Creative design and build is an enthralling journey that transforms ideas into tangible realities. It’s a process that weaves together imagination, technical prowess, and a deep understanding of human needs. From groundbreaking products to immersive experiences, creative design and build empowers us to shape a better future.
This comprehensive guide delves into the principles, practices, and tools that underpin creative design and build. We’ll explore the fundamentals of design thinking, user experience, visual communication, and sustainable practices. Along the way, we’ll uncover inspiring case studies and expert insights to equip you with the knowledge and skills to bring your creative visions to life.
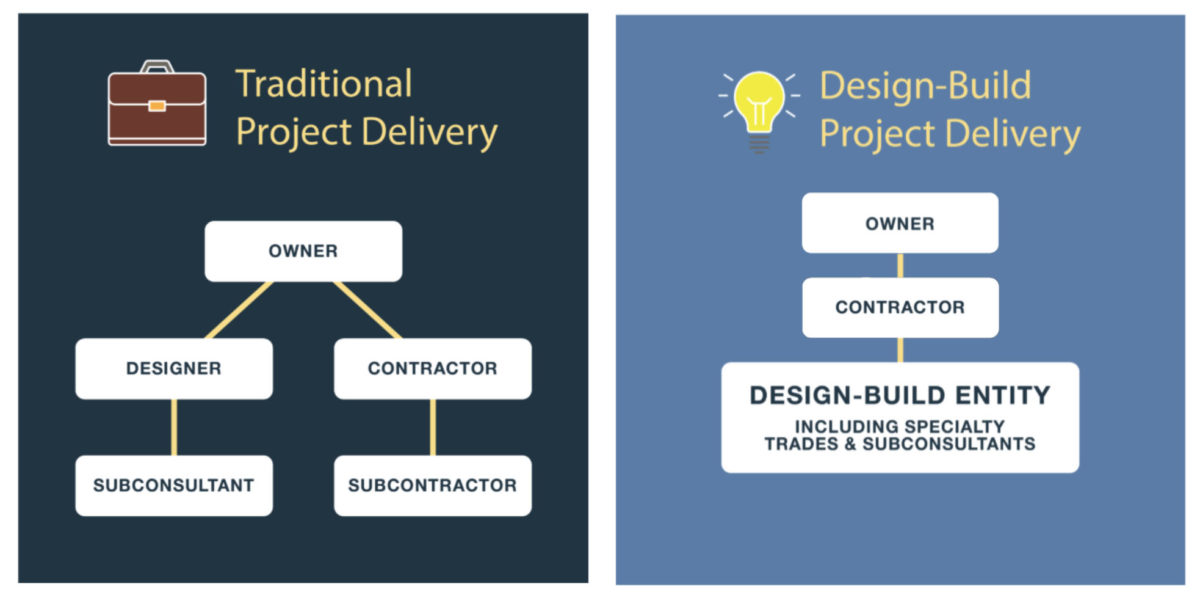
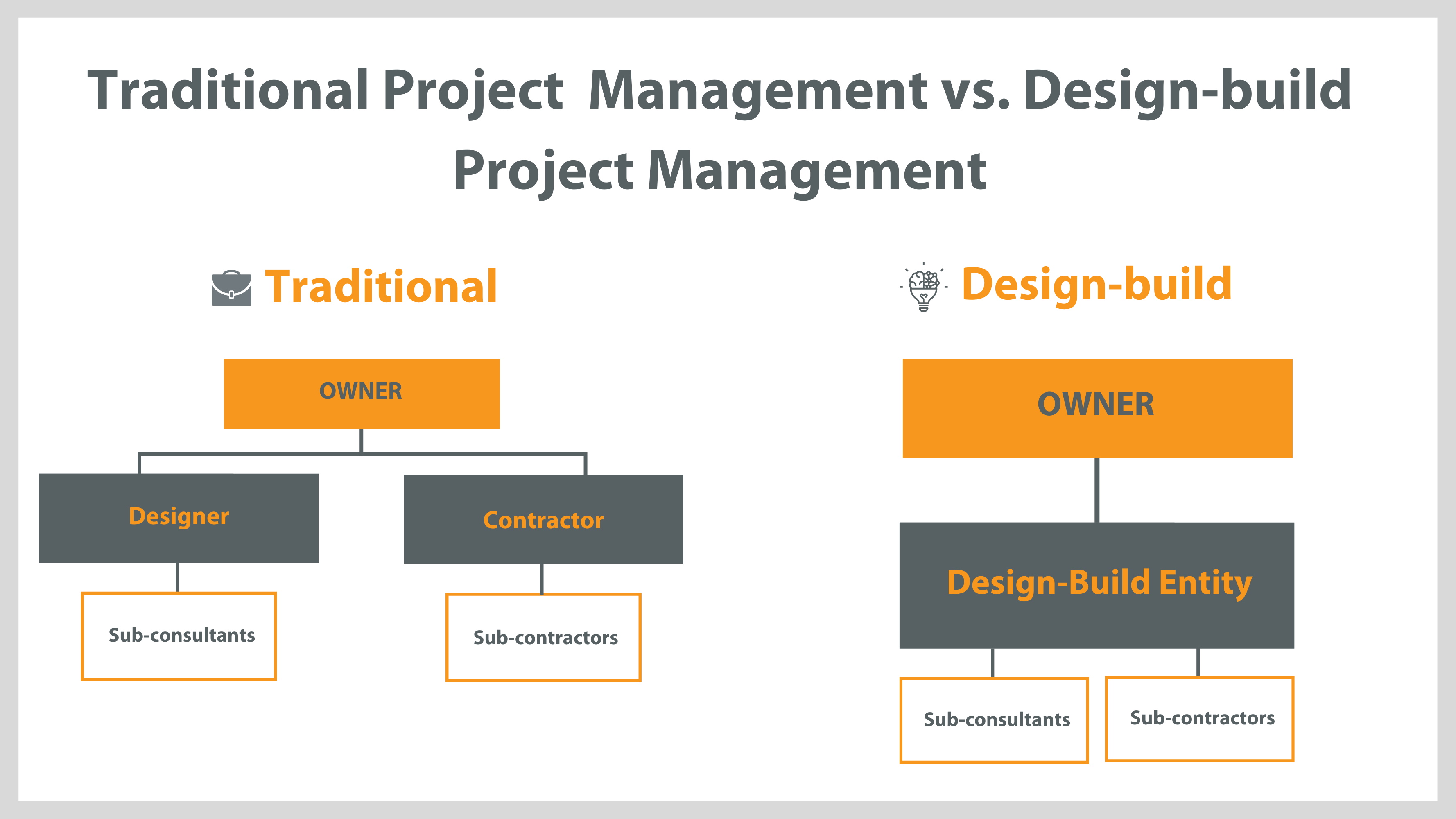
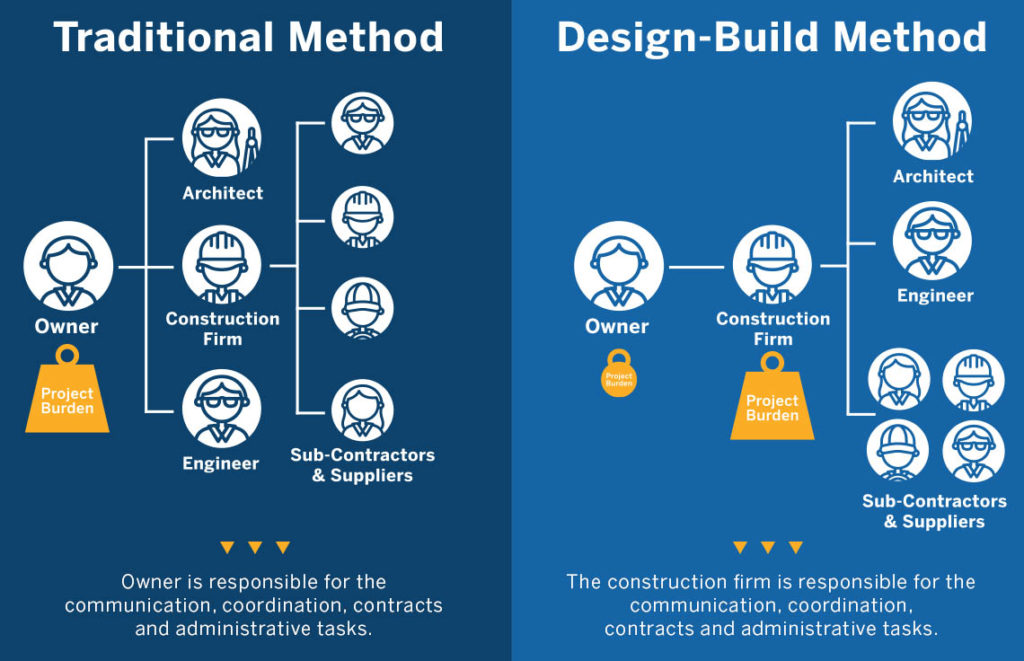
Creative Design Principles: Creative Design And Build

Creative design is the process of developing visual concepts that communicate ideas. It involves the use of various elements, such as color, shape, line, and texture, to create visually appealing and effective designs.
There are several fundamental principles that guide creative design. These principles help designers create designs that are balanced, harmonious, and visually appealing.
Balance, Creative design and build
Balance refers to the distribution of visual weight in a design. There are two types of balance: symmetrical and asymmetrical.
Symmetrical balance is achieved when the visual weight is evenly distributed on both sides of a central axis. Asymmetrical balance is achieved when the visual weight is unevenly distributed, creating a more dynamic and interesting design.
Contrast
Contrast refers to the difference between two or more elements in a design. Contrast can be created using various elements, such as color, shape, size, and texture.
Contrast can be used to create visual interest and emphasis. It can also be used to guide the viewer’s eye through a design.
Harmony
Harmony refers to the pleasing arrangement of elements in a design. Harmony can be achieved through the use of similar colors, shapes, and textures.
Harmony creates a sense of unity and cohesion in a design. It can also make a design more visually appealing and relaxing.
Emphasis
Emphasis refers to the visual importance of an element in a design. Emphasis can be created using various techniques, such as color, size, shape, and contrast.
Emphasis is used to draw the viewer’s attention to a particular element in a design. It can also be used to create a focal point or hierarchy of importance.
Embarking on a creative design and build project? Discover the inspiration you need at the creative space , a vibrant hub for design enthusiasts. Explore a world of ideas, connect with like-minded creatives, and gain insights to enhance your own design and build journey.
Provide examples of how research, sketching, and prototyping can be used effectively in the design process.
Research, sketching, and prototyping are essential tools in the design process. They allow designers to gather information, explore ideas, and test solutions before committing to a final design.
Researchcan be used to gather information about the target audience, the problem that the design is trying to solve, and the existing solutions. This information can help designers to identify opportunities and constraints, and to develop a design that is tailored to the specific needs of the users.
Sketchingis a quick and inexpensive way to explore different design ideas. Sketches can be used to capture ideas, to communicate concepts to others, and to refine designs. By sketching out different ideas, designers can identify the most promising solutions and develop them further.
Prototypingis the process of building a physical or digital model of a design. Prototypes can be used to test the functionality of a design, to get feedback from users, and to refine the design before committing to a final version.
Examples of how research, sketching, and prototyping can be used effectively in the design process:
- A designer might use research to identify the needs of users with disabilities. This information could then be used to develop a design for a website that is accessible to all users.
- A designer might use sketching to explore different ideas for a new product. These sketches could then be used to communicate the concept to engineers and other stakeholders.
- A designer might use prototyping to test the functionality of a new design. This prototype could be used to get feedback from users and to identify any potential problems.
Design Thinking

Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that emphasizes understanding the needs of users and creating solutions that are both effective and desirable. It is a collaborative process that involves brainstorming, prototyping, and testing ideas.
Design thinking has been used to solve a wide range of complex design problems, including the development of new products, services, and experiences. For example, the design thinking process was used to develop the first Apple iPhone. The design team started by understanding the needs of users and then brainstorming ideas for a new type of mobile phone.
They then prototyped and tested their ideas until they arrived at a final design that was both user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
Benefits of Design Thinking
- Helps to understand the needs of users
- Encourages creativity and innovation
- Leads to the development of effective and desirable solutions
- Can be used to solve a wide range of problems
Challenges of Design Thinking
- Can be time-consuming and expensive
- Requires a team of skilled designers
- Can be difficult to get buy-in from stakeholders
Tips for Applying Design Thinking to Your Own Creative Projects
- Start by understanding the needs of your users.
- Brainstorm ideas and then prototype and test your solutions.
- Be open to feedback and be willing to iterate on your ideas.
- Don’t be afraid to fail. Failure is a natural part of the design process.
User Experience (UX) Design
User Experience (UX) design is a crucial aspect of creative design and build, focusing on creating user-friendly and engaging experiences for users interacting with digital products or services. It encompasses various aspects of the design process, including research, sketching, prototyping, and testing, to ensure that the end product meets the needs and expectations of the users.
The key principles of UX design include understanding user needs, designing for usability, and creating a visually appealing and intuitive interface. UX designers employ various research methods, such as user interviews, surveys, and usability testing, to gather insights into user behavior, preferences, and pain points.
Importance of UX Design
- Enhances user satisfaction and engagement
- Improves website or application performance
- Increases conversion rates and revenue
- Builds brand loyalty and reputation
Best Practices of UX Design
- User-centered design:Focus on understanding and meeting the needs of the target users.
- Iterative design:Conduct regular testing and feedback gathering to refine and improve the design.
- Accessibility:Ensure the product is accessible to users with diverse abilities and backgrounds.
- Visual hierarchy:Organize content and elements in a clear and visually appealing manner.
- Consistency:Maintain a consistent design language and user flow throughout the product.
Visual Design
Visual design is the art of combining text and images to create a visually appealing and informative experience for users. It encompasses the use of color, typography, and imagery to communicate effectively.
Color is one of the most important elements of visual design. It can be used to create a mood, set a tone, and highlight important information. For example, warm colors like red and orange can be used to create a sense of excitement or urgency, while cool colors like blue and green can be used to create a sense of calm or serenity.
Typography is another important element of visual design. It refers to the style, size, and arrangement of text. The right typography can make text more readable and engaging. For example, a large, bold font can be used to draw attention to a headline, while a smaller, more subtle font can be used for body text.
Imagery is also an important element of visual design. It can be used to illustrate concepts, add interest to a page, and break up text. For example, a photograph of a product can be used to show users what it looks like, while a diagram can be used to explain how it works.
When used effectively, visual design can help to create a more engaging and memorable experience for users. It can also help to improve communication and understanding.
Color
Color is a powerful tool that can be used to create a variety of effects in visual design. It can be used to attract attention, create a mood, and convey information.
There are three main properties of color: hue, saturation, and value.
- Hueis the pure color, such as red, blue, or green.
- Saturationis the intensity of the color, or how much of the pure color is present.
- Valueis the lightness or darkness of the color.
When choosing colors for a design, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The purpose of the design.What do you want the design to communicate?
- The target audience.Who are you designing for?
- The context of the design.Where will the design be used?
Once you have considered these factors, you can start to choose colors that will be effective for your design.
Typography
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable, and appealing when displayed.
There are many different elements of typography, including:
- Font.The font is the overall style of the type. There are many different fonts available, each with its own unique look and feel.
- Size.The size of the type is measured in points. The larger the point size, the larger the type will be.
- Color.The color of the type can be used to create contrast and emphasis.
- Alignment.The alignment of the type can be used to create different effects. For example, left-aligned text is often used for body text, while centered text is often used for headlines.
When choosing typography for a design, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The purpose of the design.What do you want the design to communicate?
- The target audience.Who are you designing for?
- The context of the design.Where will the design be used?
Once you have considered these factors, you can start to choose typography that will be effective for your design.
Imagery
Imagery is the use of images to communicate information. Images can be used to illustrate concepts, add interest to a page, and break up text.
There are many different types of imagery, including:
- Photographs.Photographs are realistic images that can be used to show people, places, and things.
- Illustrations.Illustrations are created by artists and can be used to create a variety of effects, from realistic to abstract.
- Icons.Icons are small, simple images that are often used to represent concepts or actions.
- Charts and graphs.Charts and graphs can be used to display data in a visual way.
When choosing imagery for a design, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The purpose of the design.What do you want the design to communicate?
- The target audience.Who are you designing for?
- The context of the design.Where will the design be used?
Once you have considered these factors, you can start to choose imagery that will be effective for your design.
– Discuss the different approaches to building creative solutions, including prototyping, experimentation, and collaboration.
Creative solutions are often the result of a combination of approaches, including prototyping, experimentation, and collaboration. Prototyping allows designers to create a physical or digital model of their solution, which can be used to test the solution’s feasibility and get feedback from users.
Experimentation involves testing different ideas and approaches to see what works best. Collaboration brings together different perspectives and expertise to help generate creative ideas and solutions.
Prototyping
Prototyping is a powerful tool for developing creative solutions. It allows designers to quickly and cheaply test their ideas and get feedback from users. Prototypes can be used to explore different design options, test the feasibility of a solution, and get feedback on the user experience.
Experimentation
Experimentation is another important approach to building creative solutions. Experimentation involves testing different ideas and approaches to see what works best. This can involve trying different design options, testing different materials, or using different methods to solve a problem. Experimentation can help designers to identify the best solution for a given problem.
Collaboration
Collaboration is essential for building creative solutions. Collaboration brings together different perspectives and expertise to help generate creative ideas and solutions. Collaboration can involve working with other designers, engineers, users, or even customers. Collaboration can help to ensure that the solution is feasible, meets the needs of users, and is innovative.
Sustainable Design

Sustainable design is a process for creating environmentally conscious designs that minimize the negative impact on the environment. It involves considering the entire lifecycle of a product, from its creation to its disposal, to ensure that it is as sustainable as possible.The principles of sustainable design include:
- Using renewable resources
- Minimizing waste
- Reducing energy consumption
- Using non-toxic materials
Best practices of sustainable design include:
- Using recycled materials
- Designing products that are easy to repair and recycle
- Using energy-efficient technologies
- Using natural light and ventilation
Design for Social Impact

Design can play a crucial role in addressing social issues and creating positive change. By applying design thinking and user experience principles, designers can develop solutions that meet the needs of underserved communities and empower individuals to make a difference.
Examples of Design for Social Impact
* Community-led design:Engaging local communities in the design process ensures that solutions are tailored to their specific needs and aspirations. For example, the “Designing Out Crime” initiative in the UK involved residents in designing safer public spaces, resulting in a reduction in crime rates.
Assistive technology
Design can empower individuals with disabilities by creating assistive devices and technologies that enhance their independence and quality of life. For instance, the “Adaptive Gloves” project developed by MIT Media Lab allows people with limited hand mobility to use touchscreens and other electronic devices.
Environmental sustainability
Design can promote environmental sustainability by creating products and systems that minimize waste, conserve resources, and reduce carbon emissions. The “Solar Bottle Bulb” project provides a low-cost lighting solution for communities without access to electricity, using recycled plastic bottles filled with water and bleach.
Emerging Design Trends

The creative design industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts, and environmental concerns. Emerging design trends are shaping the future of the industry, offering innovative solutions and transforming the way we interact with the world around us.
One of the most significant trends is the rise of generative AI, which enables designers to create unique and complex designs using artificial intelligence. Generative AI can generate images, text, and even music, allowing designers to explore new possibilities and push the boundaries of creativity.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is another growing trend, driven by the increasing availability of data. Designers are using data visualization techniques to create clear and concise representations of complex data, making it easier for users to understand and make informed decisions.
For example, the data visualization company Tableau has developed a range of tools that allow users to create interactive dashboards and visualizations. These tools have been used to create data-driven dashboards for businesses, governments, and non-profit organizations, providing valuable insights into complex data.
Sustainable Design
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the design industry, as consumers and businesses become more aware of the environmental impact of their products and services. Sustainable design focuses on creating products and services that minimize environmental impact and promote social responsibility.
For example, the design firm IDEO has developed a range of sustainable design solutions, including the “Rainmaker” water filtration system and the “Eco Stove” cookstove. These products are designed to meet the needs of communities in developing countries, while also minimizing environmental impact.
The Future of Design
The future of design is bright, with emerging trends promising to transform the way we interact with the world around us. Generative AI, data visualization, and sustainable design are just a few of the trends that are shaping the future of the industry.
As technology continues to advance and cultural shifts continue to occur, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking design solutions in the years to come.
Design for Accessibility

Accessibility in design ensures that everyone can access and use a product or service, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. Inclusive design principles aim to create user interfaces that are accessible to all users, including those with visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor impairments.
Examples of designing for accessibility include:
- Using alt text to describe images for visually impaired users
- Providing closed captions for videos for deaf or hard of hearing users
- Designing interfaces that are easy to navigate with a keyboard or assistive technology for users with motor impairments
- Using clear and concise language that is easy to understand for users with cognitive impairments
Design Education

Design education encompasses a wide range of programs that equip students with the skills and knowledge necessary for a successful career in creative design. These programs provide a solid foundation in design principles, techniques, and software, while also fostering creativity and innovation.
Types of Design Education Programs
- Associate’s Degree Programs:Typically two-year programs that provide a general overview of design fundamentals, including drawing, color theory, and typography.
- Bachelor’s Degree Programs:Four-year programs that offer a more comprehensive education in design, with specializations in areas such as graphic design, web design, and interior design.
- Master’s Degree Programs:One- to two-year programs that provide advanced training in specific design disciplines, such as user experience (UX) design or design management.
- Certificate Programs:Short-term programs that focus on specific design skills, such as web development or digital marketing.
Skills and Knowledge Required for a Successful Career in Creative Design
Individuals pursuing a career in creative design should possess a strong foundation in the following skills and knowledge:
- Artistic Ability:A keen eye for aesthetics, color, and composition.
- Technical Proficiency:Familiarity with industry-standard design software, such as Adobe Creative Suite.
- Communication Skills:Ability to effectively communicate design ideas and concepts to clients and colleagues.
- Problem-Solving Skills:Capacity to identify and solve design challenges through creative and innovative solutions.
- Understanding of Design Principles:Knowledge of the fundamental principles of design, including balance, contrast, and hierarchy.
Design Case Studies
Design case studies are in-depth analyses of successful design projects. They provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to success, and can help designers improve their own work. There are many different ways to conduct a design case study, but some common steps include:
1. Identify a successful design project.
2. Research the project to learn about its context, goals, and outcomes.
3. Interview the designers involved in the project.
4. Analyze the project to identify the key factors that contributed to its success.
5. Present your findings in a case study.
Design case studies can be a valuable resource for designers at all levels. They can help you learn from the successes of others, and improve your own design work.
Table: Case Study Analysis
The following table provides a brief overview of some of the most common design case studies.
| Project Name | Award/Recognition | Key Success Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Example Project 1 | A’ Design Award | Innovative concept, user-centric design, high-quality execution |
| Example Project 2 | Red Dot Award | Aesthetic appeal, functionality, sustainability |
| Example Project 3 | iF Design Award | Ergonomics, material selection, attention to detail |
Blockquote: Designer Interview
The following quote from a lead designer involved in an award-winning project provides some insights into the key factors that contributed to its success:
“The key to success was understanding the user’s needs and translating them into a functional and visually appealing design.”
Design Portfolio

A design portfolio is a curated collection of your best creative work that showcases your skills, experience, and design philosophy. It’s an essential tool for any creative professional looking to land a job or freelance work.
Importance of Creating a Strong Design Portfolio
- Demonstrates your design skills and abilities.
- Highlights your creativity and unique perspective.
- Provides potential employers with a clear understanding of your design process.
- Helps you stand out from the competition.
- Can lead to more job opportunities and higher salaries.
Tips on How to Showcase Your Creative Work Effectively
Choose your best work
Only include your strongest and most relevant pieces.
Organize your portfolio
Use a clear and logical structure to make it easy for viewers to navigate.
Provide context
Include brief descriptions of each project, explaining the goals, challenges, and outcomes.
Use high-quality images
Showcase your work in the best possible light with professional-quality images.
Get feedback
Ask for feedback from other designers, mentors, or potential employers to improve your portfolio.
Different Types of Design Portfolios
Online portfolios
Hosted on a website or platform like Behance or Dribbble.
Print portfolios
Physical portfolios that you can present in person.
Interactive portfolios
Digital portfolios that allow viewers to interact with your work.
Key Elements of a Successful Design Portfolio
Strong visuals
Your portfolio should be visually appealing and showcase your design skills.
Clear organization
Use a logical structure to make it easy for viewers to find the information they need.
Concise descriptions
Provide brief and informative descriptions of each project.
Tailored to specific job applications
Highlight the skills and experience that are most relevant to the job you’re applying for.
Examples of Effective Design Portfolios
[Example 1
Name of portfolio]
[Example 2
Name of portfolio]
[Example 3
Name of portfolio]
Conclusion
Creating a strong design portfolio is essential for any creative professional. By following these tips, you can create a portfolio that will showcase your skills and help you land your dream job.
Design Collaboration
Design collaboration is a process in which multiple designers and professionals work together to create a solution. This can involve a variety of different roles and responsibilities, from brainstorming ideas to developing prototypes and testing them with users. Collaboration can be a powerful tool for innovation, as it allows designers to share their expertise and perspectives, and to learn from each other.
There are many benefits to design collaboration. One of the most important is that it can help to improve the quality of the final product. When multiple designers are working on a project, they can bring different skills and perspectives to the table, which can lead to more creative and innovative solutions.
Collaboration can also help to reduce the risk of errors, as designers can check each other’s work and provide feedback.
Challenges of Design Collaboration
However, design collaboration also has some challenges. One of the biggest challenges is that it can be difficult to manage the different personalities and working styles of multiple designers. It is important to create a collaborative environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing their ideas and opinions.
Another challenge is that collaboration can be time-consuming, as it requires designers to spend time communicating and coordinating with each other.
Successful Design Collaborations
Despite the challenges, there are many examples of successful design collaborations. One example is the collaboration between Apple and Nike on the Nike+iPod Sport Kit. This collaboration brought together two of the world’s leading brands in their respective fields, and resulted in a product that was both innovative and successful.
Roles and Responsibilities of Designers and Other Professionals in a Collaborative Design Process
In a collaborative design process, designers and other professionals play a variety of different roles and responsibilities. Designers are responsible for the creative aspects of the project, such as developing concepts and creating prototypes. Other professionals, such as engineers and marketers, can provide input on the technical and business aspects of the project.
Managing Conflicts and Building Consensus in a Collaborative Design Environment
It is inevitable that conflicts will arise in a collaborative design environment. However, it is important to manage these conflicts in a constructive way. One way to do this is to establish clear communication channels and to encourage open and honest dialogue.
It is also important to be willing to compromise and to find solutions that meet the needs of all stakeholders.
Tips for Effective Communication and Collaboration in a Design Team
There are a number of things that designers can do to improve communication and collaboration in a design team. These include:
- Establish clear communication channels.
- Encourage open and honest dialogue.
- Be willing to compromise.
- Find solutions that meet the needs of all stakeholders.
Tools and Technologies that Can Be Used to Facilitate Design Collaboration
There are a number of tools and technologies that can be used to facilitate design collaboration. These include:
- Project management software
- Collaboration software
- Prototyping tools
- User testing tools
Case Studies of Successful Design Collaborations
There are a number of case studies of successful design collaborations. These case studies can provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to successful collaborations.
- Nike+iPod Sport Kit
- IDEO and Steelcase
- Google and IDEO
Ethical Implications of Design Collaboration
It is important to consider the ethical implications of design collaboration. Designers have a responsibility to ensure that all stakeholders are treated fairly and that the final product is used for good.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Design Collaborations
It is important to evaluate the effectiveness of design collaborations. This can be done by measuring the quality of the final product, the time and cost of the collaboration, and the satisfaction of the stakeholders.
Design Management
Design management is the process of leading and managing creative teams to achieve specific design goals. It involves planning, organizing, directing, and controlling the design process to ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
Effective design management requires a combination of technical skills, such as knowledge of design principles and software, and soft skills, such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving.
Key Responsibilities
- Developing and managing design briefs
- Leading and motivating creative teams
- Planning and scheduling design projects
- Managing design budgets
- Ensuring that designs meet the required quality standards
- Communicating with clients and stakeholders
- Representing the design team to senior management
Key Skills
- Leadership
- Communication
- Problem-solving
- Knowledge of design principles
- Knowledge of design software
- Project management skills
- Business acumen
Popular Questions
What is the importance of user research in creative design?
User research provides valuable insights into the needs, preferences, and behaviors of your target audience. By understanding their pain points and aspirations, you can design solutions that are truly user-centric and effective.
How can I foster a creative environment within my organization?
Encourage open communication, provide opportunities for brainstorming and experimentation, and celebrate diversity of thought. Create a culture where risk-taking is embraced and failure is seen as a valuable learning opportunity.
What are the key principles of sustainable design?
Sustainable design focuses on minimizing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Key principles include using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste, and designing for longevity and recyclability.