Examples Creativity: A Journey Through Originality and Innovation sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Prepare to embark on a captivating exploration of the multifaceted nature of creativity, its manifestations across diverse fields, and the profound impact it has on our lives.
Creativity is not merely a buzzword; it is a vital force that drives progress, fuels imagination, and enriches our experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the depths of creativity, examining its cognitive processes, cultural influences, and the myriad factors that shape its expression.
Along the way, we will encounter inspiring examples of creativity in action, from groundbreaking scientific discoveries to breathtaking works of art.
Brainstorming Creative Solutions
Brainstorming is a group creativity technique by which efforts are made to find a conclusion for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas spontaneously contributed by its members.
There are many different brainstorming techniques, but some of the most common include:
- Freewriting:Writing down any and all ideas that come to mind, without judgment or editing.
- Mind mapping:Creating a visual representation of your ideas, with branches and sub-branches connecting related concepts.
- SCAMPER:A technique that uses a series of prompts to help you generate new ideas, such as “Substitute,” “Combine,” “Adapt,” “Modify,” “Put to another use,” “Eliminate,” and “Reverse.”
- Brainwriting:A technique where participants write down their ideas on pieces of paper and then pass them around to other participants, who add their own ideas or build on the existing ones.
Brainstorming can be a very effective way to generate new ideas, but it is important to create a positive and supportive environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing their thoughts.
Some examples of successful brainstorming sessions include:
- The development of the Post-it note, which came about when a 3M employee was brainstorming ways to improve the adhesive on masking tape.
- The invention of the microwave oven, which was inspired by a radar engineer who noticed that a magnetron could heat food.
- The creation of the World Wide Web, which was developed by Tim Berners-Lee as a way to share information between researchers.
Problem-Solving with Creativity

Creativity is not limited to artistic endeavors; it is a powerful tool that can be applied to problem-solving in any field.
When faced with a complex problem, creative thinking can help us to generate new ideas, see the situation from different perspectives, and develop innovative solutions.
Benefits of Creative Thinking in Problem-Solving
- Enhanced problem understanding:Creativity encourages us to explore the problem from various angles, leading to a deeper understanding of its underlying causes and complexities.
- Generation of novel ideas:Creative thinking breaks away from conventional approaches, fostering the generation of unique and unconventional solutions.
- Improved decision-making:With a wider range of options to consider, creative problem-solving enables better-informed decision-making.
- Increased adaptability:Creative solutions often involve flexibility and adaptability, making them more resilient to changing circumstances.
Cultivating Creativity in Individuals

Nurturing creativity in individuals is crucial for fostering innovation, problem-solving, and personal growth. Here are strategies to cultivate creativity and examples of how it can be developed.
Strategies for Fostering Creativity, Examples creativity
- Encourage Open-mindedness and Curiosity:Create an environment that values diverse perspectives, curiosity, and exploration.
- Provide Opportunities for Experimentation:Allow individuals to experiment with different ideas, materials, and approaches.
- Foster Collaboration and Idea Sharing:Facilitate teamwork, brainstorming sessions, and knowledge exchange.
- Provide Access to Resources:Offer access to books, workshops, mentors, and online platforms that stimulate creativity.
Examples of Nurturing Creativity
- Art Classes:Engaging in artistic activities, such as painting, music, or dance, encourages self-expression and divergent thinking.
- Problem-Solving Challenges:Presenting individuals with complex problems and encouraging them to find innovative solutions.
- Creative Writing Exercises:Engaging in creative writing prompts or exercises that stimulate imagination and storytelling abilities.
- Mind Mapping:Utilizing mind mapping techniques to connect ideas, generate new concepts, and explore different perspectives.
Creativity in Different Fields

Creativity knows no bounds, manifesting itself in a myriad of disciplines, each with its unique expressions and innovative achievements.
In the realm of art, creativity bursts forth in vibrant hues and expressive strokes. From the evocative canvases of abstract painters to the intricate sculptures that capture the essence of form, artists channel their imagination to create masterpieces that stir emotions and inspire awe.
Science
In the world of science, creativity drives the quest for knowledge and innovation. Scientists explore the unknown, pushing the boundaries of understanding with their ingenious experiments and groundbreaking theories. From the discovery of the double helix to the development of cutting-edge technologies, scientific creativity has transformed our world.
Technology
Technology, a testament to human ingenuity, thrives on creativity. Engineers, designers, and programmers collaborate to create devices and systems that enhance our lives. From sleek smartphones to self-driving cars, technological advancements are fueled by the imaginative minds behind them.
Creativity and Innovation in Business

Creativity plays a pivotal role in driving innovation within organizations. It allows businesses to develop new ideas, products, services, and processes that give them a competitive edge. By embracing creativity, companies can foster a culture of innovation, leading to increased productivity, profitability, and growth.
Case Studies of Successful Companies
- Apple:Known for its innovative products, such as the iPhone and iPad, Apple has a strong culture of creativity and design thinking.
- Google:Google encourages employees to spend 20% of their time on personal projects, leading to the development of successful products like Gmail and Google Maps.
- Amazon:Amazon’s “customer-centric” approach has driven its success. The company constantly innovates to meet customer needs, such as through its Prime membership program and Alexa voice assistant.
Challenges to Fostering Creativity
- Organizational Structure:Rigid hierarchies and bureaucratic processes can stifle creativity.
- Fear of Failure:Employees may be hesitant to take risks and experiment due to the fear of making mistakes.
- Lack of Resources:Creativity often requires time, funding, and access to specialized knowledge, which may not always be available.
Strategies for Promoting Creativity
- Encourage Idea Generation:Create brainstorming sessions, idea boards, and other platforms for employees to share their thoughts.
- Provide Training and Resources:Offer workshops, mentorship programs, and access to creative tools to enhance employee skills.
- Foster a Supportive Culture:Encourage open communication, experimentation, and risk-taking.
Examples in Specific Business Functions
- Product Development:Creativity can lead to the development of new products or enhancements to existing ones.
- Marketing:Creative campaigns can attract customers and build brand loyalty.
- Customer Service:Creative solutions can enhance customer experiences and resolve issues effectively.
Measuring and Evaluating Creativity

Assessing creativity poses challenges due to its subjective and multifaceted nature. However, several methods and metrics have been developed to evaluate creative output, providing insights into the effectiveness and impact of creative solutions.
One common approach involves using creativity tests, such as the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking, which measure various aspects of creativity, including fluency, originality, and flexibility.
Metrics for Evaluating Creativity
- Fluency:The number of ideas generated within a given time frame.
- Originality:The uniqueness and novelty of ideas.
- Flexibility:The ability to generate ideas from different perspectives and approaches.
- Elaboration:The level of detail and development in creative ideas.
Tools for Evaluating Creativity
- Creativity checklists:Predefined criteria against which creative output is assessed.
- Peer reviews:Feedback from colleagues or experts in the field.
- User testing:Gathering feedback from the intended audience of the creative product.
- Data analysis:Tracking metrics such as website traffic, sales figures, or social media engagement to measure the impact of creative initiatives.
Cognitive Processes of Creativity

Creativity involves a complex interplay of cognitive processes that facilitate the generation, development, and evaluation of novel ideas. These processes include:
- Ideation:The initial stage of creativity where individuals generate a wide range of ideas through brainstorming, free association, and exploration.
- Incubation:A period of subconscious processing where ideas are allowed to incubate, leading to the formation of new connections and insights.
- Illumination:The “aha” moment when a sudden insight or solution emerges, often after a period of incubation.
- Verification:The final stage where ideas are tested, evaluated, and refined to ensure their feasibility and effectiveness.
Divergent and convergent thinking play crucial roles in creativity. Divergent thinking involves generating multiple, unconventional ideas, while convergent thinking focuses on narrowing down and selecting the most appropriate solution.Neuroimaging studies have identified specific neural mechanisms underlying creativity. The prefrontal cortex is involved in higher-order cognitive functions, including planning, decision-making, and working memory.
The temporal lobes are associated with memory, language, and emotional processing. The limbic system plays a role in motivation, emotion, and reward, providing the drive and inspiration for creative pursuits.Creativity is related to intelligence, particularly working memory and fluid intelligence.
Working memory allows individuals to hold and manipulate information temporarily, while fluid intelligence enables them to adapt to novel situations and solve problems effectively.In various domains, cognitive processes contribute to creative problem-solving and innovation. In art, divergent thinking generates novel artistic concepts, while convergent thinking helps refine and develop these ideas into finished works.
In science, incubation periods foster new insights and discoveries, while verification ensures the validity of scientific theories. In technology, ideation leads to innovative product designs, and convergent thinking aids in selecting and refining the most promising solutions.
Cultural Influences on Creativity
Creativity is not simply a product of individual genius but is also deeply shaped by the cultural context in which it arises. Cultural factors, such as societal norms, values, traditions, beliefs, and rituals, can significantly influence the nature and expression of creativity within a society.
Impact of Societal Norms and Values
Societal norms and values establish the boundaries of acceptable behavior and thought, which can influence the range of creative expression. In cultures that emphasize conformity and tradition, creativity may be constrained by rigid expectations and fear of deviating from established norms.
Conversely, in cultures that value individualism and innovation, creativity may be encouraged and celebrated.
Historical Perspectives on Creativity
The concept of creativity has undergone a significant evolution over time, influenced by cultural, societal, and technological shifts. This historical journey has shaped our understanding of creativity and its role in various fields.
In ancient times, creativity was often attributed to divine inspiration or supernatural forces. Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle explored the nature of creativity, linking it to imagination and reason.
Key Thinkers and Their Contributions
- Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519):Emphasized the importance of observation, experimentation, and a multidisciplinary approach to creativity.
- René Descartes (1596-1650):Introduced the concept of “cogito ergo sum” (I think, therefore I am), highlighting the role of self-reflection and rational thought in creativity.
- Immanuel Kant (1724-1804):Distinguished between genius and talent, arguing that genius is an innate ability to create original works.
Changing Cultural and Societal Contexts
The Renaissance and Enlightenment periods witnessed a shift towards individualism and the celebration of human potential. Creativity became associated with originality and the pursuit of knowledge.
The Industrial Revolution brought about new technologies and mass production, leading to a focus on efficiency and standardization. However, it also gave rise to new artistic movements that challenged traditional norms.
Creativity knows no bounds, with endless examples that showcase its power. One such example is trophy creative , where innovative ideas and stunning designs converge. Trophy creative pushes the boundaries of visual communication, demonstrating how creativity can transform even the simplest concepts into extraordinary works of art.
Impact of Major Historical Events
World wars and other major events have had a profound impact on creativity. Periods of upheaval and uncertainty can foster innovation as people seek new solutions and expressions.
For example, the post-World War II era saw the emergence of abstract expressionism and other avant-garde art movements.
Role of Technology
Technological advancements have played a crucial role in shaping historical perspectives on creativity. From the printing press to digital tools, technology has expanded the possibilities for creative expression and dissemination.
However, it has also raised questions about the nature of originality and the impact of technology on the creative process.
Neurobiology of Creativity: Examples Creativity

Creativity is a complex cognitive process that involves the interaction of multiple brain regions and processes. Recent advancements in neuroimaging techniques have allowed researchers to gain insights into the neurological basis of creativity, providing valuable information about the brain mechanisms underlying creative thinking.
Brain Regions Involved in Creativity
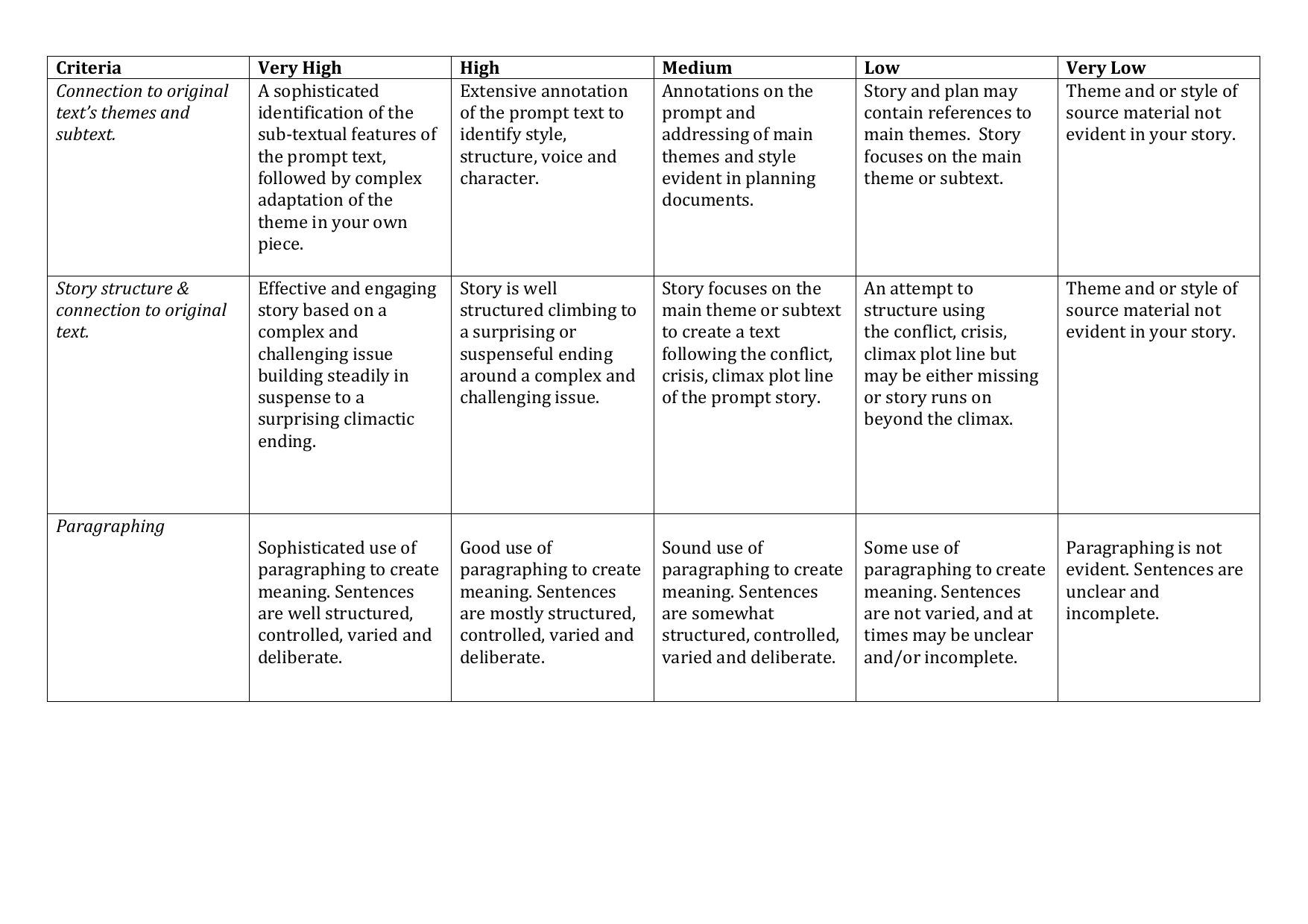
Various brain regions have been implicated in creativity, each playing distinct roles in different aspects of the creative process. A summary of the key brain regions involved in creativity, their functions, and the evidence supporting their role is provided in the table below:
| Brain Region | Function | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Prefrontal Cortex | Higher-order cognitive functions, including planning, decision-making, and working memory | Studies have shown increased activation in the prefrontal cortex during creative problem-solving tasks. |
| Temporal Lobes | Memory, language, and semantic processing | Individuals with damage to the temporal lobes often exhibit impaired creativity. |
| Parietal Lobes | Spatial processing, attention, and numerical cognition | Neuroimaging studies have linked increased parietal lobe activity to creative insight and problem-solving. |
| Default Mode Network | Mind wandering, self-referential processing, and autobiographical memory | The default mode network is thought to be involved in the generation of novel ideas and the integration of different perspectives. |
“Our findings provide evidence for the involvement of the default mode network in creative thinking, suggesting that mind wandering and self-referential processing may play a role in the generation of novel ideas.”- Beaty et al., 2018
Further Research Directions
The field of neurobiology of creativity is still in its early stages, and further research is needed to fully understand the complex brain mechanisms underlying creative thinking. Future research directions may include:
- Investigating the role of specific neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in creativity.
- Examining the impact of environmental factors on the development and expression of creativity.
- Developing interventions to enhance creativity based on our understanding of the neurobiology of creativity.
Artificial Intelligence and Creativity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and the creative sector is no exception. AI tools are being developed to assist human creators in a wide range of tasks, from generating ideas to producing finished works. This collaboration between humans and AI has the potential to enhance human creativity, but it also raises ethical questions that need to be addressed.
Potential of AI in Enhancing Creativity
AI can enhance human creativity in several ways. AI algorithms can generate new ideas and concepts that humans might not have come up with on their own. AI can also be used to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human creators to focus on more creative aspects of their work.
Additionally, AI can help creators to connect with new audiences and collaborate with other creators around the world.
Ethical Implications of AI in Creative Processes
The use of AI in creative processes also raises a number of ethical concerns. One concern is the issue of ownership. Who owns the copyright to works created with the assistance of AI? Another concern is the potential for bias.
AI algorithms can be biased, and this bias can be reflected in the works that they create. It is important to ensure that AI tools are developed and used in a way that minimizes bias.
Case Studies of Successful AI-Human Collaborations
There are a number of successful examples of AI-human collaborations in the creative sector. One example is the collaboration between the musician Grimes and the AI artist Mario Klingemann. Together, they created an AI-generated music video for Grimes’ song “We Appreciate Power.” The video was a critical and commercial success, and it demonstrated the potential of AI to enhance human creativity.Another example of a successful AI-human collaboration is the development of the AI-powered writing assistant Grammarly.
Grammarly uses AI to help writers improve their grammar, spelling, and style. Grammarly has been used by millions of writers around the world, and it has helped them to produce better-written work.
Future of AI-Assisted Creativity
The future of AI-assisted creativity is bright. AI is becoming increasingly sophisticated, and it is likely that AI tools will play an even greater role in the creative process in the years to come. AI could be used to create new forms of art and entertainment, and it could help humans to solve some of the world’s most pressing problems.
Creativity in Education
Fostering creativity in educational settings is crucial for nurturing the cognitive and imaginative abilities of students. By encouraging creative thinking, educators can help students develop problem-solving skills, enhance their communication abilities, and cultivate a lifelong love for learning.
Creative teaching methods and curriculum designs can take various forms. Here are a few examples:
Project-Based Learning
- Involves students working on projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills in practical ways.
- Encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
- Examples: Science fair projects, building prototypes, creating multimedia presentations.
Inquiry-Based Learning
- Focuses on students asking questions, conducting research, and developing their own understanding of concepts.
- Promotes curiosity, critical thinking, and independent learning.
- Examples: Science experiments, historical research projects, literary analysis.
Differentiated Instruction
- Tailors instruction to meet the individual needs and learning styles of students.
- Allows students to learn at their own pace and explore topics that interest them.
- Examples: Flexible seating arrangements, choice boards, tiered assignments.
Technology Integration
- Leverages technology to enhance creativity and engagement in learning.
- Provides students with access to a wider range of resources and tools.
- Examples: Virtual reality simulations, online collaboration platforms, digital storytelling.
Identify common challenges and barriers to interdisciplinary collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration, the merging of diverse perspectives and expertise from different disciplines, offers a wealth of benefits. However, it also presents unique challenges and barriers that can hinder its effectiveness.One significant challenge lies in communication. Individuals from different disciplines often use specialized jargon and have distinct ways of thinking, making it difficult to convey ideas and understand each other’s perspectives.
This can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and a lack of shared understanding.Another barrier is the lack of a common language or framework for collaboration. Different disciplines have their own methodologies, assumptions, and values, which can create difficulties in finding a common ground for working together.
This can lead to conflicts, power imbalances, and a lack of trust among team members.Additionally, organizational structures and reward systems often do not support interdisciplinary collaboration. Traditional academic and research institutions tend to be organized into silos, with limited opportunities for collaboration across disciplines.
Furthermore, reward systems often favor individual contributions over collaborative efforts, discouraging researchers from engaging in interdisciplinary projects.
Questions and Answers
What are some common techniques for generating creative ideas?
Brainstorming, mind mapping, freewriting, and lateral thinking are effective techniques for generating creative ideas.
How can creativity be applied to solve complex problems?
Creativity can be used to reframe problems, generate innovative solutions, and challenge conventional approaches to problem-solving.
What are some strategies for fostering creativity in individuals?
Encouraging curiosity, providing opportunities for experimentation, and creating a supportive environment can foster creativity in individuals.