Are We Getting a Tropical Storm? The question hangs in the air, a silent whisper of anxiety and anticipation. Tropical storms, with their swirling winds and torrential rain, are a force of nature that can disrupt lives and reshape landscapes.
These powerful weather systems are born from the warm waters of the tropics, fueled by the energy of the sun. Their unpredictable paths and intensifying strength have captivated scientists and residents alike, prompting questions about their formation, potential impacts, and the preparations necessary to weather their wrath.
Understanding the science behind tropical storms, analyzing current weather patterns, and preparing for their potential arrival are crucial steps in mitigating their devastating effects. From the intricacies of their formation to the importance of emergency preparedness, we delve into the world of tropical storms, exploring their origins, their potential impacts, and the steps we can take to ensure our safety.
Understanding Tropical Storms: Are We Getting A Tropical Storm

Tropical storms are powerful weather events that can cause significant damage and disruption. They are characterized by strong winds, heavy rainfall, and the potential for flooding. Understanding the nature and formation of tropical storms is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Defining Tropical Storms
Tropical storms are rotating weather systems that form over warm ocean waters. They are classified as storms with sustained wind speeds ranging from 39 to 73 miles per hour (63 to 118 kilometers per hour). These storms are typically accompanied by heavy rainfall, high waves, and storm surges.
The Formation Process of Tropical Storms
Tropical storms develop over warm ocean waters, typically in regions with temperatures above 80°F (26.5°C). The process involves several key factors:
- Warm Ocean Waters:Tropical storms require warm ocean waters to provide the necessary heat and moisture for their formation and development. The warm waters act as a fuel source for the storm.
- Low-Pressure System:A low-pressure system is essential for the formation of a tropical storm. The low pressure creates an area of upward airflow, which draws in warm, moist air from the surrounding ocean.
- Coriolis Effect:The Coriolis effect, caused by the Earth’s rotation, causes the air to rotate around the low-pressure center. This rotation creates the characteristic swirling pattern of a tropical storm.
- Lack of Wind Shear:Strong wind shear, which is a change in wind speed or direction with altitude, can disrupt the formation of a tropical storm. A lack of wind shear allows the storm to organize and intensify.
Examples of Tropical Storm Names and Their Origins
Tropical storms are given names to help with identification and communication. The naming conventions vary by region, with each region having its own list of names.
- North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific:The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) maintains a list of names for tropical storms in the North Atlantic and Eastern Pacific. The names are chosen alphabetically, alternating between male and female names.
- Western Pacific:The WMO also maintains a list of names for tropical storms in the Western Pacific. The names are chosen from a list of Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese names.
Potential Impacts of Tropical Storms
Tropical storms can have significant impacts on various regions, including:
- Coastal Areas:Coastal areas are particularly vulnerable to the effects of tropical storms, which can bring high waves, storm surges, and flooding. Storm surges are a rise in sea level caused by the storm’s winds pushing water towards the shore.
- Inland Areas:Even inland areas can experience significant impacts from tropical storms. Heavy rainfall can lead to flooding, landslides, and other hazards. The strong winds associated with tropical storms can also cause damage to infrastructure and trees.
- Agriculture:Tropical storms can have a devastating impact on agriculture, causing crop damage, livestock losses, and disruptions to food production.
Current Weather Conditions
Staying informed about current weather patterns is crucial when it comes to potential tropical storm development. This section will delve into the latest weather conditions, satellite imagery analysis, potential areas of tropical storm development, and forecasts from meteorological agencies.
Satellite Imagery Analysis
Satellite imagery plays a vital role in monitoring weather patterns and identifying potential tropical storm development. Meteorologists use various types of satellite imagery, including infrared and visible imagery, to analyze cloud formations, wind patterns, and other key indicators. Infrared imagery reveals cloud top temperatures, which can indicate the presence of thunderstorms and potential for intensification.
Visible imagery provides a visual representation of cloud cover and movement.
Potential Areas of Tropical Storm Development
Based on current satellite imagery and weather patterns, meteorologists identify specific areas where tropical storm development is more likely. These areas are often characterized by warm ocean temperatures, low wind shear, and atmospheric instability. For example, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) regularly issues advisories and forecasts regarding potential tropical storm development in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Eastern Pacific basins.
Weather Forecasts and Advisories
Meteorological agencies around the world provide regular weather forecasts and advisories to keep the public informed about potential tropical storm development. These agencies utilize advanced computer models and satellite data to predict the path, intensity, and potential impacts of developing storms.
The NHC, for instance, issues tropical weather outlooks, which highlight areas with a higher chance of tropical storm formation.
The weather forecast is looking a little stormy, and it’s always best to be prepared. If you’re concerned about a potential tropical storm, you might want to consider applying for a FEMA storm shelter grant. Learn more about how to apply for a FEMA storm shelter grant and make sure you’re protected no matter what the weather brings.
Remember, it’s always better to be safe than sorry, and a storm shelter can provide peace of mind during a turbulent storm.
Predicted Path and Intensity of Developing Tropical Storms
Once a tropical storm develops, meteorological agencies closely monitor its movement and intensity. Forecasts are issued regularly, providing updates on the predicted path and intensity of the storm. These forecasts consider various factors, including wind patterns, ocean currents, and atmospheric conditions.
For example, the NHC provides detailed track forecasts and intensity projections for named tropical storms and hurricanes.
Preparation and Safety Measures

Tropical storms can pose significant threats to life and property. Therefore, proactive preparation and adherence to safety measures are crucial to minimize risks and ensure well-being during such events. This section Artikels essential steps and resources to prepare for a tropical storm.
Emergency Supplies
Having an emergency kit readily available is essential for any tropical storm event. It should include essential supplies to sustain you and your family for several days in case of power outages or disruptions to services. Here’s a table outlining essential emergency supplies for a tropical storm:
| Category | Items |
|---|---|
| Water | One gallon of water per person per day for at least three days |
| Food | Non-perishable food items, such as canned goods, energy bars, and dried fruit |
| First Aid | First aid kit with bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, and other essential medical supplies |
| Shelter | Tarp, duct tape, and rope for covering windows and doors |
| Communication | Battery-powered radio, extra batteries, and a whistle for signaling |
| Lighting | Flashlights, lanterns, and extra batteries |
| Other | Cash, copies of important documents, and a map of the area |
Home and Business Preparation
Preparing your home or business for a potential tropical storm involves taking proactive measures to mitigate potential damage and ensure safety. Here’s a checklist for preparing your property:
- Secure Outdoor Objects:Secure or bring inside loose objects that could be blown away by strong winds, such as patio furniture, grills, and trash cans.
- Trim Trees and Branches:Trim trees and branches that are close to your house or power lines to prevent them from falling during the storm.
- Protect Windows and Doors:Cover windows and doors with storm shutters or plywood to protect them from flying debris.
- Fill Bathtubs and Containers:Fill bathtubs and large containers with water for flushing toilets and other essential uses in case of water supply disruptions.
- Charge Electronics:Charge all electronic devices, such as cell phones, laptops, and flashlights, to ensure they are ready in case of power outages.
- Prepare a Communication Plan:Establish a communication plan with family members and colleagues, including designated meeting points and contact numbers.
- Stock Up on Fuel:Fill up your car’s gas tank and have extra gasoline on hand for generators or other vehicles.
- Review Insurance Policies:Review your insurance policies to ensure you have adequate coverage for potential damage from a tropical storm.
Evacuation Procedures and Safe Shelter Options
Evacuation orders are issued when authorities deem it necessary to ensure public safety during a tropical storm. It is crucial to follow these orders promptly and seek safe shelter. Here are some essential points to consider:
- Stay Informed:Stay informed about evacuation orders and warnings through official sources such as local news, radio, and emergency alerts.
- Plan Evacuation Routes:Plan multiple evacuation routes and have a designated meeting point for your family.
- Safe Shelter Options:Seek shelter in designated evacuation centers, hotels, or with family or friends in a safe location outside the storm’s path.
- Secure Your Home:Before evacuating, secure your home by closing and locking windows and doors, turning off water and gas, and disconnecting electrical appliances.
Communication Methods and Resources
Maintaining communication during a tropical storm is crucial for receiving updates, coordinating with authorities, and staying connected with loved ones. Here are some communication methods and resources:
- Battery-Powered Radio:A battery-powered radio is essential for receiving emergency broadcasts and weather updates.
- Cell Phones:Ensure your cell phone is charged and have a backup battery or charger.
- Social Media:Follow official government and emergency agencies on social media for updates and instructions.
- Text Messaging:Text messaging often works even when phone calls are unavailable.
- Satellite Phones:Consider using satellite phones for communication if cellular service is unavailable.
Historical Context
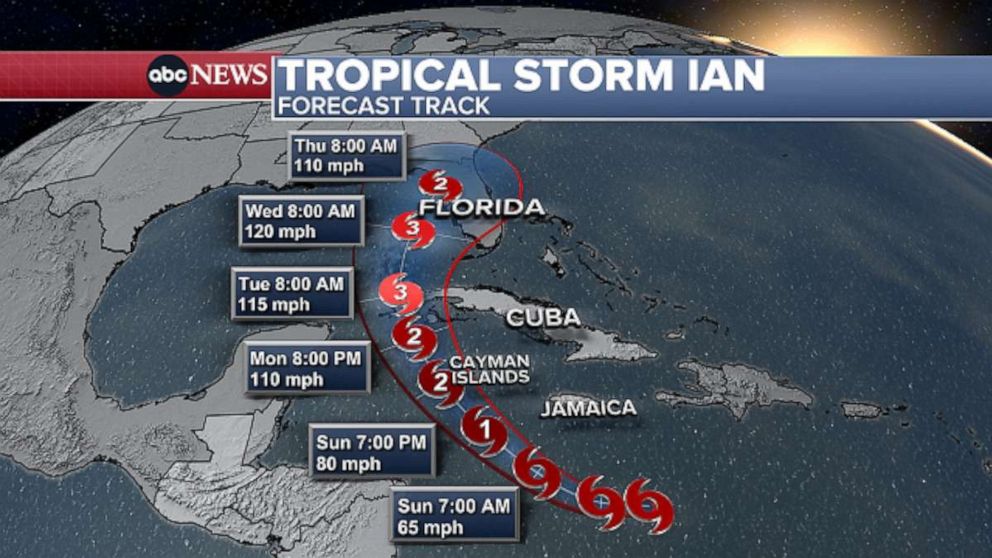
Understanding the historical context of tropical storms is crucial for appreciating their evolving nature and the challenges they pose. By examining the frequency, intensity, and impact of these storms over time, we can gain insights into the long-term trends and the role of climate change in shaping their behavior.
Frequency and Intensity of Tropical Storms
Analyzing historical data reveals significant variations in the frequency and intensity of tropical storms over the past decades. While the overall number of storms may fluctuate, there’s evidence suggesting an increase in the proportion of intense hurricanes, particularly in certain regions.
- The Atlantic hurricane season, for example, has witnessed an increase in the number of major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher) since the 1980s. This trend is linked to factors such as warmer sea surface temperatures and changes in atmospheric circulation patterns.
- The Pacific Ocean has also experienced fluctuations in tropical storm activity, with periods of heightened activity followed by relative calm. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, a natural climate pattern, plays a significant role in influencing the frequency and intensity of tropical storms in this region.
Climate Change and Tropical Storm Activity
The influence of climate change on tropical storm activity is a subject of ongoing research and debate. While there is a strong scientific consensus that global warming is contributing to a rise in sea levels and warmer ocean temperatures, the precise impact on tropical storms remains complex.
- Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for storm development and intensification. This can lead to stronger hurricanes with higher wind speeds and heavier rainfall.
- Climate change may also influence atmospheric circulation patterns, potentially altering the paths and frequency of tropical storms. For example, some studies suggest that climate change could lead to more frequent and intense hurricanes in the Atlantic basin.
Historical Examples of Significant Tropical Storms
Throughout history, numerous tropical storms have left indelible marks on human civilization, causing widespread devastation and altering the course of history. These events serve as stark reminders of the immense power of nature and the importance of preparedness.
- The Great Hurricane of 1780, also known as the “San Calixto” hurricane, is considered one of the deadliest hurricanes in recorded history. It devastated the Caribbean islands, claiming an estimated 22,000 lives.
- Hurricane Katrina in 2005, a Category 3 hurricane that struck the Gulf Coast of the United States, caused catastrophic damage to New Orleans and surrounding areas. The storm’s impact highlighted the vulnerability of coastal communities to extreme weather events.
- Typhoon Hagibis in 2019, a powerful typhoon that hit Japan, resulted in widespread flooding and landslides, causing significant damage and loss of life. The storm’s intensity and impact underscored the increasing threat posed by extreme weather events in Asia.
Evolution of Storm Prediction and Forecasting Technology
Advancements in technology have revolutionized our ability to predict and forecast tropical storms, providing valuable lead time for preparation and mitigation efforts.
- The development of weather satellites has significantly improved our understanding of storm formation and movement. Satellites provide continuous monitoring of storm systems, allowing meteorologists to track their development and potential impact.
- Computer models, powered by supercomputers, have become increasingly sophisticated in simulating the behavior of tropical storms. These models can predict storm paths, intensity, and potential impacts with greater accuracy.
- Improved communication technologies, such as the internet and social media, enable rapid dissemination of storm warnings and advisories to the public. This helps ensure that people have timely information to make informed decisions about safety and preparedness.
Impact on Human Life and Environment
Tropical storms, while a natural phenomenon, have a significant impact on human life and the environment. Their destructive power can disrupt economies, damage infrastructure, and pose risks to human health.
Economic and Social Consequences
Tropical storms cause substantial economic and social damage. The destruction of property, businesses, and infrastructure leads to significant financial losses. Disruptions to transportation, communication, and power supply further exacerbate these losses. The social consequences are equally profound. Displacement of populations, loss of livelihoods, and disruption of daily life can have long-lasting impacts on communities.
Environmental Impact
Tropical storms have a significant impact on ecosystems and infrastructure. * Coastal Erosion:Powerful waves and storm surges can cause extensive coastal erosion, damaging beaches, dunes, and coastal ecosystems.
Flooding
Heavy rainfall and storm surges lead to widespread flooding, inundating homes, businesses, and agricultural lands.
Damage to Infrastructure
Storms can damage roads, bridges, power lines, and other infrastructure, disrupting transportation, communication, and essential services.
Pollution
Storm runoff can carry pollutants, including sewage, chemicals, and debris, into waterways, contaminating water sources and harming aquatic life.
Disease Outbreaks and Health Risks
Following a tropical storm, there is an increased risk of disease outbreaks and health problems. * Waterborne Diseases:Contaminated water sources can lead to outbreaks of waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid fever, and dysentery.
Respiratory Infections
Mold growth and poor air quality following flooding can trigger respiratory problems.
Mental Health Issues
The trauma and stress of a storm can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Long-Term Recovery Efforts, Are we getting a tropical storm
The recovery process after a major storm is a long and challenging endeavor.
| Phase | Activities |
|---|---|
| Immediate Response | Search and rescue operations, providing emergency medical care, distributing food and water, and securing temporary shelter. |
| Short-Term Recovery | Clearing debris, restoring essential services, repairing damaged infrastructure, and providing temporary housing. |
| Long-Term Recovery | Reconstruction of damaged buildings and infrastructure, economic revitalization, community development, and addressing long-term health and mental health needs. |
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A tropical storm is a rotating storm system with maximum sustained wind speeds of 39 to 73 miles per hour (mph). When wind speeds reach 74 mph or higher, it is classified as a hurricane.
How long does a tropical storm typically last?
The duration of a tropical storm can vary greatly, ranging from a few days to several weeks. Factors such as wind shear, ocean temperatures, and other atmospheric conditions influence their lifespan.
Are tropical storms becoming more frequent or intense due to climate change?
Scientific evidence suggests that climate change may be contributing to an increase in the intensity and frequency of some tropical storms. However, it’s important to note that attributing any specific storm to climate change is complex.
What are some tips for staying safe during a tropical storm?
Stay informed about weather advisories, have a plan for evacuation if necessary, secure loose objects outdoors, and have an emergency kit readily available.