewards
Mastering the Thai language unlocks a rich tapestry of cultural experiences. You’ll gain a deeper understanding of Thai literature, music, and art, and appreciate the nuances of Thai humor and storytelling. The Thai language is known for its poetic beauty and expressive power, reflecting the rich cultural heritage of Thailand.
Learning Thai provides a unique window into the soul of this fascinating country.
Embracing the Journey
Learning Thai is a journey of discovery and self-improvement. It requires patience, persistence, and a willingness to embrace challenges. As you navigate the complexities of the Thai language, you’ll develop a sense of accomplishment and a newfound appreciation for the beauty and diversity of human communication.
Don’t be afraid to make mistakes, as they are an integral part of the learning process. Embrace the journey, celebrate your progress, and enjoy the incredible rewards of learning Thai.
FAQ Summary
What are some common mistakes that Thai learners make?
Common mistakes include mispronouncing tones, confusing similar-sounding words, and not using proper honorifics. It’s important to focus on pronunciation, vocabulary, and cultural context to avoid these errors.
Is it better to learn Thai in Thailand or online?
Both methods have their advantages. Immersion in Thailand provides a rich cultural experience and constant exposure to the language, but online learning offers flexibility and affordable resources. The best approach depends on your learning style and preferences.
How can I find a Thai language tutor?
Online platforms like Verbling and iTalki connect learners with qualified Thai tutors. You can also check local language schools and universities for Thai language classes.
Are there any free resources for learning Thai?
Yes, there are many free resources available, including online courses, language exchange apps, and YouTube channels dedicated to Thai language learning. A quick search will reveal a wealth of options.