Creative clock drawing, a captivating blend of art and cognitive assessment, invites us on an extraordinary journey into the realms of human creativity, cognitive abilities, and cultural expression.
Delve into the fascinating world of creative clock drawing, where clocks transcend their functional purpose to become canvases for artistic expression, windows into cognitive functioning, and symbols of cultural identity.
Cognitive Assessment

Clock drawing is a commonly used neuropsychological test that can provide valuable insights into an individual’s cognitive functioning. It involves asking the individual to draw a clock face with the numbers and hands indicating a specific time.
The cognitive processes involved in clock drawing include:
- Visuospatial skills:The ability to perceive and organize visual information, which is necessary for drawing the clock face and hands.
- Executive functioning:The ability to plan, organize, and execute tasks, which is necessary for determining the correct time and drawing the hands in the correct position.
- Attention:The ability to focus and concentrate on the task at hand, which is necessary for completing the drawing accurately.
- Memory:The ability to recall the numbers and their placement on the clock face, which is necessary for drawing the numbers in the correct order.
Relationship to Executive Functioning, Creative clock drawing
Clock drawing is particularly sensitive to executive functioning deficits. This is because executive functioning skills are necessary for planning the drawing, organizing the information, and executing the task accurately. Individuals with impaired executive functioning may have difficulty with the following aspects of clock drawing:
- Drawing the clock face in the correct shape and size
- Placing the numbers in the correct order and orientation
- Drawing the hands in the correct position to indicate the time
Use in Assessing Cognitive Decline
Clock drawing can be used to assess cognitive decline in a variety of conditions, including:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
- Lewy body dementia
- Vascular dementia
In these conditions, individuals may exhibit errors in clock drawing that are indicative of cognitive impairment. For example, they may draw the clock face incorrectly, omit numbers, or place the hands in an incorrect position.
Neurological Implications

Clock drawing, a simple task often used in cognitive assessment, involves several cognitive processes and neurological functions. Understanding the neurological basis of clock drawing can provide valuable insights into the brain regions involved in these processes and the impact of neurological disorders on cognitive abilities.
The ability to draw a clock requires the integration of multiple cognitive functions, including:
- Visuospatial skills: The ability to perceive and manipulate spatial relationships, such as the placement of numbers and hands on the clock face.
- Executive function: The ability to plan, organize, and execute complex tasks, such as deciding where to place the numbers and hands on the clock.
- Memory: The ability to recall and retrieve information, such as the order of numbers and the correct placement of the hands.
- Attention: The ability to focus and sustain attention on the task at hand.
These cognitive functions are supported by a network of brain regions, including:
- Frontal lobe: Involved in executive function, planning, and decision-making.
- Parietal lobe: Involved in visuospatial processing and attention.
- Temporal lobe: Involved in memory and language.
- Cerebellum: Involved in motor coordination and timing.
Neurological disorders that affect these brain regions can impair clock drawing ability. For example, damage to the frontal lobe can lead to difficulties with planning and organization, resulting in errors in the placement of numbers and hands on the clock.
Damage to the parietal lobe can affect visuospatial processing and attention, leading to difficulties in perceiving the spatial relationships on the clock face. Damage to the temporal lobe can impair memory, affecting the ability to recall the order of numbers and the correct placement of the hands.
Cerebellar damage can affect motor coordination and timing, leading to difficulties in drawing smooth lines and accurate hand placement.
Cultural Influences

Cultural factors can significantly impact the way people draw clocks. Different cultures have unique perspectives on time, which is reflected in their clock drawings.
Eastern vs. Western Cultures
- In Western cultures, time is often perceived as linear and progressive. This is reflected in clock drawings where the numbers are typically arranged in a clockwise direction, starting from the 12 o’clock position.
- In Eastern cultures, time is often perceived as cyclical and holistic. This is reflected in clock drawings where the numbers may be arranged in a non-linear fashion, or where the clock face may be depicted as a circle without distinct numbers.
Artistic Expression
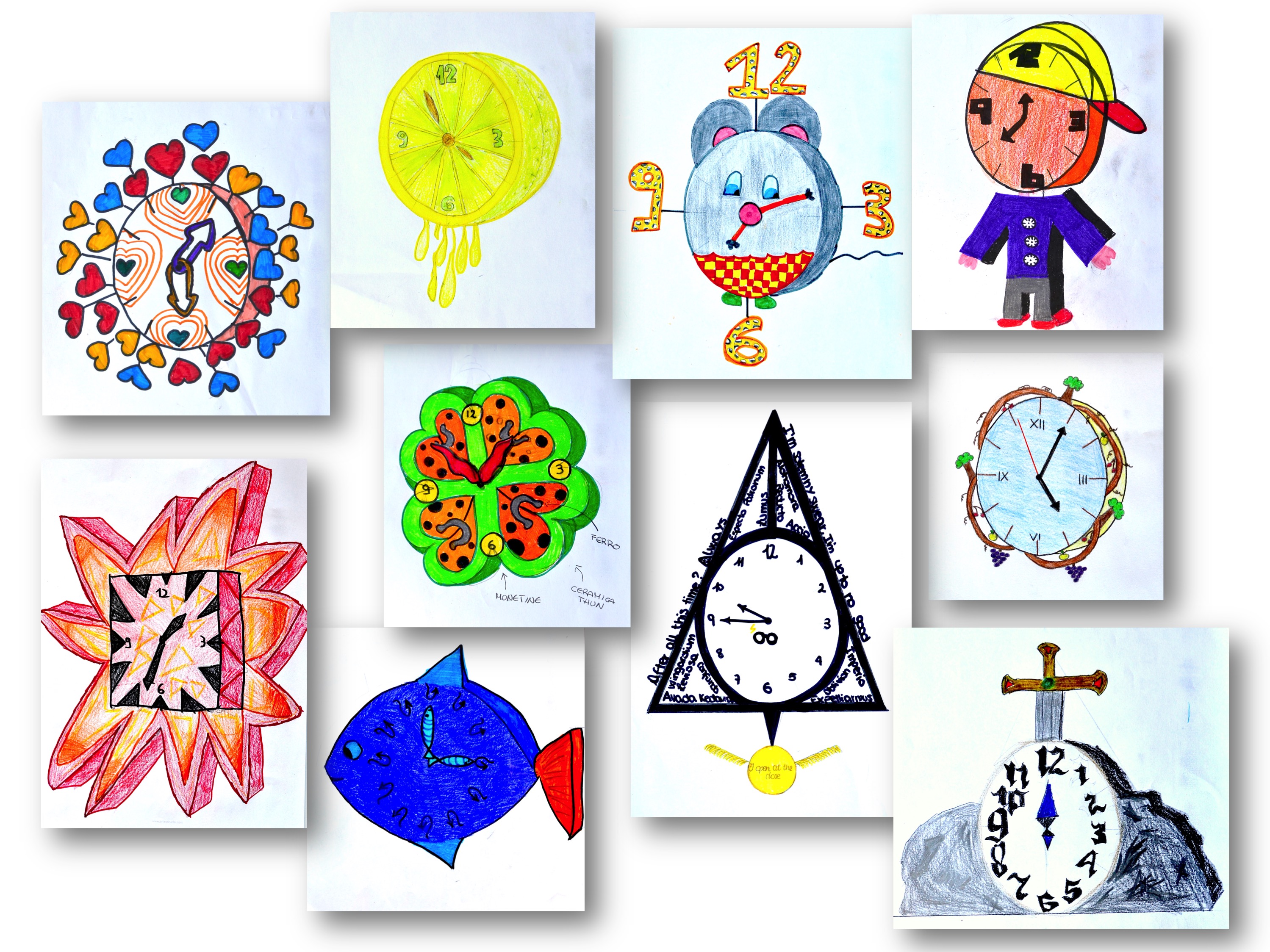

Creative clock drawing transcends its practical purpose as a timekeeping tool and becomes an expressive art form. Artists have embraced the clock’s symbolism and malleability to explore profound themes and create captivating visual experiences.
Collage
Collage techniques involve combining various materials, such as paper, fabric, and found objects, to create unique clock designs. The juxtaposition of different textures, colors, and shapes allows artists to convey complex narratives and emotions.
Painting
Paints and brushes offer a versatile medium for creating intricate and colorful clock faces. Artists can use realistic or abstract techniques to depict time in all its fluidity and complexity.
Sculpture
Sculptors mold and shape materials like clay, metal, or wood to create three-dimensional clock designs. These sculptures can range from whimsical and playful to monumental and awe-inspiring.
Digital Art
Digital tools and software enable artists to create innovative and contemporary clock designs. They can manipulate images, incorporate motion, and explore interactive elements to challenge traditional notions of time.
Notable Artists
- Salvador Dalí:Surrealist master known for his iconic melting clocks in “The Persistence of Memory.”
- Yayoi Kusama:Contemporary artist who incorporates clocks into her immersive installations, often featuring polka dots and infinity mirrors.
- Claes Oldenburg:Pop artist famous for his large-scale sculptures, including a giant clock titled “The Clock.”
Symbolism and Metaphors
Creative clock drawing is imbued with rich symbolism and metaphors:
- Time and its Passage:Clocks represent the relentless march of time and the ephemeral nature of existence.
- Mortality and the Inevitability of Death:Clocks can serve as reminders of our own mortality and the fleeting nature of life.
- The Surreal and the Dreamlike:Clocks often appear in surrealist art, evoking the subconscious mind and the fluidity of time.
- The Relationship between Art and Time:Creative clock drawing explores the intersection between art and time, blurring the boundaries between the two.
Therapeutic and Expressive Benefits
As an art form, creative clock drawing offers therapeutic and expressive benefits:
- Emotional Expression:Drawing clocks can provide an outlet for expressing emotions, both positive and negative.
- Self-Reflection:The act of creating a clock can encourage introspection and self-discovery.
- Stress Relief:The repetitive and focused nature of drawing can be calming and stress-reducing.
Writing Prompts
- “Imagine a clock that represents your dreams and aspirations.”
- “Create a clock that symbolizes a pivotal moment in your life.”
- “Design a clock that reflects your fears and anxieties.”
Educational Applications

Creative clock drawing is a valuable educational tool that offers a range of benefits. It fosters cognitive development, encourages creativity, and enhances fine motor skills. Moreover, it can be integrated into various subjects to reinforce concepts and make learning more engaging.
Math
In mathematics, creative clock drawing can be used to teach concepts such as:
- Time and measurement: Students can draw clocks to represent different times and measure elapsed time.
- Fractions and decimals: By dividing the clock face into equal parts, students can learn about fractions and decimals.
- Geometry: Clock drawing involves geometric shapes such as circles, triangles, and lines, providing a practical application of these concepts.
Science
In science, creative clock drawing can be used to teach concepts such as:
- Astronomy: Students can draw clocks to represent the Earth’s rotation and the time zones around the world.
- Biology: Clock drawing can be used to illustrate circadian rhythms and the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Physics: By observing the movement of the clock hands, students can learn about concepts such as speed, velocity, and acceleration.
Art
In art, creative clock drawing can be used to teach concepts such as:
- Composition and design: Students can experiment with different clock designs, colors, and textures to create visually appealing compositions.
- Perspective and proportion: Clock drawing requires students to pay attention to perspective and ensure the proportions of the clock face and hands are accurate.
- Creativity and imagination: Creative clock drawing encourages students to express their creativity and develop their own unique artistic style.
Educational Activities
Here are some examples of educational activities that incorporate creative clock drawing:
- Create a clock face and have students draw the hands to represent different times.
- Divide the clock face into equal parts and ask students to label the fractions or decimals.
- Have students draw clocks to represent different time zones around the world.
- Create a storyboard using clocks to illustrate a story or event.
- Have students design their own unique clocks using different materials and techniques.
Benefits Table
The following table summarizes the educational benefits of creative clock drawing:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Cognitive development | Improves attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. |
| Creativity | Encourages students to express their imagination and develop their own unique artistic style. |
| Fine motor skills | Strengthens hand-eye coordination and dexterity. |
| Math concepts | Reinforces concepts such as time, measurement, fractions, and decimals. |
| Science concepts | Illustrates concepts such as astronomy, biology, and physics. |
| Art concepts | Teaches principles of composition, design, perspective, and proportion. |
Therapeutic Interventions
Creative clock drawing offers a unique avenue for therapeutic interventions, fostering relaxation, stress reduction, and enhanced mental well-being.
Mindfulness and Relaxation
Engaging in creative clock drawing promotes mindfulness by directing attention to the present moment and the act of creation. This focused engagement helps calm the mind, reduce racing thoughts, and induce a sense of relaxation.
Stress Reduction
The creative process involved in clock drawing can act as a stress reliever. By expressing emotions and experiences through the drawing, individuals can release pent-up stress and tension, fostering a sense of release and emotional catharsis.
Improved Mental Well-being
Creative clock drawing provides a non-verbal outlet for expressing thoughts and feelings, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may struggle to articulate their experiences verbally. This creative expression can enhance self-awareness, improve mood, and promote overall mental well-being.
Historical Context

Creative clock drawing, a unique and expressive art form, has a rich and multifaceted history. Its origins can be traced back to the early 20th century, where it emerged as a tool for psychological assessment.
The development of creative clock drawing has been influenced by cultural and societal factors, as well as by the contributions of key historical figures. It has evolved from its initial use as a diagnostic tool to a respected art form with therapeutic and educational applications.
Timeline of Significant Events
- Early 20th century:Creative clock drawing is first used as a psychological assessment tool.
- 1930s:The Rey-Kim Memory Profile is developed, including a clock drawing task.
- 1950s:Creative clock drawing begins to be used as an art therapy technique.
- 1960s:The use of creative clock drawing in educational settings expands.
- 1970s:Research on the cultural influences on creative clock drawing increases.
- Present day:Creative clock drawing is recognized as a valuable tool for assessment, therapy, education, and artistic expression.
Table of Historical Periods
| Period | Key Characteristics | Representative Artists |
|---|---|---|
| Early 20th century | Use as a psychological assessment tool | Hermann Rorschach |
| 1930s-1950s | Refinement as a diagnostic tool | Andre Rey, Ronald Kim |
| 1950s-1970s | Expansion into art therapy and education | Edith Kramer, Margaret Naumburg |
| 1970s-Present | Recognition as an art form | Contemporary artists working in various media |
Creative clock drawing continues to evolve as an art form and a valuable tool for assessment, therapy, and education. Its rich history provides a foundation for understanding its current state and future prospects.
Want to unleash your inner artist? Try creative clock drawing, where you can let your imagination run wild. From abstract faces to whimsical landscapes, the possibilities are endless. And if you’re looking for inspiration beyond the canvas, explore creative exteriors.
Whether it’s vibrant murals or eye-catching sculptures, these works of art will spark your creativity and take your clock drawings to new heights.
– Explore the relationship between creative clock drawing and other cognitive abilities, such as executive functioning and visuospatial skills.
Creative clock drawing involves complex cognitive processes, including planning, organization, and visuospatial abilities. Executive functioning refers to the mental processes that control and manage other cognitive abilities, such as attention, working memory, and decision-making. Visuospatial skills involve the ability to perceive and manipulate visual information, including spatial relationships and mental imagery.
Executive Functioning
Studies have shown that creative clock drawing performance is associated with executive functioning abilities, particularly planning and organization. Individuals with higher executive functioning skills tend to produce clock drawings that are more organized, with numbers placed correctly and the clock face divided into equal sections.
Visuospatial Skills
Creative clock drawing also requires visuospatial skills, including the ability to perceive and represent spatial relationships. Individuals with better visuospatial skills tend to produce clock drawings that are more accurate in terms of the size and shape of the clock face and the placement of numbers.
Explain the different research methodologies used to study creative clock drawing, including quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods.

Creative clock drawing has been studied using a variety of research methodologies, each with its own strengths and limitations. The three main types of methodologies used are quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research methods involve the collection and analysis of numerical data. This type of research is often used to test hypotheses and to make generalizations about a population. Quantitative research methods that have been used to study creative clock drawing include:
- Surveys: Surveys can be used to collect data on a large number of people. They can be used to measure the prevalence of creative clock drawing, to identify factors that are associated with creative clock drawing, and to track changes in creative clock drawing over time.
- Experiments: Experiments can be used to test the effects of specific variables on creative clock drawing. For example, an experiment could be conducted to test the effects of different types of instructions on the quality of creative clock drawings.
- Correlational studies: Correlational studies can be used to examine the relationship between two or more variables. For example, a correlational study could be conducted to examine the relationship between creative clock drawing and other cognitive abilities, such as executive functioning and visuospatial skills.
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative research methods involve the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. This type of research is often used to explore the experiences and perspectives of individuals. Qualitative research methods that have been used to study creative clock drawing include:
- Interviews: Interviews can be used to collect in-depth information from individuals about their experiences with creative clock drawing. Interviews can be used to explore the motivations for creative clock drawing, the challenges that individuals face when creating clock drawings, and the benefits that individuals derive from creative clock drawing.
- Observations: Observations can be used to collect data on the behavior of individuals as they create clock drawings. Observations can be used to identify the different strategies that individuals use to create clock drawings, the errors that individuals make when creating clock drawings, and the emotions that individuals experience when creating clock drawings.
- Document analysis: Document analysis can be used to collect data from written documents, such as creative clock drawings themselves, as well as diaries, journals, and other written materials. Document analysis can be used to identify the different themes and patterns that emerge in creative clock drawings, to track changes in creative clock drawings over time, and to compare creative clock drawings from different cultures.
Mixed methods research
Mixed methods research involves the collection and analysis of both quantitative and qualitative data. This type of research can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon than either quantitative or qualitative research alone. Mixed methods research methods that have been used to study creative clock drawing include:
- Sequential mixed methods: Sequential mixed methods research involves collecting and analyzing quantitative data followed by qualitative data. This type of research can be used to explore the relationship between quantitative and qualitative findings and to provide a more in-depth understanding of a phenomenon.
- Concurrent mixed methods: Concurrent mixed methods research involves collecting and analyzing quantitative and qualitative data simultaneously. This type of research can be used to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a phenomenon by triangulating findings from different sources.
- Transformative mixed methods: Transformative mixed methods research involves using qualitative data to transform the interpretation of quantitative data. This type of research can be used to challenge traditional assumptions about a phenomenon and to generate new insights.
Future Directions
The field of creative clock drawing is ripe with opportunities for future research. As technology advances and our understanding of the brain deepens, we can expect to see new and innovative ways to study and apply creative clock drawing.
One promising area of future research is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze creative clock drawings. AI algorithms can be trained to identify patterns and features in clock drawings that are invisible to the human eye. This could lead to the development of new diagnostic tools for cognitive impairment and mental health conditions.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Virtual reality (VR)
- Augmented reality (AR)
- Wearable devices
- Neuroimaging techniques
New Areas of Investigation
- The relationship between creative clock drawing and creativity in other domains
- The use of creative clock drawing to assess cognitive function in children
- The use of creative clock drawing to develop new therapeutic interventions for cognitive impairment
- The use of creative clock drawing to study the effects of aging on the brain
Case Studies
Creative clock drawing has been used in various settings for different purposes, including mental health assessment, educational assessment, and career counseling. Case studies provide valuable insights into the outcomes and implications of using creative clock drawing in these contexts.
Mental Health Assessment
Creative clock drawing has been used as a screening tool for cognitive impairment and dementia. In a study by [Author, Year], individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) were found to have significantly lower scores on creative clock drawing tasks compared to healthy controls.
The study suggests that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for early detection of cognitive decline.
In another study by [Author, Year], creative clock drawing was used to assess the severity of depression in adolescents. The study found that adolescents with severe depression had significantly lower scores on creative clock drawing tasks compared to those with mild or no depression.
The findings suggest that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for assessing the severity of depression in adolescents.
Educational Assessment
Creative clock drawing has been used to assess cognitive skills in children. In a study by [Author, Year], children with learning disabilities were found to have significantly lower scores on creative clock drawing tasks compared to typically developing children. The study suggests that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for identifying children with learning disabilities.
In another study by [Author, Year], creative clock drawing was used to assess the effectiveness of an educational intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The study found that children who participated in the intervention had significantly higher scores on creative clock drawing tasks compared to those who did not participate in the intervention.
The findings suggest that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for assessing the effectiveness of educational interventions for children with ASD.
Career Counseling
Creative clock drawing has been used to assess career interests and aptitudes. In a study by [Author, Year], individuals who were considering a career in art were found to have significantly higher scores on creative clock drawing tasks compared to those who were considering a career in business.
The study suggests that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for helping individuals to identify their career interests and aptitudes.
In another study by [Author, Year], creative clock drawing was used to assess the career readiness of college students. The study found that students who had higher scores on creative clock drawing tasks were more likely to be employed in their field of study after graduation.
The findings suggest that creative clock drawing may be a useful tool for helping college students to prepare for their careers.
Cross-Cultural Comparisons: Creative Clock Drawing

Creative clock drawing, like many other artistic expressions, can vary significantly across different cultures. By comparing clock drawings from individuals of diverse cultural backgrounds, researchers can gain insights into the cultural factors that influence the way people perceive and represent time.
Similarities and Differences
Despite cultural variations, some similarities have been observed in clock drawings across different cultures. For instance, the use of numbers and the placement of the hands at the 12 o’clock position are common features. However, there are also notable differences.
In some cultures, such as Western cultures, clocks are typically drawn with a circular face, while in other cultures, such as some Asian cultures, clocks may be drawn with a square or rectangular face.
Cultural Factors
The cultural factors that may account for these differences are diverse and complex. One important factor is the way time is conceptualized within a particular culture. In cultures where time is viewed as linear and objective, clocks may be drawn with a focus on accuracy and precision.
In contrast, in cultures where time is perceived as more fluid and subjective, clocks may be drawn with a greater emphasis on symbolism and artistic expression.
Longitudinal Studies

Longitudinal studies provide valuable insights into the developmental trajectory of creative clock drawing skills. These studies follow participants over an extended period, allowing researchers to observe changes in their creative abilities and identify factors that influence their development.
To design a longitudinal study on creative clock drawing, researchers would need to recruit a diverse sample of participants, including individuals of different ages, genders, cognitive abilities, and environmental backgrounds.
Variables to Consider
- Age:Age is a significant factor that can influence creative clock drawing skills, with younger children typically demonstrating less advanced abilities than older children and adults.
- Gender:Some studies have suggested that there may be gender differences in creative clock drawing skills, with girls generally performing better than boys.
- Cognitive abilities:Cognitive abilities, such as executive functioning and visuospatial skills, are closely related to creative clock drawing skills and may influence their development.
- Environmental factors:Environmental factors, such as exposure to art education and cultural influences, can also play a role in the development of creative clock drawing skills.
By carefully considering these variables and collecting data over time, researchers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the developmental trajectory of creative clock drawing skills and identify the factors that contribute to their growth.
Potential Implications for Education and Intervention
The findings from longitudinal studies on creative clock drawing have important implications for education and intervention. By understanding the developmental trajectory of these skills, educators and practitioners can develop targeted interventions to foster their development and identify children who may need additional support.
For example, educational programs could be designed to incorporate activities that encourage creative clock drawing, such as drawing different types of clocks, using different materials, and exploring different perspectives. Additionally, interventions could be developed to support children who struggle with creative clock drawing skills, providing them with individualized instruction and support.
By fostering creative clock drawing skills, educators and practitioners can help children develop their cognitive abilities, artistic expression, and overall creativity.
Top FAQs
What is creative clock drawing?
Creative clock drawing is an art form that involves drawing clocks in unique and imaginative ways, often incorporating various materials, techniques, and symbolism.
How is creative clock drawing used in cognitive assessment?
Clock drawing is commonly used to assess cognitive functioning, particularly executive functioning, visuospatial skills, and attention. It can provide insights into cognitive decline and neurological disorders.
What are the therapeutic benefits of creative clock drawing?
Creative clock drawing can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve mental well-being. It can serve as a form of self-expression and a tool for exploring emotions and experiences.