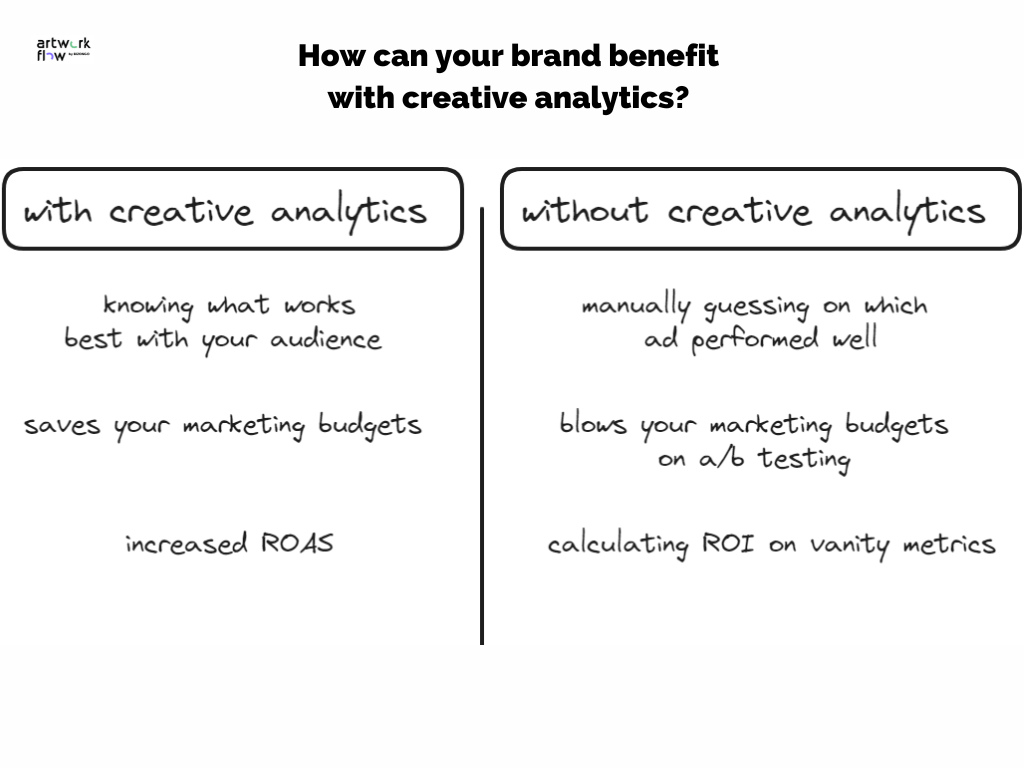
Creative analytics is a game-changer in today’s marketing landscape. By harnessing the power of data, we can now measure, analyze, and optimize our creative campaigns like never before. This exciting field empowers us to make informed decisions, drive successful marketing initiatives, and achieve tangible results.
Creative analytics is not just about collecting data; it’s about understanding the story behind the numbers. By analyzing creative performance, we gain valuable insights into what resonates with our audience, what drives engagement, and what ultimately leads to conversions.
Defining Creative Analytics

Creative analytics is a specialized field that combines marketing analytics with creativity to understand how creative content performs and resonates with audiences. Unlike traditional marketing analytics, which focuses on campaign performance metrics like clicks and conversions, creative analytics delves deeper into the emotional impact, engagement, and overall effectiveness of creative assets.
Role of Data in Creative Performance
Data plays a pivotal role in creative analytics, providing insights into how audiences interact with creative content. Metrics such as dwell time, emotional response, and social media engagement help measure the effectiveness of creative campaigns. Key performance indicators (KPIs) like brand lift and purchase intent track the impact of creative on brand perception and sales.
Benefits of Creative Analytics
Creative analytics empowers marketers to make informed decisions about their creative strategies. By understanding what resonates with audiences, they can optimize campaigns for greater impact. It also allows for A/B testing and multivariate testing, enabling marketers to compare different creative variations and identify the most effective ones.
Examples of Creative Analytics in Successful Campaigns
- Nike’s “Find Your Greatness” campaign used creative analytics to track emotional response and engagement, resulting in a 25% increase in brand awareness.
- Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign leveraged creative analytics to measure social media buzz and purchase intent, leading to a 10% increase in sales.
Metrics for Creative Analytics

Measuring the effectiveness of creative content is crucial in creative analytics. Key metrics provide insights into how well creative campaigns resonate with target audiences, drive engagement, and achieve desired outcomes.
Specific metrics used vary depending on campaign goals and industry. However, some common metrics include:
Engagement Metrics
- Click-Through Rate (CTR):Percentage of people who click on an ad or link.
- Bounce Rate:Percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page.
- Dwell Time:Amount of time spent on a website or specific page.
Conversion Metrics
- Conversion Rate:Percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
- Return on Investment (ROI):Financial benefit gained from a creative campaign compared to its cost.
Brand Metrics
- Brand Awareness:Extent to which a brand is recognized and remembered.
- Brand Perception:Audience’s overall perception and attitude towards a brand.
Tools and Technologies
Creative analytics relies on a range of tools and technologies to collect, analyze, and interpret data. These include:
Data Visualization and Analysis Tools
These tools help visualize and analyze data, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Examples include:
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Google Analytics
Machine Learning and AI Algorithms
Machine learning and AI algorithms can automate data analysis tasks, identify hidden patterns, and make predictions. Examples include:
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Computer vision
- Predictive analytics
Natural Language Processing Tools
NLP tools can analyze text data, extract insights, and generate natural language responses. Examples include:
- Google NLP API
- Amazon Comprehend
- OpenAI GPT-3
Advantages and Limitations
The choice of tools and technologies depends on several factors:
- Data type and size:Different tools are suitable for different data types (e.g., structured, unstructured) and sizes (e.g., small, large).
- Analytical goals:The tools used should align with the specific analytical goals, such as identifying trends, predicting outcomes, or generating insights.
- Resources available:The cost, availability, and expertise required to use different tools should be considered.
Examples
These tools and technologies have been used to drive creative insights and improve creative outcomes in various ways:
- Identifying audience preferences:NLP tools can analyze social media data to identify audience preferences, interests, and demographics.
- Predicting campaign performance:Machine learning algorithms can predict the performance of creative campaigns based on historical data.
- Generating creative ideas:AI-powered tools can generate creative ideas and concepts based on user inputs.
Data Collection and Analysis
Effective creative analytics relies on collecting and analyzing relevant data to gain insights into creative performance and make informed decisions. This process involves a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches, each offering unique perspectives.
Data Collection Methods
Choosing the right data collection method depends on the specific goals and objectives of the analysis. Here’s a summary of common methods along with their strengths, weaknesses, and appropriate use cases:
| Method | Strengths | Weaknesses | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surveys | Quantitative, large sample size, customizable | Bias, social desirability | Measuring audience preferences, feedback |
| Interviews | Qualitative, in-depth insights | Time-consuming, small sample size | Understanding user motivations, experiences |
| Focus Groups | Qualitative, group dynamics | Limited sample size, influenced by group dynamics | Exploring ideas, generating feedback |
| Website Analytics | Quantitative, real-time data | Limited qualitative insights | Tracking website traffic, user behavior |
| Social Media Analytics | Quantitative, engagement metrics | Incomplete data, privacy concerns | Measuring social media performance, audience insights |
Data Analysis Process
Once data is collected, it undergoes a series of steps to extract meaningful insights. The data analysis process typically involves:
- Data Cleaning:Removing errors, inconsistencies, and outliers.
- Data Transformation:Converting data into a format suitable for analysis.
- Data Exploration:Identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
- Data Modeling:Creating statistical or predictive models to explain or predict creative performance.
- Insights Generation:Interpreting the results and extracting actionable insights.
Data Visualization and Interpretation
Data visualization is crucial for presenting insights in a clear and concise manner. Common visualization techniques include:
- Charts and Graphs: Line charts, bar charts, pie charts, scatterplots
- Tables: Organizing data into rows and columns
- Infographics: Combining text, images, and data to convey complex information
When interpreting data, it’s essential to consider context, biases, and limitations. Avoid overgeneralizing or drawing conclusions beyond the scope of the data.
Ethical Considerations
Data collection and analysis must be conducted ethically, respecting privacy, informed consent, and data security. Researchers should adhere to industry guidelines and regulations to ensure the ethical use of data.
Creative Testing: Creative Analytics
Creative testing is an essential part of creative analytics. It allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of your creative assets and make data-driven decisions about your creative strategy.
There are a variety of testing methodologies that can be used for creative testing, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common testing methodologies include:
A/B Testing
A/B testing is a simple but effective way to test two or more versions of a creative to determine which performs better. In an A/B test, you randomly assign users to see one of the two versions of the creative, and then you track which version performs better based on your chosen metrics.
Multivariate Testing
Multivariate testing is a more complex type of testing that allows you to test multiple elements of a creative simultaneously to determine which combination performs best. In a multivariate test, you create a pool of different creative elements (such as headlines, images, and body copy), and then you randomly combine these elements to create a variety of different creative variations.
You then track which variation performs best based on your chosen metrics.
User Experience Testing
User experience testing is a type of testing that evaluates the user experience of a creative to identify areas for improvement. In a user experience test, you ask users to interact with your creative and then you observe their behavior and collect their feedback.
This feedback can then be used to improve the user experience of your creative.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a Creative Testing Campaign
- Define your goals and objectives.
- Choose the right testing methodology.
- Create your creative variations.
- Run your test.
- Analyze your results.
- Make informed decisions about your creative strategy.
Data analysis is an essential part of creative testing. By analyzing your test results, you can identify which creative elements are performing well and which are not. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about your creative strategy.
Optimization and Iteration
Optimization and iteration are essential processes in creative analytics. They allow you to refine your creative based on data and insights, ensuring that it is as effective as possible.
Define Key Metrics for Success
The first step in optimization is to define key metrics for success. These metrics will vary depending on your specific goals, but some common ones include:
- Engagement: This measures how well your creative is capturing attention and interest.
- Conversion: This measures how well your creative is driving desired actions, such as clicks, purchases, or sign-ups.
- Brand recall: This measures how well your creative is building brand awareness and recall.
Use A/B Testing to Compare Different Versions of Creative
Once you have defined your key metrics, you can use A/B testing to compare different versions of your creative. A/B testing is a process of randomly assigning users to see different versions of your creative, and then measuring the results.
This allows you to see which version of your creative performs better.
Analyze Results and Make Data-Driven Decisions
Once you have run your A/B test, you need to analyze the results and make data-driven decisions. This means looking at the data and identifying which version of your creative performed better. You can then use this information to make changes to your creative and improve its performance.
Create a Feedback Loop to Gather Insights from Users
In addition to A/B testing, you can also create a feedback loop to gather insights from users. This can be done through surveys, interviews, or other methods. By gathering feedback from users, you can learn what they like and dislike about your creative, and use this information to make improvements.
Use Qualitative and Quantitative Research to Refine Creative
In addition to feedback from users, you can also use qualitative and quantitative research to refine your creative. Qualitative research methods, such as focus groups and interviews, can help you understand the motivations and behaviors of your target audience. Quantitative research methods, such as surveys and data analysis, can help you measure the effectiveness of your creative.
Continuously Test and Improve to Maximize Impact
Optimization and iteration are ongoing processes. You should continuously test and improve your creative to maximize its impact. By following these steps, you can ensure that your creative is as effective as possible.
Case Studies

Creative analytics has proven its worth in numerous successful implementations. Let’s explore some notable case studies that showcase its value and the lessons learned from them.
Uber: Optimizing Driver Onboarding
Uber utilized creative analytics to enhance its driver onboarding process. By tracking key metrics like conversion rates and completion times, they identified areas for improvement. They tested different creative variations, such as simplifying the onboarding flow and providing personalized guidance, resulting in a significant increase in driver sign-ups and reduced onboarding time.
Emerging Trends in Creative Analytics

Creative analytics is a rapidly evolving field, with new trends emerging all the time. Two of the most exciting trends are the use of AI for content generation and the analysis of consumer behavior through social media data.
AI for Content Generation
AI can be used to generate creative content, such as text, images, and videos. This can save businesses time and money, and it can also help to create more engaging and personalized content.
- For example, AI can be used to generate personalized email campaigns, create social media content, and even write blog posts.
Analysis of Consumer Behavior through Social Media Data
Social media data can be a goldmine of information for businesses. By analyzing this data, businesses can gain insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends.
- This information can be used to create more effective marketing campaigns, develop new products and services, and improve customer service.
– Create a scatter plot visualizing the correlation between AI-generated content length and human-generated content length.
To visualize the correlation between AI-generated content length and human-generated content length, we can create a scatter plot. Each data point on the scatter plot represents a pair of content pieces, one generated by AI and the other by a human.
The x-axis of the scatter plot shows the length of the AI-generated content, and the y-axis shows the length of the human-generated content.
Add a regression line to the scatter plot to show the trend.
To show the trend in the data, we can add a regression line to the scatter plot. The regression line is a straight line that best fits the data points. The slope of the regression line indicates the direction and strength of the correlation between the two variables.
Creative analytics involves exploring data to uncover insights and tell stories. For instance, how tall is link in tiktok ? Creative analytics can help answer this question by analyzing data from multiple sources. It’s a powerful tool for understanding your audience and creating content that resonates with them.
A positive slope indicates a positive correlation, while a negative slope indicates a negative correlation.
Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient to quantify the strength of the correlation.
To quantify the strength of the correlation between the two variables, we can calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient. The Pearson correlation coefficient is a value between -1 and 1. A value of 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, a value of -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, and a value of 0 indicates no correlation.
Visual Storytelling

Data visualization is a powerful tool for communicating complex information in a clear and engaging way. When used effectively, data visualization can help you tell compelling stories that resonate with your audience. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind:
Choosing the Right Visuals
The type of data visualization you choose should be based on the data you have and the story you want to tell. Some common types of data visualizations include:
- Bar charts:Used to compare different categories or values.
- Line charts:Used to show trends over time.
- Scatterplots:Used to show the relationship between two variables.
- Maps:Used to show data geographically.
- Infographics:Used to present complex information in a visually appealing way.
Making Your Visualizations Clear and Concise
Your data visualizations should be easy to understand and interpret. Avoid cluttering your visualizations with too much information. Use clear and concise labels and titles, and make sure your visualizations are visually appealing.
Using Data Visualization to Tell a Story, Creative analytics
Once you have chosen the right visuals and made them clear and concise, you can start to use them to tell a story. Your story should have a clear beginning, middle, and end. Use your data visualizations to support your story and make your points clear.
Creative analytics is a field that combines creativity with data analysis to create new insights. This can be applied to a wide range of areas, such as marketing, product development, and even art. One of the most famous examples of creative analytics is the work of Marcel Duchamp, who used found objects to create new works of art.
By understanding the creative process, we can better understand how to use creative analytics to solve problems and create new opportunities.
Examples of Effective Data Visualizations
Here are a few examples of effective data visualizations:
- The New York Times’ “The Upshot”uses data visualization to tell stories about current events.
- The Washington Post’s “Monkey Cage”uses data visualization to analyze political data.
- The Guardian’s “Data Blog”uses data visualization to explore a wide range of topics.
Social Media Analytics
Creative analytics can be a powerful tool for optimizing social media campaigns. By tracking and analyzing key metrics, marketers can gain insights into what content is performing well, who their target audience is, and how to improve their overall social media strategy.
Measuring Social Media Performance
There are a number of different metrics that can be used to measure social media performance. Some of the most important include:
- Reach: The number of people who see your content.
- Engagement: The number of people who interact with your content, such as by liking, commenting, or sharing it.
- Conversion: The number of people who take a desired action, such as clicking on a link or making a purchase.
By tracking these metrics, marketers can get a better understanding of how their social media campaigns are performing and identify areas for improvement.
Strategies for Optimizing Social Media Campaigns
There are a number of different strategies that marketers can use to optimize their social media campaigns. Some of the most effective include:
- Creating high-quality content: The content you post on social media should be interesting, engaging, and relevant to your target audience.
- Using social media analytics to track your progress: By tracking key metrics, you can identify what content is performing well and what content is not. This information can then be used to improve your content strategy.
- Experimenting with different strategies: There is no one-size-fits-all approach to social media marketing. Experiment with different strategies to see what works best for your brand.
By following these tips, marketers can use creative analytics to optimize their social media campaigns and achieve better results.
Influencer Marketing

Creative analytics plays a crucial role in influencer marketing, enabling brands to assess the effectiveness of their campaigns and optimize their strategies.
To evaluate influencer effectiveness, brands can use metrics such as engagement rates, reach, and website traffic. They can also track conversions and sales generated through influencer partnerships.
ROI Measurement
- Conversion tracking:Measuring the number of conversions (e.g., purchases, sign-ups) generated through influencer campaigns.
- Sales tracking:Tracking the amount of sales revenue directly attributed to influencer partnerships.
- Cost-per-acquisition (CPA):Calculating the cost of acquiring a customer through influencer marketing by dividing the total cost of the campaign by the number of conversions generated.
Attribution Modeling

Attribution modeling assigns credit for conversions and other marketing outcomes to different marketing touchpoints. It helps marketers understand the effectiveness of their campaigns and allocate their budgets more efficiently.There are different attribution models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Some of the most common models include:
- Last-click attribution:This model assigns all credit to the last touchpoint before a conversion.
- First-click attribution:This model assigns all credit to the first touchpoint in a conversion path.
- Linear attribution:This model assigns equal credit to all touchpoints in a conversion path.
- Time-decay attribution:This model assigns more credit to touchpoints that occur closer to a conversion.
- Position-based attribution:This model assigns more credit to touchpoints that occur at the beginning or end of a conversion path.
The choice of attribution model depends on the specific goals of a marketing campaign. For example, if a marketer is interested in understanding the impact of a particular ad campaign, they might use a last-click attribution model. If a marketer is interested in understanding the overall effectiveness of their marketing efforts, they might use a linear attribution model.Attribution modeling can be challenging, especially when there are multiple touchpoints in a conversion path.
However, by understanding the different attribution models and their advantages and disadvantages, marketers can make informed decisions about how to attribute credit for conversions.
Challenges of Attribution Modeling
There are a number of challenges associated with attribution modeling, including:
- Data accuracy:Attribution models rely on data from multiple sources, which can be inaccurate or incomplete.
- Cross-device tracking:Consumers often use multiple devices to interact with brands, which can make it difficult to track their conversion paths.
- Ad blocking:Ad blockers can prevent marketers from tracking conversions, which can lead to inaccurate attribution data.
Best Practices for Attribution Modeling
There are a number of best practices that marketers can follow to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of their attribution modeling, including:
- Use multiple attribution models:No single attribution model is perfect, so it’s important to use multiple models to get a more complete picture of your marketing performance.
- Test different attribution models:Experiment with different attribution models to see which one works best for your specific goals.
- Use a data-driven approach:Use data to inform your attribution decisions. This includes data on your target audience, your marketing campaigns, and your conversion rates.
- Be transparent:Be transparent about the attribution model you’re using and how it affects your marketing decisions.
Ethical Considerations

As creative analytics gains prominence, it’s imperative to address the ethical considerations associated with its use.
One key ethical concern is potential biasin data collection and analysis. Algorithms used in creative analytics may inadvertently perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair or inaccurate results. For instance, if an algorithm is trained on a dataset that underrepresents certain demographic groups, its predictions may be skewed towards those groups that are overrepresented in the data.
Privacy Concerns
Creative analytics often involves collecting and analyzing personal data, such as user behavior and preferences. This raises concerns about privacy and data protection. It’s crucial to ensure that data is collected and used ethically, with proper consent and transparency.
FAQ
What is the difference between creative analytics and traditional marketing analytics?
Creative analytics focuses specifically on measuring and analyzing the performance of creative content, such as ads, social media posts, and website design, while traditional marketing analytics encompasses a broader range of metrics related to marketing campaigns, including website traffic, lead generation, and sales.
How can creative analytics help improve creative decision-making?
Creative analytics provides data-driven insights into what creative elements are most effective, allowing marketers to make informed decisions about their creative strategies. By understanding what resonates with their audience, they can optimize their campaigns for maximum impact.
What are some examples of how creative analytics has been used to drive successful marketing campaigns?
Numerous companies have leveraged creative analytics to improve their marketing campaigns. For example, Netflix uses A/B testing to optimize its movie thumbnails, resulting in a significant increase in click-through rates. Coca-Cola used social media analytics to identify and engage with key influencers, leading to a substantial boost in brand awareness.