How hard to learn java – How hard is it to learn Java? This question is a common one for aspiring programmers. Java, a powerful and versatile programming language, has been a mainstay in the tech world for decades. Its popularity stems from its robustness, platform independence, and vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks.
But learning any new programming language requires time, dedication, and a strategic approach.
The difficulty of learning Java depends on several factors, including your prior programming experience, your learning style, the amount of time you dedicate to practice, and the resources available to you. While Java has a steeper learning curve than some other languages, its comprehensive nature and vast job market make it a worthwhile investment for anyone interested in a career in software development.
Java’s Popularity and Use Cases
Java’s enduring popularity stems from its versatility, reliability, and robust ecosystem. It’s a language that’s been used to build a wide array of applications, from enterprise software to mobile apps, making it a highly sought-after skill in the tech industry.Java’s popularity is a result of several key factors, including its platform independence, strong community support, and its ability to handle complex, large-scale projects.
These factors have contributed to Java’s widespread adoption across various industries.
Real-World Applications of Java
Java is a workhorse language used in numerous real-world applications. Here are some prominent examples:
- Enterprise Applications:Java is the backbone of many enterprise applications, including banking systems, e-commerce platforms, and financial trading systems. Its ability to handle large amounts of data and complex transactions makes it ideal for these demanding applications.
- Android Development:Android, the world’s most popular mobile operating system, is built on Java. Developers use Java to create a vast majority of Android apps, from simple games to complex productivity tools.
- Web Applications:Java is widely used in web development, particularly for server-side applications. Java frameworks like Spring and Jakarta EE provide robust tools for building scalable and secure web applications.
- Big Data and Analytics:Java plays a crucial role in big data and analytics projects. Frameworks like Hadoop and Spark, built using Java, are used to process and analyze massive datasets, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights.
- Scientific Computing and Research:Java’s powerful libraries and its ability to handle complex calculations make it suitable for scientific computing and research projects. It’s used in areas like bioinformatics, simulations, and data analysis.
Java’s Prevalence in the Tech World
Java’s popularity is reflected in its consistent ranking in programming language popularity surveys. The TIOBE Index, a well-known indicator of programming language popularity, consistently ranks Java among the top three most popular languages.
Java is a mature and reliable language with a strong ecosystem, making it a valuable asset for developers and businesses alike.
Java Fundamentals and Core Concepts
Welcome to the world of Java programming! This section will delve into the fundamental building blocks of Java, equipping you with the essential knowledge to write your first programs. We’ll cover the basic structure of Java code, explore essential data types and variables, understand different operators, and introduce the core concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP).
Java Code Structure and Syntax
Every Java program consists of a series of instructions organized in a specific structure. The basic unit of a Java program is a class, which acts as a blueprint for creating objects. Here’s a breakdown of the essential elements:
“`javapublic class MyProgram public static void main(String[] args) // Code goes here “`
`public class MyProgram`
This line declares a class named “MyProgram” and makes it accessible from anywhere.
`public static void main(String[] args)`
This is the entry point of your program, where execution begins.
Curly Braces “
These delimit code blocks. The code within the curly braces of the `main` method is executed when the program runs. Declaring Variables: Variables are containers that store data. You declare a variable by specifying its data type and name:
“`javaint age = 25; // Declares an integer variable named ‘age’ and assigns it the value 25.String name = “Alice”; // Declares a string variable named ‘name’ and assigns it the value “Alice”.“`
Performing Arithmetic Operations: Java supports basic arithmetic operations:
“`javaint sum = 10 + 5; // Additionint difference = 15
7; // Subtraction
int product = 3
4; // Multiplication
int quotient = 20 / 5; // Divisionint remainder = 17 % 3; // Modulus (remainder after division)“`
Comments: Comments are essential for explaining your code and making it more readable.
Single-line Comments
Start with `//`.
Multi-line Comments
Enclosed between `/*` and `*/`.
“`java// This is a single-line comment/*This is a multi-line comment.It can span multiple lines.
/
“`
Fundamental Data Types and Variables
Java provides eight primitive data types, representing different types of data:
- `byte`: Stores whole numbers from -128 to 127.
- `short`: Stores whole numbers from -32,768 to 32,767.
- `int`: Stores whole numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. This is the most commonly used integer type.
- `long`: Stores whole numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807.
- `float`: Stores single-precision floating-point numbers (numbers with decimal points).
- `double`: Stores double-precision floating-point numbers, providing higher precision than `float`.
- `char`: Stores single characters, enclosed in single quotes (e.g., `’A’`, `’%’`, `’1’`).
- `boolean`: Stores truth values, either `true` or `false`.
Declaring Variables and Assigning Values:
“`javabyte age = 25; // ‘age’ is a byte variable holding the value 25short quantity = 1000; // ‘quantity’ is a short variable holding the value 1000int population = 5000000; // ‘population’ is an int variable holding the value 5,000,000long distance = 10000000000L; // ‘distance’ is a long variable holding the value 10,000,000,000 (note the ‘L’ suffix)float temperature = 25.5f; // ‘temperature’ is a float variable holding the value 25.5 (note the ‘f’ suffix)double pi = 3.141592653589793; // ‘pi’ is a double variable holding the value 3.141592653589793char initial = ‘A’; // ‘initial’ is a char variable holding the character ‘A’boolean isLoggedIn = true; // ‘isLoggedIn’ is a boolean variable holding the value ‘true’“`
Type Conversion: Sometimes you need to convert data from one type to another.
Explicit Type Casting
You manually convert a value to a different type using a cast operator:
“`javadouble price = 10.5;int wholePrice = (int) price; // Explicitly cast ‘price’ (double) to an integer, discarding the decimal part“`
Implicit Type Casting
Java automatically converts a value to a compatible type if there’s no loss of data:
“`javaint num1 = 10;double num2 = num1; // Implicitly converts ‘num1’ (int) to a double“`
Using Variables: You can use variables in calculations, comparisons, and conditional statements:
“`javaint age = 25;int ageNextYear = age + 1; // Calculate age next yearboolean isAdult = age >= 18; // Check if age is greater than or equal to 18if (isAdult) System.out.println(“You are an adult.”); else System.out.println(“You are not an adult yet.”);“`
Operators in Java
Java provides various operators to perform operations on data. Arithmetic Operators:
- `+` (Addition):Adds two operands.
- `-` (Subtraction):Subtracts the second operand from the first.
- `*` (Multiplication):Multiplies two operands.
- `/` (Division):Divides the first operand by the second.
- `%` (Modulus):Returns the remainder of a division.
- `++` (Increment):Increases the value of an operand by 1.
- `–` (Decrement):Decreases the value of an operand by 1.
Relational Operators:
- `==` (Equal to):Checks if two operands are equal.
- `!=` (Not equal to):Checks if two operands are not equal.
- `>` (Greater than):Checks if the first operand is greater than the second.
- `<` (Less than):Checks if the first operand is less than the second.
- `>=` (Greater than or equal to):Checks if the first operand is greater than or equal to the second.
- `<=` (Less than or equal to):Checks if the first operand is less than or equal to the second.
Logical Operators:
- `&&` (Logical AND):Returns `true` if both operands are `true`.
- `||` (Logical OR):Returns `true` if at least one operand is `true`.
- `!` (Logical NOT):Inverts the truth value of an operand.
Bitwise Operators:
- `&` (Bitwise AND):Performs a bitwise AND operation on each bit of the operands.
- `|` (Bitwise OR):Performs a bitwise OR operation on each bit of the operands.
- `^` (Bitwise XOR):Performs a bitwise XOR operation on each bit of the operands.
- `~` (Bitwise NOT):Inverts the bits of an operand.
- `<<` (Left shift):Shifts the bits of an operand to the left.
- `>>` (Right shift):Shifts the bits of an operand to the right.
- `>>>` (Unsigned right shift):Shifts the bits of an operand to the right, filling the leftmost bits with zeros.
Assignment Operators:
- `=` (Assignment):Assigns the value of the right operand to the left operand.
- `+=` (Add and assign):Adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `-=` (Subtract and assign):Subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `*=` (Multiply and assign):Multiplies the right operand by the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `/=` (Divide and assign):Divides the left operand by the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `%=` (Modulus and assign):Calculates the remainder of dividing the left operand by the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `&=` (Bitwise AND and assign):Performs a bitwise AND operation on the operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `|=` (Bitwise OR and assign):Performs a bitwise OR operation on the operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `^=` (Bitwise XOR and assign):Performs a bitwise XOR operation on the operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `<<=` (Left shift and assign):Shifts the bits of the left operand to the left by the number of positions specified by the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `>>=` (Right shift and assign):Shifts the bits of the left operand to the right by the number of positions specified by the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- `>>>=` (Unsigned right shift and assign):Shifts the bits of the left operand to the right by the number of positions specified by the right operand, filling the leftmost bits with zeros, and assigns the result to the left operand.
Operator Precedence: Operators have a specific order of precedence, determining the order in which operations are performed. For example, multiplication and division have higher precedence than addition and subtraction. Parentheses `()` can be used to override the default precedence.
“`javaint result = 10 + 5
2; // Result is 20 (multiplication performed first)
int result2 = (10 + 5)
2; // Result is 30 (addition performed first due to parentheses)
“`
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts in Java
OOP is a programming paradigm that focuses on representing data as objects, which encapsulate both data (attributes) and behavior (methods). Java is a fully object-oriented language, adhering to the core OOP principles: Encapsulation: Data and methods are bundled together within a class, hiding internal implementation details and exposing only necessary information through methods.
Abstraction: Focusing on essential features and hiding complex details. Interfaces and abstract classes play a key role in abstraction. Inheritance: Creating new classes (subclasses) that inherit properties and methods from existing classes (superclasses). This promotes code reuse and a hierarchical structure.
Polymorphism: The ability of objects to take on multiple forms. This allows you to write code that can work with objects of different types, making your code more flexible and adaptable. Classes and Objects:
Class
A blueprint for creating objects. It defines the attributes (fields) and methods that objects of that class will have.
Object
An instance of a class. Each object has its own set of data values for the attributes defined in the class. Creating Classes:
“`javapublic class Car String model; // Attribute (field) to store the car model int year; // Attribute (field) to store the car year public void start() // Method to start the car System.out.println(“Car started.”); public void accelerate() // Method to accelerate the car System.out.println(“Car accelerating.”); “`
Creating Objects:
“`javaCar myCar = new Car(); // Create an object ‘myCar’ of the ‘Car’ classmyCar.model = “Toyota Camry”; // Assign a value to the ‘model’ attributemyCar.year = 2023; // Assign a value to the ‘year’ attributemyCar.start(); // Call the ‘start’ method on the ‘myCar’ objectmyCar.accelerate(); // Call the ‘accelerate’ method on the ‘myCar’ object“`
Writing a Simple Java Program
Let’s write a Java program that prompts the user for their name and age, then displays a personalized greeting message:
“`javaimport java.util.Scanner;public class GreetingProgram public static void main(String[] args) Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object to read user input System.out.print(“Enter your name: “); String name = scanner.nextLine(); // Read the user’s name System.out.print(“Enter your age: “); int age = scanner.nextInt(); // Read the user’s age System.out.println(“Hello, ” + name + “! You are ” + age + ” years old.”); // Display the greeting message “`
Explanation:
1. Import Statement
`import java.util.Scanner;` imports the `Scanner` class, which is used for reading user input from the console.
2. Scanner Object
`Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);` creates a `Scanner` object to read input from the standard input stream (`System.in`).
3. Prompt for Name
`System.out.print(“Enter your name: “);` displays a prompt asking the user to enter their name.
4. Read Name
`String name = scanner.nextLine();` reads the user’s name from the console and stores it in the `name` variable.
5. Prompt for Age
`System.out.print(“Enter your age: “);` displays a prompt asking the user to enter their age.
6. Read Age
`int age = scanner.nextInt();` reads the user’s age from the console and stores it in the `age` variable.
7. Display Greeting
`System.out.println(“Hello, ” + name + “! You are ” + age + ” years old.”);` displays a personalized greeting message using the user’s name and age.
Additional Resources
Official Java Documentation
[https://docs.oracle.com/javase/](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/)
Oracle Java Tutorials
[https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/)
W3Schools Java Tutorial
[https://www.w3schools.com/java/](https://www.w3schools.com/java/)
Java Brains
[https://www.javabrains.io/](https://www.javabrains.io/)
Codecademy Java Course
[https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-java](https://www.codecademy.com/learn/learn-java) Advanced OOP Concepts:
Interfaces
Define contracts that classes can implement.
Abstract Classes
Classes that cannot be instantiated directly but can be extended by subclasses.
Packages
Organize related classes and interfaces into logical groups.
3. Learning Resources and Tools
Embarking on your Java learning journey requires access to the right resources and tools. This section provides a curated list of popular online courses, beginner-friendly YouTube channels, and essential IDEs for Java development. We’ll also delve into key Java libraries and frameworks that will empower you to build robust applications.
Online Courses and Tutorials
Online courses offer a structured and comprehensive approach to learning Java. Here are some highly recommended courses:
- Java Programming Masterclass for Software Developers(Udemy): This comprehensive course covers the fundamentals of Java programming, object-oriented programming concepts, and advanced topics like data structures and algorithms. It includes numerous coding exercises and real-world projects.
- Java Programming and Software Engineering Fundamentals Specialization(Coursera): This specialization provides a solid foundation in Java programming, focusing on core concepts, data structures, algorithms, and software design principles. It includes hands-on projects and quizzes.
- Introduction to Java Programming(edX): This course offers a beginner-friendly introduction to Java programming, covering syntax, data types, control flow, and object-oriented programming concepts. It includes interactive exercises and programming assignments.
YouTube channels and websites offer free Java tutorials that cater to different learning styles. Here are some excellent resources:
- freeCodeCamp.org: This popular platform provides a vast library of free coding tutorials, including a comprehensive Java course that covers the basics, object-oriented programming, and advanced concepts.
- Derek Banas: Derek Banas’s YouTube channel features a wide range of Java tutorials, from beginner to advanced topics, presented in a clear and concise manner.
- TheNewBoston: This channel offers a collection of Java tutorials that cover various aspects of the language, including basic syntax, object-oriented programming, and advanced topics like networking and databases.
IDEs for Java Development
An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) provides a comprehensive set of tools for Java development, enhancing productivity and streamlining the development process.
| IDE Name | Key Features | Pros | Cons | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eclipse | Code completion, debugging tools, project management, plugin support | Open-source, widely used, extensive plugin ecosystem | Can be resource-intensive, interface may seem outdated | Free |
| IntelliJ IDEA | Advanced code completion, intelligent code analysis, refactoring tools, integrated version control | Excellent performance, intelligent code assistance, user-friendly interface | Paid version for professional features, resource-intensive | Free (Community Edition), Paid (Ultimate Edition) |
| NetBeans | Code completion, debugging tools, project management, visual design tools | User-friendly interface, comprehensive features, good for beginners | May feel less advanced compared to IntelliJ IDEA, limited plugin support | Free |
IDEs offer significant advantages for Java development, including:
- Code Completion:IDEs provide intelligent code completion suggestions, reducing typing errors and improving coding efficiency.
- Debugging Tools:Built-in debugging tools allow you to step through code, inspect variables, and identify errors, making it easier to troubleshoot and fix bugs.
- Project Management:IDEs facilitate project management by providing features for organizing files, managing dependencies, and building projects.
Essential Java Libraries and Frameworks
Java libraries and frameworks provide pre-built components and functionalities that streamline development and enhance application capabilities.
- Spring Framework: A comprehensive framework for building enterprise-grade Java applications, offering features for dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and web development. Official Documentation
- Apache Commons: A collection of reusable Java components that provide common utilities, such as string manipulation, collections, and file handling. Official Documentation
- Guava: A Google-developed library that provides utility classes for collections, caching, and concurrency, enhancing code readability and efficiency. Official Repository
- JUnit: A popular testing framework for Java, enabling developers to write and execute unit tests for their code. Official Documentation
- Hibernate: An object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database interactions, allowing developers to work with objects instead of SQL queries. Official Documentation
Writing a Simple Java Program
Let’s write a basic Java program that prints “Hello, World!” to the console. Here’s the code:
public class HelloWorld
public static void main(String[] args)
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
Explanation of the code:
public class HelloWorld: This line declares a public class namedHelloWorld. In Java, every program must have at least one public class.public static void main(String[] args): This line defines the main method, which is the entry point of the program. It is a static method that takes an array of strings as arguments (args).System.out.println("Hello, World!");: This line prints the text “Hello, World!” to the console using theprintln()method of theSystem.outobject.
To compile and run this program, follow these steps:
- Save the codein a file named
HelloWorld.java. - Open a terminal or command promptand navigate to the directory where you saved the file.
- Compile the programusing the command
javac HelloWorld.java. This will generate aHelloWorld.classfile. - Run the programusing the command
java HelloWorld. This will execute the compiled class file and print “Hello, World!” to the console.
Setting up a Java development environment involves installing the Java Development Kit (JDK) and choosing an IDE. The JDK provides the necessary tools for compiling and running Java programs. IDEs offer a user-friendly interface and tools for development, as discussed earlier.
Time Commitment and Effort Required
Learning Java, like any skill, requires dedication and effort. The time commitment needed to become proficient varies depending on your goals and circumstances. Let’s explore the time ranges and factors that influence your learning journey.
Time Estimates for Different Proficiency Levels
The time required to reach different levels of proficiency in Java can vary greatly. Here’s a general estimate for each level:
- Beginner:A basic understanding of Java syntax and concepts can be achieved in a few weeks to a couple of monthsof dedicated study. This involves learning the fundamentals of Java programming, including data types, variables, operators, control flow, and basic object-oriented concepts.
- Intermediate:To be able to build small applications and use common libraries, you’ll need several months to a yearof consistent learning and practice. At this level, you’ll delve deeper into Java’s object-oriented features, learn to use collections, work with files and databases, and explore popular frameworks like Spring.
- Advanced:Mastering Java’s advanced features and becoming proficient in designing complex systems requires several yearsof continuous learning and experience. This involves understanding advanced concepts like concurrency, generics, reflection, and design patterns. You’ll also need to gain practical experience working on real-world projects.
Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several factors can influence how quickly you learn Java:
- Prior Programming Experience:If you have experience with other programming languages, you’ll likely pick up Java faster. Many concepts are transferable across languages, allowing you to focus on Java’s specific features and syntax.
- Learning Style:Your preferred learning style can impact your progress. Visual learners might benefit from interactive tutorials and diagrams, while hands-on learners might prefer coding exercises and building projects.
- Time Dedicated to Practice:Consistent practice is crucial for mastering Java. Dedicate regular time to coding exercises, build small projects, and actively apply what you’ve learned. The more you practice, the faster you’ll improve.
- Availability of Resources:Access to high-quality learning resources, such as online courses, books, and mentors, can significantly accelerate your learning. Choose resources that align with your learning style and provide clear explanations and practical examples.
Importance of Consistent Practice and Dedication
“Deliberate practice is the key to mastery.”
Deliberate practice involves actively engaging with Java concepts, identifying areas for improvement, and working on specific challenges to enhance your skills.
- Set Achievable Goals:Break down your learning journey into smaller, manageable goals. This will keep you motivated and track your progress. Start with simple projects and gradually work your way up to more complex ones.
- Track Your Progress:Regularly assess your understanding and identify areas where you need more practice. Keep a record of your learning journey to see how far you’ve come and stay motivated.
- Real-World Projects and Challenges:Working on real-world projects or participating in coding challenges can provide valuable experience and motivation. It allows you to apply your knowledge in a practical setting and receive feedback from others.
5. Challenges and Potential Roadblocks for Java Beginners
Learning Java can be an exciting journey, but it also comes with its share of challenges, especially for beginners. Understanding these obstacles and developing strategies to overcome them is crucial for a smooth learning experience. This section will explore common hurdles faced by Java learners and provide practical solutions to navigate them effectively.
Setting up the Development Environment
Setting up the development environment is often the first hurdle for Java beginners. This involves installing the Java Development Kit (JDK) and choosing an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA.
- Installing the JDK:The JDK is essential for compiling and running Java programs. Download the latest JDK version from Oracle’s official website. The installation process involves accepting the license agreement, choosing the desired installation directory, and following the on-screen instructions.
- Setting up Eclipse:Eclipse is a popular open-source IDE widely used for Java development. Download the Eclipse IDE for Java Developers from the Eclipse Foundation website. Once downloaded, extract the archive, launch the Eclipse application, and choose a workspace directory to store your projects.
- Setting up IntelliJ IDEA:IntelliJ IDEA is another powerful IDE known for its advanced features and user-friendly interface. Download the Community Edition from JetBrains’ website. During installation, choose the default settings or customize them based on your preferences.
Understanding Core Java Concepts
Java’s core concepts can be overwhelming for beginners. Grasping these fundamentals is essential for writing effective Java programs.
- Data Types:Java uses various data types to represent different kinds of data, such as integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and booleans. Understanding these data types is crucial for storing and manipulating data in your programs. For example, you can use the `int` data type to store whole numbers, `double` for decimal numbers, and `char` for single characters.
- Variables:Variables are used to store data in Java. They have a name, data type, and a value. For instance, you can declare a variable named `age` of type `int` and assign it the value 25.
- Operators:Operators are special symbols used to perform operations on data. Common operators include arithmetic operators (like +,-,*,/), relational operators (like ==, !=, >, <), and logical operators (like &&, ||, !).
- Control Flow Statements:Control flow statements determine the order in which statements are executed in a program. They include `if-else` statements for conditional execution, `for` and `while` loops for repetitive execution, and `switch` statements for multiple-choice scenarios.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):Java is an object-oriented programming language, which means it uses objects to represent real-world entities. Key OOP principles include encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Understanding these concepts allows you to design modular and reusable code.
Debugging and Troubleshooting Errors
Debugging is an integral part of software development, and Java beginners often encounter various errors.
- Syntax Errors:These errors occur when the code violates Java’s syntax rules. The compiler will usually point out the location of the error, helping you identify and fix the issue.
- Runtime Errors:These errors occur during program execution. They are often caused by logical errors in the code, such as attempting to access an array element outside its bounds or dividing by zero.
- Logical Errors:These errors occur when the code executes without throwing an exception but produces incorrect results. Debugging these errors can be challenging, requiring careful analysis of the code and its execution flow.
- Using the Debugger:IDEs like Eclipse and IntelliJ IDEA provide powerful debugging tools. The debugger allows you to step through your code line by line, inspect variable values, and identify the source of errors.
- Logging:Logging is a useful technique for tracking program execution and identifying potential issues. You can use logging statements to print messages to the console, which can help you understand the flow of your program and pinpoint errors.
- Online Resources:Stack Overflow is a popular online community for programmers where you can find solutions to common problems and get help from experienced developers.
Java’s Versatility and Career Opportunities

Java’s widespread adoption and versatile nature have made it a highly sought-after skill in the tech industry, opening doors to a diverse range of career paths. This section delves into the various applications that Java supports and the abundant job opportunities it offers.
Java’s Wide Range of Applications
Java’s versatility stems from its ability to power a vast array of applications across diverse domains. This makes it a highly valuable skill for developers seeking to build robust and scalable solutions.
- Web Development:Java is a cornerstone of enterprise-level web applications, powering back-end systems, handling server-side logic, and managing databases. Frameworks like Spring and Jakarta EE simplify web development, enabling developers to build secure, scalable, and maintainable web applications.
- Mobile App Development:While Java’s role in Android app development has evolved with the emergence of Kotlin, it remains a foundational language for Android development. Java’s object-oriented nature and robust libraries make it suitable for building complex and feature-rich Android apps.
- Big Data and Analytics:Java plays a crucial role in big data processing and analytics. Frameworks like Hadoop and Spark leverage Java’s capabilities to handle massive datasets, enabling efficient data analysis and insights generation.
- Cloud Computing:Java is widely used in cloud computing environments, powering applications running on platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Its ability to handle concurrency and distributed systems makes it ideal for cloud-based applications.
- Desktop Applications:Java’s platform independence enables the creation of cross-platform desktop applications. Swing and AWT are Java’s graphical user interface (GUI) toolkits, allowing developers to build interactive and user-friendly desktop applications.
- Game Development:Java is a popular choice for developing games, particularly for mobile and desktop platforms. Its performance and libraries, such as LWJGL, make it suitable for creating graphics-intensive games.
- Scientific Computing and Research:Java’s numerical computation libraries and its ability to handle complex data structures make it a valuable tool for scientific computing and research. It’s used in areas like bioinformatics, financial modeling, and simulation.
Career Paths for Java Developers
The demand for Java developers remains strong across various industries, offering a wide range of career paths with promising growth potential.
- Java Developer:This is the entry-level position for Java programmers. Developers in this role typically write code, test, and debug Java applications, collaborating with teams to deliver software solutions.
- Senior Java Developer:With experience and expertise, Java developers can advance to senior roles, leading teams, mentoring junior developers, and taking on complex projects with greater responsibility.
- Software Architect:Software architects are responsible for designing and implementing the overall structure and architecture of software systems, ensuring scalability, maintainability, and performance. Java skills are highly valuable for software architects.
- Big Data Engineer:As big data continues to grow, the demand for big data engineers skilled in Java is increasing. These professionals design and implement big data solutions, leveraging Java frameworks like Hadoop and Spark.
- Cloud Architect:Cloud architects are responsible for designing, deploying, and managing cloud infrastructure and applications. Java skills are crucial for building and managing cloud-based applications.
Job Market Demand for Java Professionals
The job market for Java professionals remains robust, with consistently high demand across various industries. This is attributed to Java’s widespread adoption and its relevance in key technological domains.
“Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, and the demand for Java developers is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.”
Indeed.com
According to Stack Overflow’s 2023 Developer Survey, Java ranks among the top five most popular programming languages, with a significant number of developers using it. This indicates a strong demand for Java skills in the tech industry.
- High Demand:Job postings for Java developers are consistently high, reflecting the ongoing need for skilled professionals in this area.
- Diverse Industries:Java’s applications extend across various industries, including finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and technology, creating diverse job opportunities.
- Competitive Salaries:Java developers command competitive salaries, reflecting the high demand and value of their skills.
7. Comparing Java to Other Programming Languages
Choosing the right programming language for a project can be a daunting task, especially with so many options available. Java, Python, C++, and JavaScript are among the most popular and versatile languages, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Comparative Analysis
This section delves into a comprehensive comparison of Java, Python, C++, and JavaScript, examining key aspects like syntax, performance, ecosystem, and community support.
Syntax and Readability
- Java: Known for its strict syntax and verbose nature, Java emphasizes clarity and explicitness. It uses curly braces to define code blocks and requires explicit type declarations. This can make Java code more structured and easier to maintain, but it can also be more verbose and less concise compared to other languages.
- Python: Python’s syntax is often praised for its simplicity and readability. It uses indentation to define code blocks, eliminating the need for curly braces. Python’s dynamic typing allows for less code verbosity, making it easier to write and understand.
- C++: C++ is a powerful language with a more complex syntax than Java or Python. It offers low-level control and supports both procedural and object-oriented programming paradigms. C++’s syntax can be challenging for beginners, but it provides flexibility and efficiency for advanced applications.
- JavaScript: JavaScript is a dynamic language designed for web development. Its syntax is similar to C++, but it features a more flexible approach to data types and functions. JavaScript’s dynamic nature can make it more concise and easier to learn, but it can also lead to potential errors if not used carefully.
Performance and Efficiency
- Java: Java is known for its performance and efficiency. Its Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and garbage collection mechanisms optimize code execution and memory management. Java’s strong type system and static nature contribute to its reliability and predictability.
- Python: Python is generally considered slower than Java due to its dynamic typing and interpreted nature. However, Python’s performance has improved significantly with the introduction of optimized interpreters and frameworks like PyPy. Python’s focus on readability and ease of use often outweighs performance concerns in many applications.
- C++: C++ is renowned for its performance and efficiency. It offers low-level control over hardware resources and supports advanced optimization techniques. C++ is often used for applications where performance is critical, such as game development and high-frequency trading.
- JavaScript: JavaScript’s performance has improved significantly over the years with advancements in JavaScript engines and frameworks. While it can be slower than Java or C++ in some cases, JavaScript’s ability to run directly in web browsers makes it a popular choice for web applications.
Ecosystem and Libraries
- Java: Java boasts a vast and mature ecosystem with a wide range of libraries and frameworks for various programming tasks. The Java ecosystem includes popular frameworks like Spring, Hibernate, and Apache Struts, which provide robust solutions for enterprise application development, web development, and data persistence.
- Python: Python has a thriving ecosystem with numerous libraries and frameworks for data science, machine learning, web development, and more. Popular libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn, and Django offer powerful tools for data analysis, scientific computing, and web application development.
- C++: C++ has a vast and mature ecosystem with libraries and frameworks for various domains, including game development, embedded systems, and high-performance computing. Libraries like Boost, Qt, and OpenCV provide comprehensive solutions for these areas.
- JavaScript: JavaScript’s ecosystem is rapidly evolving, with a wide array of libraries and frameworks for web development, front-end design, and mobile app development. Popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js provide robust tools for building interactive and dynamic web applications.
Community Support and Learning Resources
- Java: Java has a large and active developer community with extensive documentation, forums, and online resources. The availability of numerous books, tutorials, and online courses makes learning Java relatively easy.
- Python: Python enjoys a massive and supportive community, with abundant learning resources, forums, and online communities. Python’s simplicity and focus on readability have contributed to its popularity among beginners and experienced developers alike.
- C++: C++ has a strong and active community, with numerous books, tutorials, and online resources available. The language’s complexity and wide range of applications have fostered a dedicated community of developers.
- JavaScript: JavaScript has a vast and vibrant community, with a wealth of learning resources, forums, and online communities. The language’s popularity for web development has driven the growth of its community and resources.
Java’s Ecosystem and Community
Java boasts a thriving and supportive ecosystem that plays a crucial role in its widespread adoption and success. The vibrant Java community, consisting of developers, enthusiasts, and experts, contributes significantly to the language’s evolution, providing a wealth of resources and fostering collaboration.
Open-Source Libraries and Frameworks
Open-source libraries and frameworks are essential components of the Java ecosystem, offering pre-built solutions that streamline development and accelerate project completion. These libraries and frameworks provide reusable code components, simplifying common tasks and enabling developers to focus on building unique features.
- Spring Framework: A comprehensive framework for building enterprise-grade Java applications, providing support for dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and web application development.
- Apache Maven: A build automation tool that simplifies the process of managing project dependencies, compiling code, and packaging applications.
- Hibernate: An object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that facilitates interaction between Java objects and relational databases, simplifying data persistence and retrieval.
Building a Solid Foundation in Java
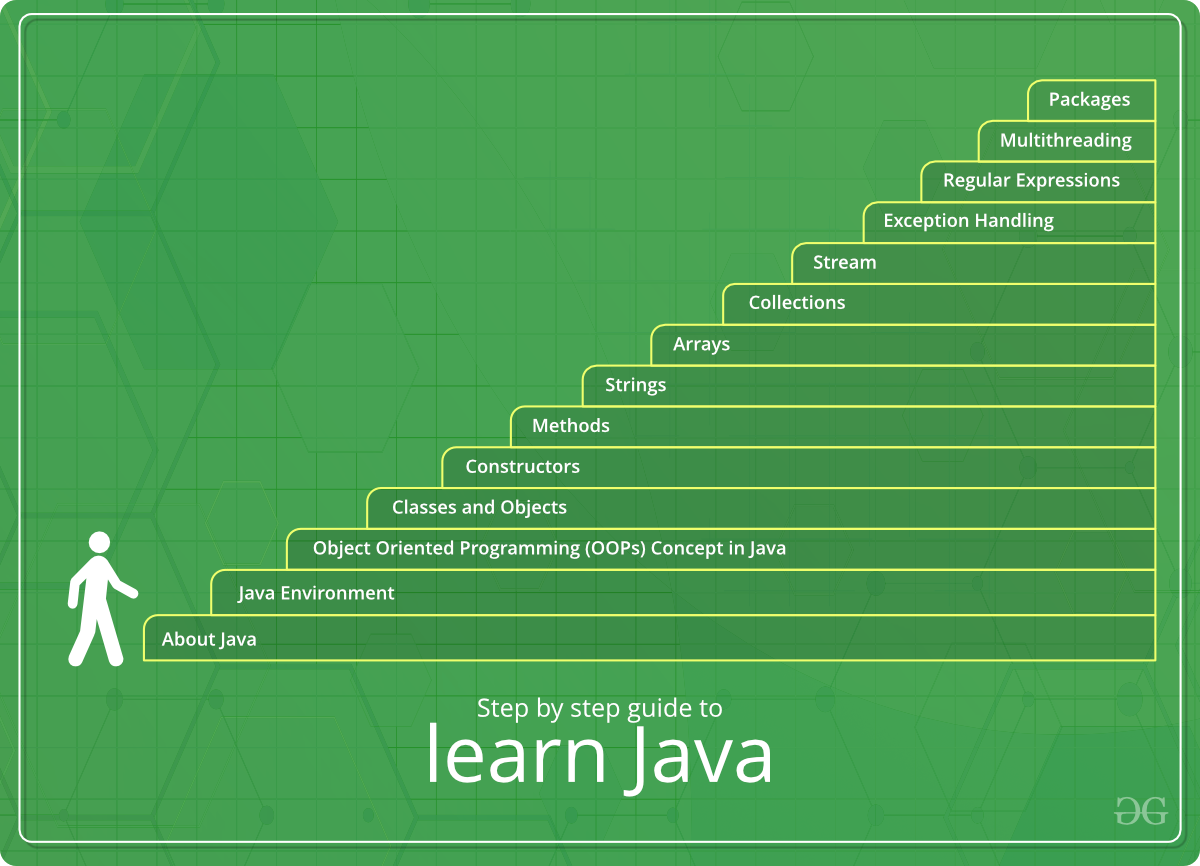
Laying a strong foundation in Java is crucial for any aspiring developer. This involves understanding the core concepts and mastering fundamental skills. By following a structured learning plan, you can progressively build your proficiency and become confident in your Java abilities.
Step-by-Step Learning Plan
A well-structured learning plan helps you navigate the vast world of Java effectively. This plan focuses on key areas, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the language.
- Start with the Basics:Begin by learning the fundamentals of programming, including variables, data types, operators, control flow statements (if-else, loops), and basic input/output operations. These concepts are essential building blocks for more complex programming tasks.
- Master Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):Java is an object-oriented language, so understanding OOP concepts is critical. Learn about classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction. These concepts allow you to organize code effectively and create reusable components.
- Explore Core Java Libraries:Familiarize yourself with essential Java libraries, such as Collections, IO, and Date & Time. These libraries provide pre-built functionalities for common tasks, saving you time and effort.
- Dive into Advanced Concepts:Once you have a solid grasp of the basics, delve into more advanced topics like multithreading, exception handling, generics, and lambda expressions. These concepts enhance your ability to write efficient and robust code.
- Practice with Real-World Projects:Building real-world projects is the best way to solidify your knowledge. Start with small projects and gradually increase complexity as you gain experience. This practical approach helps you apply your skills and learn from your mistakes.
Key Skills and Concepts
During the initial learning stages, focus on mastering these key skills and concepts:
- Syntax and Semantics:Understand the basic syntax of Java, including s, data types, operators, and control flow statements. This forms the foundation for writing valid Java code.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):Grasp the core principles of OOP, including classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction. This allows you to design and implement modular and reusable code.
- Data Structures and Algorithms:Learn about fundamental data structures like arrays, lists, sets, and maps, along with algorithms for sorting, searching, and manipulating data. These concepts are essential for efficient problem-solving and program optimization.
- Exception Handling:Understand how to handle errors and exceptions gracefully using try-catch blocks. This helps prevent program crashes and ensures code robustness.
- Debugging and Testing:Develop the ability to identify and fix errors in your code. Learn about debugging tools and techniques, as well as best practices for unit testing and integration testing.
Roadmap for Proficiency
A progressive roadmap helps you structure your learning journey and track your progress.
- Beginner Level:Focus on fundamental concepts, basic syntax, and simple programs. Explore online tutorials, books, and interactive coding platforms.
- Intermediate Level:Dive into object-oriented programming, core Java libraries, and advanced concepts like multithreading and exception handling. Start building small projects to apply your knowledge.
- Advanced Level:Explore frameworks, libraries, and design patterns. Work on larger, more complex projects to gain experience in real-world scenarios. Contribute to open-source projects to learn from experienced developers.
The Importance of Practice and Projects
You’ve learned the fundamentals of Java, explored its uses, and even compared it to other languages. Now, it’s time to put your knowledge into action! The key to truly mastering Java lies in hands-on practice and building real projects.
Think of it like learning to play an instrument. You can read all the theory about music, but until you pick up a guitar and start strumming, you won’t truly understand the concepts. The same applies to programming.
The Benefits of Hands-On Practice
Building projects helps you solidify theoretical concepts. You’ll learn how different pieces of code work together and how to apply your knowledge to solve real-world problems. It’s also a great way to develop problem-solving skills. You’ll encounter challenges, debug errors, and learn to think creatively to find solutions.
Beginner-Friendly Java Projects
Here are some ideas for beginner-friendly Java projects to build your portfolio:
Project Ideas by Difficulty
| Difficulty | Project Idea | Description | Required Skills |
|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Simple Calculator | Create a basic calculator that performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. | Basic arithmetic operations, user input, output. |
| Easy | Guessing Game | Develop a game where the user has to guess a random number within a specified range. | Random number generation, loops, conditional statements, user input, output. |
| Medium | To-Do List App | Build a simple application that allows users to create, view, edit, and delete tasks. | Data structures (arrays or lists), file handling, user interface (optional). |
| Medium | Text-Based Adventure Game | Create a simple adventure game where the user makes choices that affect the story. | Conditional statements, loops, user input, output, basic game logic. |
| Hard | Simple Database Application | Develop a basic application that interacts with a database to store and retrieve data. | Database connectivity, SQL queries, data manipulation, user interface (optional). |
Resources for Finding Project Ideas and Tutorials, How hard to learn java
GitHub
Explore open-source projects for inspiration and code examples.
FreeCodeCamp
Offers tutorials and projects for beginners and experienced developers.
Codecademy
Provides interactive courses and projects to learn Java.
Udemy
Offers a wide range of Java courses, including project-based learning.
Java Coding Challenges
Coding challenges are another great way to practice your Java skills. Websites like HackerRank, LeetCode, and Codewars offer a variety of challenges that can help you improve your problem-solving abilities, practice algorithms, and build a competitive coding profile.
Popular Coding Challenge Websites
- HackerRank:Provides a platform for practicing coding skills, participating in contests, and finding job opportunities.
- LeetCode:Focuses on algorithm and data structure problems, popular for preparing for technical interviews.
- Codewars:Offers a gamified approach to coding challenges, allowing users to earn points and climb ranks.
Choosing Appropriate Challenges
Start with beginner-level challenges and gradually work your way up to more difficult ones. Focus on areas where you need to improve, such as data structures, algorithms, or specific Java libraries.
The Importance of Consistent Practice
Remember, mastering Java takes time and effort. Consistent practice and building projects are essential for becoming a proficient Java developer. Don’t be afraid to embrace challenges and actively apply your knowledge to real-world problems. The more you practice, the more confident you’ll become in your abilities.
Java’s Evolution and Future Trends

Java has been a dominant force in the programming world for decades, consistently evolving and adapting to the ever-changing technological landscape. From its humble beginnings as a platform-independent language to its current role as a powerhouse in enterprise applications, cloud computing, and mobile development, Java’s journey is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
Java’s Continuous Evolution
Java’s evolution is a continuous process driven by the need to address emerging trends and challenges. Over the years, Java has undergone significant updates and enhancements, introducing new features, improving performance, and enhancing its capabilities.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Enhancements:The JVM, the runtime environment for Java programs, has undergone significant improvements over time, resulting in better performance, memory management, and garbage collection.
- Language Features:Java has introduced new language features such as generics, annotations, lambdas, and modules, enhancing code readability, maintainability, and performance.
- New Libraries and APIs:Java has expanded its library ecosystem with new APIs for tasks such as web development, concurrency, data analysis, and machine learning, providing developers with powerful tools for modern application development.
Java’s Role in the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly expanding field, with billions of devices connecting to the internet, transforming various industries and aspects of our lives. Java, with its robust features and expansive ecosystem, has emerged as a leading force in this domain.
Its versatility, security, and platform independence make it an ideal choice for developing and managing diverse IoT applications.
Java’s Applications in the IoT Space
Java’s widespread use in the IoT landscape stems from its ability to handle the complex demands of connected devices, from data processing and communication to security and scalability. Here are some key areas where Java shines:
- Smart Home Automation:Java plays a pivotal role in creating seamless smart home experiences. It powers applications that control and manage smart home devices like thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, and appliances. For instance, Java can be used to develop applications that allow users to remotely control their home’s temperature, adjust lighting levels, or monitor security cameras from their smartphones.
Java’s ability to handle complex logic and interact with various hardware components makes it a perfect fit for building sophisticated smart home automation systems.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT):Java is extensively used in industrial automation systems, enabling data collection, analysis, and predictive maintenance. It powers applications that monitor sensor data from machines, analyze performance metrics, and detect potential issues before they occur. Java’s robust features, like its threading capabilities and support for distributed systems, make it ideal for managing large-scale industrial IoT deployments.
For example, Java can be used to develop applications that monitor the performance of machinery in factories, analyze sensor data to predict potential failures, and optimize production processes for increased efficiency.
- Wearable Technology:Java finds its way into wearable devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring systems. It powers applications that collect and analyze data from sensors, providing insights into user health and activity levels. Java’s ability to run on resource-constrained devices and its support for mobile platforms make it a popular choice for developing wearable applications.
For instance, Java can be used to develop applications that track users’ heart rate, steps taken, sleep patterns, and other health metrics, providing personalized insights and recommendations.
Java’s Suitability for Embedded Systems
While Java is often associated with enterprise applications, its capabilities extend to the development of resource-constrained embedded systems. Here’s how Java addresses the challenges of resource limitations:
- Resource Management:Java’s memory management and garbage collection mechanisms are designed to optimize resource usage, making it suitable for devices with limited memory and processing power. Java’s runtime environment efficiently manages memory allocation and deallocation, ensuring that resources are used effectively.
This allows Java applications to run smoothly on embedded systems without consuming excessive resources.
- Lightweight Frameworks:Java offers lightweight frameworks specifically tailored for embedded systems, such as Java ME (Micro Edition) and embedded Java libraries. These frameworks provide a reduced footprint and optimized performance, making them ideal for resource-constrained environments. Java ME, for example, is a subset of the Java platform designed for mobile and embedded devices, offering a streamlined set of APIs and a smaller runtime environment.
- Hardware Integration:Java provides a comprehensive set of APIs and libraries for interacting with various sensors, actuators, and communication protocols commonly used in IoT devices. Java applications can easily access data from sensors, control actuators, and communicate with other devices over different protocols like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular networks.
This allows Java developers to build applications that seamlessly integrate with the hardware components of IoT devices.
Java’s Impact on Big Data and Analytics: How Hard To Learn Java
Java’s robust nature, extensive libraries, and mature ecosystem make it a powerful tool for tackling the challenges of big data processing and analytics. Its ability to handle large datasets, perform complex computations, and integrate with various data sources has solidified its position as a key player in this domain.
Java Frameworks for Big Data
Java frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Spark are widely used for data manipulation and analysis in big data environments. These frameworks provide a foundation for distributed computing, enabling the processing of massive datasets across multiple machines.
- Apache Hadoop: Hadoop is a distributed file system and processing framework that enables the storage and processing of massive datasets across clusters of commodity hardware. Java plays a central role in Hadoop, providing the foundation for its core components, including the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and the MapReduce framework.
- Apache Spark: Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing framework that can handle both batch and real-time data processing. It utilizes Java for its core functionalities and provides a rich set of APIs for data manipulation, transformation, and analysis.
Real-World Applications of Java in Big Data
Java finds applications in various big data scenarios, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights from their data. Here are a few examples:
- Fraud Detection: Financial institutions use Java-based big data solutions to analyze transaction patterns and identify potential fraudulent activities.
- Customer Analytics: E-commerce companies leverage Java to analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to personalize recommendations and improve marketing strategies.
- Social Media Analysis: Social media platforms use Java to process and analyze vast amounts of user data to understand trends, sentiment, and user engagement.
Java’s Contributions to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Java, a robust and versatile programming language, has carved a significant niche in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI). Its inherent strengths, coupled with a thriving ecosystem of libraries and frameworks, make Java an ideal choice for building sophisticated AI systems.
Learning Java can be tough, especially if you’re new to programming. It’s like learning a new language, and just like you might wonder how hard is Persian to learn , you might also question the difficulty of Java. But with dedication and practice, you can master the syntax and become comfortable with the language’s complexities.
Advantages of Java for AI Development
Java offers several advantages that make it a compelling choice for developing AI applications:
- Platform Independence:Java’s “write once, run anywhere” philosophy ensures that AI applications developed in Java can run seamlessly across diverse platforms without requiring significant code modifications. This portability is crucial for deploying AI solutions in various environments, from cloud servers to embedded systems.
- Robust Libraries:Java boasts a rich collection of libraries specifically designed for AI development, encompassing areas like machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. These libraries provide pre-built functionalities and algorithms, accelerating the development process and enabling developers to focus on building intelligent applications.
- Strong Community Support:Java enjoys a vast and active community of developers, contributing to a wealth of resources, tutorials, and forums. This strong community support ensures that developers can readily find solutions to challenges, learn from experienced peers, and stay abreast of the latest advancements in AI and Java.
Java Libraries and Frameworks for Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Java provides a comprehensive set of libraries and frameworks that simplify the development of machine learning and deep learning applications:
- Weka:This open-source machine learning library offers a wide range of algorithms for tasks like classification, regression, clustering, and association rule mining. Weka provides a user-friendly interface for data analysis and model building, making it accessible to both beginners and experienced data scientists.
- Deeplearning4j:As a deep learning library for Java and Scala, Deeplearning4j provides tools for building and deploying deep neural networks. It supports various deep learning architectures, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, making it suitable for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and time series analysis.
- Apache Spark MLlib:This machine learning library built on top of the Apache Spark framework offers distributed machine learning algorithms for large-scale data processing. MLlib provides algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, collaborative filtering, and dimensionality reduction, enabling the development of scalable AI solutions for big data applications.
Examples of AI Projects Built with Java
Java has been instrumental in the development of numerous real-world AI applications across various domains:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):Java-based NLP systems power applications like chatbots, sentiment analysis tools, and machine translation systems. These applications leverage Java libraries like Apache OpenNLP and Stanford CoreNLP for tasks like text classification, named entity recognition, and part-of-speech tagging.
- Computer Vision:Java libraries like OpenCV and JavaCV enable the development of computer vision applications for image recognition, object detection, and video analysis. These applications find applications in areas like autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and security systems.
- Robotics:Java’s ability to control hardware and interact with sensors makes it a suitable language for robotics applications. Java-based robotic systems are used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, for tasks like assembly, manipulation, and navigation.
Java’s Influence on Mobile App Development
Java has played a pivotal role in shaping the mobile app landscape, particularly for Android devices. Its robust features and extensive ecosystem make it a powerful tool for building high-quality, feature-rich applications.
Android App Development with Java
Java serves as the primary programming language for developing Android apps. The Android operating system is built on a Java-based runtime environment, making Java a natural choice for developers. The Android SDK (Software Development Kit) provides a comprehensive set of tools and libraries that allow developers to leverage Java’s capabilities to create engaging mobile experiences.
Tools and Frameworks for Android Development with Java
Android development with Java involves a combination of tools and frameworks that streamline the development process.
- Android Studio: The official IDE (Integrated Development Environment) for Android development, offering features like code completion, debugging, and testing.
- Gradle: A build automation tool used to manage dependencies, compile code, and package Android apps.
- Android SDK: A collection of tools, libraries, and documentation that enables developers to build Android apps. It includes components like the Android emulator, a virtual environment for testing apps.
- Android Support Libraries: A set of libraries that provide backward compatibility and access to newer features across different Android versions.
- Android Jetpack: A collection of libraries, tools, and guidance that helps developers build high-quality Android apps more easily.
FAQ Section
What are some common challenges for Java beginners?
Setting up the development environment, understanding core Java concepts like object-oriented programming, and debugging errors are some of the common hurdles for beginners. But with patience and the right resources, these challenges can be overcome.
Is Java still relevant in today’s tech world?
Absolutely! Java remains highly relevant, with a strong presence in enterprise applications, Android development, and emerging technologies like big data and artificial intelligence. Its vast ecosystem and continuous evolution ensure its continued relevance in the future.
What are some good resources for learning Java?
There are plenty of great resources available, including online courses on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and edX, beginner-friendly YouTube channels, and official Java documentation. Choose resources that align with your learning style and learning goals.