Do schools kill creativity transcript – In the realm of education, the debate on whether schools stifle creativity has been a persistent topic. This transcript delves into the intricate relationship between schools and creativity, exploring the factors that may hinder or nurture this vital human capacity.
From rigid schedules to standardized curricula, we will uncover the potential roadblocks that schools may present to creative expression. Conversely, we will also highlight innovative approaches, successful implementations, and strategies that can foster creativity in the classroom.
School Environments and Creativity
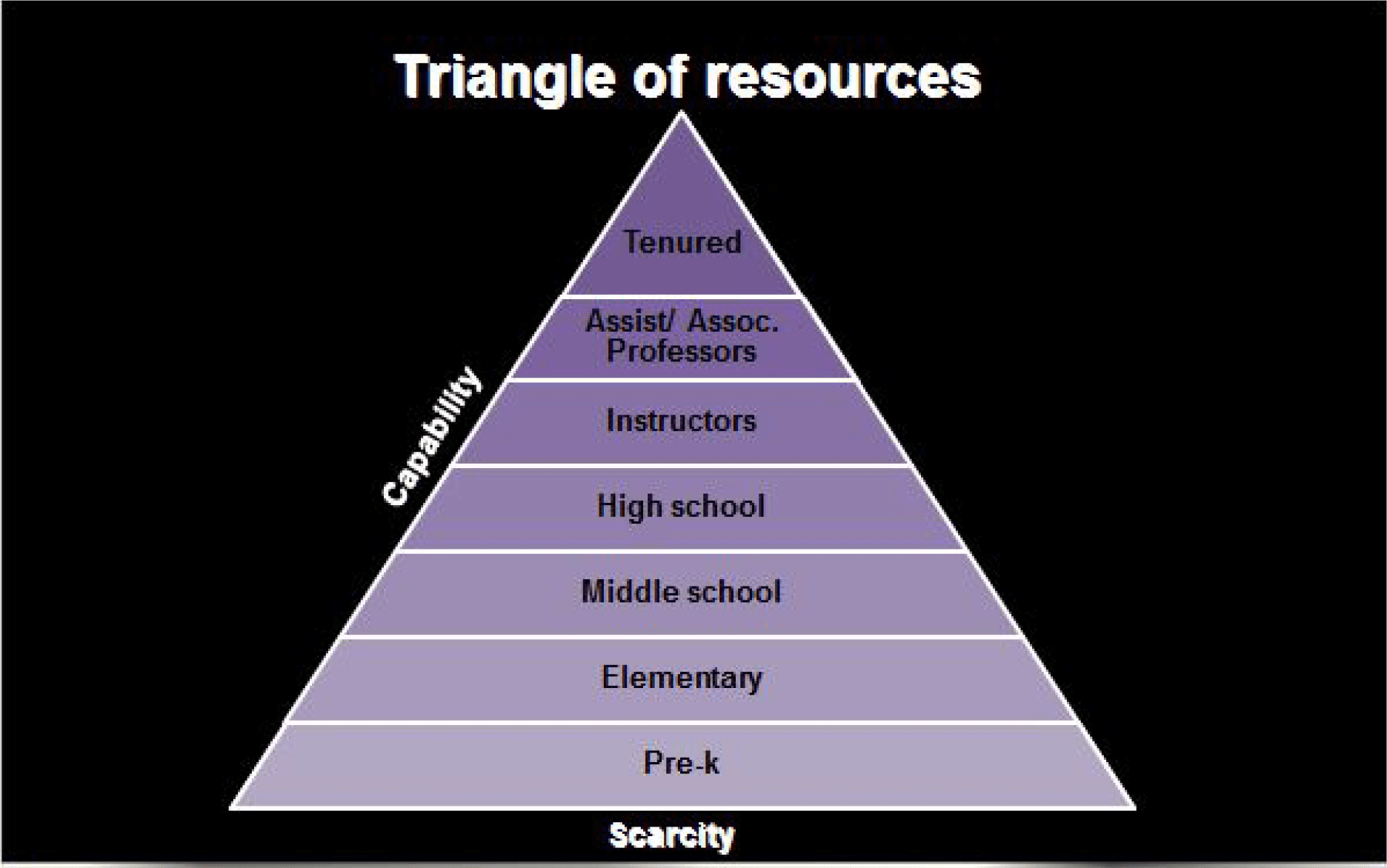
Traditional school environments often prioritize academic performance over creativity, with a focus on standardized testing and rigid schedules. This can limit students’ opportunities to explore their imaginations and develop their creative thinking skills.
Standardized testing, in particular, can stifle creativity by narrowing the curriculum and encouraging students to memorize facts and formulas rather than engage in critical thinking and problem-solving. The emphasis on standardized testing can also lead to teachers focusing on teaching to the test, which can further limit students’ exposure to diverse perspectives and creative activities.
Rigid Schedules
Rigid school schedules can also hinder creativity by limiting the time and flexibility that students have to pursue their interests and explore new ideas. When students are constantly rushing from one class to the next, they may not have the time or energy to engage in creative activities.
Lack of Creative Activities
Traditional school environments often lack opportunities for students to engage in creative activities. The curriculum may be heavily focused on core subjects such as math, science, and language arts, with little time allocated for art, music, or other creative pursuits.
This lack of creative activities can limit students’ ability to develop their creative thinking skills and express themselves in non-traditional ways.
Curricula and Creativity
Standardized curricula, with their emphasis on standardized testing and measurable outcomes, can inadvertently suppress creativity. This is particularly evident in subjects like art, music, and literature, where creativity is often subjective and difficult to quantify.
Incorporating creative activities and projects into lesson plans is crucial for fostering creativity. For instance, in art classes, students can be encouraged to experiment with different mediums and techniques, while in music classes, they can compose their own melodies or lyrics.
Literature classes can incorporate creative writing assignments that allow students to express their imaginations.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches that combine creative subjects with STEM fields can also enhance creativity. For example, a science project that involves designing and building a model can foster both scientific inquiry and artistic expression. By breaking down the barriers between different subjects, students can develop a more holistic and creative approach to learning.
Strategies for Teachers
Teachers can encourage creativity in the classroom by providing opportunities for students to take risks, experiment, and express themselves. They can also use strategies such as brainstorming, mind mapping, and peer feedback to stimulate creative thinking.
Challenges and Technology
Balancing standardized curricula with the need to foster creativity can be challenging. However, by incorporating creative activities into lesson plans and providing opportunities for students to explore their creativity, teachers can help students develop their creative potential.
Technology can both enhance and hinder creativity in educational settings. On the one hand, it can provide students with access to a wide range of creative tools and resources. On the other hand, it can also be a distraction and lead to students spending less time on creative activities.
Teacher Attitudes and Creativity

Teacher beliefs and attitudes can significantly influence student creativity. Teachers who believe that creativity is essential and that all students can be creative are more likely to create a classroom environment that supports and encourages creative thinking. They are also more likely to use teaching methods that promote creativity, such as problem-based learning and project-based learning.Teachers who are passionate about their subject matter and who are enthusiastic about teaching are more likely to inspire their students to be creative.
They are also more likely to be open to new ideas and to encourage their students to take risks.
Encouraging and Supporting Creative Thinking
Teachers can encourage and support creative thinking in a variety of ways. They can:
- Create a classroom environment that is safe and supportive, where students feel comfortable taking risks and sharing their ideas.
- Use teaching methods that promote creativity, such as problem-based learning and project-based learning.
- Provide students with opportunities to explore their interests and to develop their own creative projects.
- Encourage students to think critically and to question the status quo.
- Be open to new ideas and to encourage students to take risks.
Assessment and Creativity

Assessment is an integral part of education, but traditional methods can often stifle creativity. These methods typically focus on rote memorization and regurgitation of facts, leaving little room for students to express their own ideas or take risks.
Alternative assessment strategies, on the other hand, can promote creative expression by allowing students to demonstrate their learning in a variety of ways. These strategies include:
Portfolios
- Portfolios allow students to collect and present their work over time, providing a comprehensive picture of their learning journey.
- Portfolios can include a variety of materials, such as writing samples, artwork, projects, and reflections.
Performance tasks
- Performance tasks require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world situations.
- Performance tasks can take many forms, such as presentations, debates, or experiments.
Open-ended questions
- Open-ended questions allow students to explore their own ideas and demonstrate their understanding in a variety of ways.
- Open-ended questions can be used in both written and oral assessments.
Peer Influence and Creativity
Peer influence plays a significant role in shaping an individual’s creativity. From a young age, children interact with their peers, forming social networks that can either encourage or suppress their creative expression.
Peer Pressure and Suppression of Creativity
Peer pressure can be a powerful force that discourages individuals from expressing their creativity. When peers disapprove of or mock non-conforming ideas, individuals may conform to social norms to avoid ridicule or exclusion. This can lead to the suppression of unique and original ideas.
Research by Csikszentmihalyi (1996) found that students who were exposed to peer pressure were less likely to engage in creative activities and had lower levels of creative self-efficacy.
Creating a Supportive Classroom Environment
To foster creativity, it is essential to create a supportive and inclusive classroom environment where students feel safe to express their ideas without fear of judgment.
- Encourage open-mindedness and respect for diverse perspectives.
- Provide opportunities for students to collaborate and share their ideas.
- Celebrate and reward creativity, even if it does not conform to traditional norms.
Peer Feedback and Enhancing Creativity
Peer feedback can be a valuable tool for enhancing creativity. When peers provide constructive and supportive feedback, it can help individuals refine their ideas, gain new perspectives, and improve their creative output.
- Establish clear guidelines for peer feedback, emphasizing respect and constructive criticism.
- Train students on how to provide effective feedback that is specific, actionable, and encouraging.
Social Media and Peer Influence on Creativity
Social media has become an increasingly influential factor in peer relationships. While it can provide opportunities for connection and collaboration, it can also have both positive and negative effects on creativity.
- Positive Effects:Social media can expose individuals to a wider range of ideas and perspectives, inspiring creativity.
- Negative Effects:Social media can also create a culture of comparison and self-doubt, which can inhibit creative expression.
Cultural Context and Peer Influence on Creativity
The impact of peer influence on creativity can vary across different cultural contexts.
- In individualistic cultures, peer pressure may be less influential, allowing for greater freedom of expression.
- In collectivist cultures, peer pressure may be stronger, emphasizing conformity and discouraging non-conforming ideas.
Social and Cultural Factors
Creativity is shaped by the social and cultural environment in which individuals live. Societal expectations, cultural norms, and the availability of resources all play a role in fostering or hindering creativity.
Diversity and Inclusion
Diversity and inclusion are essential for creativity. When people from different backgrounds and perspectives come together, they bring a wider range of ideas and experiences to the table. This can lead to more innovative and creative solutions.
- Example:A study by the University of California, Berkeley found that diverse teams are more likely to come up with creative solutions to problems than homogeneous teams.
Social Media and Technology
Social media and technology can both help and hinder creativity. On the one hand, they can provide access to a wealth of information and inspiration. On the other hand, they can also be a source of distraction and comparison, which can stifle creativity.
- Positive:Social media can connect people with like-minded individuals and provide a platform for sharing creative work.
- Negative:The constant bombardment of information and the pressure to conform to social norms can discourage people from taking creative risks.
Education and Socialization
Education and socialization play a significant role in the development of creativity. Schools can provide opportunities for students to explore their creativity and develop their creative skills. However, they can also stifle creativity if they focus too much on standardized testing and rote learning.
- Positive:Schools that provide a supportive and encouraging environment for creativity can help students develop their creative potential.
- Negative:Schools that emphasize conformity and discourage risk-taking can stifle creativity.
Summary
Social and cultural factors have a significant impact on creativity. Diversity and inclusion, social media and technology, and education and socialization all play a role in shaping the creative potential of individuals.
Technology and Creativity: Do Schools Kill Creativity Transcript

Technology has become an integral part of our lives, and its impact on creativity is a topic of much debate. On the one hand, technology can provide us with new tools and resources that can help us to express our creativity in new and innovative ways.
On the other hand, technology can also be a distraction, and it can be easy to get caught up in the endless stream of information and entertainment that is available online.
So, how can we use technology to enhance creativity while avoiding its potential pitfalls? Here are a few tips:
Benefits of Technology for Creativity
- Access to information:Technology gives us access to a vast amount of information that can inspire our creativity. We can use the internet to research different topics, find new ideas, and connect with other creative people.
- Collaboration:Technology makes it easier than ever to collaborate with others on creative projects. We can use online tools to share ideas, work on projects together, and get feedback from others.
- New tools and resources:Technology has given us access to new tools and resources that can help us to express our creativity in new and innovative ways. For example, we can use digital cameras to take photos, video editing software to create movies, and music software to create music.
Drawbacks of Technology for Creativity
- Distraction:Technology can be a distraction, and it can be easy to get caught up in the endless stream of information and entertainment that is available online. This can make it difficult to focus on our creative work.
- Isolation:Technology can also lead to isolation, as we spend more time interacting with our devices and less time interacting with other people. This can stifle our creativity, as we need to be exposed to new ideas and experiences in order to be creative.
If you’ve ever wondered whether schools stifle creativity, check out the “Do Schools Kill Creativity?” transcript. It explores this topic in depth. If you’re looking to enhance your creativity, consider seeking guidance from a creative consulting professional. They can help you develop strategies to unlock your creative potential and navigate the challenges of expressing yourself in educational settings.
- Dependence:We can become too reliant on technology, and this can stifle our creativity. For example, we may become so used to using digital tools that we forget how to create things by hand.
Neuroscience and Creativity

Neuroscience has made significant strides in understanding the neurological processes associated with creativity. By examining brain activity patterns, researchers have identified several key areas involved in creative thinking.
One crucial region is the prefrontal cortex, responsible for higher-order cognitive functions like planning, decision-making, and working memory. The default mode network, a group of brain areas active during rest, is also implicated in creativity, particularly in generating novel ideas.
Brain Connectivity and Creativity
Creativity involves the interplay of various brain regions, and research suggests that enhanced connectivity between these areas is associated with higher creative potential. For instance, individuals with greater connectivity between the prefrontal cortex and the temporal lobes, responsible for language and memory, exhibit increased verbal creativity.
Neurochemicals and Creativity
Neurochemicals, such as dopamine and serotonin, also play a role in creativity. Dopamine is involved in reward and motivation, while serotonin influences mood and cognitive flexibility. Studies have shown that individuals with higher levels of dopamine and serotonin tend to be more creative.
Implications for Education
Understanding the neurological underpinnings of creativity can inform educational practices to foster creativity in students. This includes:
- Encouraging divergent thinking and exploration to stimulate the default mode network.
- Providing opportunities for collaboration and idea-sharing to enhance brain connectivity.
- Creating environments that promote positive emotions and reduce stress, which can enhance neurochemical activity associated with creativity.
Alternative Educational Models
Alternative educational models prioritize creativity and diverge from traditional teaching methods. These models emphasize experiential learning, hands-on activities, and fostering critical thinking skills. They aim to nurture students’ natural curiosity and encourage them to explore their creativity.
Montessori Method
The Montessori method, developed by Maria Montessori, emphasizes self-directed learning and individualized instruction. It provides a prepared environment where children can choose activities that interest them and learn at their own pace. Key features include:
- Mixed-age classrooms, fostering peer learning
- Sensorial materials to engage different senses
- Emphasis on practical life skills and independence
Waldorf Education
Waldorf education, founded by Rudolf Steiner, takes a holistic approach to education. It incorporates arts, music, and movement into the curriculum, emphasizing the development of the whole child. Key features include:
- Age-specific curricula that align with child development
- Emphasis on imaginative play and storytelling
- Integration of practical skills and artistic expression
Reggio Emilia Approach
The Reggio Emilia approach, originated in Italy, views children as capable and competent learners. It fosters collaboration, exploration, and documentation of children’s learning experiences. Key features include:
- Emergent curriculum based on children’s interests
- Project-based learning and hands-on exploration
- Strong emphasis on documentation and reflection
Student Perspectives
Students often feel that their creativity is stifled in school. They may be told to follow specific rules and guidelines, and their ideas may be criticized or dismissed. This can make it difficult for students to develop their creative potential.
However, there are things that students can do to advocate for their own creative needs. They can talk to their teachers and administrators about their concerns. They can also join or start clubs and groups that focus on creativity. Additionally, students can write letters to their school board or local newspaper to express their views.
Successful Advocacy for Creativity
There are many examples of students who have successfully advocated for more creative opportunities in their schools. In one case, a group of students in California started a club called the “Creativity Club.” The club met weekly to discuss creative ideas and projects.
The students also organized a school-wide art show to showcase their work.
In another case, a student in New York City wrote a letter to her school board about the lack of creative opportunities in her school. The school board responded by creating a new program that provides students with more opportunities to explore their creativity.
Quotes from Students
“I feel like my creativity is always being stifled in school. I’m always told to follow the rules and do things the ‘right’ way. I wish there were more opportunities for me to be creative and express myself.”
Student from California
“I started the Creativity Club because I wanted to create a space where students could feel free to be creative. I’m so glad that the club has been successful and that it has helped to make our school a more creative place.”
Student from California
“I wrote a letter to my school board because I was frustrated by the lack of creative opportunities in my school. I’m so glad that the school board listened to my concerns and created a new program that provides students with more opportunities to be creative.”
Student from New York City
Table: Key Points of Student Advocacy for Creativity
| Key Point | Description ||—|—|| Importance of student voice | Students should have a say in their own education, including the opportunities they have to develop their creativity. || Strategies for advocacy | Students can advocate for their creativity through various means, such as talking to teachers, administrators, and school boards.
|| Benefits of advocacy | Advocating for creativity can lead to positive changes in the school environment, such as the creation of new programs or initiatives that support student creativity. |
Historical Examples

Educational settings can significantly influence creativity. History offers numerous examples of individuals whose creativity was either stifled or fostered within these environments.
Factors such as teaching methods, curriculum, and social dynamics play crucial roles in shaping creativity. Understanding these historical examples can provide insights into how educational systems can support or hinder creative development.
Suppression of Creativity
Albert Einstein:Einstein’s non-conformist ideas often clashed with the rigid educational system of his time. His questioning nature and unconventional thinking were met with criticism and discouragement, leading him to drop out of school and pursue his intellectual pursuits independently.
Marie Curie:As a woman in the late 19th century, Curie faced significant barriers in pursuing her scientific interests. Despite her exceptional abilities, she was denied admission to prestigious universities and faced prejudice from male colleagues, which hindered her career advancement.
Nurturing of Creativity
Leonardo da Vinci:Leonardo’s creativity flourished in the supportive environment of the Renaissance, where art and science were highly valued. His apprenticeship under Verrocchio provided him with a comprehensive education that fostered his diverse interests and artistic skills.
Charles Darwin:Darwin’s education at Cambridge University exposed him to natural history and scientific inquiry. His mentors, such as John Stevens Henslow, encouraged his curiosity and provided him with opportunities to develop his groundbreaking theory of evolution.
Compare and contrast educational approaches to creativity in different countries, such as Finland, Japan, and the United States.
Educational approaches to creativity vary significantly across countries, influenced by cultural and societal factors.In Finland, creativity is highly valued and integrated into the national curriculum. Schools emphasize play-based learning, hands-on activities, and interdisciplinary projects. Students are encouraged to take risks, experiment, and collaborate, fostering a culture of innovation.In contrast, Japan’s education system traditionally emphasizes rote learning and conformity.
However, recent reforms have introduced elements of creativity, such as project-based learning and design thinking. Schools are also encouraging students to develop problem-solving skills and express themselves creatively.In the United States, creativity is often associated with individual achievement and self-expression.
Schools typically offer elective courses in arts and music, and students are encouraged to pursue their passions. However, there is also a strong focus on standardized testing, which can sometimes limit opportunities for creative exploration.
Recommendations for Change
To foster creativity in schools, several changes in educational practices can be implemented. These changes may present challenges, but they also offer significant potential benefits for students’ creativity.
Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Incorporate hands-on, project-based learning activities that encourage exploration, experimentation, and problem-solving.
- Provide students with choices in their learning and allow them to pursue their interests.
- Emphasize critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills, which are essential for creative problem-solving.
Assessment
- Use a variety of assessment methods that measure creativity, such as portfolios, exhibitions, and performances.
- Provide students with feedback that focuses on their strengths and areas for growth.
- Encourage students to reflect on their creative process and identify ways to improve their work.
Teacher Training
- Provide teachers with professional development opportunities to learn about creativity and how to foster it in their classrooms.
- Create a supportive school culture where teachers feel comfortable taking risks and experimenting with new teaching methods.
- Encourage teachers to collaborate with each other and share best practices for fostering creativity.
Challenges and Benefits
Implementing these changes may present challenges, such as resistance from traditionalists, lack of time and resources, and the need for teacher training. However, the potential benefits of fostering creativity in schools are significant. Creative students are more likely to be:
- Innovative and adaptable
- Problem-solvers
- Effective communicators
- Successful in a variety of fields
Case Studies

Case studies of successful creative learning strategies provide valuable insights into the key elements that contribute to their effectiveness. By examining these case studies, we can identify best practices and learn from the experiences of others.
One notable case study is the High Tech High network of charter schools in California. These schools have a long track record of success in implementing creative learning strategies, such as project-based learning, hands-on activities, and student-centered instruction. As a result, High Tech High students consistently outperform their peers on standardized tests and have high college acceptance rates.
Key Elements of Success
The key elements that have contributed to the success of creative learning strategies at High Tech High and other schools include:
- Student-centered learning:Students are given choice and autonomy in their learning, and the curriculum is tailored to their individual needs and interests.
- Hands-on learning:Students learn by doing and experiencing, and they are given opportunities to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts.
- Project-based learning:Students work on projects that are meaningful and engaging, and they are given the time and resources to complete them successfully.
- Technology integration:Technology is used to support and enhance learning, and students are given opportunities to use technology to create and share their work.
- Collaboration:Students work together to learn and solve problems, and they are encouraged to share their ideas and perspectives.
Specific Creative Learning Strategies
Some of the specific creative learning strategies that have been used successfully at High Tech High and other schools include:
- Project-based learning:Students work on projects that are meaningful and engaging, and they are given the time and resources to complete them successfully.
- Problem-based learning:Students are given a problem to solve, and they work together to find a solution.
- Inquiry-based learning:Students are given a question to investigate, and they work together to find the answer.
- Design thinking:Students use a design thinking process to solve problems and create innovative solutions.
- Maker education:Students use tools and materials to create their own products and projects.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing creative learning strategies can be challenging, but there are a number of ways to overcome these challenges.
- Lack of time:Creative learning strategies can be time-consuming, but there are a number of ways to make them more efficient, such as using technology and collaborating with other teachers.
- Lack of resources:Creative learning strategies can require additional resources, such as materials and technology, but there are a number of ways to find these resources, such as grants and partnerships with community organizations.
- Resistance from students:Some students may be resistant to creative learning strategies, but there are a number of ways to overcome this resistance, such as providing choice and autonomy, and making learning fun and engaging.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement
Creative learning strategies have a positive impact on student learning and engagement. Students who are engaged in creative learning are more likely to:
- Be motivated to learn
- Develop critical thinking skills
- Develop problem-solving skills
- Develop creativity and innovation
- Collaborate with others
- Communicate effectively
Examples of Student Work
Here are some examples of student work that demonstrates the use of creative learning strategies:
- A student-created video that explains a complex scientific concept
- A student-designed website that promotes a local business
- A student-built robot that solves a real-world problem
- A student-written song that expresses a personal experience
- A student-created painting that reflects the student’s unique perspective
Table: Key Elements of Successful Creative Learning Strategies
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Student-centered learning | Learning is tailored to the individual needs and interests of students. |
| Hands-on learning | Students learn by doing and experiencing. |
| Project-based learning | Students work on projects that are meaningful and engaging. |
| Technology integration | Technology is used to support and enhance learning. |
| Collaboration | Students work together to learn and solve problems. |
Conclusion

In conclusion, fostering creativity in education is crucial for students’ overall development and success in a rapidly changing world. By providing a supportive and stimulating learning environment, encouraging risk-taking, and incorporating creative activities into the curriculum, educators can nurture students’ creativity and prepare them to thrive in the 21st century.
Here are some specific examples of how creativity can be fostered in the classroom:
Examples of Creative Activities in the Classroom, Do schools kill creativity transcript
- Design a comic book to illustrate a historical event (History, grades 6-8)
- Create a dance routine to represent a scientific concept (Science, grades 9-12)
- Write a song about the causes and effects of climate change (Environmental Science, grades 11-12)
Practical tips for teachers on how to create a more creative learning environment include:
Tips for Fostering Creativity in the Classroom
- Provide students with opportunities to explore different perspectives and ideas.
- Encourage students to ask questions and challenge assumptions.
- Create a classroom environment where students feel safe to take risks and make mistakes.
- Provide students with access to a variety of resources and materials.
- Celebrate students’ creativity and innovation.
By implementing these strategies, educators can help students develop their creativity and prepare them for success in the 21st century workforce.
FAQ Compilation
Can creativity be taught in schools?
While creativity is an inherent human trait, schools can play a significant role in fostering and developing it through targeted instruction, hands-on experiences, and supportive environments.
How can I encourage creativity in my classroom?
Create a safe and inclusive space where students feel comfortable taking risks. Encourage collaboration, provide open-ended assignments, and incorporate hands-on activities that stimulate imagination.
What are the benefits of fostering creativity in schools?
Creativity enhances problem-solving skills, critical thinking, innovation, self-expression, and overall well-being. It prepares students to thrive in a rapidly changing world that values these abilities.