Embark on an intellectual adventure as we delve into the realm of creative thinking synonyms, unlocking a treasure trove of alternative expressions that will ignite your imagination and expand your vocabulary. Prepare to be amazed by the kaleidoscope of words that capture the essence of this extraordinary mental process.
From the familiar to the unexpected, we’ll explore a symphony of synonyms that paint a vivid picture of creative thinking’s multifaceted nature. Get ready to expand your linguistic horizons and discover the perfect words to articulate your innovative ideas with precision and flair.
Alternative Expressions for Creative Thinking
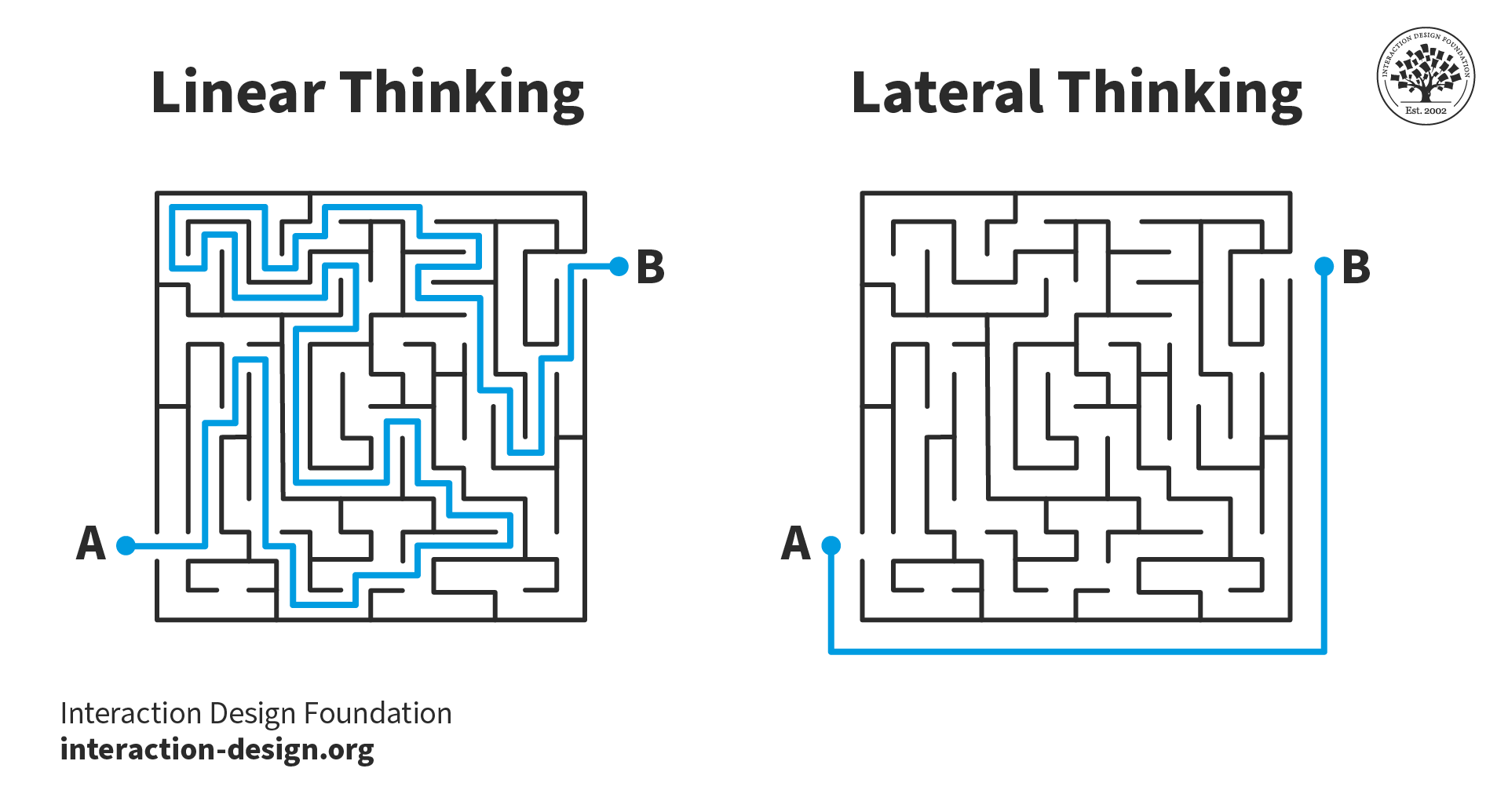
Creative thinking is a crucial skill that allows us to generate innovative ideas and solutions. While the term “creative thinking” is commonly used, it has several synonyms that can be more precise or appropriate in different contexts.
To expand our vocabulary and enhance our communication, let’s explore the diverse range of alternative expressions for creative thinking, organized into categories based on their formality and usage.
Formal Synonyms
In formal settings, such as academic papers or professional presentations, the following synonyms can convey the concept of creative thinking with a sense of sophistication:
- Cognitive flexibility
- Divergent thinking
- Ideation
- Lateral thinking
- Problem-solving
Informal Synonyms
In more informal settings, such as brainstorming sessions or casual conversations, these synonyms can express creative thinking in a relatable and approachable way:
- Brainstorming
- Coming up with ideas
- Imagination
- Thinking outside the box
- Visionary thinking
Comparative Table
To further clarify the nuances and usage of each synonym, the following table provides a comparison:
| Synonym | Formality | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive flexibility | Formal | Refers to the ability to shift perspectives and consider multiple viewpoints. |
| Divergent thinking | Formal | Focuses on generating a wide range of ideas, even if they are unconventional. |
| Ideation | Formal | Specifically refers to the process of generating and developing ideas. |
| Lateral thinking | Formal | Emphasizes unconventional and indirect approaches to problem-solving. |
| Problem-solving | Formal | Encompasses the entire process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems. |
| Brainstorming | Informal | A collaborative process for generating ideas in a free and open environment. |
| Coming up with ideas | Informal | A general term for the act of generating ideas, regardless of the context. |
| Imagination | Informal | Refers to the ability to create mental images and explore possibilities. |
| Thinking outside the box | Informal | A metaphor for breaking away from conventional thinking and exploring new perspectives. |
| Visionary thinking | Informal | Emphasizes the ability to envision and create a desired future. |
Methods for Fostering Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a valuable skill that can be fostered and developed through various techniques and approaches. These methods aim to stimulate the cognitive processes involved in creative thinking, such as divergent thinking, problem-solving, and idea generation.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a classic technique that involves generating a large number of ideas in a short amount of time. Participants are encouraged to think freely and come up with as many ideas as possible, without judgment or criticism. This method helps break down barriers and allows for the exploration of a wide range of perspectives.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual technique that helps organize and connect ideas. It involves creating a diagram with a central topic and branching out to related concepts and s. This method allows for a comprehensive exploration of a topic and can help identify connections and patterns that might not be apparent in a linear thought process.
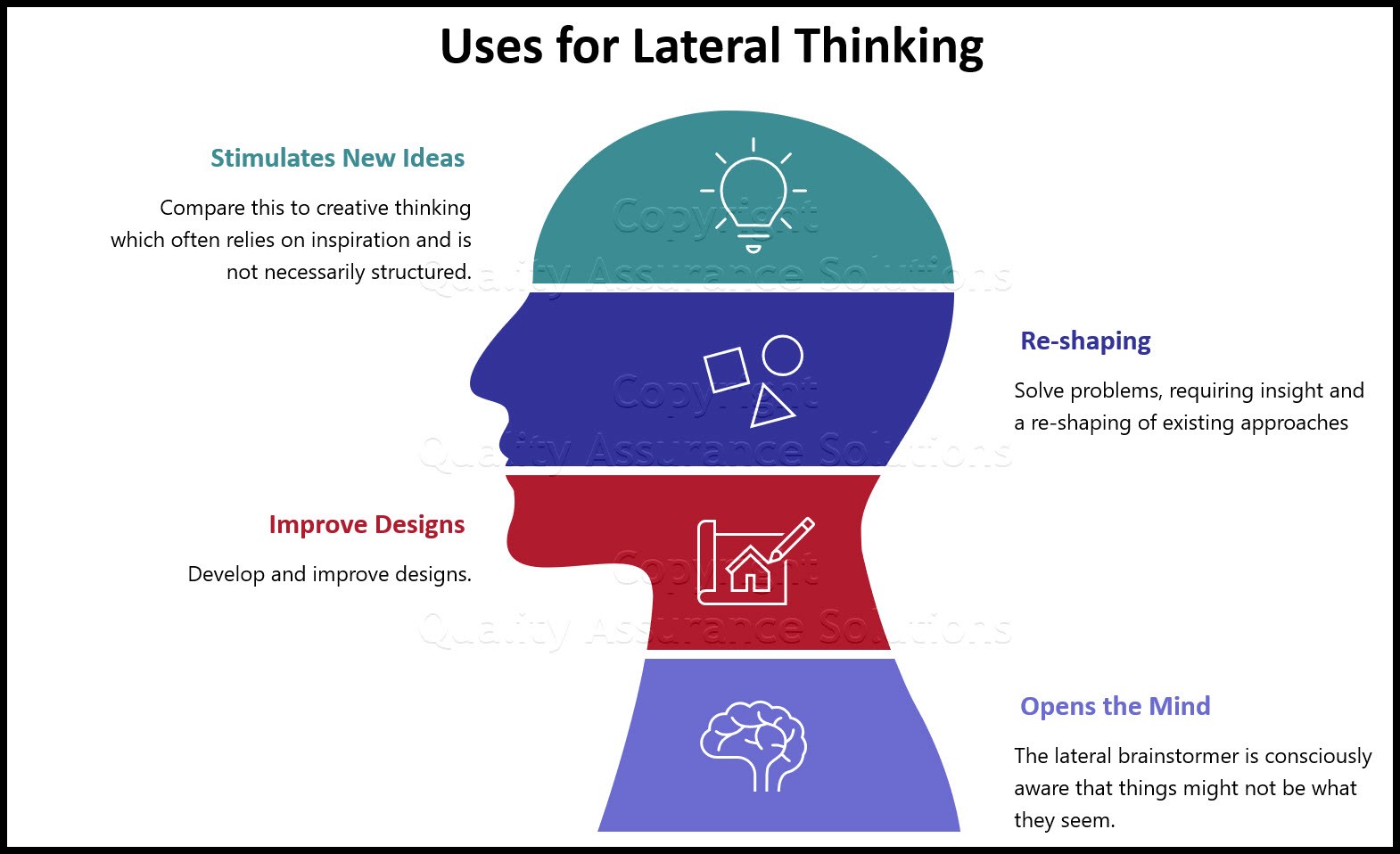
Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking involves challenging assumptions and exploring alternative ways of thinking. It encourages the use of indirect and unconventional approaches to problem-solving and idea generation. By breaking away from conventional patterns, lateral thinking can lead to innovative and unexpected solutions.
SCAMPER Technique
SCAMPER is an acronym that stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. It is a structured approach to idea generation that encourages the exploration of different perspectives and possibilities. By applying these operations to an existing idea or problem, new and innovative solutions can be discovered.
Freewriting
Freewriting is a technique that involves writing down whatever comes to mind without any editing or judgment. It allows for the exploration of subconscious thoughts and ideas that might not be easily accessible through conscious thinking. By writing freely, individuals can tap into their creativity and generate new perspectives.
Research on Fostering Creative Thinking
Research has shown that engaging in creative thinking exercises can enhance cognitive flexibility, problem-solving abilities, and innovation. Studies have also found that a positive and supportive environment, as well as exposure to diverse perspectives, can foster creative thinking. By understanding the methods and underlying principles of creative thinking, individuals can develop strategies to enhance their creativity and generate innovative ideas.
Benefits of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a crucial skill that empowers individuals to approach challenges from novel perspectives, leading to innovative solutions and personal growth. It fosters problem-solving abilities, ignites innovation, and enhances emotional intelligence.
Problem-Solving and Innovation
Creative thinking breaks conventional thinking patterns, allowing individuals to generate unconventional solutions to complex problems. By exploring multiple perspectives and challenging assumptions, creative thinkers can uncover hidden opportunities and develop innovative ideas.
Case Study:The invention of the Post-it note is a testament to the power of creative thinking. Spencer Silver, a 3M scientist, accidentally created a weak adhesive that was initially deemed a failure. However, his colleague, Art Fry, recognized its potential as a bookmark that could be easily removed and repositioned.
This led to the development of the Post-it note, a revolutionary product that has become an indispensable tool in offices and homes worldwide.
Personal Growth
Creative thinking promotes personal growth by fostering curiosity, adaptability, and resilience. Individuals who engage in creative pursuits develop a growth mindset, embracing challenges as opportunities for learning and innovation. They are more likely to persist in the face of setbacks and adapt to changing circumstances.
Cognitive Processes and Techniques
Creative thinking involves a complex interplay of cognitive processes, including divergent thinking, lateral thinking, and emotional intelligence. Divergent thinking encourages the generation of multiple ideas, while lateral thinking challenges established patterns and assumptions. Emotional intelligence allows individuals to manage their emotions and connect with others, enhancing their ability to collaborate and generate innovative solutions.
Overcoming Obstacles
Obstacles to creative thinking include fear of failure, self-doubt, and a lack of support. To overcome these barriers, individuals can practice self-compassion, seek feedback, and surround themselves with a supportive environment that encourages risk-taking and experimentation.
Creative thinking is also known as divergent thinking, which is a process of generating many ideas or solutions to a problem. Creative Beginnings Preschool focuses on developing this skill in children by providing a nurturing environment that encourages exploration and experimentation.
By fostering creative thinking, children can develop their problem-solving abilities, imagination, and self-confidence.
Obstacles to Creative Thinking

Creative thinking is not always easy, and there are many obstacles that can hinder it. These obstacles can be psychological, environmental, or organizational. Understanding these obstacles is the first step to overcoming them and promoting a more creative mindset.
Psychological Obstacles
- Fear of failure:The fear of failure can prevent people from taking risks and trying new things. This fear can be paralyzing, and it can keep people from even starting to think creatively.
- Negative self-talk:Negative self-talk can also hinder creative thinking. When people tell themselves that they are not creative, they start to believe it. This can create a self-fulfilling prophecy, and it can make it difficult to break out of a creative rut.
- Fixed mindset:A fixed mindset is the belief that intelligence is fixed and cannot be changed. People with a fixed mindset are less likely to take risks and try new things, because they believe that they will not be successful. This can stifle creativity.
Environmental Obstacles
- Lack of time:In today’s fast-paced world, it can be difficult to find the time to think creatively. People are often so busy with work, family, and other commitments that they do not have the time to sit down and let their minds wander.
- Lack of resources:Creative thinking often requires access to resources, such as books, materials, and equipment. People who do not have access to these resources may find it difficult to think creatively.
- Uninspiring environment:An uninspiring environment can also hinder creative thinking. People who work in drab, cluttered, or noisy environments may find it difficult to focus and think creatively.
Organizational Obstacles
- Bureaucracy:Bureaucracy can stifle creativity by creating a culture of fear and conformity. People who work in bureaucratic organizations may be afraid to take risks or try new things, because they do not want to upset the status quo.
- Lack of support:Creative thinking often requires support from others. People who do not have support from their colleagues, supervisors, or organization may find it difficult to think creatively.
- Reward system:The reward system in an organization can also hinder creative thinking. If the reward system is based on conformity and productivity, people may be less likely to take risks and try new things.
Creativity in Different Domains: Creative Thinking Synonym

Creativity is not limited to a single field or discipline. It manifests in diverse ways across different domains of knowledge and practice, driving innovation and progress. In this section, we will explore how creative thinking manifests in various fields, the unique challenges and opportunities it presents, and strategies for fostering creativity in each domain.
Arts
In the arts, creativity finds expression through the creation of new and innovative works. This includes the development of new musical instruments and genres, groundbreaking visual art techniques, and captivating literary forms. For example, the invention of the electric guitar revolutionized popular music, while abstract expressionism challenged traditional notions of painting.
Creative thinking in the arts often involves experimentation, risk-taking, and the exploration of unconventional ideas.
Science
Science is another domain where creativity plays a crucial role. Scientific discoveries often emerge from the ability to think outside the box and challenge established paradigms. Examples include the development of the theory of relativity by Albert Einstein, the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming, and the invention of the transistor by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley.
Creative thinking in science requires a combination of analytical thinking, curiosity, and the willingness to explore uncharted territories.
Technology
Technology is a rapidly evolving field that heavily relies on creative thinking. The development of new technologies often involves combining existing ideas in novel ways or finding innovative solutions to complex problems. Examples include the invention of the internet, the development of artificial intelligence, and the creation of virtual reality experiences.
Creative thinking in technology requires a strong understanding of technical concepts, problem-solving skills, and the ability to envision future possibilities.
Business
Creativity is essential for success in business. Developing new products and services, finding innovative marketing strategies, and optimizing business processes all require creative thinking. Examples include the creation of the iPod by Apple, the development of online shopping by Amazon, and the implementation of lean manufacturing techniques by Toyota.
Creative thinking in business involves understanding customer needs, identifying market opportunities, and adapting to changing market conditions.
Social Sciences
Social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, also benefit from creative thinking. Developing new theories, conducting innovative research, and understanding complex social phenomena require creative approaches. Examples include the development of cognitive behavioral therapy, the study of social networks, and the analysis of cultural practices.
Creative thinking in social sciences involves empathy, observation skills, and the ability to think critically about human behavior.
Assessment of Creative Thinking
Evaluating creative thinking skills is a complex and multifaceted process. Various methods and criteria are employed to assess creativity, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Methods for Assessing Creative Thinking
- Divergent Thinking Tests:These tests measure the ability to generate multiple and varied ideas, such as the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking.
- Convergent Thinking Tests:These tests assess the ability to find a single, correct solution to a problem, such as intelligence tests.
- Problem-Solving Tests:These tests evaluate the ability to solve problems creatively, such as the Creative Problem Solving Test.
- Real-World Assessments:These assessments involve observing and evaluating individuals’ creative performance in real-world settings, such as design competitions or artistic endeavors.
Criteria for Assessing Creativity
Several criteria are considered in assessing creativity, including:
- Originality:The extent to which an idea is novel and unexpected.
- Fluency:The ability to generate a large number of ideas.
- Flexibility:The ability to shift perspectives and approach problems from different angles.
- Elaboration:The ability to develop and refine ideas.
- Impact:The potential of an idea to make a significant contribution to a field or domain.
Challenges and Limitations of Measuring Creative Thinking
Assessing creative thinking poses several challenges:
- Subjectivity:Creative thinking is often subjective, making it difficult to establish objective criteria for evaluation.
- Context Dependence:Creativity is influenced by cultural and situational factors, making it challenging to generalize findings across different contexts.
- Time Constraints:Many assessments are time-limited, which can hinder the generation of truly creative ideas.
- Limited Predictive Power:Creative thinking tests have limited predictive validity for future creative success.
Creative Thinking in Teams
Creative thinking in teams involves the collaborative generation and development of new ideas, solutions, and approaches. Teams leverage the diverse perspectives, skills, and experiences of their members to foster innovation and problem-solving.
Roles and Responsibilities
Leaders
Establish a supportive environment, encourage open communication, and facilitate idea sharing.
Facilitators
Guide brainstorming sessions, ensure equitable participation, and manage conflict constructively.
Contributors
Share ideas, build on others’ suggestions, and actively engage in the creative process.
Artificial Intelligence and Creative Thinking
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has sparked significant interest in its potential impact on creative thinking. AI systems, with their ability to process vast amounts of data, learn patterns, and generate new ideas, are poised to augment and enhance human creativity in various ways.
Augmenting Human Creativity, Creative thinking synonym
- Idea generation:AI algorithms can generate a wide range of ideas based on existing knowledge and patterns. This can help humans overcome creative blocks and explore new possibilities.
- Data analysis:AI systems can analyze large datasets to identify trends, correlations, and insights that may not be apparent to humans. This can provide valuable input for creative decision-making.
- Collaboration:AI assistants can facilitate collaboration by organizing ideas, tracking progress, and providing feedback. This can enhance teamwork and lead to more innovative outcomes.
Ethical and Societal Implications
While AI holds great promise for enhancing creativity, it also raises ethical and societal concerns that need to be carefully considered:
- Bias:AI systems are trained on data that may contain biases. These biases can be reflected in the ideas and recommendations generated by AI, potentially limiting creativity.
- Job displacement:AI systems may automate tasks that were previously performed by humans, raising concerns about job displacement in creative industries.
- Authenticity:AI-generated ideas may lack the emotional depth and originality that are often associated with human creativity. This raises questions about the authenticity and value of AI-assisted creative products.
Historical Perspectives on Creative Thinking

The concept of creative thinking has undergone significant evolution throughout history. From ancient philosophical musings to modern scientific investigations, our understanding of creativity has been shaped by a diverse range of thinkers and theories.
In ancient Greece, philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle recognized the importance of imagination and inspiration in the creative process. Plato’s theory of Forms suggested that true creativity involved accessing a realm of perfect ideas that existed beyond the physical world.
Key Thinkers and Theories
- Aristotle:Emphasized the role of observation, experience, and logic in creative thinking.
- Leonardo da Vinci:Known for his polymathic approach to art, science, and engineering, da Vinci believed in the importance of curiosity, experimentation, and imagination.
- Immanuel Kant:Introduced the concept of the sublime, arguing that creative experiences could evoke feelings of awe and wonder.
- Francis Bacon:Advocated for inductive reasoning and the systematic collection of data to foster creative insights.
- Henri Bergson:Proposed that creativity was an intuitive process that transcended rational thought.
In the 20th century, psychologists and cognitive scientists began to study creativity more empirically. Gestalt psychologists such as Max Wertheimer and Wolfgang Köhler investigated the role of insight and problem-solving in creative thinking.
Cultural and Societal Factors
Cultural and societal factors have also played a significant role in shaping our understanding of creativity. In some cultures, creativity is highly valued and encouraged, while in others it may be seen as disruptive or eccentric.
Social norms, educational systems, and economic structures can all influence the development of creative thinking. For example, societies that emphasize conformity and standardization may stifle creativity, while those that encourage exploration and innovation may foster it.
Creative Thinking in Education

Fostering creative thinking in educational settings is crucial for nurturing students’ problem-solving abilities, adaptability, and innovation. Teachers and the curriculum play pivotal roles in promoting creativity, and innovative teaching methods can encourage students to think outside the box.
Role of Teachers
Teachers who foster creative thinking create a classroom environment that encourages risk-taking, collaboration, and experimentation. They provide students with opportunities to express their ideas freely and offer constructive feedback that helps them refine their thinking.
Role of Curriculum
A creative curriculum incorporates activities that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and imaginative expression. It includes hands-on projects, open-ended assignments, and opportunities for students to explore their interests and develop their creativity.
Innovative Teaching Methods
- Project-based learning:Students work on real-world projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills creatively.
- Design thinking:Students use a human-centered approach to solve problems by understanding the needs of others and generating innovative solutions.
- Inquiry-based learning:Students actively engage in asking questions, investigating problems, and constructing knowledge through hands-on experiences.
- Gamification:Games and simulations can make learning more engaging and encourage students to think creatively to overcome challenges.
Creative Thinking in Business
In today’s fast-paced business environment, creative thinking is a crucial skill for driving innovation and success. It enables businesses to adapt to changing market dynamics, develop new products and services, and gain a competitive edge. This section explores the role of creative thinking in business, discusses ways to foster a culture of creativity, provides case studies, and offers strategies for overcoming challenges.
Different Ways Businesses Can Create a Culture of Creativity
Fostering a culture of creativity requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some key strategies businesses can implement:
- Encourage open communication and collaboration, where ideas are shared freely and respected.
- Provide opportunities for employees to experiment and take calculated risks.
- Celebrate and reward creative ideas, regardless of whether they lead to successful outcomes.
- Provide access to resources and training that support creative thinking, such as workshops and design thinking tools.
- Create a physical environment that is conducive to creativity, with flexible workspaces and access to nature.
Creative Thinking in Design

Creative thinking is a crucial aspect of design, as it allows designers to generate innovative and practical solutions to design challenges. Designers engage in cognitive processes such as divergent thinking, where they explore multiple perspectives and generate a wide range of ideas.
They also utilize techniques like brainstorming, mind mapping, and sketching to stimulate creativity.
Cognitive Processes
Designers employ various cognitive processes to foster creative thinking. Divergent thinking is a key aspect, enabling designers to generate multiple solutions by exploring different perspectives and ideas. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, helps designers refine and converge on a single solution that meets the design requirements.
When we think of creative thinking, synonyms like “lateral thinking” or “out-of-the-box thinking” might come to mind. But what about “creativity in planning”? Planning is often seen as a linear process, but it doesn’t have to be. By embracing creativity in planning, we can generate more innovative and effective solutions.
Check out this article on creativity in planning for more insights into how you can use your creative thinking skills to enhance your planning process.
Techniques
Designers utilize a range of techniques to stimulate creative thinking. Brainstorming is a popular method where designers collaborate to generate a large number of ideas in a short period. Mind mapping is another technique where designers create a visual representation of their thoughts, connecting ideas and concepts in a non-linear manner.
Sketching is also widely used to explore ideas visually and generate multiple design concepts.
Iconic Designs
The power of creative thinking in design is evident in numerous iconic designs. The Apple iPhone, for instance, showcases the innovative integration of hardware, software, and user experience, revolutionizing the mobile phone industry. Another example is the Ford Mustang, which captured the spirit of freedom and adventure through its sleek design and powerful engine.
Creative Thinking in Art
Creative thinking is an indispensable aspect of artistic expression. It empowers artists to break away from conventional boundaries, convey their unique perspectives, and create captivating works of art.
Different Ways Artists Use Creative Thinking
Artists utilize creative thinking in myriad ways to convey their ideas and emotions:
- Abstract Representation:Artists often use abstract forms, colors, and textures to evoke emotions and convey complex concepts that may be difficult to express literally.
- Symbolism:Creative thinking allows artists to imbue objects, images, and colors with symbolic meanings, enriching their artworks with layers of interpretation.
li> Metaphorical Expression:Artists employ metaphors and analogies to create thought-provoking connections between disparate elements, inviting viewers to engage with their works on a deeper level.
Transformative Power of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking can profoundly transform artworks, as exemplified by the following examples:
- Pablo Picasso’s “Guernica”:This powerful anti-war painting vividly depicts the horrors of war through distorted figures and fragmented imagery, leaving an indelible mark on viewers.
- Jackson Pollock’s “Number 1A, 1948”:Pollock’s innovative drip painting technique created mesmerizing patterns and textures, challenging traditional notions of artistic representation.
- Yayoi Kusama’s “Infinity Mirror Rooms”:Kusama’s immersive installations utilize mirrors and repetitive patterns to create surreal and disorienting experiences, blurring the boundaries between reality and illusion.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite its transformative potential, creative thinking in art also faces challenges:
- Fear of Failure:The prospect of criticism or negative feedback can hinder artists from taking creative risks and exploring new ideas.
- Artistic Conventions:Established artistic norms and expectations can sometimes limit creative expression and stifle innovation.
- Lack of Resources:Access to materials, studio space, and financial support can influence an artist’s ability to fully explore their creative potential.
Relationship with Innovation
Creative thinking is inextricably linked to innovation in the art world:
- Pushing Boundaries:Creative thinking encourages artists to challenge established norms and experiment with new techniques and materials, leading to groundbreaking artistic innovations.
- Unique Perspectives:Creative thinking allows artists to approach familiar subjects from novel angles, resulting in fresh and innovative interpretations.
- Inspiration for Others:Innovative artworks can inspire and influence other artists, fostering a cycle of creativity and innovation within the art community.
Resources for Developing Creative Thinking Skills
Artists seeking to enhance their creative thinking skills can utilize the following resources:
- Workshops and Classes:Engaging in workshops and classes led by experienced artists can provide valuable insights and practical exercises.
- Online Courses:Numerous online platforms offer courses specifically designed to develop creative thinking skills in artists.
- Mentorship Programs:Connecting with established artists through mentorship programs can provide guidance and support in fostering creative growth.
– Creative Thinking in Science
Creative thinking is crucial in scientific discovery and innovation. It involves generating novel ideas, exploring new possibilities, and challenging established norms. In science, creative thinking leads to groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements that shape our understanding of the world.
Role of Imagination and Experimentation
Imagination allows scientists to envision new possibilities and generate hypotheses. Experimentation then tests these ideas, leading to discoveries and insights. Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity, for example, emerged from his imaginative thought experiments.
Scientific Breakthroughs Sparked by Creative Thinking
- Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation:Inspired by the falling apple, Newton imagined a universal force attracting objects.
- Pasteur’s Germ Theory:Pasteur’s experiments challenged the prevailing theory of spontaneous generation, leading to the understanding of microorganisms.
- Watson and Crick’s Discovery of DNA:Their creative model-building approach led to the discovery of the DNA double helix.
Challenges to Fostering Creative Thinking
- Institutional Constraints:Rigid research structures and funding pressures can stifle creativity.
- Cognitive Biases:Confirmation bias and groupthink can limit exploration of alternative ideas.
- Lack of Interdisciplinary Collaboration:Siloed research can hinder the exchange of diverse perspectives.
Strategies for Promoting Creative Thinking
- Encourage Open-Ended Questions:Promote inquiry and curiosity by asking questions that challenge assumptions.
- Foster a Culture of Experimentation:Provide resources and support for scientists to explore new ideas and take risks.
- Promote Interdisciplinary Collaboration:Encourage collaboration between scientists from different fields to bring fresh perspectives.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration fosters creative thinking by bringing together diverse knowledge and perspectives. For example, collaborations between biologists and engineers led to the development of biomaterials and biomedical devices.
Role of Technology
Technology can enhance creative thinking in science by providing tools for data analysis, visualization, and modeling. Computational simulations and machine learning algorithms can explore complex systems and generate novel insights.
Creative Thinking in Everyday Life
Creative thinking is not limited to artists and scientists. It’s a valuable skill that can be applied in all aspects of life, from solving problems to improving our well-being. By embracing creative thinking, we can unlock our potential and make a positive impact on the world around us.Practical Applications of Creative ThinkingCreative thinking can help us solve problems in many ways.
For example, it can help us find new and innovative solutions to everyday challenges, such as finding a way to fix a broken appliance or coming up with a new recipe. It can also help us overcome obstacles and achieve our goals.
For example, a student who is struggling with a difficult math problem might use creative thinking to come up with a new way to solve it.Tips for Fostering Creative ThinkingThere are many things we can do to foster creative thinking in our everyday lives.
One simple technique is to brainstorm ideas. When you’re faced with a problem, take some time to brainstorm as many possible solutions as you can. Don’t judge your ideas at this stage, just let them flow freely. Once you have a list of ideas, you can start to evaluate them and choose the best one.Importance of Creative ThinkingCreative thinking is essential for personal and societal growth.
It helps us solve problems, improve our lives, and make a positive impact on the world around us. By embracing creative thinking, we can unlock our potential and live more fulfilling lives.
FAQ Summary
What is a synonym for “creative thinking”?
Innovative thinking, divergent thinking, imaginative thinking, original thinking, out-of-the-box thinking
How can I improve my creative thinking skills?
Engage in brainstorming, practice divergent thinking, seek inspiration from diverse sources, challenge assumptions, and embrace experimentation.
What are the benefits of creative thinking?
Enhanced problem-solving, increased innovation, improved decision-making, greater adaptability, and personal growth.