In the ever-evolving landscape of the creative industries, creative producer jobs are at the forefront of bringing innovative and captivating content to life. As a creative producer, you’ll orchestrate the entire creative process, from concept development to final distribution, ensuring that your vision is translated into a cohesive and impactful production.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of creative producer jobs, exploring the responsibilities, skills, and industry trends that shape this dynamic field. We’ll also provide practical advice, case studies, and resources to empower you in your pursuit of a successful career as a creative producer.
Job Description
A creative producer is a multifaceted role that bridges the gap between creative vision and production execution. They are responsible for managing and overseeing all aspects of creative projects, from concept development to final delivery.
Depending on the industry, a creative producer’s responsibilities may vary. In the film industry, they work closely with directors, writers, and other creatives to bring a film to life. In television, they oversee the production of TV shows, ensuring that they meet the network’s creative and financial goals.
In music, they work with artists and record labels to produce albums, singles, and music videos.
Key Skills and Qualifications
To be successful in this role, creative producers need a strong understanding of the creative process, as well as excellent communication, project management, and budgeting skills. They must be able to think strategically and creatively, and be able to work effectively with a variety of stakeholders.
- Strong understanding of the creative process
- Excellent communication skills
- Project management skills
- Budgeting skills
- Strategic thinking
- Creativity
- Ability to work effectively with a variety of stakeholders
Industry Landscape

The creative production industry is a vast and dynamic sector that encompasses various creative disciplines, including film, television, music, advertising, and video games. With its global reach and significant impact on cultural and economic landscapes, the industry has experienced steady growth in recent years.
Technology has played a pivotal role in shaping the industry, introducing innovative tools and platforms that have revolutionized content creation, distribution, and consumption. The rise of streaming services, social media, and virtual reality has expanded the industry’s reach and provided new opportunities for content creators.
Impact of Technology
- Advanced production technologies, such as digital cameras, motion capture systems, and computer-generated imagery (CGI), have enhanced the quality and efficiency of content creation.
- Streaming services have disrupted traditional distribution models, allowing consumers to access a wide range of content on-demand, anytime, and anywhere.
- Social media platforms have become essential marketing tools for content creators, enabling them to connect with audiences and promote their work.
- Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are opening up new possibilities for immersive storytelling and interactive experiences.
Major Industry Players
The creative production industry is highly competitive, with a diverse range of players, including:
- Major film studios, such as Warner Bros., Disney, and Universal Pictures
- Television networks, such as NBC, ABC, and HBO
- Streaming services, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Hulu
- Independent production companies
- Advertising agencies
- Video game developers
Industry Value Chain
The creative production industry operates within a complex value chain, involving various stages from content creation to distribution and consumption:
- Content Creation:Involves the development and production of original content, including writing, directing, acting, and animation.
- Pre-Production:Includes planning, budgeting, and securing financing for the production.
- Production:The actual filming, recording, or development of the content.
- Post-Production:Involves editing, sound mixing, and visual effects to finalize the content.
- Distribution:Making the content available to audiences through various channels, such as theaters, streaming services, and physical media.
- Consumption:The end stage where audiences engage with and experience the content.
- Copyright laws to protect intellectual property rights
- Media regulations to ensure responsible content distribution
- Labor laws to protect the rights of creative professionals
- Environmental regulations to minimize the industry’s environmental impact
- Ideation: Generating and brainstorming ideas.
- Research: Gathering information and conducting thorough research.
- Concept Development: Refining and developing the best ideas.
- Storyboarding: Creating visual representations of the concept.
- Pre-production: Planning and preparing for the production phase.
- Production: Capturing and assembling the creative content.
- Post-production: Editing, refining, and finalizing the content.
- Leading the creative team and providing guidance throughout the process.
- Ensuring that the creative vision is maintained throughout all stages of production.
- Managing the project budget and timeline.
- Collaborating with stakeholders, including clients, writers, designers, and production crew.
- Reviewing and approving creative materials.
- Different perspectives and priorities among stakeholders
- Time constraints and tight deadlines
- Geographical dispersion of team members
- Language barriers or cultural differences
- Establish clear communication protocols
- Use a project management tool for task tracking and file sharing
- Conduct regular team meetings to discuss progress and address challenges
- Foster a culture of open and honest communication
- Provide opportunities for informal communication and team building
- Establish communication channels (email, instant messaging, video conferencing)
- Set up a regular meeting schedule
- Create a shared document for project updates and notes
- Use a project management tool for task tracking and file sharing
- Encourage open and honest communication
- Provide opportunities for informal communication and team building
- Be respectful of others’ opinions and perspectives
- Listen actively and ask clarifying questions
- Communicate clearly and concisely
- Be open to feedback and criticism
- Be willing to compromise and find solutions that work for everyone
- Detailed estimates of all project expenses, including production costs, marketing, and distribution.
- An Artikel of revenue streams and projected income.
- A contingency fund for unexpected expenses.
- Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and GoFundMe.
- Grants from government agencies or foundations.
- Private investors or sponsorships.
- Regularly tracking expenses against the budget.
- Identifying areas where costs can be reduced without compromising quality.
- Negotiating with vendors and suppliers to secure the best possible deals.
- A theater company successfully raised funds through crowdfunding to produce a new play, enabling them to cover production costs and marketing expenses.
- A filmmaker implemented cost control measures by negotiating lower rates with the crew and using donated equipment, allowing them to complete their film within the allocated budget.
- Moving from a junior producer to a senior producer role.
- Specializing in a particular genre or medium, such as documentary filmmaking or live theater.
- Becoming a line producer, responsible for the day-to-day operations of a production.
- Transitioning into a role as a creative director or executive producer, overseeing the overall creative vision of a project.
- Taymor’s innovative use of puppetry and masks created a visually stunning and immersive experience.
- She also collaborated closely with the creative team to develop a compelling storyline and memorable characters.
- Taymor’s leadership and vision ensured that The Lion King became a global phenomenon.
- Jacobson’s expertise in young adult fiction helped her to identify the potential of The Hunger Games.
- She also worked closely with the filmmakers to ensure that the films remained faithful to the source material.
- Jacobson’s involvement in the project helped to make The Hunger Games one of the most successful film franchises of all time.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to automate tasks such as editing, color correction, and sound design, freeing up creative producers to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their work.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are creating new immersive experiences that are transforming the way audiences engage with content.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools are making it easier for creative teams to work together remotely, regardless of their location.
- Audiences are increasingly demanding personalized and interactive experiences. They want to be able to choose what they watch, when they watch it, and how they watch it.
- Consumers are also more likely to trust and engage with content that is authentic and relatable.
- The rise of social media has given audiences a powerful voice, and creative producers need to be aware of the potential impact of their work on social media platforms.
- Streaming services are providing new opportunities for creative producers to reach global audiences.
- Social media platforms are becoming increasingly important for promoting and distributing content.
- Interactive formats such as video games and immersive experiences are creating new ways for audiences to engage with content.
- Exceptional Characterization:The game features deeply flawed and relatable characters whose struggles and relationships resonate with players.
- Immersive Environment:The game’s post-apocalyptic setting is meticulously crafted, creating a sense of realism and atmosphere.
- Innovative Gameplay:“The Last of Us” seamlessly blends action, stealth, and puzzle elements, keeping players engaged throughout.
- Asana:A cloud-based platform for task management, collaboration, and project tracking.
- Trello:A visual collaboration tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize projects.
- Jira:A software development tool that can be adapted for creative production workflows.
- Slack:A messaging and collaboration platform for real-time communication.
- Google Workspace:A suite of tools for document sharing, video conferencing, and collaboration.
- Microsoft Teams:A unified communication and collaboration platform.
- QuickBooks:A cloud-based accounting software for managing finances.
- FreshBooks:An invoicing and accounting software designed for small businesses.
- Buddi:A free and open-source personal finance manager.
- Hootsuite:A social media management platform for scheduling and tracking social media campaigns.
- Mailchimp:An email marketing platform for creating and sending email campaigns.
- Vimeo:A video hosting and distribution platform.
- The increasing use of AI in creative production
- The growing popularity of VR and AR
- The convergence of media and technology
- The globalization of the creative economy
- Stay up-to-date on the latest technologies
- Experiment with new technologies
- Collaborate with other creatives
- Be open to change
Regulatory Environment
The creative production industry is subject to various regulations and laws, including:
Creative Process
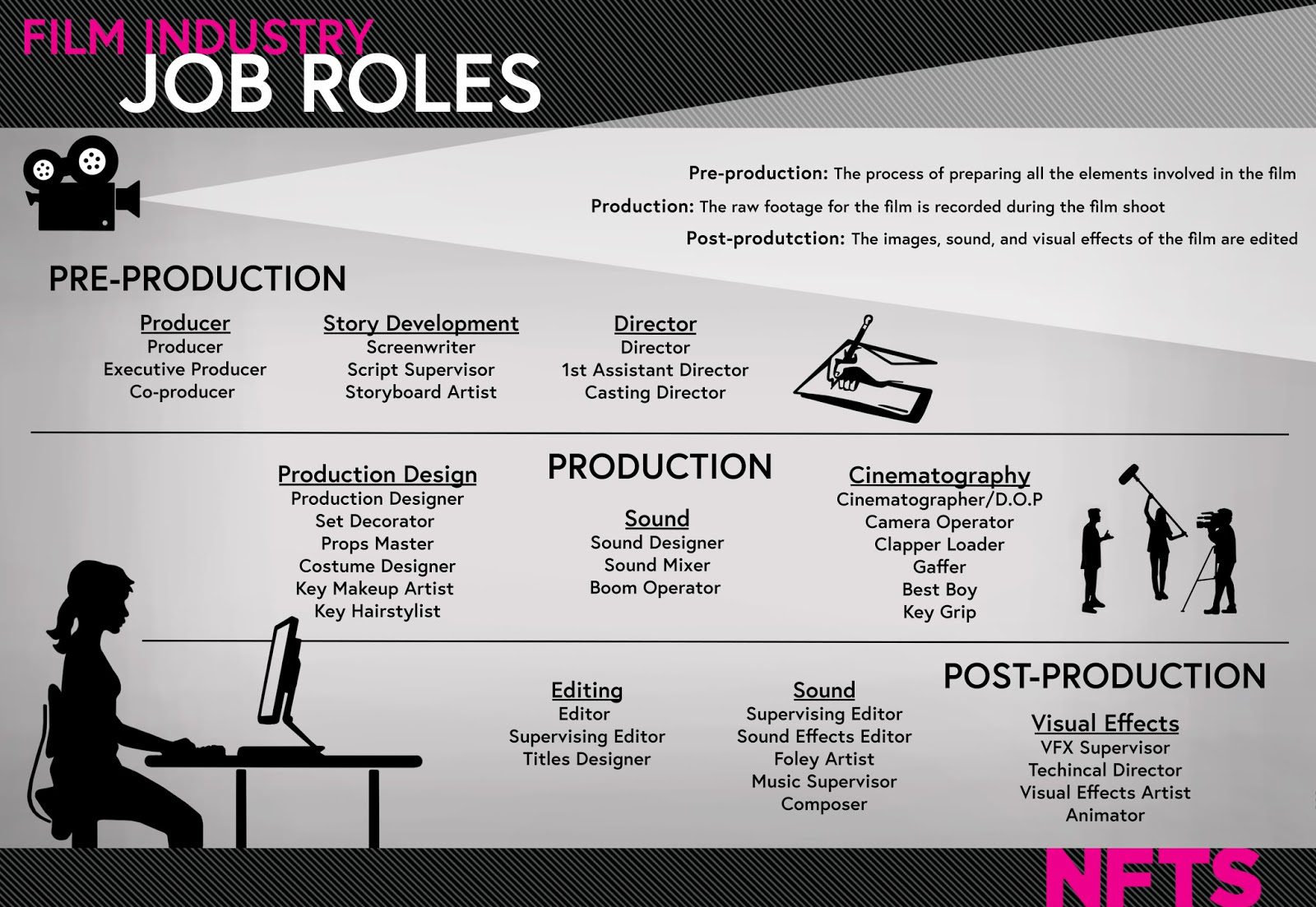
The creative process involved in developing and producing creative content encompasses a series of steps and stages, each with its unique purpose and significance. The creative producer plays a pivotal role in managing and guiding this process, ensuring that the final product aligns with the project’s vision and objectives.
The creative process typically involves the following stages:
Role of the Creative Producer
The creative producer serves as the central figure in managing and guiding the creative process. Their responsibilities include:
Effective creative producers possess a combination of artistic vision, project management skills, and interpersonal abilities. They are able to inspire and motivate their team, while also ensuring that the project remains on track and within budget.
Collaboration and Communication

Collaboration and communication are vital for successful creative production. They foster a shared understanding, streamline workflows, and ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.The creative producer acts as a facilitator, bridging the gap between diverse stakeholders, including clients, creatives, production crew, and distributors.
They establish clear communication channels, set expectations, and foster an environment of respect and open dialogue.
Challenges of Communication and Collaboration
Communication and collaboration in creative production can be challenging due to:
Strategies for Improving Communication and Collaboration
To improve communication and collaboration:
Sample Email Outlining the Importance of Collaboration and Communication
Subject: Importance of Collaboration and Communication in Creative ProductionDear Stakeholders,Collaboration and communication are essential for the success of our creative production project. By working together, we can ensure that everyone is on the same page and that we are all working towards the same goals.I encourage you to be open and communicative throughout the project.
Share your ideas, ask questions, and provide feedback. The more we communicate, the better our final product will be.Thank you for your commitment to this project. I look forward to working with you all.Sincerely,[Your Name]
Key Stakeholders in Creative Production
| Stakeholder | Role |
|---|---|
| Client | Defines the project vision and goals |
| Creative Producer | Facilitates communication and collaboration |
| Creatives | Develop the creative concept and content |
| Production Crew | Produces and delivers the final product |
| Distributors | Distributes the final product to the target audience |
Communication Plan for a Creative Production Project
Guidelines for Effective Communication and Collaboration
– the financial aspects of creative production, including budgeting, fundraising, and cost control

Understanding the financial aspects of creative production is crucial for ensuring a successful project. This involves managing the project’s budget, fundraising, and cost control.
Budgeting for a Creative Project
Creating a budget for a creative project is essential for planning and managing its financial resources. A well-structured budget should include:
Fundraising for Creative Projects
Fundraising is often necessary to supplement a project’s budget. There are various methods for fundraising, including:
Cost Control in Creative Production
Cost control is vital to ensure that a project stays within its budget. This involves:
Examples of Effective Financial Management
Legal and Ethical Considerations

In creative production, understanding and adhering to legal and ethical considerations is crucial to ensure the integrity and safety of the production process and its outcomes. The creative producer plays a significant role in navigating these considerations and ensuring compliance.
Legal considerations include copyright laws, defamation laws, and privacy concerns. Copyright laws protect the rights of creators to control the use of their original works, and violating these laws can lead to legal consequences. Defamation laws protect individuals from false and damaging statements, and creative producers must ensure that any portrayal of individuals in their productions does not violate these laws.
Privacy concerns involve the protection of personal information, and creative producers must obtain consent before using any such information in their productions.
As a creative producer, you’ll have a keen eye for spotting trends. When it comes to pottery painting, creative pottery painting ideas are a great way to explore your creativity and produce unique pieces. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends, you can ensure that your work stands out from the crowd.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations in creative production include ensuring fair treatment of individuals, avoiding harm, and promoting diversity and inclusion. Fair treatment involves respecting the rights and dignity of all individuals involved in the production, including actors, crew members, and participants. Avoiding harm means ensuring that the production process and its outcomes do not cause physical, emotional, or psychological harm to anyone involved.
Promoting diversity and inclusion means ensuring that the production reflects and values the diversity of the community it represents, and that it creates opportunities for individuals from all backgrounds to participate in the creative process.
Best Practices
To avoid legal and ethical issues, creative producers should follow best practices such as obtaining necessary permissions and clearances, ensuring accurate representation, and seeking legal advice when necessary. Obtaining permissions and clearances involves securing the rights to use copyrighted materials, locations, and personal information.
Accurate representation means ensuring that the production portrays individuals and events fairly and without bias. Seeking legal advice can help creative producers navigate complex legal and ethical issues and ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
Marketing and Distribution

Marketing and distribution are essential to the success of any creative content. They ensure that the content reaches its target audience and achieves its desired impact. The creative producer plays a key role in developing and implementing marketing and distribution strategies.
Target Audience Identification
Identifying the target audience is the foundation of any marketing campaign. The creative producer must understand the demographics, psychographics, and media consumption habits of the people they want to reach. This information helps to tailor the marketing message and select the most effective distribution channels.
Message Development
The marketing message should be clear, concise, and persuasive. It should communicate the value proposition of the creative content and motivate the target audience to take action. The creative producer works with the marketing team to develop a message that resonates with the target audience and aligns with the overall marketing goals.
Media Selection
The choice of media channels is crucial to the success of any marketing campaign. The creative producer must consider the reach, cost, and effectiveness of each channel. They must also consider the target audience’s media consumption habits and select channels that are likely to reach them.
Distribution Channels
Distribution channels are the means by which creative content is delivered to the target audience. Traditional channels include television, radio, and print. Digital channels include social media, streaming platforms, and websites. The creative producer must select the distribution channels that are most appropriate for the target audience and the content itself.
Market Research
Market research is essential for developing effective marketing and distribution strategies. The creative producer must gather and analyze data about the target audience, the competition, and the market landscape. This information helps to inform decision-making and ensure that the marketing and distribution strategies are aligned with the overall business goals.
Technology
Technology plays a vital role in the marketing and distribution of creative content. Data analytics and automation tools can help to track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and optimize distribution strategies. The creative producer must stay up-to-date on the latest technology trends and use them to their advantage.
Examples of Successful Marketing and Distribution Campaigns
There are many examples of successful marketing and distribution campaigns for creative content. One example is the marketing campaign for the film “Black Panther.” The campaign targeted the African-American community and used a variety of marketing channels, including social media, print advertising, and community outreach.
The campaign was a huge success and helped the film to become one of the highest-grossing films of all time.Another example is the distribution strategy for the television series “Game of Thrones.” The series was distributed through a variety of channels, including HBO, streaming platforms, and DVD sales.
The distribution strategy helped to reach a wide audience and make the series one of the most popular shows in history.
Career Path and Advancement
The career path for a creative producer typically involves starting as a production assistant or coordinator, then progressing to roles with increasing responsibility and decision-making authority.
Advancement Opportunities
Within the field, creative producers may specialize in particular areas, such as film, television, or theater. Advancement opportunities can include:
Continuing Education and Development
Continuing education and professional development are important for creative producers to stay abreast of industry trends and best practices. This can include attending industry events, workshops, and conferences, as well as pursuing formal education through graduate programs or certifications.
Case Studies

Case studies provide valuable insights into the success factors of creative production projects. They showcase the role of the creative producer and the strategies that led to their successful execution.
By examining these case studies, aspiring creative producers can learn from the experiences of others, identify best practices, and gain a deeper understanding of the industry.
Case Study: The Lion King
The Lion King is a Broadway musical that has been running for over two decades and has grossed over $1 billion worldwide. The creative producer, Julie Taymor, played a pivotal role in the project’s success.
Case Study: The Hunger Games
The Hunger Games film franchise is another example of a successful creative production project. The creative producer, Nina Jacobson, was responsible for overseeing the development and production of the films.
Industry Trends: Creative Producer Jobs

The creative production industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and the emergence of new platforms and formats. These trends are having a profound impact on the role of the creative producer, requiring them to adapt their skills and strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
One of the most significant trends is the rise of digital content. The proliferation of streaming services, social media platforms, and mobile devices has led to an explosion in demand for digital content, including videos, podcasts, and interactive experiences. This has created new opportunities for creative producers, but it has also increased competition and made it more difficult to stand out from the crowd.
Technological Advancements
Changing Consumer Behaviors
Emergence of New Platforms and Formats
Provide concrete examples of successful creative productions that demonstrate best practices

To illustrate the principles of effective creative production, let’s explore some notable examples that showcase best practices in the industry.
Case Study: “The Last of Us” (Video Game)
The critically acclaimed video game “The Last of Us” is a testament to the power of immersive storytelling and character development. Its success can be attributed to:
Tools and Resources

Creative producers rely on a range of tools and resources to streamline their work and achieve exceptional results. These tools empower producers to manage projects efficiently, collaborate seamlessly, and deliver high-quality productions.
Let’s explore some of the most valuable tools and resources available to creative producers:
Project Management Tools
Collaboration Tools, Creative producer jobs
Budgeting and Finance Tools
Marketing and Distribution Tools
Future Outlook

The creative production industry is constantly evolving, and the future holds many exciting challenges and opportunities for creative producers.
One of the most significant challenges facing creative producers is the rapid pace of technological change. The rise of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR), is having a major impact on the way that creative content is produced and consumed.
Creative producers need to be able to adapt to these new technologies in order to stay ahead of the curve.
Key Trends
These trends are shaping the future of creative production, and creative producers need to be aware of them in order to succeed.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are having a major impact on creative production. AI is being used to create new forms of content, such as personalized videos and interactive experiences. VR and AR are being used to create immersive experiences that can transport audiences to other worlds.
The convergence of media and technology is creating new opportunities for cross-platform storytelling.
Creative producers need to be able to harness the power of these new technologies in order to create innovative and engaging content.
Recommendations for Creative Producers
In order to prepare for the future, creative producers should:
By following these recommendations, creative producers can position themselves for success in the future.
Common Queries
What are the key responsibilities of a creative producer?
Creative producers oversee all aspects of content creation, including concept development, budgeting, hiring crew, managing production, and ensuring the final product aligns with the creative vision.
What skills are essential for success as a creative producer?
Strong communication, leadership, and problem-solving skills are crucial. Creative producers must also have a deep understanding of the creative process and the technical aspects of production.
What is the job outlook for creative producers?
The demand for creative producers is expected to grow as the entertainment industry continues to expand and new platforms for content distribution emerge.