How hard is it to learn acoustic guitar? This question pops up in the minds of countless aspiring musicians. It’s a journey that can be both challenging and rewarding, filled with the joy of creating music and the satisfaction of mastering a new skill.
Learning any instrument requires dedication, but the acoustic guitar offers a unique path, blending the accessibility of simple chords with the depth of complex techniques.
The difficulty of learning acoustic guitar depends on a variety of factors. Your natural aptitude, the time you dedicate to practice, and the learning resources you choose all play a role. While some might pick up the basics quickly, others may find it takes more time and effort.
The key is to embrace the journey, celebrate your progress, and enjoy the process of becoming a guitarist.
Difficulty Level
Learning any musical instrument takes dedication and effort, and the acoustic guitar is no exception. While it’s a popular choice for beginners, it presents its own set of challenges. Let’s delve into the difficulty level of learning acoustic guitar compared to other instruments and explore what makes it unique.
Comparison to Other Instruments
The difficulty of learning acoustic guitar can be compared to other instruments by considering factors like finger dexterity, coordination, and theoretical understanding.
- Piano:Learning piano requires strong finger independence and coordination, as you need to play multiple notes simultaneously. The piano is also known for its complex theoretical foundation, with scales, chords, and music theory playing a crucial role. While the layout of the keys might seem intuitive, mastering piano requires a significant time investment.
- Violin:Violin is known for its demanding finger placement and bowing technique. It requires a high level of coordination and fine motor control. Learning to play in tune can be challenging, and achieving a good sound requires practice and proper technique.
- Drums:Drums demand physical stamina and coordination. You need to use both hands and feet to play different rhythms and patterns. Learning to play drums involves mastering timing, dynamics, and different drum techniques. It’s a physically demanding instrument, requiring strength and endurance.
- Singing:Singing requires vocal control, breath support, and a good understanding of musical theory. While it’s not technically an instrument, it’s a skill that needs to be developed through practice and technique. Finding your vocal range and learning to control your voice can be challenging, but with proper training, anyone can improve their singing.
Acoustic guitar, while challenging, offers a relatively accessible entry point for beginners. It’s a versatile instrument that can be played in various styles, from folk and blues to classical and rock. However, it still requires developing finger dexterity, hand coordination, and understanding basic music theory.
Comparison to Electric Guitar
The difference between learning acoustic and electric guitar lies mainly in technique, equipment, and musical styles.
- Technique:Acoustic guitar techniques emphasize fingerpicking and strumming, while electric guitar allows for a wider range of techniques, including bending, vibrato, and using a pick. The use of a pick on an electric guitar can make it easier to play fast and complex riffs, while acoustic guitar often relies on fingerpicking or using a pick with a lighter touch.
- Equipment:Electric guitars are amplified, allowing for a wider range of sounds and effects. The use of pedals and amplifiers gives electric guitar players greater control over their tone and sound. Acoustic guitars, on the other hand, rely on their natural sound and resonance.
While acoustic guitars can be amplified, the focus is on the natural sound of the instrument.
- Musical Styles:Electric guitars are often associated with rock, metal, and blues, while acoustic guitars are used in genres like folk, country, and classical. The amplification and effects available with electric guitars allow for a more distorted and aggressive sound, which is ideal for these genres.
Acoustic guitars, with their natural sound, are better suited for genres that emphasize melody and harmony.
While electric guitars offer greater complexity due to the wide range of techniques and effects, both instruments require dedication and practice to master. The choice between acoustic and electric guitar ultimately depends on personal preference and the type of music you want to play.
Timeframe for Basic Proficiency
Defining “basic proficiency” on the acoustic guitar means being able to play simple chords and melodies. The timeframe for achieving this level varies depending on factors like practice frequency, natural aptitude, and learning resources.
- Practice Frequency:Consistent practice is key. Aim for at least 30 minutes of practice daily to see noticeable progress. The more you practice, the faster you’ll learn and improve your skills.
- Natural Aptitude:Some people have a natural inclination for music and may pick up the guitar more quickly than others. However, with dedication and practice, anyone can learn to play the guitar. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t progress as quickly as someone else.
- Learning Resources:There are many resources available for learning acoustic guitar, including online tutorials, books, and private lessons. Finding the right resources that suit your learning style can make a big difference in your progress.
Based on these factors, a realistic timeframe for achieving basic proficiency on acoustic guitar can range from a few months to a year or more. Don’t be discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Consistency and dedication are key to success.
Key Factors Contributing to Difficulty
Learning acoustic guitar involves several factors that contribute to its difficulty. These include:
Finger dexterity, hand coordination, understanding basic music theory, and developing a good ear for music.
While these factors may seem daunting, with consistent practice and the right approach, anyone can learn to play the acoustic guitar. Remember to enjoy the process, be patient with yourself, and celebrate your progress along the way.
Physical Demands
Learning to play the acoustic guitar requires more than just musical knowledge and practice. It also involves a significant amount of physical exertion, demanding strength, dexterity, and proper posture. Mastering these physical aspects can enhance your playing experience and prevent injuries.
Hand Strength and Dexterity
Playing the acoustic guitar engages various muscles in your hands, particularly those involved in fretting and strumming. Fretting requires precise finger placement and pressure to produce clear notes, while strumming involves rhythmic and coordinated movements of the wrist and forearm.Strong hands are essential for playing complex chords and intricate fingerpicking patterns.
With sufficient hand strength, you can apply the necessary pressure to fret notes without buzzing or muting them. This allows you to play chords with clarity and control, even when transitioning between different finger positions. Dexterity enables you to move your fingers independently and with precision, allowing for fast picking, intricate fingerpicking patterns, and smooth chord changes.Here are some exercises to strengthen your hands and fingers:
- Finger Stretches:Spread your fingers wide apart and then slowly bring them together, repeating this motion several times. You can also try curling your fingers into a fist and then extending them, focusing on isolating each finger.
- Hand Grip Exercises:Use a hand grip strengthener or a tennis ball to squeeze and release, targeting the muscles in your hand and forearm.
- Fingertip Push-Ups:Place your fingertips on a table and slowly lower your body until your chest touches the surface. Push back up using only your fingertips, strengthening the muscles responsible for fretting.
Posture and Its Impact
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for playing the acoustic guitar comfortably and effectively. The correct posture involves keeping your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and arms at a comfortable angle.
- Back:Keep your back straight and slightly arched, avoiding slouching or hunching over the guitar. This helps maintain proper alignment and prevents strain on your spine.
- Shoulders:Relax your shoulders and avoid raising them towards your ears. Keep your shoulders down and back, allowing for natural arm movement.
- Arms:Position your arms at a comfortable angle, avoiding excessive tension or strain. Your elbows should be slightly bent, and your wrists should be relaxed.
Poor posture can lead to muscle strain, discomfort, and limitations in technique. It can also contribute to long-term injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis.Here are some tips for maintaining proper posture during long practice sessions:
- Use a Footstool:Elevating your feet with a footstool helps maintain a comfortable position and prevents strain on your legs and back.
- Adjust Guitar Height:Adjust the guitar’s height so that the neck is at a comfortable angle for your arm and wrist. This reduces strain on your shoulders and neck.
- Take Breaks:Regularly take short breaks during practice to stretch and relax your muscles. This helps prevent fatigue and promotes proper posture.
“Proper posture is essential for any musician, but especially for guitarists. It allows for optimal movement, reduces strain, and prevents injuries.”
[Insert name of expert or source]
3. Learning Resources: How Hard Is It To Learn Acoustic Guitar
Learning how to play acoustic guitar doesn’t have to be a solo journey. There are numerous resources available to help you on your musical adventure. Choosing the right learning resource depends on your learning style, budget, and personal preferences. This section explores some of the most common options, outlining their pros and cons to help you make an informed decision.
Learning Resource Comparison
The following table provides a comparison of different guitar learning resources:| Resource Type | Description | Pros | Cons ||—|—|—|—|| Online Courses | Interactive platforms offering structured lessons, exercises, and feedback.
Examples
Fender Play, JustinGuitar, Guitar Tricks |
Flexibility and convenience
learn at your own pace and time.
- Affordable options available.
- Access to a wide range of learning materials and ors. |
- Can lack personalized feedback.
- May require self-discipline to stay motivated.
- Limited opportunities for hands-on interaction. |
| Books | Comprehensive guides covering theory, techniques, and repertoire.
Examples
“Hal Leonard Guitar Method,” “Guitar for Dummies,” “The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Guitar” |
- Detailed explanations and diagrams.
- Can be used as a reference tool.
- Often affordable. |
- Can be overwhelming for beginners.
- Limited opportunities for practice feedback. |
| In-Person Lessons | One-on-one with a qualified teacher.
Examples
Local music schools, private ors |
- Personalized feedback and guidance.
- Opportunity to ask questions and receive immediate feedback.
- Develop good technique and habits from the start. |
- Can be expensive.
- Limited flexibility in scheduling.
- May not be readily available in all locations. |
Online courses and in-person lessons offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. While online courses provide flexibility and affordability, they may lack personalized feedback and require self-motivation. In contrast, in-person lessons offer personalized guidance and immediate feedback but can be expensive and less flexible.
The ideal choice depends on your individual needs and learning preferences.
4. Basic Skills and Concepts
Mastering the fundamentals is crucial for any aspiring guitarist. This section will guide you through essential skills and concepts that form the foundation of your acoustic guitar journey.
Essential Skills and Concepts
Understanding basic guitar concepts is key to playing music. These include tuning, chords, strumming patterns, and scales. Let’s dive in!
- Tuning: Tuning refers to adjusting the pitch of each string to achieve the correct sound. The standard tuning for an acoustic guitar is E-A-D-G-B-E, with each string representing a different note. The frequencies for each string are as follows:
- E: 82.41 Hz
- A: 110 Hz
- D: 146.83 Hz
- G: 196 Hz
- B: 246.94 Hz
- E: 329.63 Hz
- Alternate Tunings: While standard tuning is the most common, alternate tunings can add unique sounds and textures to your playing. Examples of popular alternate tunings include:
- Open G Tuning: D-G-D-G-B-D, often used in folk and blues music.
- Open D Tuning: D-A-D-G-B-E, known for its use in slide guitar and blues.
- DADGAD Tuning: D-A-D-G-A-D, a versatile tuning used in various genres.
- Chords: Chords are combinations of notes played simultaneously to create a harmonious sound. The most common basic chords for beginners include:
- C Major: A basic major chord with a bright and cheerful sound.
- G Major: Another common major chord, often used in folk and rock music.
- D Major: A major chord with a slightly fuller sound than C or G.
- A Minor: A minor chord with a melancholic feel.
- E Minor: Another minor chord, often used in blues and rock music.
- Chord Inversions: Chord inversions involve rearranging the notes within a chord, creating variations in sound and texture. For example, a C major chord in root position is C-E-G, while its first inversion is E-G-C.
- Strumming Patterns: Strumming patterns are rhythmic sequences of downstrokes and upstrokes that create different grooves and dynamics. Examples of basic strumming patterns include:
- Down-Up-Down-Up: A simple and versatile pattern for beginners.
- Down-Down-Up-Down: A pattern that creates a slightly more driving feel.
- Down-Up-Down-Down-Up: A pattern that adds a bit of complexity and rhythm.
- Basic Scales: Scales are sequences of notes that form the foundation of melodies and chords. The major scale is a fundamental scale with a bright and cheerful sound. For example, the C major scale consists of the notes C-D-E-F-G-A-B.
Tuning an Acoustic Guitar
Tuning your guitar is essential for playing in tune. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Use a Tuning Tool: Choose a tuning fork or a digital tuner to determine the correct pitch for each string.
- Tune the Sixth String (E): Start by tuning the thickest string (E) to the desired pitch. Use the tuning pegs to tighten or loosen the string until it matches the reference pitch.
- Tune the Fifth String (A): Tune the fifth string (A) by fretting the second fret of the sixth string and adjusting the fifth string until it matches the pitch. This creates a perfect fifth interval between the two strings.
- Tune the Fourth String (D): Tune the fourth string (D) by fretting the second fret of the fifth string and adjusting the fourth string until it matches the pitch. This creates a perfect fifth interval between the two strings.
- Tune the Third String (G): Tune the third string (G) by fretting the third fret of the fourth string and adjusting the third string until it matches the pitch. This creates a perfect fifth interval between the two strings.
- Tune the Second String (B): Tune the second string (B) by fretting the fourth fret of the third string and adjusting the second string until it matches the pitch. This creates a perfect fifth interval between the two strings.
- Tune the First String (E): Tune the first string (E) by fretting the fifth fret of the second string and adjusting the first string until it matches the pitch. This creates a perfect fifth interval between the two strings.
Practice Routine
Consistent practice is crucial for developing guitar skills. Here’s a suggested practice routine for beginners:
- Tuning: Start each practice session by tuning your guitar. This ensures that your instrument is in tune and ready to play.
- Chords: Practice playing the basic chords you’ve learned, focusing on clear and accurate finger placement. Start with slow tempos and gradually increase the speed as you become more comfortable.
- Strumming: Practice different strumming patterns over the chords you’ve learned. Experiment with variations in rhythm and dynamics to create different musical grooves.
- Scales: Practice playing the major scale in different keys. This will help you develop finger dexterity and understand the relationship between notes and chords.
- Song Learning: Choose songs you enjoy and learn to play them. This will help you apply the skills you’ve learned in a musical context.
Writing
Writing your own songs can be a rewarding experience. Here’s a basic understanding of song structure and songwriting tips:
- Song Structure: A typical song structure consists of:
- Verse: The main part of the song that introduces the theme and lyrics.
- Chorus: The catchy and memorable part of the song that repeats throughout.
- Bridge: A section that provides a contrast or change in mood or melody.
- Outro: The final section of the song that brings it to a close.
- Chord Progressions: Simple chord progressions can be used as the foundation for songwriting. Here are a few examples:
- I-IV-V: A classic progression often used in blues and rock music (e.g., C-G-Am).
- I-vi-IV-V: A common progression with a more melancholy feel (e.g., C-Am-F-G).
- I-V-vi-IV: A progression with a circular feel (e.g., C-G-Am-F).
- Lyrics: Writing lyrics involves expressing your thoughts and feelings in a poetic and engaging way. Consider using metaphors, similes, and imagery to create vivid and memorable lyrics.
Common Challenges
Learning acoustic guitar can be a rewarding experience, but it also comes with its share of challenges. Beginners often face hurdles like finger pain, frustration, and a lack of motivation.
Finger Pain and Hand Strength
Finger pain is a common issue for beginners, as the muscles and tendons in your hands are not accustomed to the repetitive motions and pressure required for playing guitar. Here are some strategies for overcoming finger pain and improving hand strength:
- Start slowly:Don’t try to play for long periods initially. Begin with short practice sessions and gradually increase the duration as your fingers get stronger.
- Warm up properly:Before you start practicing, take a few minutes to warm up your hands with simple stretches and exercises.
- Use proper finger placement:Make sure your fingers are positioned correctly on the strings to minimize strain. Consult online resources or a guitar teacher for proper technique.
- Take breaks:If your fingers start to ache, stop playing and give them a rest. It’s better to take frequent breaks than to push through the pain and risk injury.
- Strength training exercises:Incorporate hand and finger strengthening exercises into your routine. This can include squeezing a stress ball, using a hand gripper, or practicing finger exercises like picking up small objects.
Motivation and Setting Realistic Goals
Staying motivated is crucial when learning a new skill. It can be easy to get discouraged when you don’t see immediate progress. Here are some tips for staying motivated and setting realistic goals:
- Focus on small achievements:Instead of aiming for perfection right away, celebrate small milestones like learning a new chord or playing a simple song.
- Set achievable goals:Don’t overwhelm yourself with unrealistic expectations. Break down your learning journey into smaller, manageable steps.
- Find a learning partner or group:Playing with others can be motivating and provide encouragement.
- Practice regularly:Consistency is key. Even short practice sessions on a regular basis will lead to significant improvement over time.
- Choose songs you enjoy:Learning songs that you like will make the process more enjoyable and keep you motivated.
Learning Styles
Learning styles are the different ways people prefer to receive and process information. Understanding your learning style can be a valuable tool in your guitar journey, helping you choose the right learning materials and techniques for efficient learning.
Visual Learners, How hard is it to learn acoustic guitar
Visual learners retain information best through seeing and observing. They benefit from visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and videos.
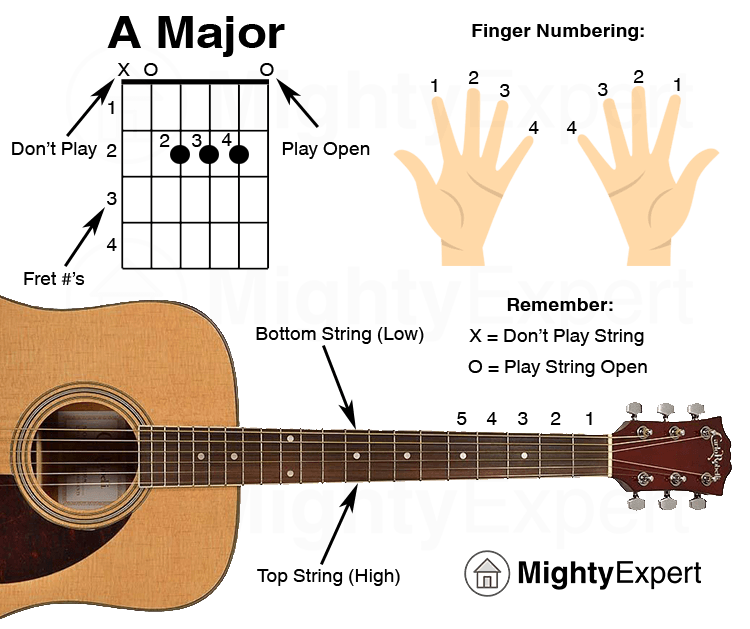
- Chord diagrams:These diagrams show the finger placement for each chord, making it easier for visual learners to understand the shape and position of their fingers.
- Tablature:Tablature is a visual representation of music that shows which strings to play and where to place your fingers.
- Online lessons:Many online guitar lessons use visual aids, such as animated fingerings and close-up shots of the guitar neck.
Auditory Learners
Auditory learners learn best by listening and hearing information. They thrive on audio resources, music, and spoken instructions.
- Music theory lessons:Understanding music theory helps you learn the structure of songs and how chords and melodies work together.
- Guitar tutorials:Audio-based guitar tutorials can be a great way for auditory learners to pick up new techniques and songs.
- Playing along with recordings:Playing along with recordings of songs helps auditory learners to internalize the rhythm and melody.
Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners learn best by doing and experiencing. They benefit from hands-on activities and physical practice.
- Guitar lessons:In-person guitar lessons provide hands-on instruction and personalized feedback.
- Practice routines:Consistent practice is crucial for kinesthetic learners, allowing them to develop muscle memory and refine their technique.
- Jamming with others:Playing with other musicians can be a fun and engaging way for kinesthetic learners to learn new songs and improve their skills.
Finding a Teacher
Learning from a qualified guitar teacher can significantly accelerate your progress and enhance your understanding of the instrument. A good teacher can provide personalized guidance, correct your technique, and introduce you to new concepts and styles.
Finding a Reputable Guitar Teacher
Finding a reputable guitar teacher requires research and careful consideration. Here are some tips to help you find a teacher who aligns with your learning style and goals:
- Seek Recommendations:Ask friends, family, or fellow musicians for recommendations. Word-of-mouth referrals are often a good starting point.
- Check Online Directories:Websites like TakeLessons, TeacherFinder, and Local Music Stores often list guitar teachers in your area. You can filter by experience, style, and teaching approach.
- Visit Music Schools and Studios:Many music schools and studios offer guitar lessons. You can visit their websites or contact them directly to inquire about their instructors and programs.
- Attend Open Houses and Workshops:Some guitar teachers host open houses or workshops where you can observe their teaching style and interact with them.
Assessing Teacher Experience and Qualifications
It’s important to assess a teacher’s experience and qualifications before committing to lessons.
- Inquire about Teaching Experience:Ask the teacher about their teaching experience, the number of students they’ve taught, and their teaching philosophy.
- Verify Credentials:If applicable, inquire about the teacher’s music education background, degrees, or certifications. This can indicate their expertise and commitment to teaching.
- Review Student Testimonials:Check online reviews or ask the teacher for testimonials from previous students. This can provide insights into their teaching effectiveness and student satisfaction.
Finding a Teacher Who Aligns with Your Learning Style and Goals
It’s crucial to find a teacher who understands your learning style and goals.
- Discuss Your Learning Style:Be upfront about your preferred learning methods, whether you prefer visual, auditory, or kinesthetic approaches.
- Clarify Your Goals:Communicate your specific goals, whether you want to learn basic chords, play specific songs, or develop advanced techniques.
- Ask About Teaching Approach:Inquire about the teacher’s teaching approach and whether they use structured lessons, improvisation, or a combination of both.
Importance of Practice
Practice is the cornerstone of mastering the acoustic guitar. It’s not just about playing the right notes; it’s about developing muscle memory, improving coordination, and building your musical ear. Consistent practice allows you to internalize techniques and develop a deep understanding of the instrument.
Effective Practice Routines for Beginners
A structured approach to practice is essential for beginners. This ensures that you’re covering all the essential aspects of playing the guitar. Here are some examples of effective practice routines:
- Warm-up: Start each practice session with a few minutes of finger exercises to warm up your hands and improve dexterity. This could include scales, arpeggios, or simple finger stretches.
- Chords: Spend time practicing basic chords and transitions between them. Use a chord chart or online resources to learn new chords and practice strumming patterns.
- Scales: Practice major and minor scales to develop your finger strength and understanding of musical intervals. Start with simple scales and gradually progress to more complex ones.
- Songs: Dedicate time to learning and practicing your favorite songs. This will help you apply the skills you’ve learned and build confidence.
- Ear Training: Include exercises that focus on developing your musical ear. This could involve identifying notes, chords, or melodies by listening. Online ear training apps and websites can be helpful for this.
Breaking Down Practice Sessions
Breaking down your practice sessions into smaller, manageable chunks can be highly effective. Instead of trying to practice for hours at a time, aim for shorter, focused sessions throughout the day. This approach allows you to maintain your concentration and avoid burnout.
- Consistency is Key: It’s more beneficial to practice for 15-20 minutes daily than to have one long session once a week. Regular practice helps you retain information and build skills gradually.
- Focus on Specific Goals: For each practice session, set a clear goal. This could be learning a new chord, mastering a specific technique, or practicing a particular song. Having a goal helps you stay focused and track your progress.
- Variety is Important: Don’t be afraid to mix up your practice routine. Include a variety of exercises and songs to keep things interesting and prevent boredom.
Setting Goals
Setting clear and achievable goals is crucial for your acoustic guitar learning journey. It provides direction, motivation, and a sense of accomplishment as you progress. Without goals, it’s easy to get lost in the vast world of guitar knowledge and feel overwhelmed.
Types of Goals
Different types of goals can be set, each serving a specific purpose.
- Short-Term Goals: These are smaller, immediate objectives that can be achieved within a few weeks or months. Examples include learning a specific chord progression, mastering a basic strumming pattern, or memorizing a short song.
- Long-Term Goals: These are ambitious objectives that take months or even years to achieve. Examples include learning to play a complex song, performing in front of an audience, or developing a specific guitar technique.
- Skill-Based Goals: These focus on developing specific guitar skills, such as improving fingerpicking, increasing dexterity, or enhancing your ear training abilities.
- Performance-Based Goals: These are centered around performing music, such as learning to play a specific genre of music, joining a band, or participating in a guitar competition.
Tracking Progress and Celebrating Milestones
Tracking your progress is essential for staying motivated and seeing how far you’ve come. Consider using a journal, a spreadsheet, or a dedicated app to record your practice sessions, new skills learned, and songs mastered. This allows you to visualize your journey and identify areas for improvement.Celebrating milestones, big or small, is equally important.
Reaching a goal, no matter how minor, deserves recognition. Treat yourself to something you enjoy, share your accomplishment with friends and family, or simply take a moment to appreciate your hard work and dedication.
10. Motivation and Persistence

Learning guitar is a journey, not a sprint. It requires dedication, patience, and a healthy dose of motivation to keep you going through the inevitable ups and downs. Staying motivated is crucial for achieving your guitar goals and enjoying the process.
10.1. Strategies for Staying Motivated
Staying motivated during guitar practice can be a challenge, especially when you encounter difficult techniques or hit a plateau. However, there are strategies you can implement to keep your passion for music alive and your fingers flying.
- Set Realistic Goals: Don’t try to learn everything at once. Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps. This creates a sense of accomplishment and keeps you moving forward.
- Break Down Practice into Smaller Chunks: Instead of practicing for long periods, break your sessions into shorter, more manageable chunks. This can help prevent burnout and make practice feel less daunting.
- Reward Yourself: When you reach a milestone or achieve a specific goal, reward yourself with something you enjoy. This reinforces positive behavior and keeps you motivated.
- Find a Practice Buddy: Having a friend to practice with can provide motivation, accountability, and a fun social aspect to your guitar journey.
- Visualize Success: Imagine yourself successfully playing a challenging piece. This visualization technique can boost your confidence and help you overcome practice plateaus. By picturing yourself playing flawlessly, you program your mind for success and enhance your motivation.
10.2. Overcoming Challenges
The road to becoming a proficient guitarist is paved with challenges. It’s natural to encounter obstacles, but it’s how you overcome them that defines your journey.
- Frustration with Slow Progress: It’s easy to get discouraged when progress seems slow. Remember that learning takes time and consistent effort. Celebrate small victories and focus on the long-term goal.
- Feeling Overwhelmed by Complex Techniques: Break down complex techniques into smaller, more manageable steps. Practice each step individually before combining them. Be patient and persistent, and you’ll eventually master the technique.
- Lack of Time for Practice: Schedule dedicated practice time, even if it’s just for 15 minutes a day. Consistency is key. Find ways to incorporate practice into your daily routine, like practicing during your commute or during breaks at work.
10.3. Common Mistakes and Solutions
Here’s a table outlining common mistakes guitarists make during practice and their corresponding solutions:
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Practicing too long without breaks | Take regular breaks to avoid fatigue and maintain focus. |
| Focusing solely on speed | Prioritize accuracy and technique over speed. |
| Ignoring proper posture and hand position | Practice with good posture and hand position to prevent injuries and improve technique. |
| Not listening to yourself play | Pay attention to your sound and identify areas for improvement. |
| Giving up too easily | Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth and persistence. |
10.4. Inspiring Stories
- Jimi Hendrix, a legendary guitarist, faced numerous challenges in his career, including racism and prejudice. He persevered through these obstacles, using his music as a powerful voice for social change. His unwavering passion and determination inspired countless musicians and continues to influence generations of guitarists.
10.5. Community Support
Joining a guitar community can provide invaluable support and encouragement on your musical journey. Connecting with other guitarists allows you to:
- Access Resources: Learn from experienced guitarists, share knowledge, and discover new learning materials.
- Share Experiences: Connect with others who understand the challenges and triumphs of learning guitar.
- Receive Encouragement: Find support and motivation from fellow musicians who share your passion.
Here are some online platforms and local communities where you can connect with guitarists:
- Online Forums: Guitar forums like “Guitar Forums” and “The Gear Page” provide a platform for discussion, advice, and support.
- Social Media Groups: Facebook groups and Instagram communities dedicated to guitarists offer a space for sharing music, asking questions, and connecting with other players.
- Local Guitar Stores: Many guitar stores host workshops, jam sessions, and open mics, creating opportunities to meet and connect with other guitarists in your area.
Choosing an Acoustic Guitar
Choosing the right acoustic guitar is crucial for a beginner’s journey. It’s the first step towards making music and enjoying the instrument. The right guitar will inspire you to practice, making the learning process more enjoyable and rewarding.
Acoustic Guitar Body Sizes
The body size of an acoustic guitar significantly impacts its volume, tone, and playability. Here are three popular body sizes:
- Dreadnought:The largest and most common body size, known for its loud, booming sound and powerful projection. Dreadnoughts are well-suited for strumming and playing fingerstyle, offering a full, rich sound.
- Concert:A smaller body size than the dreadnought, offering a more balanced sound with less bass and a brighter tone.
Concert guitars are comfortable to play and are often preferred for fingerstyle playing due to their smaller size.
- Parlor:The smallest body size, characterized by a delicate and intimate sound. Parlor guitars are ideal for solo fingerstyle playing and are often used for traditional folk music.
| Body Size | Length (inches) | Width (inches) | Volume | Tonal Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dreadnought | 20 | 16 | Loud, powerful, full-bodied | Rich bass, balanced mids, clear highs |
| Concert | 19 | 15 | Moderate, balanced | Brighter tone, less bass, good for fingerstyle |
| Parlor | 18 | 14 | Soft, intimate | Delicate, warm, good for solo playing |
Woods Used for Acoustic Guitars
The type of wood used for the top, back, and sides of an acoustic guitar significantly affects its sound. Different woods produce distinct tonal qualities, such as brightness, warmth, and projection.
- Top Wood:The top wood is the most crucial factor in determining the guitar’s tone.
- Back and Side Wood:The back and side woods contribute to the guitar’s overall volume, resonance, and sustain.
| Wood | Sonic Qualities |
|---|---|
| Top Wood | |
| Spruce | Bright, clear, responsive |
| Cedar | Warm, mellow, good for fingerstyle |
| Mahogany | Warm, balanced, good for all playing styles |
| Back and Side Wood | |
| Mahogany | Warm, balanced, good for all playing styles |
| Rosewood | Rich, full-bodied, warm |
| Walnut | Warm, clear, good for both strumming and fingerstyle |
Steel-String vs. Nylon-String Acoustic Guitars
The type of strings used on an acoustic guitar significantly impacts its sound and playing style.
- Steel-String Acoustic Guitars:The most common type of acoustic guitar, known for their bright, loud sound and their ability to handle both strumming and fingerstyle playing. Steel-string guitars are often used in genres such as folk, rock, and country.
- Nylon-String Acoustic Guitars:Also known as classical guitars, nylon-string guitars have a softer, warmer sound and are often used for classical music, flamenco, and Latin genres.
Nylon strings are softer on the fingers and require a different playing technique than steel strings.
Choosing an Acoustic Guitar for Beginners
When choosing your first acoustic guitar, there are a few key factors to consider:
- Budget:Entry-level acoustic guitars typically range in price from $100 to $500.
- Beginner-Friendly Features:Look for guitars with a comfortable neck, a smooth action (the distance between the strings and the fretboard), and a light gauge of strings.
- Neck Width:A wider neck can be more challenging for beginners to play.
A narrower neck might be more comfortable.
- String Gauge:Lighter gauge strings are easier to press down, making it easier for beginners to play.
- Action:The action is the distance between the strings and the fretboard. A lower action makes it easier to press down on the strings.
Trying Out Different Guitars
The best way to choose the right acoustic guitar is to try out several different guitars. Each guitar has a unique sound and feel, and what sounds good to one person may not sound good to another.
Learning acoustic guitar can be a fun and rewarding journey, but it’s not always easy. You’ll need to practice regularly to build finger strength and dexterity. A good way to visualize what you’re learning is to use some “what are we learning today clipart” what are we learning today clipart images to help you grasp the concepts.
With consistent effort and dedication, you’ll be strumming your favorite tunes in no time!
- Playability:Make sure the guitar is comfortable to hold and play. The neck should feel good in your hand, and the strings should be easy to press down.
- Tone:Listen to the guitar’s sound. Does it sound full and rich, or thin and tinny?
Do you like the tone when you strum or play fingerstyle?
- Comfort:Make sure the guitar feels comfortable to hold and play for extended periods.
Guitar Accessories
Investing in the right guitar accessories can significantly enhance your learning experience and make your journey more enjoyable. These tools can help you practice effectively, maintain your instrument, and even inspire you to play more.
Essential Guitar Accessories
The following accessories are essential for beginner guitarists:
- Picks:Picks are small, thin pieces of plastic, nylon, or other materials used to pluck the strings of a guitar. They come in various shapes, sizes, and thicknesses, affecting the tone and volume of your playing.
- Thin Picks:Produce a brighter and lighter tone, suitable for strumming and fingerstyle playing.
- Thick Picks:Produce a heavier and more powerful tone, ideal for aggressive playing and rhythm sections.
- Capo:A capo is a device that clamps onto the neck of a guitar, effectively shortening the string length and raising the pitch of all the strings. This allows you to play in different keys without having to retune your guitar.
- Traditional Capos:Use a spring mechanism to clamp onto the neck.
- Trigger Capos:Feature a lever that allows for quick and easy attachment and removal.
- Tuner:A tuner is an essential tool for ensuring that your guitar is in tune. They come in various forms, including digital tuners, clip-on tuners, and smartphone apps.
- Digital Tuners:Offer precise tuning with a display that shows the note and frequency.
- Clip-on Tuners:Attach to the headstock of your guitar for convenient tuning.
- Guitar Stand:A guitar stand provides a safe and stable place to store your guitar when not in use. It helps prevent damage to the instrument and keeps it readily accessible.
- Folding Stands:Compact and portable, suitable for travel.
- A-Frame Stands:Offer a sturdy and secure base.
Importance of Quality Accessories
While inexpensive accessories may seem tempting, investing in quality accessories can make a significant difference in your playing experience.
- Picks:Quality picks are more durable, provide better grip, and produce a more consistent tone.
- Capos:High-quality capos are more reliable, clamp securely, and minimize the risk of damaging your guitar.
- Tuners:Accurate tuners ensure that your guitar is in tune, which is crucial for playing in key and achieving a good sound.
- Guitar Stands:Sturdy stands protect your guitar from accidental falls and scratches, ensuring its longevity.
“Investing in quality accessories is an investment in your guitar playing journey. It will make your practice sessions more efficient, your playing more enjoyable, and your guitar more protected.”
13. Basic Guitar Maintenance

Taking care of your acoustic guitar is crucial for maintaining its beauty, functionality, and longevity. Just like any prized possession, your guitar needs regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure it plays its best and lasts for years to come. Neglecting these basic tasks can lead to problems like string buzz, poor tone, and even damage to the instrument.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining your guitar’s appearance and functionality. Dust, fingerprints, and grime can accumulate on the body, neck, and fretboard, affecting the guitar’s playability and tone.
- Cleaning removes dirt and grime, preventing them from accumulating and affecting the guitar’s sound and feel.
- Regular cleaning helps maintain the guitar’s aesthetic appeal, keeping it looking its best.
Changing strings regularly is crucial for maintaining optimal playability and tone. Old strings can become dull, lose their elasticity, and affect the guitar’s intonation.
- Fresh strings provide a brighter, more resonant sound, improving the overall playing experience.
- Changing strings regularly prevents them from breaking, which can be a safety hazard and lead to damage to the guitar.
The truss rod is a metal rod running along the inside of the guitar neck. Adjusting it helps maintain proper neck relief, preventing warping and ensuring the strings are at the correct height above the fretboard.
- A properly adjusted truss rod ensures optimal string action, making it easier to play and preventing buzzing.
- Regular truss rod adjustments can prevent the neck from warping, extending the guitar’s lifespan.
Step-by-Step Acoustic Guitar Cleaning Guide
Here’s a step-by-step guide to cleaning your acoustic guitar:
Materials Needed
- Microfiber cloth
- Guitar polish
- String cleaner
Cleaning Process
- Remove the strings:Before cleaning, remove the strings to access all areas of the guitar. Use a string winder to make this process easier.
- Clean the body:Use a microfiber cloth to wipe down the body of the guitar, removing dust, fingerprints, and grime. For stubborn stains, use a guitar polish specifically designed for acoustic guitars. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
- Clean the neck:Use a microfiber cloth to wipe down the neck, paying attention to the fretboard. You can use a guitar polish or a dedicated fretboard cleaner for this purpose.
- Clean the strings:If you’re not replacing the strings, use a string cleaner to remove dirt and grime. This will help restore the strings’ brightness and tone.
- Polish the guitar:After cleaning, apply a thin coat of guitar polish to the body and neck. This will protect the finish and enhance the guitar’s shine.
- Replace the strings:Once the guitar is clean, replace the strings with fresh ones. Ensure the strings are properly tensioned and tuned.
Tips for Removing Dust, Fingerprints, and Grime
- Use a damp microfiber cloth for stubborn grime. Wring out excess water before cleaning to prevent damage to the guitar’s finish.
- For fingerprints, use a guitar polish or a dedicated fingerprint remover.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, as these can damage the guitar’s finish.
Guitar Lifespan Extension Tips
- Store the guitar in a case:A guitar case provides protection from dust, scratches, and temperature fluctuations.
- Maintain proper humidity:Extreme humidity can cause the guitar’s wood to warp, while low humidity can cause it to crack. Store your guitar in a humidity-controlled environment, using a humidifier or dehumidifier as needed.
- Avoid extreme temperatures:Heat and cold can damage the guitar’s finish and wood. Keep your guitar away from direct sunlight, radiators, and other sources of heat.
- Use high-quality strings:Using high-quality strings will improve the guitar’s sound and extend the lifespan of the instrument.
- Clean regularly:Regular cleaning helps prevent dirt and grime from accumulating and damaging the guitar’s finish.
- Inspect for damage:Regularly inspect your guitar for any signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or loose parts. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Building a Foundation

Imagine trying to build a house without a solid foundation. It’s likely to crumble, right? The same principle applies to learning guitar. Building a strong foundation in the basics is crucial for progressing to more advanced techniques and playing with confidence and fluency.
Think of it as learning your ABCs before tackling complex novels. You’ll be able to understand and appreciate the finer points of music much better if you have a solid grasp of the fundamentals.
Practicing Scales, Chords, and Strumming Patterns
Regular practice of scales, chords, and strumming patterns is essential for developing your guitar skills. It’s like training your fingers to dance on the fretboard and build muscle memory.
- Scales: Practicing scales helps you develop finger dexterity, improve your understanding of music theory, and enhance your ability to play melodies smoothly. Start with basic scales like the major and minor scales, and gradually work your way up to more complex scales.
- Chords: Chords are the building blocks of most songs. Mastering chords will allow you to accompany singers, play melodies, and create your own musical arrangements. Focus on learning basic open chords, barre chords, and fingerpicking patterns.
- Strumming Patterns: Strumming patterns add rhythm and groove to your playing. Experiment with different strumming patterns, incorporating variations in speed, dynamics, and accents.
Developing Good Fingerpicking Technique
Fingerpicking is a technique that involves using your individual fingers to pluck the strings, creating a more delicate and nuanced sound. Developing good fingerpicking technique requires patience and practice.
- Finger Placement: Ensure your fingers are placed correctly on the strings, using a light touch. Practice plucking individual strings with each finger, gradually increasing the speed and accuracy.
- Finger Independence: Developing finger independence is crucial for fingerpicking. Practice plucking different strings with different fingers simultaneously, working on coordinating your fingers.
- Practice Fingerpicking Patterns: Start with simple fingerpicking patterns and gradually increase the complexity. Many online resources and guitar books offer a variety of fingerpicking patterns to practice.
Embrace the Journey: Finding Joy in Learning Acoustic Guitar
Learning acoustic guitar is a rewarding journey, filled with challenges and triumphs. It’s not just about mastering chords and strumming patterns; it’s about the process of discovery, the moments of frustration that lead to breakthroughs, and the sheer joy of making music.
Embrace the journey, and you’ll find yourself not only playing the guitar but also developing a deeper appreciation for music and yourself.When I first started learning guitar, I was so focused on hitting the perfect notes and strumming patterns that I missed the joy of the process.
I was frustrated by my slow progress and felt discouraged by every mistake. But then I realized that the journey was just as important as the destination. I began to appreciate the small victories – learning a new chord, strumming a simple song, or even just holding the guitar comfortably.
I learned to enjoy the struggle, to see it as an opportunity for growth and learning.
Tips for Embracing the Learning Process
Learning a new skill, especially one as complex as guitar, can be challenging. But it’s important to remember that the journey is just as important as the destination. Here are a few tips to help you embrace the learning process and find joy in your guitar journey:
- Focus on Progress Over Perfection: Don’t get caught up in trying to be perfect. Instead, focus on making progress, no matter how small. Every time you learn a new chord, strum a new pattern, or play a song more smoothly, celebrate your progress.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Learning guitar can be a slow process, so it’s important to celebrate your small wins. When you master a new chord, learn a new song, or even just play for a longer period of time without getting frustrated, take a moment to appreciate your progress.
- Find Joy in the Struggle: Learning guitar can be challenging, but it’s also an opportunity for growth and learning. Embrace the struggle, and you’ll find yourself becoming a more patient and resilient musician.
“The most beautiful music is that which is born of the heart.” – Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Quick FAQs
What are the best resources for learning acoustic guitar?
There are numerous excellent resources available, including online courses, books, and in-person lessons. The best choice for you depends on your learning style, budget, and preferences.
How often should I practice?
Consistent practice is key to progress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of focused practice daily, but even shorter sessions can be effective if done regularly.
What if I get frustrated?
It’s natural to encounter frustration. Remember, learning takes time and effort. Don’t be afraid to take breaks, celebrate small victories, and focus on the joy of making music.
What are the most important things to learn first?
Start with the basics: tuning, chords, strumming patterns, and simple melodies. Once you have a foundation, you can explore more advanced techniques.
How do I choose the right acoustic guitar for me?
Consider your budget, body size preference, and playing style. Try out different guitars before making a purchase to find one that feels comfortable and sounds good to you.