How fast can you learn guitar? It’s a question that sparks curiosity and a touch of ambition in every aspiring guitarist. The answer, however, is not a simple one-size-fits-all timeframe. Learning guitar is a journey influenced by a multitude of factors, from your natural talent to your commitment to practice.
This exploration delves into the key elements that shape your guitar learning speed, offering insights into how you can optimize your progress and reach your musical goals. We’ll uncover the impact of natural aptitude, prior musical experience, consistent practice, quality instruction, and learning methods, all of which play a role in how quickly you can master the guitar.
Factors Influencing Learning Speed: Guitar Mastery
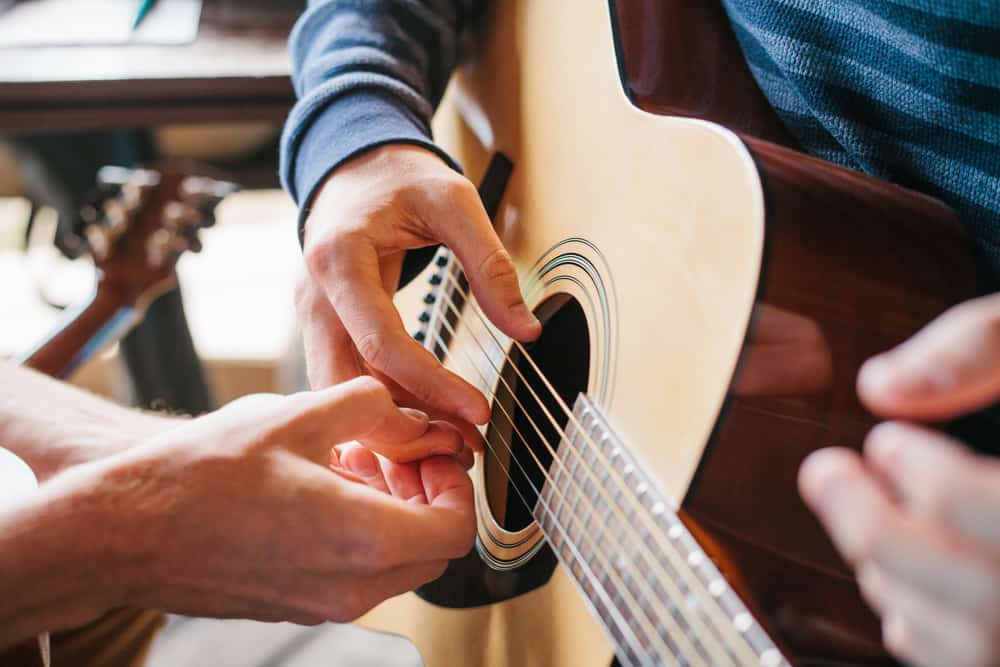

Learning guitar is a rewarding journey, but the speed at which you progress can vary significantly. Several factors influence how quickly you master the instrument, from your innate musical abilities to your learning approach. This essay will delve into the key factors that impact your learning speed, providing insights into how you can optimize your guitar learning experience.
Natural Aptitude
The influence of natural aptitude on guitar learning speed is a topic of debate. While some individuals seem to pick up the instrument effortlessly, others struggle despite consistent practice. Natural talent can manifest in various ways, such as perfect pitch, a strong sense of rhythm, or a predisposition for musicality.
Individuals with perfect pitch, for example, can identify notes by ear, potentially speeding up the process of learning scales and chords. Similarly, a natural sense of rhythm can make it easier to internalize strumming patterns and develop a feel for the music.
However, it’s important to note that natural talent alone is not a guarantee of success. Many individuals with innate musical abilities may not progress as quickly as others who are dedicated to consistent practice and effective learning strategies.
Prior Musical Experience
Previous experience with other instruments or musical genres can significantly accelerate guitar learning. The transferability of skills, such as reading music, understanding musical theory, or developing hand-eye coordination, can provide a solid foundation for guitar mastery. For example, a pianist who already understands music theory will have a head start in learning guitar chords and progressions.
Similarly, a drummer with a strong sense of rhythm will likely adapt to strumming patterns and timing more easily.
Consistent Practice Time
Consistent practice is arguably the most critical factor in accelerating guitar learning. The amount of time you dedicate to practice directly correlates with your progress. However, it’s not just about the quantity of practice; the quality is equally important.
Effective practice sessions involve focused attention, deliberate practice of specific skills, and regular review of previously learned material.
“Practice makes perfect” is a common saying, but it’s more accurate to say that “deliberate practice makes perfect”.
Quality Instruction
Receiving effective instruction from experienced guitar teachers can significantly enhance your learning speed. Structured lessons provide a personalized approach, tailored to your individual needs and learning style. A skilled teacher can identify your strengths and weaknesses, offer targeted feedback, and guide you through challenging concepts.
Learning Methods
The choice of learning method can significantly influence your progress.
Self-Taught
Learning guitar independently through online resources, books, and videos offers flexibility and convenience. However, it requires strong self-discipline, motivation, and the ability to identify and correct your own mistakes.
Lessons
Personalized instruction from a qualified teacher provides structured learning, personalized feedback, and guidance through challenging concepts. However, lessons can be expensive and may require a commitment to a set schedule.
Group Classes
Group classes offer a social learning environment, fostering motivation and camaraderie among students. However, the pace of instruction may not be tailored to individual needs, and the teacher may not be able to provide personalized feedback to each student.
2. Setting Realistic Expectations

Learning guitar is a journey, and like any journey, it’s important to have a roadmap and set realistic expectations. While the allure of becoming a guitar virtuoso overnight might be tempting, it’s crucial to understand that mastery takes time, dedication, and a balanced approach.
Timeframes for Skill Progression
The time it takes to achieve different skill levels on the guitar can vary significantly depending on individual factors like natural aptitude, practice frequency, and learning methods. However, here’s a general guideline for typical progression:
| Level | Description | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Basic chords, strumming patterns, and simple melodies | 3-6 months |
| Intermediate | More complex chords, fingerpicking, lead guitar techniques, and basic improvisation | 1-2 years |
| Advanced | Advanced improvisation, soloing, music theory, and in-depth understanding of different genres | 3+ years |
Overcoming Plateaus
Plateaus are a natural part of the learning process, and they often occur when you reach a point where you’re comfortable with your current skill level and stop pushing yourself. Here are some strategies to overcome plateaus:
- Change your approach:Experiment with different learning methods, resources, or teachers. A fresh perspective can help break through a rut.
- Seek feedback:Get constructive criticism from an experienced guitarist, teacher, or mentor. They can identify areas where you can improve.
- Take a break:Sometimes, stepping away from the guitar for a while can help you return with renewed motivation and a fresh perspective.
Achievable Goals for Beginners
Setting achievable goals is essential for maintaining motivation and tracking your progress. Here are some SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals for beginners:
- Complete a beginner-level guitar tutorial within 2 weeks.
- Learn to play 5 basic chords within 1 month.
- Practice consistently for 30 minutes a day for 3 weeks.
Maintaining Consistency without Burnout
Consistency is key to guitar learning, but it’s also important to avoid burnout. Here are some strategies to maintain a healthy balance:
- Set realistic goals:Avoid overwhelming yourself with too much practice. Start small and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- Take breaks:Incorporate rest and relaxation into your practice routine. Don’t push yourself too hard, and listen to your body.
- Celebrate milestones:Acknowledge your progress and celebrate small victories. This will keep you motivated and engaged.
3. Effective Practice Techniques
Effective practice techniques are crucial for rapid guitar learning. They enable you to maximize your time and effort, leading to faster progress and a deeper understanding of the instrument. This section explores key techniques to enhance your guitar practice and accelerate your learning journey.
3.1. Designing a Structured Practice Routine
A structured practice routine is essential for consistent progress and efficient learning. By organizing your practice time, you can ensure that you cover all the necessary aspects of guitar playing, from technical proficiency to musical expression.
| Day | Exercises |
|---|---|
| Monday | Scales (major, minor, pentatonic), arpeggios, finger exercises |
| Tuesday | Rhythm practice (strums, picking patterns), metronome work |
| Wednesday | Sight-reading, learning new chords, theory concepts |
| Thursday | Piece practice (focus on technique, accuracy, and musicality) |
| Friday | Improvisation, ear training, listening to music |
| Saturday | Performance practice, recording oneself playing |
| Sunday | Rest and relaxation |
This sample schedule provides a framework for a balanced practice routine. The specific exercises and their duration can be adjusted based on your individual goals and preferences.
- Scales and arpeggiosimprove finger dexterity, coordination, and muscle memory, laying the foundation for technical proficiency.
- Rhythm practicedevelops a strong sense of timing and groove, essential for playing with other musicians or backing tracks.
- Sight-readingenhances your ability to read music quickly and accurately, allowing you to learn new pieces more efficiently.
- Piece practicefocuses on mastering specific songs, developing musical expression, and refining your overall performance.
- Improvisationencourages creativity, musical exploration, and develops your ear for music.
- Performance practicehelps you prepare for live performances, reducing stage fright and enhancing your confidence.
For example, a typical day’s practice routine might include:
- Warm-up:5 minutes of finger exercises and scales.
- Technical exercises:10 minutes of arpeggios and picking patterns.
- Piece practice:20 minutes dedicated to mastering a specific song.
- Improvisation:10 minutes of exploring different musical ideas and techniques.
- Cool-down:5 minutes of relaxing finger exercises and stretching.
This structured approach ensures that you address all the key aspects of guitar playing, leading to well-rounded development and faster progress.
3.2. Breaking Down Complex Skills
Breaking down complex skills into smaller, manageable steps is a highly effective learning strategy. This approach simplifies the learning process, reduces frustration, and enhances your understanding of the overall skill.
- Example:Learning a complex guitar solo can be overwhelming. By breaking it down into smaller sections, you can focus on mastering each phrase individually before putting them together.
- Explanation:This approach allows you to gradually build your skills and confidence, making the learning process more enjoyable and less intimidating. By tackling smaller, more achievable steps, you can quickly see progress and stay motivated.
“The best way to eat an elephant is one bite at a time.”
Anonymous
This quote aptly illustrates the power of breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. By focusing on each individual step, you can overcome seemingly insurmountable challenges and achieve remarkable results.
3.3. Feedback and Self-Evaluation
Regular feedback and self-evaluation are essential for identifying areas for improvement and accelerating your learning progress.
- Explanation:Feedback from a teacher, recordings, or other musicians can provide valuable insights into your playing, highlighting strengths and weaknesses. Self-evaluation allows you to actively analyze your performance and identify areas that require attention.
- Example:When practicing a new guitar riff, you might notice that your timing is slightly off. By recording yourself playing, you can identify the specific points where you’re struggling and focus on improving your accuracy.
- Guidance:Regularly recording yourself playing and analyzing your performance can help you identify and address technical or musical issues. Listen to your recordings objectively, paying attention to your timing, rhythm, intonation, and overall musicality.
By actively seeking feedback and engaging in self-evaluation, you can continuously refine your playing and accelerate your progress on the guitar.
3.4. Effective Practice with Limited Time
Even with limited time, you can still make significant progress on the guitar by implementing effective practice techniques.
- Prioritize tasks:Focus on the most important areas for improvement, such as mastering specific techniques or songs that are particularly challenging.
- Utilize short practice sessions:Even short, focused practice sessions can be highly effective. Aim for consistency over duration, even if it’s just 15-20 minutes a day.
- Maintain focus:Eliminate distractions and create a dedicated practice space where you can concentrate fully on your playing.
- Set achievable goals:Break down your learning goals into smaller, manageable steps, allowing you to track progress and stay motivated.
- Example:If you have only 15 minutes to practice, focus on mastering a specific guitar lick or practicing a challenging chord progression. This focused approach allows you to make significant progress in a short amount of time.
By prioritizing tasks, utilizing short practice sessions, and maintaining focus, you can maximize your learning and achieve meaningful progress despite time constraints.
Essential Guitar Skills

Mastering the guitar involves acquiring a diverse range of skills, each contributing to your overall playing ability. Developing these skills systematically is crucial for progress, and a solid foundation in the basics will set you up for success in tackling more complex techniques.
Finger Placement and Chord Shapes
Knowing the correct finger placement on the fretboard is fundamental. Understanding chord shapes allows you to create different harmonies and melodies.
- Practice Finger Placement:Start by learning the basic open chords, such as G, C, D, and E. Focus on placing your fingers accurately and avoiding unnecessary pressure. Use a mirror to observe your hand position and correct any mistakes.
- Chord Transitions:Practice transitioning smoothly between chords, aiming for a clean and precise change. Use a metronome to develop rhythm and timing.
- Chord Inversions:Learn different inversions of chords to create variations in sound and texture. This expands your musical vocabulary and allows for more interesting chord progressions.
Picking and Strumming
Picking and strumming techniques are essential for creating different rhythms and textures.
- Picking Patterns:Practice basic picking patterns, such as down-up, up-down, and alternate picking. Focus on maintaining a consistent rhythm and speed. Use a metronome to improve accuracy and timing.
- Strumming Techniques:Learn different strumming patterns, such as down-up, up-down, and various combinations of these. Experiment with different dynamics and accents to create variation in your playing.
- Fingerpicking:Fingerpicking involves using your fingers to pluck individual strings. Practice basic fingerpicking patterns, focusing on clarity and precision.
Reading Tablature
Tablature is a system of notation that represents the guitar fretboard. It’s a valuable tool for learning new songs and understanding guitar techniques.
- Understanding Tablature:Learn the basics of reading tablature, including how to identify strings, frets, and picking directions. Practice reading simple tab examples.
- Transcribing Songs:Try transcribing simple songs into tablature. This helps you understand the relationship between tab notation and actual guitar playing.
- Tablature Resources:Utilize online resources and guitar tab websites to find tab examples for your favorite songs.
Music Theory
Understanding basic music theory concepts, such as scales, chords, and key signatures, enhances your musical understanding and allows you to improvise and create your own music.
- Scales:Learn the major and minor scales, as well as common pentatonic scales. Understanding scales helps you create melodies and improvise solos.
- Chords:Learn the construction of major and minor chords, as well as common chord progressions. This knowledge enables you to create harmonic structures and build musical arrangements.
- Key Signatures:Understand the concept of key signatures and how they affect the notes and chords within a particular key. This allows you to read and play music in different keys.
Choosing the Right Guitar
Picking the right guitar is crucial for your learning journey. The type of guitar you choose will significantly impact your experience, from comfort to sound. Think of it as choosing the right tool for the job
the wrong tool can make the job much harder.
Types of Guitars
The world of guitars offers a diverse range of options, each with its unique characteristics. For beginners, understanding the most common types is essential.
- Acoustic Guitar:Known for their natural, warm sound, acoustic guitars are excellent for beginners due to their simplicity. They come in various sizes, with smaller models being easier to play for those with smaller hands.
- Electric Guitar:These guitars are plugged into an amplifier for amplification, producing a wide range of tones and effects. While they can be more complex to set up, electric guitars offer incredible versatility.
- Classical Guitar:Characterized by their nylon strings and wider necks, classical guitars are ideal for playing classical music. They produce a mellow, rich sound and are often used in flamenco and other genres.
Choosing a Guitar That Fits Comfortably
A comfortable guitar is essential for practice and enjoyment. A guitar that’s too big or too small can cause discomfort and hinder your progress.
- Body Size:Consider the size of the guitar’s body. Smaller bodies are easier to hold and reach the strings, while larger bodies offer a fuller sound.
- Neck Width:The width of the neck influences the spacing between the strings. A wider neck can be challenging for beginners, while a narrower neck might feel cramped.
- String Action:The height of the strings above the fretboard, known as string action, affects playability. Lower action makes it easier to press down on the strings, while higher action requires more effort.
Selecting a Guitar Based on Budget and Personal Preferences
The cost of a guitar can vary significantly, from affordable beginner models to high-end instruments.
- Budget:Set a realistic budget before you start shopping. You can find quality beginner guitars within a reasonable price range. However, remember that a higher price tag doesn’t always guarantee better quality.
- Personal Preferences:Explore different guitar models and find one that resonates with your taste. Consider the sound, aesthetics, and overall feel of the guitar.
Guitar Setup
Even a well-made guitar can benefit from a proper setup. This involves adjusting the truss rod, bridge height, and other components to optimize playability and sound.
- Truss Rod Adjustment:The truss rod is a metal rod inside the neck that helps maintain the neck’s curvature. Adjusting it can correct any warping or bowing in the neck.
- Bridge Height Adjustment:The bridge height affects the string action. A skilled guitar technician can adjust the bridge to ensure the strings are at the optimal height for comfortable playing.
Building a Solid Foundation
A strong foundation is crucial for any aspiring guitarist. It provides the essential building blocks upon which you can build your skills and explore more advanced techniques.
Tuning Methods
Different tuning methods offer unique advantages and drawbacks, affecting the feel and sound of your guitar.
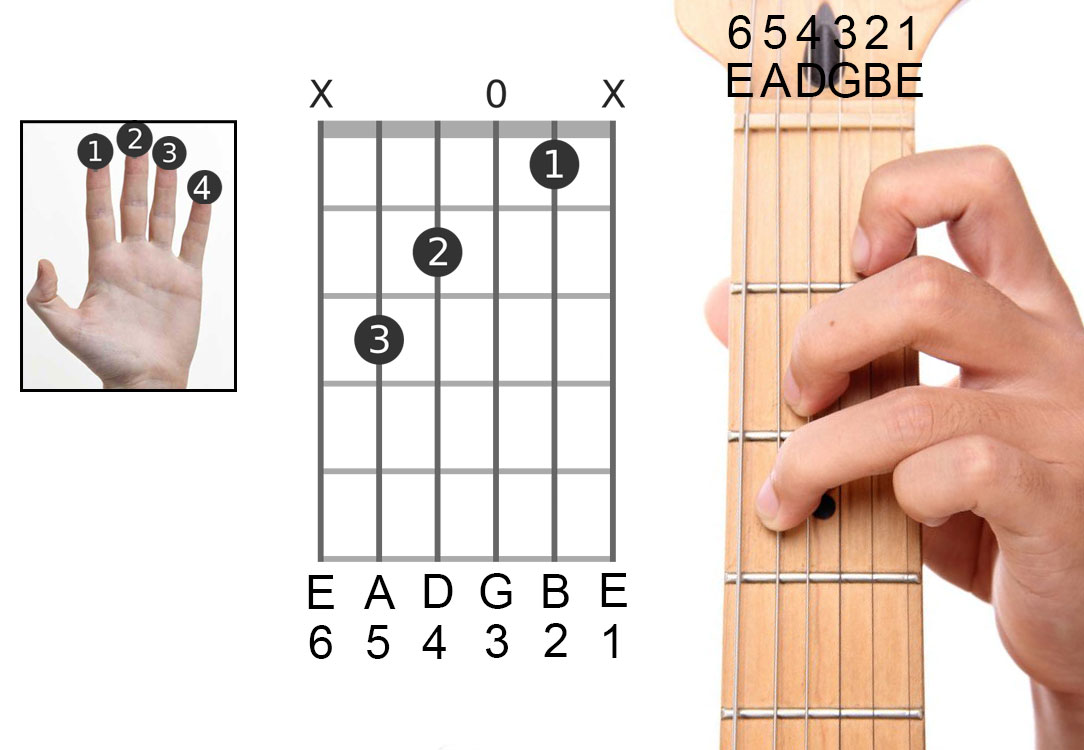
- Standard Tuning: This is the most common tuning for guitars, with strings tuned to E, A, D, G, B, and E from lowest to highest. It’s versatile and widely used for various genres, but can be challenging for beginners due to the wide string spacing.
- Drop D Tuning: Lowering the sixth string to D provides a heavier sound and makes playing power chords easier. It’s popular in genres like metal and rock, but it can limit your ability to play in standard tuning.
- Open Tuning: These tunings involve leaving some strings open, creating unique harmonies and chord voicings. They are often used in folk, blues, and slide guitar, but require a different approach to playing and chord construction.
Basic Chords and Scales
Learning basic chords and scales is essential for developing a strong musical foundation.
- Chords: These are combinations of notes played simultaneously, creating harmonies and melodies. Learning major and minor chords is a good starting point, providing a foundation for understanding chord progressions and playing songs.
- Scales: These are sequences of notes arranged in a specific pattern, providing a framework for creating melodies and improvising. Mastering scales helps you understand the relationships between notes and develop your finger dexterity.
Posture and Hand Positioning
Proper posture and hand positioning are crucial for playing comfortably and efficiently.
- Posture: Sit or stand with your back straight and your shoulders relaxed. Ensure your feet are flat on the floor, and your guitar rests comfortably on your leg. This allows for proper breathing and reduces strain on your back and neck.
- Left Hand: Place your left hand on the neck with your thumb behind the neck, supporting the hand. Keep your fingers curled and relaxed, using only the tips to press down on the strings. Avoid pressing too hard, as it can cause discomfort and hinder your speed.
- Right Hand: Position your right hand over the strings, using your fingers to pluck or strum. Keep your wrist relaxed and your fingers close to the strings. Practice different picking patterns and strumming techniques to develop your right-hand coordination.
Overcoming Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often make common mistakes that can hinder their progress.
- Tensing Up: Relax your hands and arms. Tension can lead to pain, fatigue, and poor technique. Practice regularly and focus on maintaining a relaxed grip.
- Incorrect Finger Placement: Use only the tips of your fingers to press down on the strings. Ensure your fingers are properly positioned on the fretboard to avoid buzzing or muted notes. Practice finger exercises and scales to improve your accuracy.
- Rushing: Take your time and focus on playing each note or chord accurately. Don’t rush through exercises or songs, as it can lead to mistakes and frustration. Practice at a slower tempo and gradually increase the speed as you improve.
- Lack of Practice: Consistency is key to improvement. Practice regularly, even if it’s just for a short time. Break down your practice into manageable sessions and focus on specific areas you need to improve.
Developing Musicality
Musicality is the ability to understand, interpret, and express music effectively. It encompasses various aspects, including music theory, rhythm, improvisation, and creative expression. Developing musicality is crucial for guitarists as it allows them to play with more depth, meaning, and artistic flair.
Understanding Music Theory
Music theory provides a framework for understanding the structure and organization of music. It helps you analyze and interpret musical pieces, understand how different elements interact, and create your own music.
- Scales:Scales are a sequence of notes arranged in a specific order, forming the basis of melodies and harmonies. Understanding scales allows you to create melodies and play in different keys. For example, the major scale, with its characteristic interval pattern, creates a bright and uplifting sound, while the minor scale often evokes a more somber or melancholic feeling.
- Chords:Chords are combinations of three or more notes played simultaneously, creating harmonic progressions and supporting melodies. Understanding chords allows you to create rich and complex harmonies, accompany melodies, and improvise over chord changes.
- Key Signatures:Key signatures indicate the sharps or flats that are added to a scale, determining the key of a piece of music. Understanding key signatures helps you navigate different keys and understand the relationships between notes.
By understanding music theory, you can analyze and interpret music more effectively. For instance, you can recognize chord progressions, identify key changes, and understand the structure of musical pieces. This knowledge enhances your ability to appreciate and enjoy music at a deeper level.Music theory also provides the foundation for songwriting and composition.
By understanding scales, chords, and key signatures, you can create melodies, harmonies, and progressions that express your musical ideas. For example, knowing the structure of a 12-bar blues progression allows you to create variations and experiment with different chord substitutions, leading to unique and creative musical compositions.
Developing a Sense of Rhythm and Timing
Rhythm is the organization of sounds in time. A strong sense of rhythm is essential for playing guitar accurately and expressively.
- Internal Clock:A strong internal clock is the ability to keep time accurately without relying on external cues. It allows you to play in time with other musicians, maintain a steady tempo, and feel the pulse of the music.
- Counting Rhythms:Counting rhythms accurately helps you understand the subdivisions of a beat and play complex rhythms with precision. It involves breaking down rhythms into smaller units and counting them consistently. For example, a 4/4 time signature can be counted as 1, 2, 3, 4, with each number representing a quarter note.
To improve your rhythm and timing, you can practice exercises like clapping, counting, and playing along to a metronome. These exercises help you develop a strong internal clock and refine your sense of time. Rhythm plays a crucial role in music.
Rhythmic patterns and syncopation, where notes fall on off-beats, add energy and excitement to music. Understanding and manipulating rhythm allows you to create grooves, drive the music forward, and add rhythmic complexity.
Enhancing Improvisation Skills
Improvisation is the ability to create music spontaneously and in real time. It involves responding to musical ideas, creating melodies, and expressing your creativity on the fly.
- Strong Ear:A strong ear allows you to hear and respond to musical ideas, identify melodies and harmonies, and improvise effectively. It involves developing the ability to hear intervals, chord changes, and musical phrases.
- Scales, Arpeggios, and Chord Progressions:Mastering scales, arpeggios, and chord progressions provides a framework for improvisation. They provide a vocabulary of notes and patterns that you can use to create melodies and solos. For example, playing a pentatonic scale over a blues progression allows you to create bluesy melodies and solos that fit the harmonic context.
Improvisation requires creativity and spontaneity. You need to be able to think on your feet, respond to the music, and express your musical ideas in real time. Exercises like playing scales, arpeggios, and chord progressions can help you develop the technical skills needed for improvisation, while listening to and analyzing improvisational solos from other musicians can inspire your own creativity.
Creative Musical Exercises
Engaging in creative musical exercises helps develop your musical vocabulary and encourages exploration and expression.
- Composing Melodies:Experiment with different scales, rhythms, and melodic ideas to create your own melodies. You can use music theory concepts like scales and chords as a starting point and then let your creativity guide you.
- Writing Lyrics:Combine your musical ideas with words to create songs. Explore different themes, emotions, and storytelling techniques.
- Experimenting with Different Musical Styles:Try playing in different genres, such as blues, jazz, rock, or classical. This exposes you to new musical concepts, techniques, and influences, expanding your musical vocabulary.
These exercises encourage you to take risks, explore new ideas, and develop your own unique musical voice. The creative process is about experimentation and finding what works best for you. Don’t be afraid to try new things, make mistakes, and learn from your experiences.
The Role of Motivation and Discipline
Motivation and discipline are two crucial ingredients in your guitar learning journey. They act as the driving force behind your progress, pushing you to overcome challenges and stay committed to your goals. Without them, even the most effective practice techniques and the right guitar can fall short.
Understanding Your Learning Style, How fast can you learn guitar
Knowing your learning style is essential for tailoring your guitar learning experience to your individual needs. It can help you identify the most effective ways to absorb information, practice techniques, and retain what you’ve learned.
- Visual Learners:Visual learners prefer to see information presented visually, such as diagrams, charts, and videos. They might benefit from watching instructional videos, studying guitar tabs, or using flashcards with chord diagrams.
- Auditory Learners:Auditory learners learn best by listening to information. They might find it helpful to listen to music, attend guitar lessons, or use audio recordings of scales and exercises.
- Kinesthetic Learners:Kinesthetic learners learn by doing. They might prefer to learn through hands-on practice, experimenting with different techniques, and playing along with songs.
Staying Motivated and Avoiding Quitting
Maintaining motivation is key to staying on track with your guitar learning goals. It’s easy to get discouraged when you encounter challenges or feel like you’re not progressing fast enough. Setting small, achievable goals can help you stay motivated and prevent burnout.
- Set Small, Achievable Goals:Instead of aiming for a huge goal like learning to play a complex song, break it down into smaller, more manageable steps. For example, instead of trying to learn the entire song, focus on learning a specific chord progression or a single verse.
- Find a Guitar Buddy:Having a guitar buddy can provide encouragement, accountability, and a sense of community. You can motivate each other, share tips, and practice together.
- Reward Yourself:Celebrate your progress by rewarding yourself for achieving your goals. This could be anything from buying a new guitar pick to treating yourself to a night out.
Setting Realistic Goals and Tracking Progress
Setting realistic goals is crucial for staying motivated and avoiding frustration. It’s important to acknowledge that learning guitar takes time and effort.
- Break Down Large Goals:Instead of trying to learn everything at once, break down your goals into smaller, more manageable steps. This makes the learning process feel less overwhelming and more achievable.
- Track Your Progress:Keep a practice log or chart to track your progress. This can help you stay motivated and identify areas where you need to focus your practice.
Joining a Community of Guitar Players
Connecting with other guitarists can provide valuable support, inspiration, and accountability.
- Find a Local Guitar Community:Look for local guitar stores, music schools, or community centers that offer guitar workshops or jam sessions. These can be great places to meet other guitarists and share your passion for music.
- Join an Online Forum:There are numerous online forums and communities dedicated to guitarists of all levels. These forums can be a great resource for finding information, getting advice, and connecting with other guitarists.
Resources and Learning Tools
Learning guitar effectively requires access to a variety of resources and tools. These can include online lessons, guitar apps, and even a qualified guitar teacher. Utilizing a diverse range of resources can help you learn at your own pace, address your specific needs, and keep you motivated on your musical journey.
Online Guitar Lessons and Tutorials
Online guitar lessons and tutorials offer a vast library of learning materials, covering various guitar styles, techniques, and skill levels. These resources can be incredibly beneficial for beginners and experienced guitarists alike. They provide flexibility, accessibility, and often come with detailed explanations and demonstrations.Here are some recommended online guitar lesson platforms:
- JustinGuitar:A comprehensive platform offering free and paid lessons, covering everything from beginner basics to advanced techniques. They also provide a structured learning path and a supportive community.
- Fender Play:This platform offers interactive lessons tailored to specific genres, including rock, blues, and pop. It uses a gamified approach, making learning engaging and rewarding.
- Guitar Tricks:A well-established platform with a vast library of lessons, focusing on various guitar styles, including rock, blues, and jazz. They offer personalized learning plans and access to a community forum.
- YouTube:While YouTube offers a plethora of free guitar lessons, it can be overwhelming to find reliable and structured content. Searching for specific techniques, songs, or tutorials from reputable guitar teachers can be helpful.
Guitar Apps and Software
Guitar apps and software can be valuable tools for practicing, learning new songs, and improving your skills. These tools offer a variety of features, including:
- Chord diagrams and tablatures:These can help you visualize and learn chords and guitar parts.
- Tuners:Essential for ensuring your guitar is in tune.
- Metronomes:Help you develop rhythm and timing.
- Practice tools:Offer exercises and games to enhance your skills.
- Song libraries:Provide access to a vast catalog of songs, allowing you to learn new tunes.
However, relying solely on apps and software can have drawbacks. They may not provide the personalized guidance and feedback that a teacher can offer. It’s important to use these tools as complements to your overall learning process, rather than replacements for traditional methods.
Finding a Qualified Guitar Teacher
A qualified guitar teacher can provide personalized instruction, feedback, and guidance, helping you progress more efficiently.Here are some tips for finding a suitable teacher:
- Ask for recommendations:Seek recommendations from friends, family, or other musicians.
- Check online directories:Websites like Thumbtack or Yelp can help you find local guitar teachers.
- Visit local music stores:Music stores often have a list of teachers or offer lessons themselves.
- Look for qualifications and experience:Choose a teacher with relevant experience and credentials.
- Schedule a trial lesson:This allows you to assess the teacher’s teaching style and compatibility with your learning goals.
Utilizing a Variety of Learning Resources
Combining online lessons, guitar apps, and a qualified teacher can create a comprehensive and effective learning experience.
“The best way to learn guitar is to use a variety of resources and find what works best for you.”
By incorporating different learning approaches, you can address your specific needs, keep yourself motivated, and accelerate your progress.
The Journey of Learning

Learning guitar is a journey, not a race. It’s a process of exploration, discovery, and constant growth. You’ll encounter challenges along the way, but each hurdle you overcome strengthens your skills and deepens your understanding of music.
Stages of Guitar Learning
The journey of learning guitar can be divided into distinct stages, each with its own set of challenges and rewards.
- Beginner Stage:This stage is marked by excitement and a desire to learn the basics. You’ll focus on learning chords, strumming patterns, and basic scales. The challenge lies in developing hand coordination and finger strength. You might feel frustrated at times, but remember that consistency and patience are key.
- Intermediate Stage:As you progress, you’ll develop a stronger foundation in technique and theory. You’ll start exploring more complex chords, fingerpicking, and improvisation. This stage demands dedication and practice, as you’ll need to refine your skills and expand your musical vocabulary.
- Advanced Stage:This stage is about mastering your craft and developing your own unique style. You’ll delve deeper into musical theory, explore different genres, and experiment with techniques. The challenge here is to maintain your passion and find new ways to push your boundaries.
Embracing Mistakes
Mistakes are an inevitable part of the learning process. Don’t be discouraged by them; instead, see them as opportunities for growth. Each mistake offers valuable insights into what you need to improve.
“The only way to do great work is to love what you do. If you haven’t found it yet, keep looking. Don’t settle.”
Steve Jobs
Success Stories
Many renowned guitarists faced challenges and setbacks on their journey to success. For example, Jimi Hendrix initially struggled with his left hand but persevered, ultimately becoming one of the greatest guitarists of all time. Similarly, Eric Clapton initially struggled with stage fright but overcame it to become a legendary performer.
These stories remind us that success is not a straight path but a journey filled with obstacles and triumphs.
Enjoy the Process
Learning guitar should be an enjoyable experience. Don’t get caught up in the pressure to achieve perfection or to learn quickly. Embrace the process, savor each milestone, and enjoy the journey. The more you enjoy the process, the more motivated you’ll be to keep learning and growing as a musician.
The Power of Persistence
The journey to mastering any skill, whether it’s playing the guitar, becoming a professional athlete, or excelling in academics, is not a sprint but a marathon. It requires unwavering dedication and a commitment to consistent practice. Persistence is the key that unlocks the door to true mastery.
The Importance of Consistent Practice
Consistent practice is the cornerstone of achieving mastery in any field. It’s not about practicing for hours on end without focus or direction; it’s about deliberate, focused effort that strengthens your skills and builds your knowledge base. Think of it as a sculptor meticulously chiseling away at a block of marble, gradually revealing the masterpiece within.
The benefits of consistent practice are multifaceted and far-reaching:
- Muscle Memory: Repeated practice creates neural pathways in your brain, making actions more automatic and effortless. Think of a pianist effortlessly playing scales after years of practice. The movements have become ingrained in their muscle memory, freeing up their mental energy for more complex musical interpretations.
- Improved Efficiency: Consistent practice leads to more efficient use of time and resources. A programmer who regularly practices writing code will become faster and more efficient, making fewer errors and producing cleaner, more maintainable code. This efficiency translates into better results and greater productivity.
- Increased Confidence: Success through practice breeds confidence and motivation. A student who consistently studies for exams will feel more confident in their abilities, leading to better performance and a greater sense of accomplishment. This confidence spills over into other areas of life, empowering individuals to take on new challenges and pursue their goals with greater determination.
Overcoming Obstacles and Setbacks
The path to mastery is rarely smooth. Obstacles and setbacks are inevitable, and how you handle them will determine your ultimate success. Here are some common obstacles and strategies for overcoming them:
- Obstacle: Feeling overwhelmed by the amount of material to learn.
- Strategy: Break down the material into smaller, manageable chunks and set realistic daily goals.Focus on mastering one concept at a time, building upon your knowledge gradually. Celebrate each small victory along the way to stay motivated and maintain momentum.
- Obstacle: Lack of motivation or feeling discouraged.
- Strategy: Remind yourself of your goals and the reasons why you started this journey.Connect with other learners or mentors for support and encouragement. Find ways to make practice enjoyable, incorporating elements of fun and creativity into your routine.
- Obstacle: Hitting a plateau and feeling like you’re not progressing.
- Strategy: Evaluate your practice methods and identify areas for improvement.Seek feedback from a teacher or mentor. Experiment with new techniques or resources to challenge yourself and stimulate further growth.
Staying Motivated in the Face of Challenges
“The only way to do great work is to love what you do. If you haven’t found it yet, keep looking. Don’t settle.”
Steve Jobs
When the road gets tough, remember why you started this journey. What is your ultimate goal? What motivates you to keep going? Set achievable goals for yourself, breaking down your larger aspirations into smaller, more manageable steps.
Celebrate each milestone along the way, no matter how small. Find a support system of friends, family, or mentors who believe in you and your abilities. Their encouragement and guidance can be invaluable during challenging times. Remember, every great musician, athlete, or scholar has faced setbacks and obstacles along the way.
Learning guitar is a journey, not a race. It’s about finding the right balance between practice and patience. Just like figuring out if do cats learn from negative reinforcement , it’s about understanding what works best for you. Some people pick it up quickly, others take their time.
The key is to stay consistent, enjoy the process, and celebrate your progress, no matter how small!
What sets them apart is their unwavering commitment to their craft and their willingness to persevere through adversity.
The Long-Term Rewards of Persistent Learning
Imagine a young musician named Maya, passionate about playing the guitar. She practices diligently, facing challenges and setbacks along the way. Sometimes, she feels frustrated and wants to give up. But she remembers her love for music and the joy it brings her.
She persists, seeking guidance from experienced musicians and exploring new techniques.As Maya continues to practice, she starts to see progress. Her fingers become more nimble, her chords sound clearer, and her melodies become more expressive. She discovers a sense of fulfillment and accomplishment that comes from mastering a challenging skill.
Maya’s persistence pays off. She performs at local events, shares her music with others, and inspires others to pursue their passions. Her journey is a testament to the power of persistence. It shows that with dedication and hard work, we can overcome obstacles, achieve our goals, and discover a sense of fulfillment that lasts a lifetime.
Beyond the Basics
You’ve mastered the fundamentals, now it’s time to explore the exciting world of advanced guitar techniques and musical possibilities. This section will guide you through expanding your skills and unlocking new creative avenues on the guitar.
Fingerpicking and Strumming Patterns
Fingerpicking and strumming are two distinct approaches to playing the guitar, each offering unique sonic textures and expressive possibilities. Fingerpicking involves using your individual fingers to pluck the strings, creating intricate melodies and harmonic patterns.
- Developing Finger Independence:Practice picking individual strings with each finger, gradually increasing speed and accuracy. Start with simple exercises and gradually progress to more complex patterns.
- Learning Fingerpicking Patterns:Explore traditional fingerpicking patterns used in folk, blues, and classical music. Many resources, including online tutorials and guitar tab books, offer a wide range of patterns to learn.
- Adding Dynamics and Expression:Fingerpicking allows for subtle variations in volume, tone, and rhythm, adding depth and emotion to your playing.
Strumming involves using a pick or your hand to sweep across the strings, creating a rhythmic and percussive sound.
- Mastering Basic Strumming Patterns:Learn the basic downstroke and upstroke patterns, experimenting with different rhythms and accents.
- Expanding Strumming Techniques:Explore variations like muted strums, alternating bass patterns, and rhythmic variations to create a dynamic and engaging sound.
- Developing Strumming Dynamics:Practice varying the force and speed of your strums to create a range of textures and volumes.
Learning Different Musical Genres
The guitar is a versatile instrument that can be used to play a wide variety of musical genres. Exploring different genres allows you to expand your musical vocabulary and discover new techniques and styles.
- Rock and Roll:Focus on power chords, distorted sounds, and driving rhythms. Study iconic rock guitarists like Jimi Hendrix, Jimmy Page, and Eddie Van Halen.
- Blues:Learn the pentatonic scale, bending notes, and slide guitar techniques. Explore the works of blues legends like B.B. King, Muddy Waters, and Eric Clapton.
- Jazz:Develop your improvisational skills, explore chord progressions, and study jazz guitarists like Wes Montgomery, Django Reinhardt, and Pat Metheny.
- Country:Learn fingerpicking patterns, slide guitar, and traditional country melodies. Study country guitarists like Chet Atkins, Merle Haggard, and Vince Gill.
- Classical:Master classical guitar techniques, including fingerpicking, arpeggios, and scales. Explore the works of classical guitarists like Andrés Segovia, Julian Bream, and John Williams.
Writing Your Own Guitar Music
Composing your own music is a rewarding and fulfilling aspect of guitar playing. It allows you to express your creativity and create unique pieces that reflect your personal style.
- Develop Your Musical Ear:Learn to recognize chords and melodies by ear, and experiment with different musical ideas.
- Explore Chord Progressions:Study common chord progressions used in various genres and create your own variations.
- Compose Melodies:Develop your melodic sense by experimenting with different scales, rhythms, and harmonies.
- Use Guitar Tab:Guitar tab is a notation system that allows you to write down your musical ideas quickly and easily.
- Record and Experiment:Use recording software or a simple phone app to capture your musical ideas and experiment with different arrangements.
Incorporating Other Instruments
The guitar can be seamlessly integrated with other instruments, creating rich and complex musical arrangements.
- Playing with Vocals:Accompanying vocals with guitar adds depth and texture to songs. Experiment with different strumming patterns, chord progressions, and melodies to enhance the vocal performance.
- Playing with Other Instruments:Explore the possibilities of playing with other instruments, such as piano, drums, bass, or strings. This can create a wide range of musical styles and textures.
- Joining a Band:Joining a band provides a collaborative environment where you can learn from other musicians and develop your musical skills.
The Joy of Guitar Playing
Beyond the technical skills and musical knowledge, playing guitar offers a world of emotional and social benefits that enrich our lives in countless ways. It’s a journey of self-discovery, connection, and fulfillment, where the act of making music becomes a source of joy and meaning.
Emotional Benefits
The act of playing guitar can have a profound impact on our emotional well-being. It provides a therapeutic outlet for stress and anxiety, allowing us to channel our emotions into creative expression. The repetitive motions and focus required in playing can induce a state of mindfulness, calming the mind and reducing racing thoughts.
Learning guitar can be a confidence-boosting experience. As we master new skills and techniques, our sense of accomplishment grows, leading to increased self-esteem and a feeling of personal growth. The satisfaction of creating music from scratch, whether it’s a simple melody or a complex composition, is a powerful motivator and a source of pride.
Social Benefits
Playing guitar can connect us with others in a unique and meaningful way. Sharing music with friends, family, or even strangers can foster a sense of community and belonging. It can also be a powerful tool for building relationships and deepening existing ones.
The guitar playing world is filled with opportunities for collaboration and community involvement. Joining a band, attending open mics, or participating in workshops allows us to connect with like-minded individuals, share our passion for music, and learn from each other.
Guitar playing can also enhance social skills and communication. It teaches us to listen attentively to others, to express ourselves clearly, and to work effectively in a group.
Impactful Stories
“I was going through a difficult time in my life, feeling lost and overwhelmed. Then, I decided to pick up the guitar again. It was something I had always wanted to do, but I never had the time or the courage. As I started playing, I felt a sense of calm and peace wash over me. The music became an outlet for my emotions, a way for me to express myself without words. It helped me to heal and find my way back to myself.”
Sarah, a guitar player who found solace in music.
“My grandfather was a talented musician, and I always admired his ability to play the guitar. When he passed away, I decided to learn in his memory. It was a challenging journey, but it brought me closer to my family and helped me to honor his legacy. Every time I play, I feel his presence with me, and it brings me a sense of peace and joy.”
David, a guitar player who honored his grandfather’s memory through music.
“My wife and I were struggling to communicate effectively. We were both feeling disconnected and frustrated. Then, I started taking guitar lessons, and it became a shared passion. We would spend evenings together, learning songs and jamming. It brought us closer together and helped us to rediscover the joy of being together.”
Michael, a guitar player who strengthened his relationship through music.
Finding Joy in the Learning Process
Learning guitar is a journey, not a destination. It’s important to celebrate small victories and milestones along the way. Mastering a new chord, playing a familiar song without mistakes, or even just making it through a challenging practice session are all reasons to be proud of yourself.
Embrace the challenges and setbacks as part of the learning journey. They are opportunities for growth and learning. Patience, perseverance, and a growth mindset are essential qualities for any guitar player.
Embracing the Journey
Focus on the process of learning and enjoying the music rather than solely on achieving a specific skill level. Explore different genres, experiment with different techniques, and find what brings you joy. Make guitar playing a fun and rewarding experience.
Play music you love, jam with friends, and don’t be afraid to try new things. Find personal meaning and fulfillment through guitar playing. Let it be a source of joy, expression, and connection in your life.
The Future of Guitar Learning
The world of guitar learning is constantly evolving, fueled by technological advancements and changing learning preferences. This dynamic landscape presents exciting opportunities for aspiring guitarists, offering new ways to learn, practice, and connect with the instrument.
The Impact of Technology on Guitar Education
Technology has revolutionized guitar learning, making it more accessible, engaging, and personalized. Online platforms, apps, and software provide a wealth of resources for guitarists of all levels. These tools offer interactive lessons, virtual instructors, and personalized feedback, making learning more efficient and enjoyable.
- Online Guitar Lessons:Platforms like Fender Play, Yousician, and JustinGuitar offer structured courses, interactive exercises, and personalized feedback, making learning accessible anytime, anywhere. These platforms cater to diverse learning styles and provide a structured learning path.
- Guitar Apps:Apps like GuitarTuna, Ultimate Guitar Tabs, and Songsterr offer tools for tuning, learning tabs, and practicing songs, providing a convenient and portable learning experience. These apps are designed to complement traditional learning methods and enhance practice sessions.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Guitar Lessons:VR technology is emerging as a game-changer in guitar education. VR lessons offer immersive experiences, allowing learners to interact with virtual instructors and practice in realistic virtual environments. This technology can enhance engagement and provide a unique learning experience.
Emerging Trends in Guitar Learning
The guitar learning landscape is continuously evolving, with new trends emerging to cater to the needs of modern learners. These trends are driven by technological advancements, changing learning preferences, and the desire for personalized learning experiences.
- Personalized Learning:With the rise of AI-powered learning platforms, guitar education is becoming increasingly personalized. These platforms analyze learning data and tailor content to individual needs, offering customized learning paths and feedback. This approach enhances learning efficiency and engagement.
- Gamification:Gamification is increasingly used in guitar learning platforms to make learning more engaging and motivating. Interactive challenges, rewards, and progress tracking systems enhance the learning experience and encourage consistent practice.
- Community Building:Online guitar communities are thriving, providing a space for learners to connect, share knowledge, and support each other. These communities offer a sense of belonging and foster a collaborative learning environment.
Questions and Answers: How Fast Can You Learn Guitar
What is the best age to start learning guitar?
There’s no “best” age! You can start learning guitar at any age. The most important thing is having the desire and motivation to learn.
How much time do I need to practice each day?
Even short, focused practice sessions (15-30 minutes) are better than none at all. The key is consistency, so find a practice schedule that fits your lifestyle.
Is it better to learn guitar with a teacher or self-taught?
Both options have pros and cons. A teacher can provide personalized guidance and correct bad habits, but self-teaching offers flexibility and can be cost-effective. The best choice depends on your learning style and preferences.
What kind of guitar should I buy as a beginner?
A good quality acoustic guitar is a great starting point. Look for a guitar with comfortable playability and a sound you enjoy. Don’t worry about getting the most expensive guitar right away – you can always upgrade later.