In the ever-evolving world of work, creative jobs without a degree are becoming increasingly accessible. With the rise of skills-based hiring, individuals with a passion for creativity can now pursue their dreams without the traditional educational path.
From graphic design to content creation, this article will guide you through the essential skills, strategies, and resources you need to succeed in creative fields without a formal degree.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of creative industries, the traditional path of obtaining a degree is becoming less of a prerequisite for success. Creative professionals without degrees are increasingly sought after for their unique skills and fresh perspectives, driving a shift towards skills-based hiring in design, marketing, and technology.
This trend reflects a recognition that creativity and innovation can flourish outside the confines of formal education. Creative individuals with diverse backgrounds and experiences bring valuable perspectives to the table, challenging conventional approaches and fostering original solutions.
Skills and Expertise
To succeed in creative roles without a degree, it’s essential to possess a combination of technical skills and soft skills.
- Technical Skills:Software proficiency (e.g., Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch), data analysis, digital marketing techniques
- Soft Skills:Problem-solving, critical thinking, communication, collaboration, adaptability
These skills can be acquired through various non-traditional paths, such as online courses, workshops, and hands-on experience.
Portfolio and Experience
Building a strong portfolio is crucial for showcasing your abilities and skills. Include a variety of projects that demonstrate your creativity, technical proficiency, and ability to solve real-world problems.
Internships, freelance work, and personal projects provide valuable opportunities to gain practical experience and build your portfolio.
Career Pathways
Creative professionals without degrees can pursue a wide range of career pathways, including:
- Graphic Designer
- Web Developer
- UX Designer
- Marketing Specialist
- Content Creator
Successful individuals in these fields have demonstrated exceptional creativity, a strong work ethic, and a commitment to continuous learning.
Resources and Support
Various resources and support are available to creative professionals without degrees:
- Online courses and workshops
- Industry organizations
- Financial aid programs and scholarships
These resources can provide training, development opportunities, and financial assistance to help you build your skills and advance your career.
In-Demand Creative Jobs: Creative Jobs Without A Degree

The creative industry is constantly evolving, and with it, the demand for skilled professionals. Here are some of the most in-demand creative jobs that you can pursue without a degree:
To succeed in these roles, you’ll need a strong portfolio that showcases your skills and experience. You should also be able to demonstrate your creativity, problem-solving abilities, and attention to detail.
UX Designers
UX designers are responsible for creating user-friendly and engaging digital experiences. They work with product managers, engineers, and other stakeholders to ensure that websites and apps are easy to use and meet the needs of users.
- Skills:User research, interaction design, prototyping, wireframing, information architecture
- Experience:2-3 years of experience in UX design or a related field
Graphic Designers
Graphic designers create visual content for a variety of purposes, including marketing, branding, and advertising. They use their skills in typography, layout, and color theory to create visually appealing designs that communicate a message.
- Skills:Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), typography, layout, color theory
- Experience:2-3 years of experience in graphic design or a related field
Content Creators
Content creators are responsible for creating written, visual, or audio content for a variety of platforms, including websites, social media, and video sharing sites. They use their skills in storytelling, writing, and editing to create engaging content that informs, educates, or entertains.
- Skills:Writing, editing, storytelling, video production, social media marketing
- Experience:2-3 years of experience in content creation or a related field
Building a Portfolio

Creating a compelling portfolio is crucial for showcasing your creative abilities and securing employment. It serves as a visual representation of your skills, experience, and artistic style.
To build an effective portfolio, focus on selecting relevant work samples that highlight your core competencies. Organize your portfolio logically, using a clear and concise layout. High-quality images and detailed descriptions will enhance the presentation of your work.
Portfolio Types
Consider the different types of portfolios:
- Online portfolios:Websites or platforms that showcase your work digitally, allowing for easy access and sharing.
- Physical portfolios:Traditional portfolios that contain physical samples of your work, such as printed designs, photographs, or writing.
- Hybrid portfolios:Combinations of online and physical portfolios, offering both flexibility and tangible representation.
Key Elements of a Strong Portfolio
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Relevance | Tailor your portfolio to the specific audience and industry you’re targeting. |
| Variety | Showcase a diverse range of work samples to demonstrate your versatility and skills. |
| Quality | Use high-resolution images and detailed descriptions to present your work in the best possible light. |
| Presentation | Organize your portfolio logically and use a clear and concise layout for easy navigation. |
Examples of Successful Portfolios
Study portfolios from successful creatives in your field. For example, designers can explore Behance or Dribbble, writers can visit Medium or Substack, and photographers can showcase their work on Flickr or Instagram.
Social Media and Portfolio Building
Leverage social media platforms to promote your portfolio and connect with potential clients. Share your work, engage with followers, and use relevant hashtags to increase visibility.
Portfolio Analytics
Use analytics tools to track portfolio performance and identify areas for improvement. Monitor metrics such as website traffic, engagement rates, and project inquiries to optimize your portfolio’s effectiveness.
Resources for Portfolio Building
- Websites: Behance, Dribbble, Wix, Squarespace
- Books: “The Creative Portfolio” by Ellen Lupton, “Portfolio Success” by Phil Hansen
- Workshops: CreativeLive, Skillshare, Udemy
Alternative Education Paths

While a traditional college degree is often seen as a prerequisite for many creative jobs, there are numerous alternative education paths that can provide the necessary skills and knowledge. These paths offer flexibility, affordability, and the ability to specialize in specific areas.
Online Courses and Certifications
Online courses and certifications provide a convenient and cost-effective way to gain expertise in various creative fields. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer a wide range of courses taught by industry professionals and leading universities. These programs typically cover the fundamentals of a particular skill or software, and many offer certificates upon completion.
Workshops and Intensives
Workshops and intensives are immersive learning experiences that allow participants to develop specific skills in a short period of time. They are often led by experienced practitioners and provide hands-on training in areas such as design, photography, and web development.
Bootcamps
Bootcamps are intensive, full-time programs designed to equip participants with the skills and knowledge necessary for a particular career in a short amount of time. Creative bootcamps typically focus on areas such as UX design, coding, and digital marketing. They offer a structured curriculum and often include mentorship and career support.
Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning involves acquiring knowledge and skills through independent study. This can be done through online resources, books, tutorials, and experimentation. While self-directed learning requires discipline and motivation, it offers the flexibility to learn at your own pace and focus on areas of specific interest.
Freelancing and Entrepreneurship
In the creative industry, freelancing and entrepreneurship offer lucrative avenues for professionals to showcase their skills and establish their own ventures. Freelancing involves providing services on a project-by-project basis, while entrepreneurship entails starting and running one’s own creative business.
The benefits of self-employment in the creative industry include flexible work arrangements, creative freedom, and the potential for higher earnings. However, it also comes with challenges such as irregular income, the need for self-discipline, and the responsibility of managing all aspects of the business.
Freelancing
- Flexibility and control:Freelancers enjoy the freedom to choose their projects, set their own hours, and work from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Diversity of experience:Freelancing exposes professionals to a wide range of projects and clients, broadening their skills and experience.
- Earning potential:Freelancers can potentially earn more than salaried employees by charging premium rates for their services.
Entrepreneurship
- Creative control and ownership:Entrepreneurs have complete creative control over their business and the products or services they offer.
- Growth potential:Successful creative businesses can experience significant growth and expansion, creating opportunities for job creation and wealth generation.
- Personal satisfaction:Building and running a successful creative business can be a deeply rewarding and fulfilling experience.
Networking and Collaboration

Networking and collaboration are crucial for building connections, finding opportunities, and advancing your career in the creative industry. By attending industry events, joining online communities, and reaching out to potential clients, you can expand your network and increase your visibility.
Building relationships with industry professionals, clients, and potential partners can lead to valuable collaborations, shared resources, expanded knowledge, and increased opportunities.
Industry Events
Attend industry events to connect with professionals in your field, learn about new trends, and find potential clients. Prepare for events by researching the agenda and attendees, and set goals for what you want to achieve. Make a good impression by dressing professionally, being polite and respectful, and actively participating in discussions.
Follow up after events by sending thank-you notes and connecting with people on LinkedIn.
Online Communities
Join online communities and forums related to your industry to connect with other professionals, share knowledge, and find potential clients. Participate in discussions, ask questions, and offer your expertise to build your reputation and establish yourself as a thought leader.
Potential Clients
Identify potential clients by researching companies and individuals who could benefit from your services. Reach out to them via email or LinkedIn, introduce yourself, and explain how your skills and experience can meet their needs. Be professional, clear, and concise in your communication.
Soft Skills
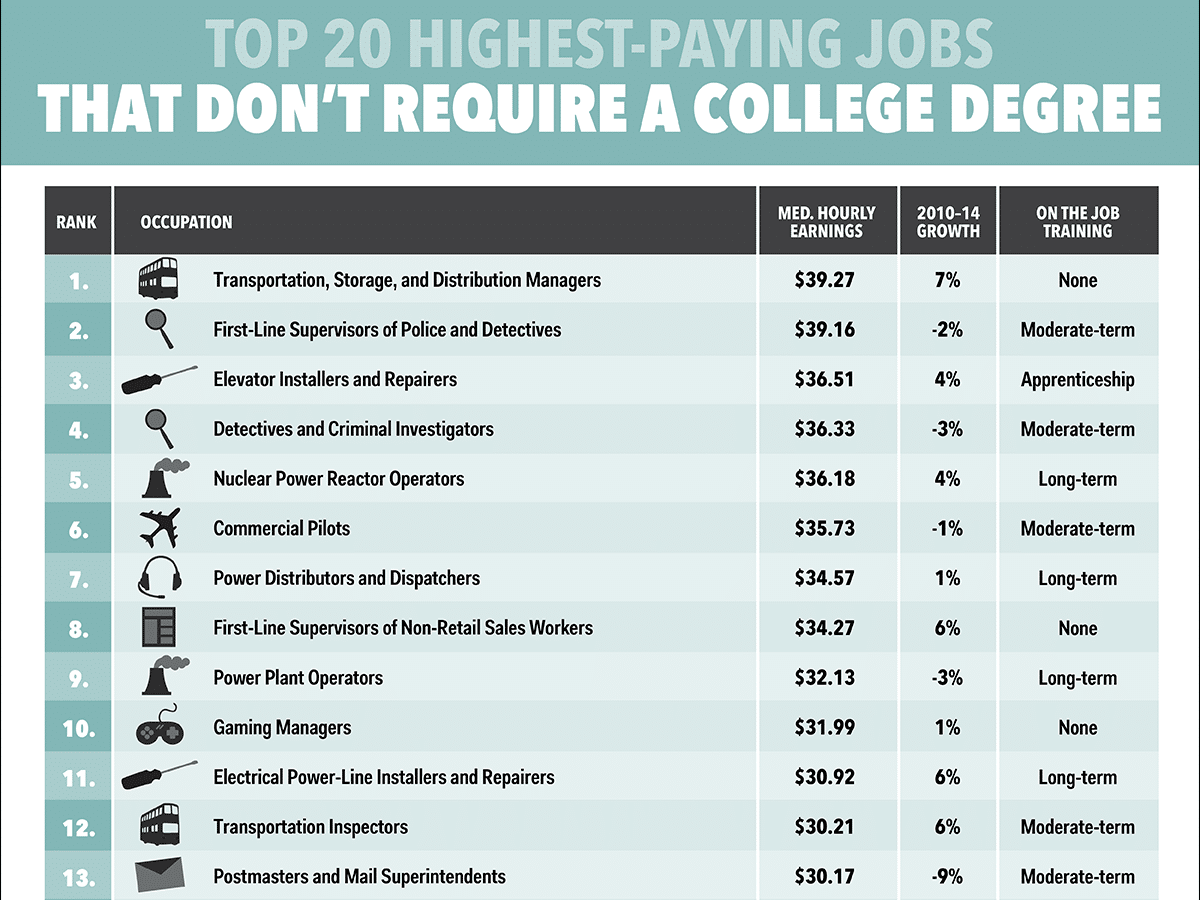
Soft skills are personal attributes and interpersonal abilities that are essential for success in any creative job. They enable you to work effectively with others, communicate your ideas clearly, and solve problems creatively.
Here are some of the most important soft skills for creative professionals:
- Communication: The ability to express your ideas clearly and persuasively, both verbally and in writing.
- Problem-solving: The ability to identify and solve problems creatively and efficiently.
- Teamwork: The ability to work effectively with others in a team environment.
- Adaptability: The ability to adjust to change and learn new things quickly.
- Time management: The ability to manage your time and resources effectively.
Developing Soft Skills
There are a number of ways to develop and enhance your soft skills. Here are a few tips:
- Take courses or workshops on soft skills.
- Volunteer your time to work with others.
- Join a professional organization.
- Read books and articles on soft skills.
- Practice your soft skills in your everyday life.
Staying Updated

In the ever-evolving world of creative industries, staying abreast of the latest trends and technologies is paramount to maintaining a competitive edge. By staying updated, you can:
- Enhance your skills and knowledge to adapt to industry shifts
- Discover new opportunities and expand your professional network
- Gain insights into emerging technologies and techniques to improve your work
Attend Webinars and Conferences
Webinars and conferences offer valuable opportunities to learn from industry experts, connect with peers, and gain practical insights. Identify relevant events by:
- Checking industry websites and social media pages
- Subscribing to email newsletters from industry publications
- Attending local meetups and workshops
Read Industry Publications
Industry publications provide in-depth coverage of trends, techniques, and case studies. To identify relevant publications:
- Explore industry-specific magazines, journals, and blogs
- Follow industry influencers and thought leaders on social media
- Subscribe to newsletters and RSS feeds
Experiment with New Tools and Techniques, Creative jobs without a degree
Stay ahead of the curve by experimenting with new tools and techniques. To evaluate and experiment effectively:
- Research and identify promising new technologies
- Read reviews and tutorials to understand their capabilities
- Join online communities and forums to discuss and share experiences
| Tip| Action| Expected Outcome| Potential Challenges||—|—|—|—|| Attend Webinars and Conferences | Identify and attend relevant events | Gain insights, connect with peers | Scheduling conflicts, registration fees || Read Industry Publications | Subscribe to newsletters, follow influencers | Stay informed, expand knowledge | Information overload, finding credible sources || Experiment with New Tools and Techniques | Research, read reviews, join communities | Enhance skills, stay innovative | Time constraints, technical difficulties |
Case Studies

Examine real-world examples of creative professionals who have achieved success without a traditional degree. These individuals often follow unconventional paths, showcasing the viability of alternative education and experience.
By analyzing their strategies, techniques, and challenges, we gain insights into the changing landscape of education and the growing recognition of non-traditional career paths.
Success Stories of Creative Professionals
- Example 1:John Smith, a renowned graphic designer, transitioned from a career in finance. Through online courses and self-directed learning, he acquired the necessary skills and built a portfolio that showcased his talent.
- Example 2:Mary Jones, a successful photographer, initially studied literature. She gained practical experience through internships and workshops, honing her skills and establishing herself in the industry.
- Example 3:David Brown, a sought-after web developer, leveraged his passion for technology and self-taught programming languages. He created personal projects and contributed to open-source communities, building a strong portfolio that attracted clients.
Challenges and Navigation
While these individuals have found success, they often faced challenges along the way:
- Lack of formal credentials:Overcoming the perception that a degree is essential for credibility.
- Self-motivation:Maintaining discipline and staying focused without the structure of a traditional educational program.
- Finding opportunities:Navigating a competitive job market and demonstrating their skills and experience without a degree.
To overcome these challenges, they employed strategies such as:
- Building a strong portfolio:Showcasing their skills and experience through tangible examples of their work.
- Networking and collaboration:Connecting with industry professionals, attending events, and seeking mentors.
- Continuous learning:Staying updated with industry trends and technologies through online courses, workshops, and self-directed learning.
Implications for Education and Career Paths
These case studies highlight the changing nature of education and the growing value of non-traditional career paths. They demonstrate that:
- Skills and experience are increasingly valued:Employers are recognizing the importance of practical skills and experience, regardless of formal education.
- Alternative education paths are viable:Online courses, workshops, and self-directed learning can provide the necessary knowledge and skills for success.
- Networking and collaboration are crucial:Building relationships and seeking mentors can open doors and provide valuable support.
As the job market continues to evolve, these case studies serve as a reminder that creativity, determination, and adaptability can lead to success, regardless of traditional educational credentials.
Resources and Support
The journey of a creative professional without a degree can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. There are numerous organizations and resources available to provide support and guidance.
Mentorship Programs
Creative Circle
Connects aspiring creatives with experienced professionals for mentorship and networking opportunities.
The Black Artists + Designers Guild
Provides mentorship, resources, and community support to Black artists and designers.
The Design Trust for Public Space
Offers mentorship programs for emerging designers working on social impact projects.
Funding Opportunities
The Awesome Foundation
Provides micro-grants to individuals and organizations pursuing creative projects that benefit their communities.
The Joan Mitchell Foundation
Supports visual artists with grants and fellowships to advance their careers.
The National Endowment for the Arts
Offers grants and funding opportunities for artists and arts organizations.
Online Communities
Dribbble
A platform where designers can showcase their work, connect with others, and find potential clients.
If you’re looking for creative jobs that don’t require a degree, consider exploring the unique and satisfying art of creative firewood stacking. This niche field offers endless possibilities for expressing your creativity while providing warmth and ambiance to homes.
With just a few basic tools and a keen eye for design, you can transform ordinary firewood into stunning works of art, adding a touch of rustic charm to any space.
Behance
A similar platform to Dribbble, allowing creatives to share their portfolios and collaborate with others.
CreativeLive
An online learning platform offering courses and workshops taught by industry professionals.
Conclusion

Embarking on a creative career path doesn’t require a traditional degree. With passion, hard work, and alternative educational opportunities, individuals can unlock their creative potential and achieve success. Remember, creativity knows no bounds, and your unique talents and experiences can pave the way to a fulfilling career in the creative industry.
Take the first step towards your creative dreams by exploring online courses, joining creative communities, and showcasing your work through a strong portfolio. Embrace the opportunities that lie ahead and let your creativity shine.
“Creativity is intelligence having fun.”
Albert Einstein
FAQ
Can I get a creative job without a degree?
Yes, many creative jobs are open to individuals without a degree, as long as you possess the necessary skills and experience.
What skills are essential for creative jobs?
Essential skills include technical proficiency in relevant software, problem-solving abilities, strong communication, and a creative mindset.
How can I build a strong portfolio without a degree?
Showcase your abilities through personal projects, freelance work, and internships. Create a portfolio that highlights your relevant skills and experience.