Another word for creative thinking is lateral thinking, which involves solving problems indirectly and creatively by using unconventional approaches. It is a skill that can be learned and improved with practice, and it is essential for success in many different fields.
This article will explore the definition, techniques, and benefits of creative thinking, and provide tips for developing this important skill.
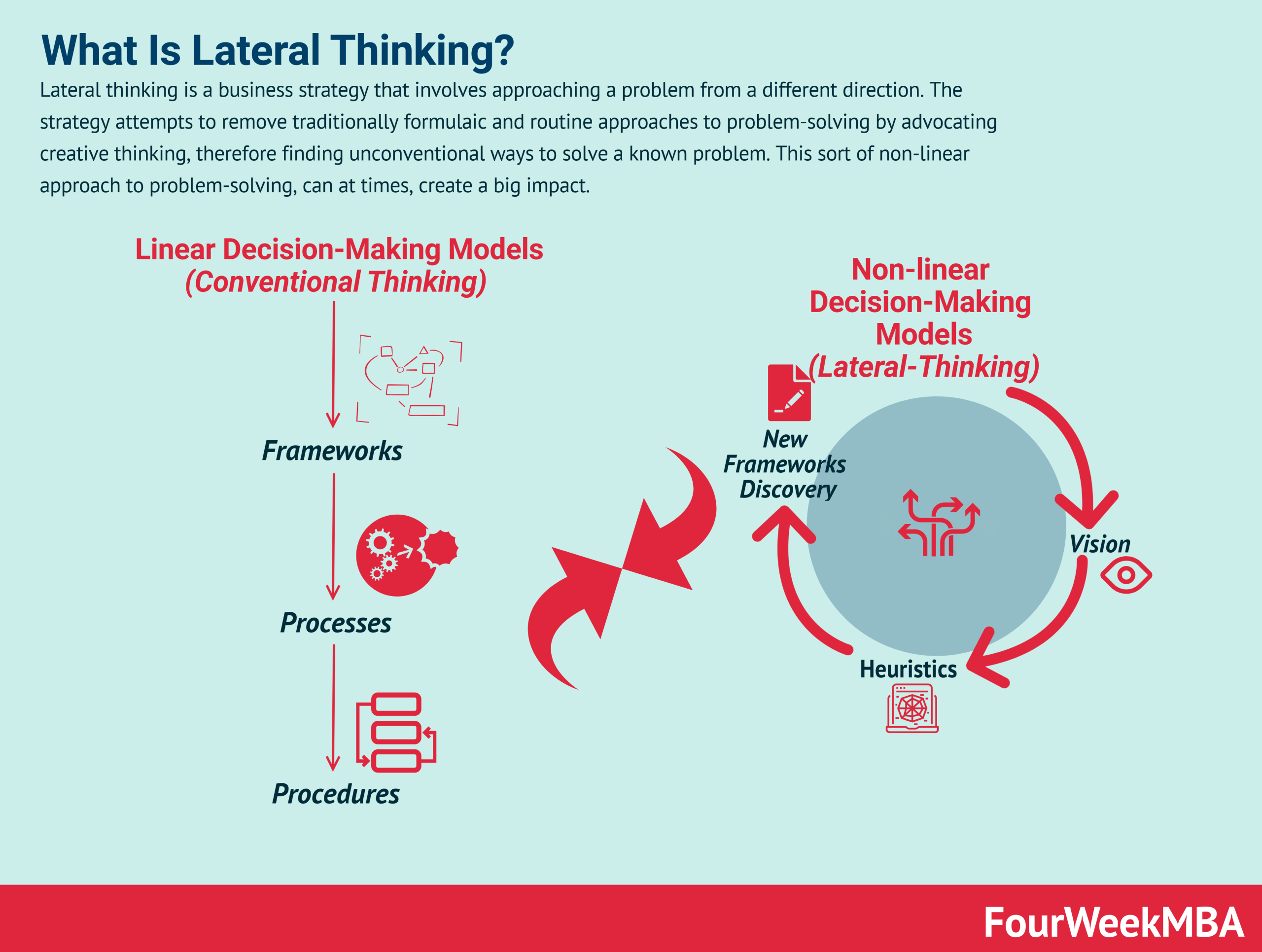
Lateral thinking is a problem-solving technique that involves thinking outside the box. It is based on the idea that there is more than one way to solve a problem, and that the best solution is not always the most obvious one.
Lateral thinking techniques can be used to solve problems in any field, from business to science to art.
Origin and Etymology: Another Word For Creative Thinking
The term “creative thinking” has its roots in the Latin word “creare,” meaning “to produce” or “to bring into being.” The concept of creativity has been explored throughout history by philosophers, artists, and scientists, each contributing to its evolving definition and understanding.
Key Historical Figures
- Plato: Viewed creativity as a divine inspiration, a gift from the gods.
- Aristotle: Emphasized the importance of observation, experience, and imagination in the creative process.
- Leonardo da Vinci: Renowned for his innovative thinking and emphasis on experimentation and observation.
- Francis Bacon: Introduced the concept of “inductive reasoning” as a method for generating new ideas.
Synonyms and Related Concepts
The concept of creative thinking encompasses a broad spectrum of terms and ideas that share similar characteristics. Understanding these synonyms and related concepts helps us appreciate the multifaceted nature of creativity.
Some common synonyms for creative thinking include:
- Innovative thinking: Generating new and original ideas.
- Lateral thinking: Approaching problems from unconventional angles.
- Divergent thinking: Exploring multiple perspectives and possibilities.
- Out-of-the-box thinking: Breaking away from established patterns.
Related concepts that complement creative thinking include:
- Problem-solving: Applying creativity to find solutions.
- Innovation: Implementing creative ideas into practical applications.
- Design thinking: Human-centered approach to problem-solving.
- Critical thinking: Analyzing and evaluating information.
While these terms overlap in some ways, they each emphasize specific aspects of the creative process. Understanding these nuances allows us to leverage different approaches to enhance our creative thinking capabilities.
Core Characteristics

Creative thinking is distinguished by a set of fundamental attributes that define its unique nature. These characteristics encompass the cognitive processes, traits, and abilities that enable individuals to generate novel and innovative ideas.
The cognitive processes involved in creative thinking include:
- Divergent thinking:The ability to generate multiple and diverse ideas from a single stimulus.
- Convergent thinking:The ability to focus and select the most appropriate idea from a range of possibilities.
- Lateral thinking:The ability to approach problems from unconventional angles and break away from established patterns.
- Associative thinking:The ability to connect seemingly unrelated concepts and ideas to create new insights.
Traits associated with creative thinking include:
- Openness to experience:A willingness to embrace new ideas and perspectives.
- Curiosity:A desire to explore and understand the world.
- Flexibility:The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and think outside of the box.
- Risk-taking:A willingness to venture into uncharted territory and try new approaches.
These core characteristics work together to enable creative thinkers to generate innovative solutions, break away from conventional thinking, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and progress.
Different Forms of Creative Thinking

Creative thinking is not a one-size-fits-all process. It can manifest in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
Here are some of the most common forms of creative thinking:
Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking involves generating multiple solutions or ideas for a given problem. It is characterized by a focus on quantity rather than quality, with the goal of exploring a wide range of possibilities.
For example, a designer brainstorming ideas for a new product might use divergent thinking to come up with as many different concepts as possible, without judging their feasibility or practicality.
Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking, on the other hand, involves narrowing down a range of possibilities to find a single, best solution. It is characterized by a focus on quality rather than quantity, with the goal of identifying the most effective or appropriate option.
For example, a scientist conducting an experiment might use convergent thinking to analyze data and identify the most likely explanation for a particular phenomenon.
Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking involves approaching a problem from an unconventional or indirect angle. It often involves breaking away from established patterns of thought and challenging assumptions.
A different way of saying creative thinking is “creative counseling”. Creative counseling is a special type of therapy that helps people with their creative thinking. If you’re looking for a therapist who can help you with your creative thinking, you might want to consider creative counseling fort collins.
This type of therapy can help you to develop your creative skills and to use them to solve problems and achieve your goals.
For example, an entrepreneur trying to develop a new business might use lateral thinking to come up with an innovative solution that no one else has considered.
Associative Thinking
Associative thinking involves making connections between seemingly unrelated ideas or concepts. It is characterized by a focus on finding similarities and patterns, often leading to unexpected or innovative solutions.
For example, a writer might use associative thinking to come up with new ideas for a story by exploring connections between different characters, events, or settings.
Importance and Benefits
Creative thinking plays a vital role in various aspects of life, from personal growth to professional success. It enhances our problem-solving abilities, fosters innovation, and contributes to our overall well-being.
Problem-Solving
Creative thinking empowers us to approach problems from unconventional perspectives. By breaking free from conventional solutions, we can generate novel ideas and strategies that lead to effective resolutions.
Innovation
Creativity is the driving force behind innovation. It enables us to challenge existing norms, explore new possibilities, and develop groundbreaking products, services, and ideas that shape the future.
Personal Growth
Engaging in creative thinking fosters personal growth and development. It encourages us to embrace new experiences, question assumptions, and expand our knowledge and perspectives, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling and enriching life.
– Identify strategies and techniques for developing and enhancing creative thinking skills
Enhancing creative thinking skills is crucial for innovation, problem-solving, and personal growth. Various strategies and techniques can help develop these skills, leading to improved ideation, problem-solving abilities, and overall cognitive flexibility.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming involves generating ideas in a group setting. It encourages participants to share their thoughts freely and build upon each other’s ideas. Some variations of brainstorming include:
- Round-robin brainstorming:Participants take turns generating ideas, building on each other’s contributions.
- Brainwriting:Participants write down ideas individually, then share and discuss them.
Freewriting
Freewriting is a technique where individuals write continuously for a set period without stopping or censoring their thoughts. It helps overcome writer’s block and generate a stream of ideas.
- Automatic writing:Participants write continuously for a set period without stopping or censoring their thoughts.
- Stream of consciousness writing:Participants write whatever comes to mind without worrying about grammar or structure.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual representation of ideas, using branches and connections to show relationships and associations. It helps organize thoughts, identify patterns, and generate new ideas.
Obstacles to Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is not always easy. There are many common barriers or challenges that can hinder our ability to think creatively. These include:
Cognitive Biases, Another word for creative thinking
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts that can lead us to make errors in judgment. They can also prevent us from seeing things from different perspectives, which is essential for creative thinking. Some common cognitive biases include:
- Confirmation bias: The tendency to seek out information that confirms our existing beliefs.
- Groupthink: The tendency to conform to the opinions of the group, even if we don’t agree with them.
- Availability heuristic: The tendency to judge the likelihood of an event based on how easily we can remember examples of it.
There are a number of strategies that we can use to mitigate the effects of cognitive biases. These include:
- Being aware of our own biases.
- Seeking out information that challenges our existing beliefs.
- Considering different perspectives.
Lack of Diversity and Inclusion
A lack of diversity and inclusion can also hinder creative thinking. When we are surrounded by people who are similar to us, we are less likely to be exposed to new ideas and perspectives. This can lead to a lack of creativity and innovation.
To foster creative environments and generate innovative ideas, it is important to promote diversity and inclusion. This means creating a workplace or learning environment where everyone feels welcome and respected, regardless of their background or beliefs.
Applications in Various Fields
Creative thinking is not limited to specific domains but finds applications across diverse fields and industries. Its value lies in generating innovative solutions, driving progress, and fostering adaptability.
Industries that highly value creative thinking include:
- Technology:Creative thinking drives innovation in product design, software development, and problem-solving.
- Business and Management:Creative thinking helps in developing strategies, marketing campaigns, and organizational structures.
- Design and Arts:Creative thinking is essential for creating innovative designs, artworks, and architectural wonders.
- Education:Creative thinking fosters problem-solving, critical thinking, and engagement in students.
- Healthcare:Creative thinking leads to new treatments, medical devices, and patient-centered care approaches.
Examples of Innovative Solutions
Here are some examples of innovative solutions and breakthroughs driven by creative thinking:
- Post-it Notes:Created by a scientist who accidentally discovered the adhesive properties of a new material.
- Self-driving Cars:Developed through advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Social Media:Created to connect people online, fostering communication and information sharing.
- mRNA Vaccines:A revolutionary technology that uses messenger RNA to induce an immune response against diseases.
Provide specific examples of how creativity can be integrated into different subject areas, such as math, science, and language arts.
Creativity is not just for artists and musicians. It is a skill that can be applied to any subject area, from math and science to language arts and social studies. When students are given the opportunity to be creative in their learning, they are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and successful.
Here are a few specific examples of how creativity can be integrated into different subject areas:
Math
- Students can create their own math problems and solve them.
- Students can use math to create art projects, such as tessellations or geometric sculptures.
- Students can use math to design and build structures, such as bridges or towers.
Science
- Students can design and conduct their own science experiments.
- Students can create models or diagrams to explain scientific concepts.
- Students can write songs or poems about science topics.
Language Arts
- Students can write creative stories, poems, and plays.
- Students can create their own newspapers, magazines, or websites.
- Students can use language arts to explore their own creativity and express themselves.
Impact on Society
Creative thinking has a profound impact on society and culture, driving innovation, progress, and societal well-being. It is the engine that fuels advancements in various fields, from technology to art to science.
Role in Innovation and Progress
- Creative thinking leads to the development of new ideas, products, and processes that improve our lives.
- For example, the invention of the computer, the internet, and smartphones has revolutionized communication, information access, and global connectivity.
Relationship with Economic Growth
Creative thinking is closely linked to economic growth. Societies that foster creativity and innovation tend to have stronger economies.
- Creative industries, such as design, media, and entertainment, are major contributors to economic output and job creation.
- Investment in research and development (R&D) drives innovation and leads to new technologies and products that boost productivity and economic competitiveness.
Potential Negative Impacts
While creative thinking is generally beneficial, it can also have negative consequences if not used responsibly.
- It can contribute to the development of harmful technologies, such as weapons of mass destruction.
- It can be used to spread misinformation or propaganda, which can have damaging effects on society.
Creative Thinking and Technology
Creative thinking and technological advancements are intertwined in a dynamic relationship. Technology can both enhance and hinder creative processes, depending on how it is used.
Technology as an Enabler of Creativity
Technology provides powerful tools that can facilitate creative expression and exploration. Digital art software, for instance, allows artists to experiment with different colors, textures, and effects, expanding their creative possibilities. Computer-aided design (CAD) software enables engineers and architects to visualize and iterate on complex designs, fostering innovation.
Technology as a Potential Barrier to Creativity
On the other hand, technology can also present challenges to creative thinking. Constant digital distractions, such as social media notifications and email alerts, can fragment attention and disrupt the flow of creative ideas. Over-reliance on technology can lead to a lack of hands-on experience and reduced engagement with the physical world, which can stifle creativity.
Measurement and Assessment
Measuring and assessing creative thinking abilities is a complex task. However, several methods and tools can provide valuable insights into an individual’s creative potential.
Divergent Thinking Tests
Divergent thinking tests measure an individual’s ability to generate multiple unique and original ideas. They typically involve tasks such as brainstorming, idea generation, and open-ended questions. These tests assess an individual’s fluency, flexibility, and originality in their thinking.
Convergent Thinking Tests
Convergent thinking tests measure an individual’s ability to find a single, correct answer to a problem. They typically involve tasks such as solving puzzles, riddles, and logic problems. These tests assess an individual’s ability to focus and concentrate on a specific problem and to use logical reasoning to find a solution.
Problem-Solving Tasks
Problem-solving tasks assess an individual’s ability to identify and solve problems in a creative and innovative way. They typically involve tasks such as designing a solution to a specific problem, developing a plan of action, or overcoming a challenge. These tasks assess an individual’s ability to think critically, generate ideas, and find practical solutions.
Idea Generation Exercises
Idea generation exercises assess an individual’s ability to generate a large number of ideas in a short amount of time. They typically involve tasks such as brainstorming, mind mapping, or freewriting. These exercises assess an individual’s ability to think fluently and flexibly and to generate original and unique ideas.
Challenges and Limitations of Creative Thinking Assessments
While these assessments can provide valuable insights into an individual’s creative thinking abilities, they also have certain challenges and limitations.
- Cultural Bias:Creative thinking assessments can be culturally biased, meaning they may favor individuals from certain cultural backgrounds or with specific experiences.
- Reliability:The reliability of creative thinking assessments can be low, meaning they may not produce consistent results over time.
- Validity:The validity of creative thinking assessments can be difficult to establish, meaning it may be unclear whether they accurately measure what they claim to measure.
Overcoming the Challenges and Limitations of Creative Thinking Assessments
Despite these challenges and limitations, creative thinking assessments can still be useful tools for informing and supporting creative thinking development. To overcome the challenges and limitations, it is important to:
- Use multiple assessments to get a more comprehensive view of an individual’s creative thinking abilities.
- Be aware of the potential for cultural bias and take steps to mitigate it.
- Use assessments in conjunction with other measures of creativity, such as portfolios or performance tasks.
Ethical Considerations in Assessing Creative Thinking Abilities
When assessing creative thinking abilities, it is important to consider the ethical implications. These include:
- Confidentiality:Maintaining the confidentiality of assessment results is essential to protect individuals’ privacy.
- Informed Consent:Individuals should be informed about the purpose and use of the assessment before they participate.
- Fairness:Assessments should be fair and equitable for all individuals, regardless of their background or abilities.
Case Studies and Examples
Creative thinking is not just a theoretical concept; it is a practical skill that can be applied in various fields and lead to tangible outcomes. Here are a few case studies and real-world examples that demonstrate the power of creative thinking:
Google’s “20% Time” Policy
Google implemented a policy where employees were given 20% of their work time to pursue personal projects and explore innovative ideas outside their regular job responsibilities. This policy led to the development of several successful products, including Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Earth.
IDEO’s Design Thinking Process
IDEO, a design and innovation firm, developed a structured process called “design thinking” that emphasizes empathy, experimentation, and iteration. This process has been used to create innovative products and services for clients in various industries, such as healthcare, education, and consumer electronics.
LEGO’s Open Innovation Model
LEGO, the toy company, has embraced open innovation by collaborating with external designers and users to generate new ideas and products. This approach has led to the creation of successful product lines, such as LEGO Mindstorms and LEGO Education.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the following lessons:
- Providing time and space for creative exploration can lead to groundbreaking innovations.
- Structured processes can facilitate creative thinking and enhance its outcomes.
- Collaboration and open innovation can bring fresh perspectives and lead to novel solutions.
– Explore the perspectives and contributions of different disciplines to the study of creative thinking.
Creative thinking is a complex process that has been studied by a variety of disciplines, including psychology, neuroscience, education, and philosophy. Each discipline has its own unique perspective on creative thinking, and this has led to a rich and diverse body of research.
One of the most important contributions of psychology to the study of creative thinking has been the development of theories about the creative process. Psychologists have identified a number of different stages in the creative process, including problem finding, problem solving, and evaluation.
They have also studied the role of individual differences in creativity, and have found that certain personality traits, such as openness to experience and tolerance for ambiguity, are associated with higher levels of creativity.
Neuroscience has also made significant contributions to the study of creative thinking. Neuroscientists have used brain imaging techniques to identify the neural networks that are involved in creative thinking. They have found that creative thinking is associated with activity in a number of different brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex, the temporal lobes, and the cerebellum.
Education has also played a role in the study of creative thinking. Educators have developed a number of different teaching methods that are designed to foster creativity in students. These methods include problem-based learning, project-based learning, and cooperative learning.
The study of creative thinking is a complex and interdisciplinary field. By combining the perspectives of different disciplines, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of this important process.
Convergence and divergence of ideas from different disciplines
The different disciplines that study creative thinking have both converged and diverged in their ideas about the nature of creativity. On the one hand, there is a growing consensus that creativity is a complex process that involves both cognitive and affective processes.
On the other hand, there are still a number of disagreements about the specific mechanisms that underlie creativity.
One of the most important areas of convergence between disciplines is the recognition that creativity is a complex process that involves both cognitive and affective processes. Cognitive processes, such as problem solving and divergent thinking, are essential for generating new ideas.
Affective processes, such as motivation and passion, are also important for driving the creative process forward.
Despite this convergence, there are still a number of disagreements about the specific mechanisms that underlie creativity. For example, some researchers believe that creativity is a unitary trait, while others believe that it is a multifaceted construct that involves a number of different abilities.
There is also disagreement about the role of unconscious processes in creativity.
These disagreements are likely to continue as researchers from different disciplines continue to study creativity. However, the growing convergence between disciplines is a positive sign that we are making progress in our understanding of this important process.
Future Directions and Research
As the field of creative thinking continues to evolve, researchers are exploring new directions and areas for future inquiry. These include:
Convergence of Disciplines and Technologies
The convergence of disciplines such as psychology, neuroscience, and computer science is providing new insights into the nature of creativity. Researchers are investigating how different disciplines can inform each other and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of creative thinking.
AI and Creativity
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are having a significant impact on the study of creativity. Researchers are exploring how AI can be used to understand and foster creativity, as well as the ethical implications of using AI in this domain.
Neuroscience and Cognitive Science
Neuroscience and cognitive science are providing valuable insights into the mechanisms of creativity. Researchers are using brain imaging techniques and other methods to investigate the neural processes involved in creative thinking.
Interdisciplinary Collaborations
Interdisciplinary collaborations are becoming increasingly important in the study of creativity. Researchers from different disciplines are working together to develop new theories and methodologies for understanding and enhancing creative thinking.
Novel Research Methodologies and Assessment Tools
Researchers are developing new research methodologies and assessment tools to capture the multifaceted nature of creativity. These include longitudinal studies, mixed-methods approaches, and the use of technology to measure creative thinking.
Practical Applications and Interventions
Researchers are also exploring ways to translate research findings into practical applications and interventions. This includes developing educational programs, workplace interventions, and community initiatives to foster creativity.
FAQ Corner
What is another word for creative thinking?
Lateral thinking is another word for creative thinking.
What are some techniques for creative thinking?
Some techniques for creative thinking include brainstorming, mind mapping, and freewriting.
What are the benefits of creative thinking?
The benefits of creative thinking include problem solving, innovation, and personal growth.