Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for navigating the complex challenges of the modern world. By embracing both, we can unlock our full potential and make a meaningful impact on our communities and the world.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating realm of critical and creative thinking, exploring their benefits, applications, and strategies for developing these invaluable skills. Join us on an enlightening journey that will empower you to think critically, innovate creatively, and make informed decisions that shape your future.
Defining Critical and Creative Thinking
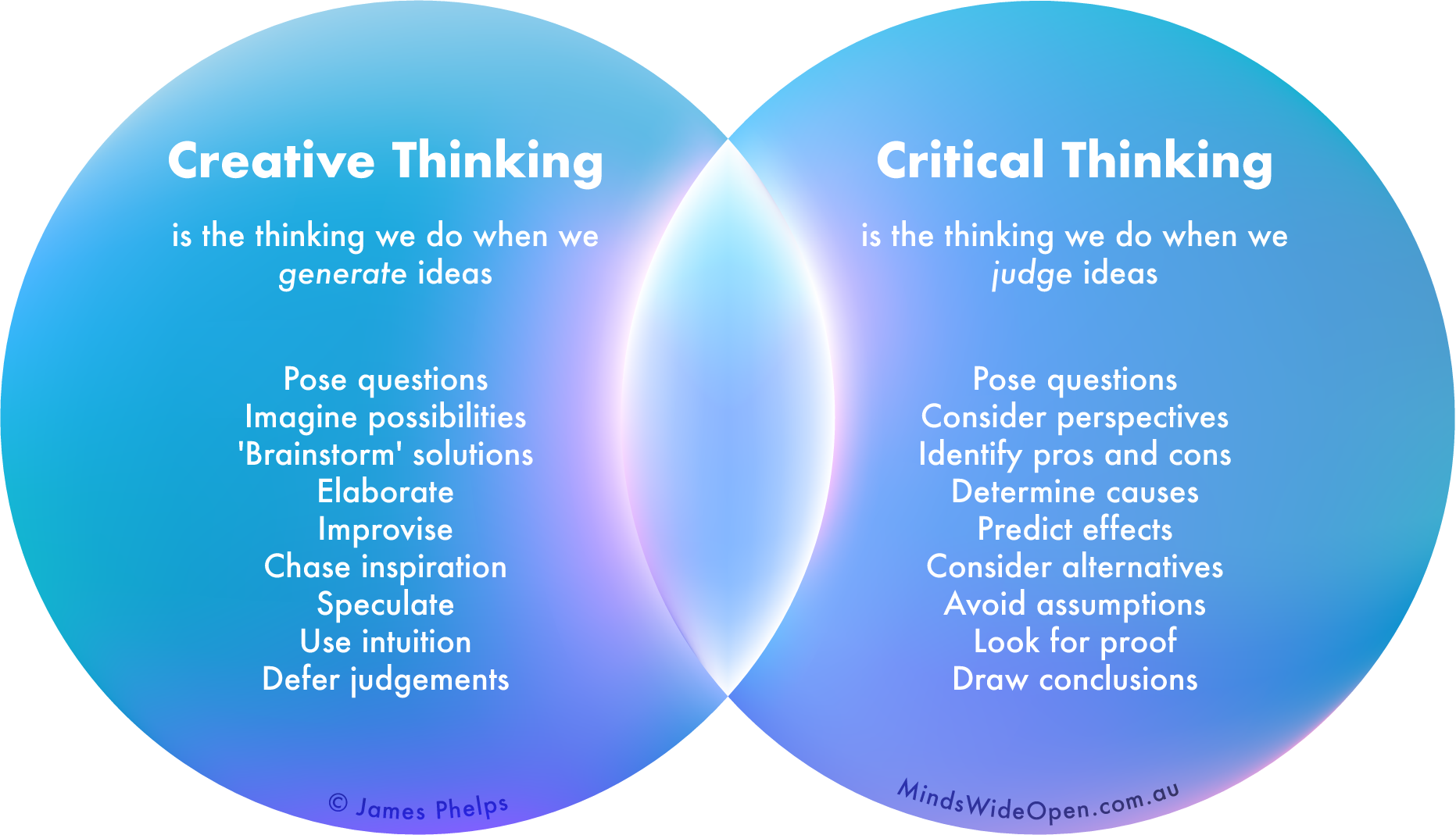
Critical and creative thinking are two essential skills for success in today’s world. Critical thinking allows us to analyze information, identify biases, and make sound judgments. Creative thinking enables us to generate new ideas, solve problems, and express ourselves in unique ways.
Critical thinking is a process of analyzing information, identifying biases, and making sound judgments. It involves evaluating evidence, considering different perspectives, and using logic and reasoning to reach a conclusion. Critical thinkers are able to recognize and avoid fallacies, and they can make decisions based on evidence rather than emotion.
Creative thinking, on the other hand, is the ability to generate new ideas, solve problems, and express oneself in unique ways. Creative thinkers are able to think outside the box, come up with new solutions, and see things from different perspectives.
They are often able to make connections between seemingly unrelated things and come up with innovative ideas.
Examples of Critical and Creative Thinking
Here are some examples of critical and creative thinking:
- Critical thinking:A doctor analyzes the symptoms of a patient and uses medical knowledge to diagnose the illness.
- Creative thinking:An artist comes up with a new painting technique that allows her to create unique and expressive works of art.
- Critical thinking:A lawyer evaluates the evidence in a case and develops a strategy for defending his client.
- Creative thinking:An entrepreneur develops a new product that meets a need in the marketplace.
Benefits of Critical and Creative Thinking
Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for success in various aspects of life. They enable us to analyze information, solve problems, and make informed decisions. Developing these skills brings numerous benefits, both in personal and professional domains.
Benefits of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking skills equip us with the ability to:
Analyze and evaluate information
Critically assessing data, arguments, and claims allows us to identify biases, fallacies, and inconsistencies.
Solve problems effectively
Breaking down complex problems into smaller components and evaluating different solutions helps us find practical and efficient resolutions.
Make informed decisions
Weighing the pros and cons of various options based on evidence and logical reasoning leads to well-informed choices.
Improve communication
Clearly articulating our thoughts and arguments, supported by evidence, enhances our communication skills and persuasiveness.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Fostering creative thinking in various fields brings about significant advantages:
Innovation and problem-solving
Encouraging unconventional ideas and perspectives leads to innovative solutions and breakthrough advancements.
Enhanced creativity
Creative thinking stimulates imagination, leading to the generation of original and novel ideas.
Improved adaptability
Embracing creative approaches allows us to adapt to changing circumstances and find solutions in unconventional ways.
Increased productivity
Fostering a creative work environment promotes collaboration, idea-sharing, and enhanced productivity.
– Provide examples of real-world applications of critical thinking.

Critical thinking is a vital skill in various aspects of life. It enables individuals to analyze, evaluate, and make sound judgments based on evidence and reason. Here are some real-world applications of critical thinking:
Problem-solving
Critical thinking is essential for solving problems effectively. It involves identifying the problem, gathering relevant information, evaluating possible solutions, and choosing the most appropriate course of action.
Decision-making
Critical thinking helps individuals make informed decisions by weighing the pros and cons of different options, considering potential consequences, and evaluating the credibility of information.
Communication
Critical thinking enhances communication skills by enabling individuals to express their ideas clearly, support their arguments with evidence, and engage in meaningful discussions.
Consumerism
Critical thinking is crucial for making informed choices as a consumer. It helps individuals evaluate product claims, compare prices, and make purchases based on facts and reason.
Education
Critical thinking is essential for academic success. It enables students to analyze and evaluate information, form their own opinions, and participate actively in learning.
Critical and creative thinking can be applied to various domains, including accounting. For instance, creative accounting monopoly illustrates how these skills can be used to manipulate financial statements. By understanding such practices, individuals can develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
Ultimately, critical and creative thinking empowers us to navigate complex situations effectively.
Developing Creative Thinking Skills
Nurturing creative thinking is crucial for problem-solving, innovation, and personal growth. Engage in these techniques and activities to enhance your creative capabilities:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a classic method for generating ideas. Gather a group or work individually to list down all possible solutions to a problem or topic. Encourage wild and unconventional ideas without judgment.
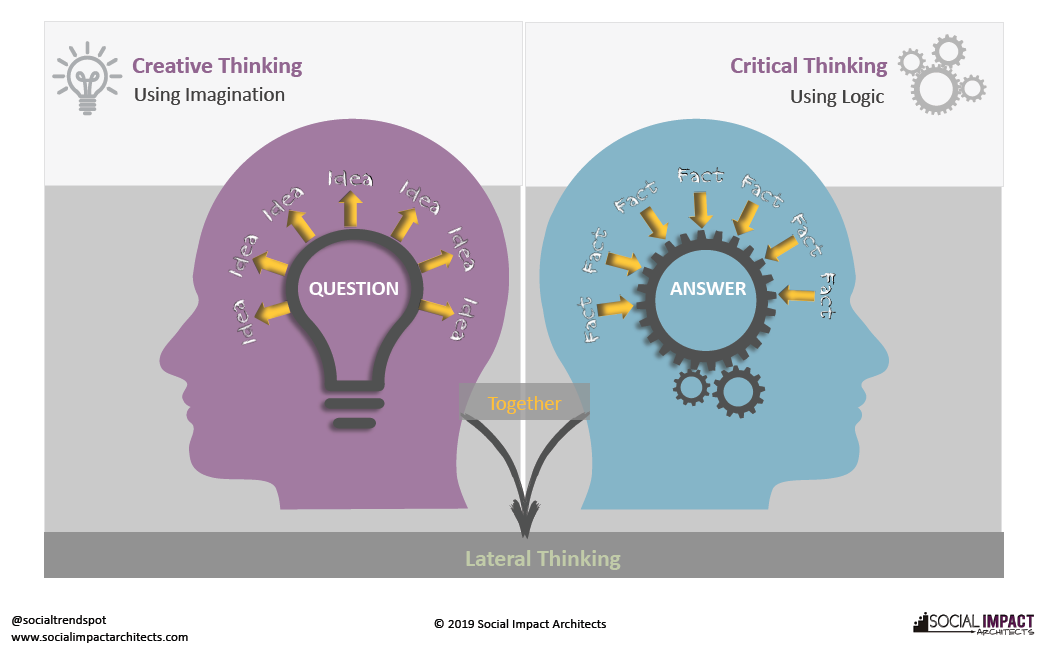
Lateral Thinking, Critical and creative thinking
Lateral thinking challenges conventional approaches by exploring alternative perspectives. Ask “what if” questions, consider different angles, and break down problems into smaller parts to uncover hidden solutions.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping visually organizes ideas by connecting them to a central concept. Start with a main topic and draw branches for related thoughts, s, and associations. This helps expand your thinking and generate new connections.
Creative Exercises
Regularly engage in activities that stimulate creativity:
- Solve puzzles and brain teasers to challenge your problem-solving abilities.
- Engage in freewriting, where you write down whatever comes to mind without editing or censorship.
- Experiment with different perspectives by writing stories or poems from the viewpoints of different characters or objects.
Creative Writing Prompts
Encourage imaginative expression through writing prompts:
- Write a short story about a talking animal that teaches a valuable lesson.
- Create a poem that captures the essence of a natural phenomenon, such as a sunrise or thunderstorm.
- Develop a screenplay for a movie that explores a unique and thought-provoking concept.
Critical and Creative Thinking in Education
Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for students to develop in order to succeed in school and beyond. By incorporating these skills into educational curricula, students can learn to think critically about information, solve problems creatively, and make informed decisions.There are many ways to integrate critical and creative thinking into lesson plans.
One way is to ask students to analyze and evaluate information. This can be done through activities such as reading comprehension exercises, debates, and research projects. Another way to promote critical thinking is to encourage students to generate their own ideas and solutions.
This can be done through activities such as brainstorming, problem-solving exercises, and creative writing assignments.
Examples of Integrating Critical and Creative Thinking into Lesson Plans
* Social Studies:Have students analyze primary and secondary sources to draw conclusions about historical events. Encourage them to consider different perspectives and interpretations of the past.
Science
Ask students to design and conduct experiments to test hypotheses. Help them to develop logical reasoning skills and the ability to draw conclusions from data.
Math
Challenge students to solve problems in multiple ways. Encourage them to think outside the box and come up with creative solutions.
Language Arts
Have students analyze literary texts to identify themes, symbols, and character development. Encourage them to express their own interpretations and insights through writing and discussion.By incorporating critical and creative thinking into educational curricula, we can help students develop the skills they need to succeed in school and beyond.
Critical and Creative Thinking in the Workplace
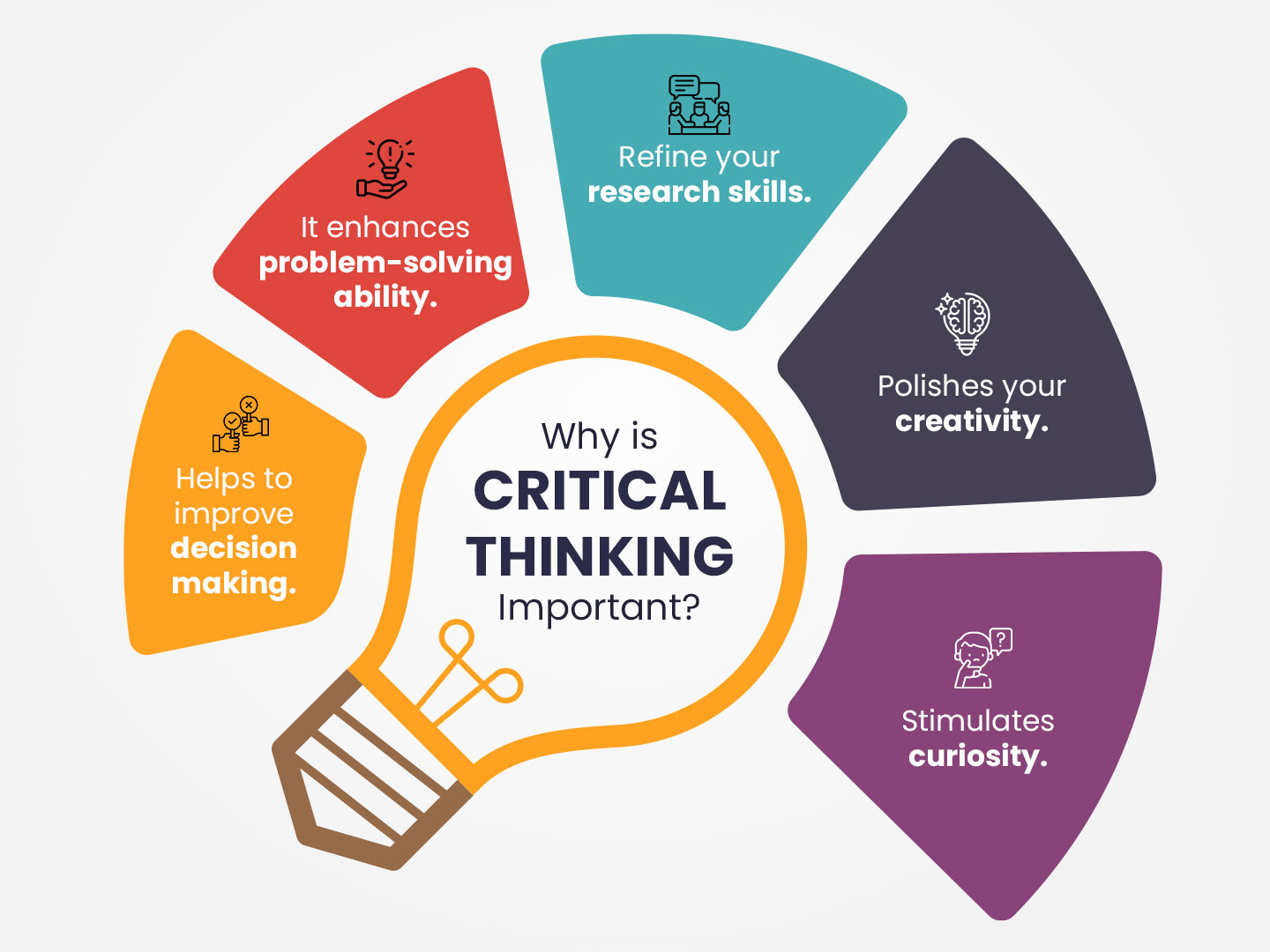
Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for success in today’s workplace. They enable individuals and teams to solve problems effectively, innovate, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Critical thinking involves analyzing information, identifying patterns, and making sound judgments. Creative thinking, on the other hand, involves generating new ideas, exploring possibilities, and finding unique solutions.
Benefits of Critical and Creative Thinking in the Workplace
- Enhanced problem-solving
- Improved decision-making
- Increased innovation
- Better communication and collaboration
- Greater adaptability to change
Techniques and Methodologies to Foster Critical and Creative Thinking
There are various techniques and methodologies that can be used to foster critical and creative thinking in the workplace. These include:
- Brainstorming
- Mind mapping
- Six Thinking Hats
- Design thinking
- Root cause analysis
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite their importance, critical and creative thinking can be hindered by certain challenges and obstacles, such as:
- Time constraints
- Cognitive biases
- Fear of failure
- Lack of support
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
To overcome these challenges, individuals and organizations can implement the following strategies:
- Allocate dedicated time for critical and creative thinking
- Create a supportive and encouraging environment
- Encourage diversity of perspectives
- Provide training and development opportunities
Real-World Case Studies
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented strategies to promote critical and creative thinking. For example:
- Google encourages its employees to spend 20% of their time on personal projects
- 3M holds regular “innovation jams” to generate new ideas
- IDEO uses design thinking to develop innovative products and services
Step-by-Step Guide to Cultivate Critical and Creative Thinking
- Identify a problem or challenge
- Gather information and analyze it
- Generate multiple solutions
- Evaluate the solutions and choose the best one
- Implement the solution and evaluate its effectiveness
Resources and Further Reading
Critical and Creative Thinking in Decision-Making
Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for making informed decisions. Critical thinking allows us to evaluate information, identify biases, and develop sound arguments. Creative thinking enables us to generate new ideas, explore alternative perspectives, and find innovative solutions.
Framework for Applying Critical and Creative Thinking to Decision-Making
To apply critical and creative thinking to decision-making, follow these steps:
Define the problem
Clearly identify the issue or decision to be made.
Gather information
Collect relevant data and perspectives from various sources.
Analyze the information
Critically evaluate the information, identify biases, and draw conclusions.
Generate ideas
Brainstorm possible solutions, considering both conventional and unconventional approaches.
Evaluate the ideas
Weigh the pros and cons of each idea, considering feasibility, effectiveness, and potential consequences.
Make a decision
Choose the best course of action based on the analysis and evaluation.
– Discuss the impact of critical thinking on problem-solving.
Critical thinking plays a pivotal role in problem-solving by enabling individuals to analyze, evaluate, and interpret information effectively. It involves breaking down a problem into smaller components, identifying underlying assumptions, and considering multiple perspectives.
Steps in critical thinking for problem-solving
- Define the problem clearly and identify the desired outcome.
- Gather and analyze relevant information from various sources.
- Identify and evaluate different perspectives and biases.
- Generate potential solutions and assess their feasibility.
- Select the best solution and implement it.
- Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution.
Obstacles to Critical and Creative Thinking

Critical and creative thinking are essential skills for success in today’s world. However, there are a number of obstacles that can prevent us from thinking critically and creatively. These obstacles can be cognitive, emotional, or environmental.
Cognitive Barriers
Cognitive barriers are obstacles that are related to our thinking processes. These barriers can include:
- Confirmation bias: The tendency to seek out and consider information that confirms our existing beliefs.
- Groupthink: The tendency to conform to the opinions of the group, even when we know that the group is wrong.
- Fixed mindset: The belief that our intelligence is fixed and cannot be changed.
Emotional Barriers
Emotional barriers are obstacles that are related to our emotions. These barriers can include:
- Fear of failure: The fear of making mistakes or looking foolish.
- Fear of success: The fear of what will happen if we achieve our goals.
- Anxiety: A general feeling of worry or unease that can make it difficult to concentrate and think clearly.
Environmental Barriers
Environmental barriers are obstacles that are related to our surroundings. These barriers can include:
- Time pressure: The feeling that we do not have enough time to think critically and creatively.
- Lack of resources: The lack of access to information, materials, or support that we need to think critically and creatively.
- Negative social norms: The belief that critical and creative thinking are not valued or rewarded in our society.
Assessing Critical and Creative Thinking Skills
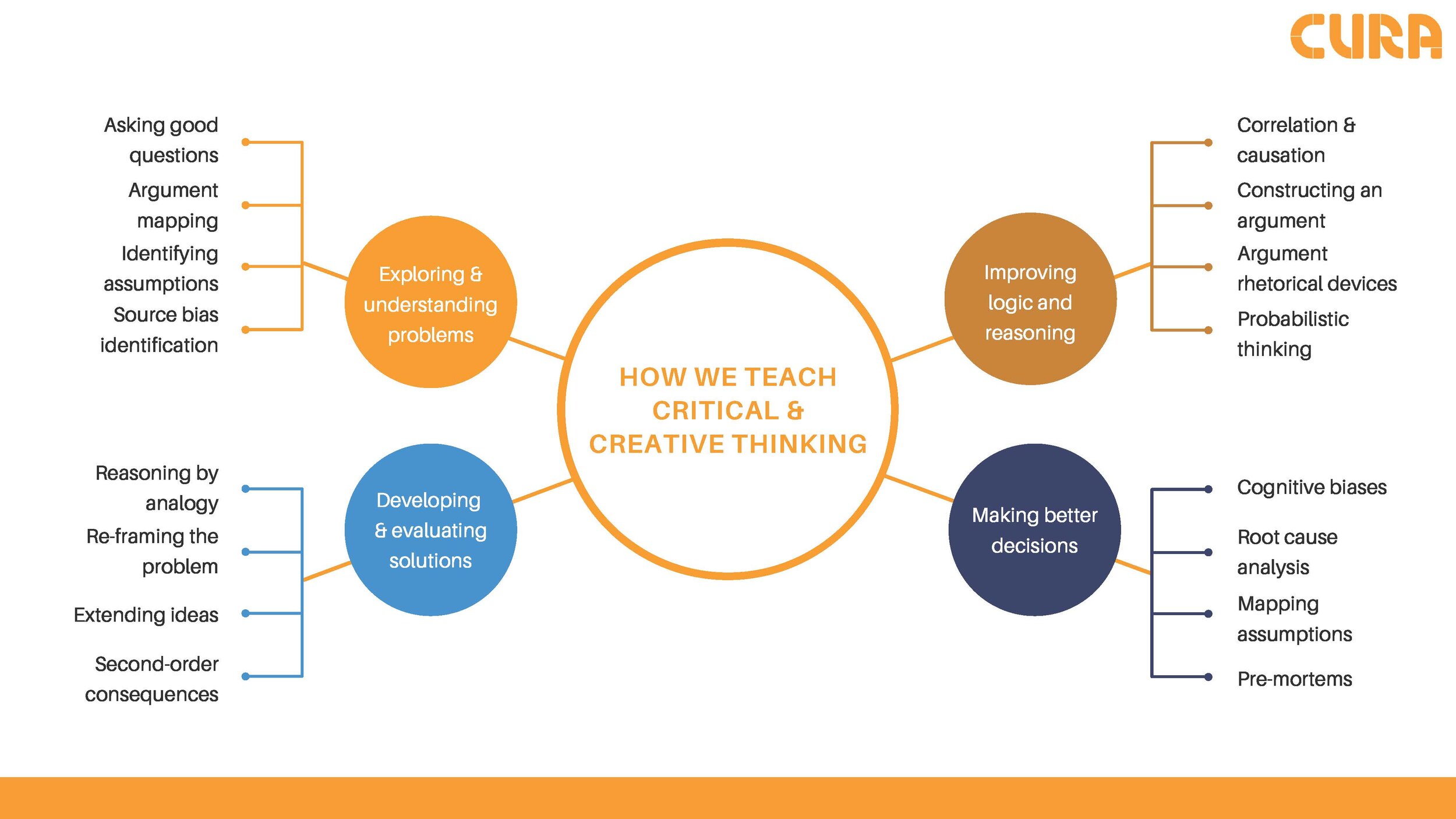
Critical and creative thinking skills are essential for success in education, the workplace, and life in general. Assessing these skills is important to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
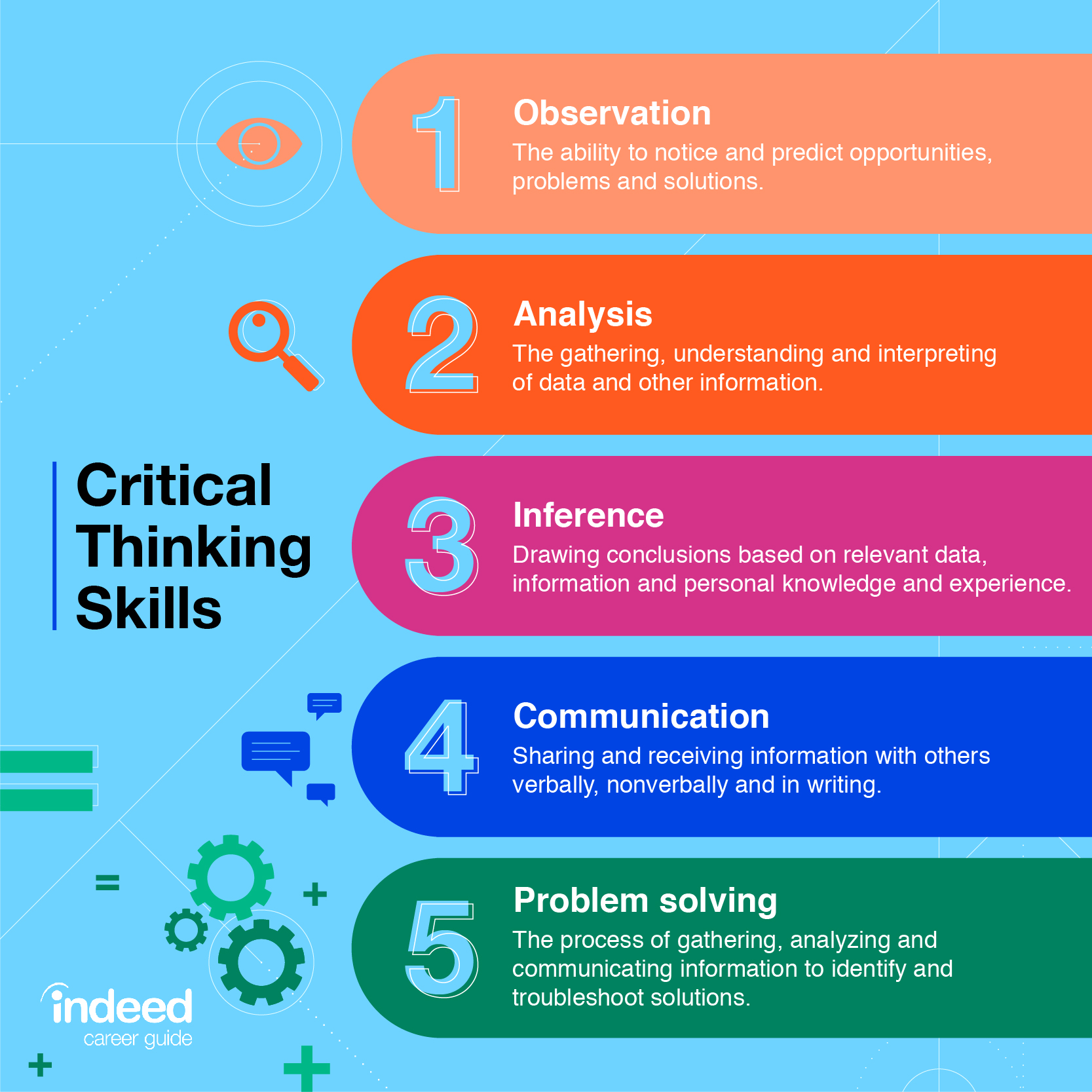
Methods for Evaluating Critical Thinking Skills
- Analysis of written work:Essays, reports, and other written assignments can provide insights into students’ critical thinking abilities. Assess their ability to analyze arguments, identify biases, and draw logical conclusions.
- Observation of student participation in discussions:Classroom discussions offer opportunities to observe students’ critical thinking skills in action. Evaluate their ability to engage in thoughtful dialogue, support their opinions with evidence, and consider alternative perspectives.
- Assessment of problem-solving abilities:Problem-solving tasks require students to apply critical thinking skills to real-world situations. Assess their ability to identify the problem, generate solutions, and evaluate the effectiveness of their solutions.
Techniques for Assessing Creative Thinking Abilities
- Divergent thinking tests:These tests measure the ability to generate multiple ideas in response to a given prompt. Assess the number, originality, and diversity of ideas generated.
- Idea generation exercises:Similar to divergent thinking tests, idea generation exercises encourage students to come up with creative solutions to problems or challenges. Evaluate the quantity and quality of ideas generated.
- Evaluation of creative products:Creative products, such as artwork, writing, or inventions, can be assessed for their originality, innovation, and aesthetic appeal. Use rubrics to evaluate specific criteria relevant to the product.
Assessment Tools and Rubrics
Various assessment tools and rubrics are available to evaluate critical and creative thinking skills. These include:
- Critical Thinking Assessment Tool (CTAT):A standardized test that measures critical thinking skills in reading, writing, and mathematics.
- Creative Thinking Rubric:A rubric that evaluates creative products based on originality, innovation, and aesthetics.
- Problem-Solving Rubric:A rubric that assesses students’ ability to identify problems, generate solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness.
By using appropriate assessment methods and tools, educators can effectively evaluate students’ critical and creative thinking skills and provide feedback to support their development.
Fostering Critical and Creative Thinking in Others
Encouraging critical and creative thinking in others requires fostering a supportive and stimulating environment. By providing guidance, mentorship, and opportunities for practice, we can empower individuals to develop these essential skills.
To cultivate critical thinking, encourage questioning, analysis, and evaluation of information. Provide opportunities for individuals to engage in discussions, debates, and problem-solving activities. Promote the use of evidence and logical reasoning in decision-making.
Creating a Supportive Environment
- Establish a culture of respect and open-mindedness, where diverse perspectives are valued.
- Encourage collaboration and teamwork, as group discussions can foster critical thinking.
- Provide access to resources and materials that stimulate curiosity and critical thinking.
- Celebrate successes and acknowledge the value of critical thinking and creativity.
Fostering Creative Thinking
- Encourage brainstorming, experimentation, and risk-taking.
- Provide opportunities for individuals to explore different perspectives and unconventional ideas.
- Support imagination and curiosity by promoting exposure to art, music, and literature.
- Encourage the development of empathy and understanding of diverse viewpoints.
The Future of Critical and Creative Thinking

The 21st century has witnessed a rapid evolution in the nature of critical and creative thinking. The increasing complexity of our world demands individuals who can navigate uncertainty, solve complex problems, and generate innovative solutions. Critical and creative thinking are becoming increasingly crucial for success in various aspects of life.
Emerging Trends
In the 21st century, critical and creative thinking are evolving in several key ways:
- Increased Emphasis on Collaboration:Critical and creative thinking are no longer seen as solitary endeavors but rather as collaborative processes. Individuals are expected to work together to solve problems and generate ideas.
- Integration of Technology:Technology is playing a significant role in shaping critical and creative thinking. Digital tools and platforms provide new opportunities for information gathering, collaboration, and idea generation.
- Focus on Real-World Applications:Critical and creative thinking are increasingly being applied to real-world problems. Individuals are expected to use their critical thinking skills to analyze information, solve problems, and make informed decisions.
- Emphasis on Cultural Sensitivity:Critical and creative thinking must be culturally sensitive. Individuals need to be aware of different cultural perspectives and values in order to make informed judgments and generate innovative solutions.
Challenges
Despite the growing importance of critical and creative thinking, several challenges remain:
- Information Overload:The vast amount of information available online can make it difficult to critically evaluate and synthesize information.
- Cognitive Biases:Individuals often fall prey to cognitive biases that can hinder critical thinking. These biases can lead to faulty reasoning and decision-making.
- Lack of Time and Resources:Individuals may not have the time or resources necessary to engage in critical and creative thinking. This can be a barrier to problem-solving and innovation.
Applications of Critical and Creative Thinking
Critical and creative thinking skills are highly valued across a wide range of fields and industries. These skills are essential for success in any role that requires problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation.
In Various Fields
- Business and Management:Critical thinking is crucial for analyzing market trends, developing strategies, and making informed decisions. Creative thinking helps generate new ideas, develop innovative products and services, and find creative solutions to challenges.
- Education:Critical thinking skills enable students to evaluate information, form their own opinions, and develop well-reasoned arguments. Creative thinking fosters imagination, problem-solving, and the ability to generate original ideas.
- Healthcare:Critical thinking is essential for diagnosing illnesses, prescribing treatments, and making life-saving decisions. Creative thinking helps develop new medical technologies, discover innovative treatments, and find solutions to complex health challenges.
- Science and Technology:Critical thinking is necessary for conducting research, analyzing data, and developing new theories. Creative thinking drives innovation, leads to groundbreaking discoveries, and pushes the boundaries of human knowledge.
- Arts and Humanities:Critical thinking skills are essential for analyzing and interpreting works of art, literature, and music. Creative thinking fosters imagination, expression, and the ability to create original and meaningful works.
Common Queries
What is the difference between critical and creative thinking?
Critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information to form judgments and make decisions. Creative thinking, on the other hand, involves generating new ideas, exploring possibilities, and finding innovative solutions.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills?
Engage in activities that challenge your assumptions, such as reading diverse perspectives, asking probing questions, and seeking evidence to support your claims.
What are some benefits of creative thinking?
Creative thinking fosters innovation, problem-solving, adaptability, and a sense of fulfillment by allowing us to explore new ideas and perspectives.