Another term for creative thinking is the ability to think outside the box and come up with new and innovative ideas. It is a skill that can be learned and improved with practice. In this article, we will discuss what creative thinking is, how to enhance it, and the benefits of doing so.
Creative thinking is the ability to generate new ideas and solutions. It is a skill that is essential for success in many different fields, from business to science to the arts. People who are good at creative thinking are able to see problems from different perspectives and come up with solutions that others may not have thought of.
Define Alternative Expressions for Creative Thinking
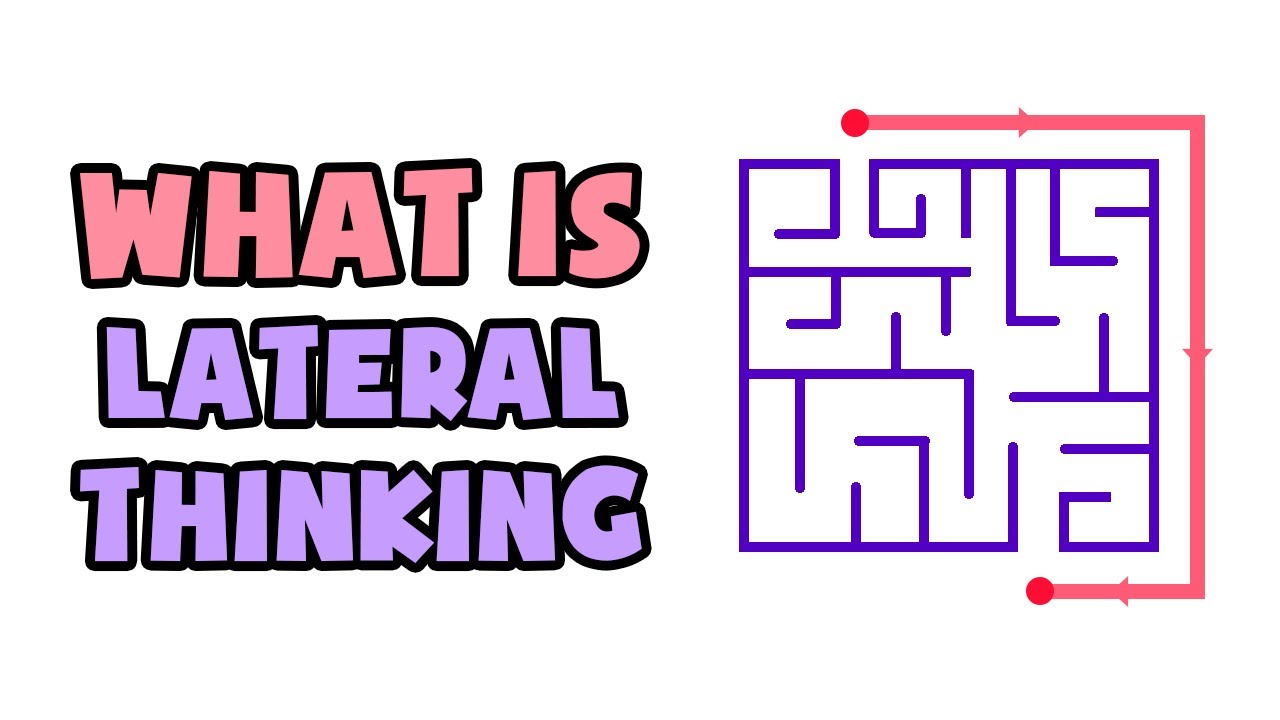
Creative thinking, also known as divergent thinking, is a thought process that generates new and unique ideas. There are several alternative expressions for creative thinking, each with its own nuances and implications.
Here is a list of alternative expressions for creative thinking, along with their meanings and usage:
- Lateral thinking: A problem-solving technique that involves thinking outside the box and finding unconventional solutions.
- Divergent thinking: A thought process that generates multiple, diverse ideas, in contrast to convergent thinking, which focuses on finding a single, correct answer.
- Out-of-the-box thinking: A mindset that challenges conventional wisdom and seeks innovative solutions.
- Disruptive thinking: A thought process that intentionally challenges the status quo and seeks to create new paradigms.
- Non-linear thinking: A thought process that does not follow a logical or sequential order, but instead explores different perspectives and ideas in a fluid manner.
In summary, these alternative expressions for creative thinking all emphasize the generation of new and unique ideas, the exploration of different perspectives, and the challenge of conventional wisdom.
Identify Characteristics of Creative Thinkers
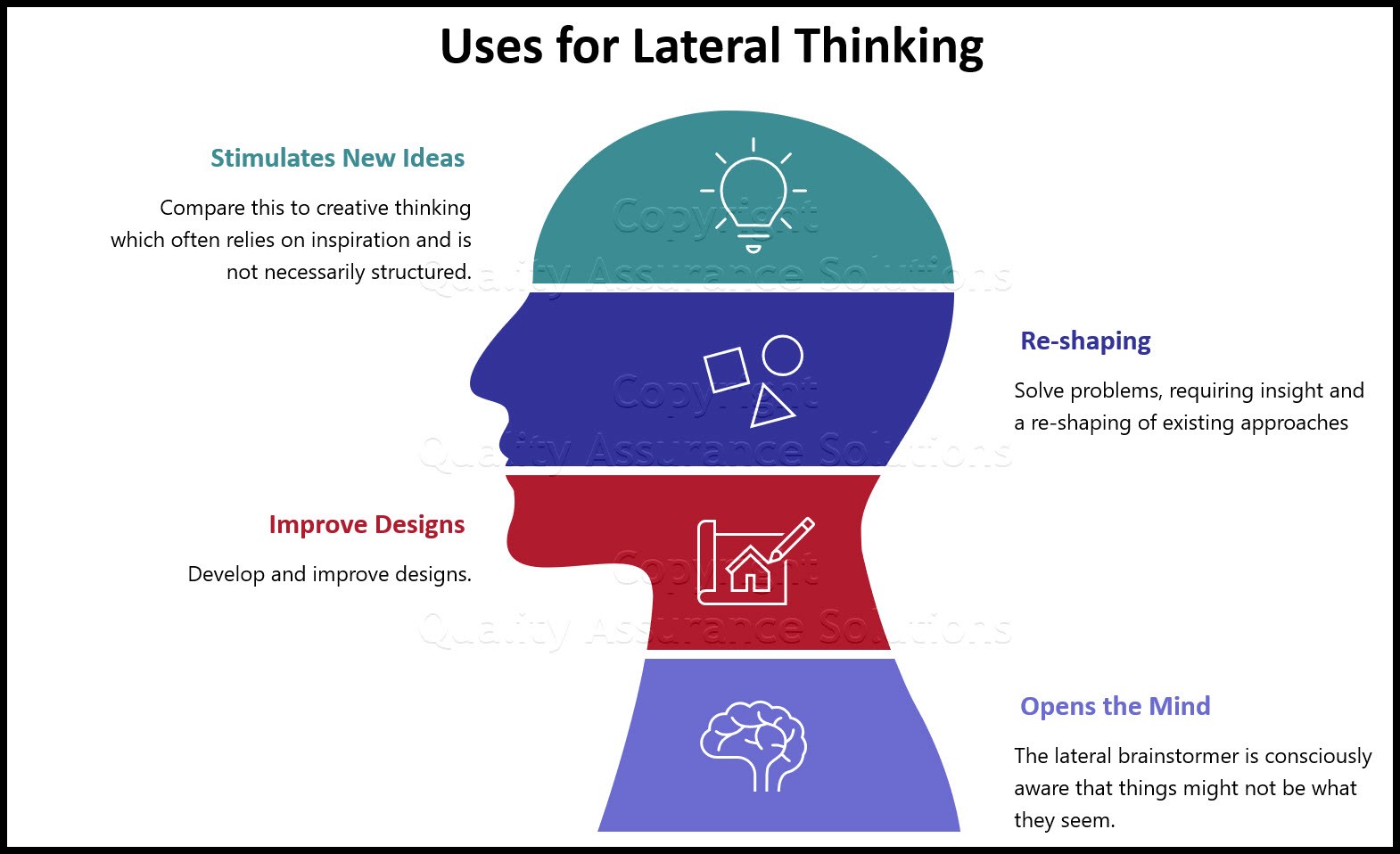
Creative thinkers possess unique characteristics that enable them to generate innovative ideas and solutions. These individuals often exhibit a combination of traits that contribute to their ability to think outside the box.
Fluency
Creative thinkers exhibit fluency in generating a large number of ideas or solutions to a problem. They can produce a wide range of options, demonstrating their ability to think flexibly and come up with diverse perspectives.
- For example, a designer might generate dozens of sketches for a new product, each with its own unique features and benefits.
Flexibility
Creative thinkers are flexible in their thinking and can easily adapt to changing circumstances. They are open to considering different perspectives and are not afraid to challenge conventional wisdom.
- For instance, an entrepreneur might be willing to pivot their business strategy if market conditions change, demonstrating their ability to adapt and innovate.
Originality
Creative thinkers produce original ideas that are unique and not easily replicated. They have the ability to come up with solutions that are fresh and innovative, setting them apart from others.
- A scientist might develop a groundbreaking new theory that challenges existing scientific dogma, demonstrating their originality and willingness to push the boundaries of knowledge.
Elaboration
Creative thinkers are able to elaborate on their ideas, providing details and refining their concepts. They can take their initial thoughts and develop them into more comprehensive and well-defined solutions.
- For example, an artist might start with a rough sketch and gradually add layers of detail and refinement, resulting in a fully realized and expressive work of art.
Evaluation
Creative thinkers can evaluate their own ideas and those of others, identifying strengths and weaknesses. They are able to assess the practicality and feasibility of their solutions and make informed decisions about which ones to pursue.
- A business leader might evaluate a new marketing campaign by considering its potential impact on sales, customer engagement, and brand reputation, demonstrating their ability to critically assess ideas.
Explore Techniques to Enhance Creative Thinking
Enhancing creative thinking is crucial for innovation and problem-solving. Here are some effective techniques to stimulate and nurture this skill:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming involves generating a large number of ideas in a collaborative setting. It’s an effective way to gather diverse perspectives and break out of conventional thinking.
- Step 1: Define the Problem:Clearly articulate the issue or challenge to be addressed.
- Step 2: Gather a Diverse Team:Assemble a group of individuals with varying backgrounds and experiences.
- Step 3: Generate Ideas:Encourage free-flowing ideas, even seemingly unconventional ones.
- Step 4: Suspend Judgment:Avoid criticizing or evaluating ideas during the brainstorming session.
- Step 5: Build on Ideas:Encourage participants to connect and expand on existing ideas.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual representation of ideas and concepts. It helps organize and connect thoughts, promoting creativity and problem-solving.
- Step 1: Start with a Central Topic:Write the main idea or problem in the center of a page.
- Step 2: Branch Out Ideas:Draw branches from the central topic, connecting related ideas and concepts.
- Step 3: Add Details:Include specific details, examples, or questions as you expand the map.
- Step 4: Use Colors and Symbols:Use different colors or symbols to categorize or highlight important ideas.
Freewriting
Freewriting is a technique where you write down whatever comes to mind without editing or censoring your thoughts. It helps break down mental barriers and generate new perspectives.
- Step 1: Set a Timer:Choose a specific time frame (e.g., 10 minutes).
- Step 2: Start Writing:Begin writing immediately, without worrying about grammar or structure.
- Step 3: Don’t Stop Writing:Continue writing until the timer goes off, even if you run out of ideas.
- Step 4: Review Your Writing:Once finished, go back and review your writing for any insights or potential ideas.
Analyze the Benefits of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a valuable skill that can benefit individuals in various aspects of life. It fosters problem-solving, innovation, cognitive flexibility, and success in educational and professional settings.
Advantages of Creative Thinking
Creative thinking offers numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced problem-solving abilities
- Increased innovation and adaptability
- Improved cognitive flexibility and memory
- Greater success in academic and professional pursuits
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous case studies and success stories demonstrate the positive impact of creative thinking:
- Google:Google’s culture of innovation and creative thinking has led to the development of groundbreaking products like Gmail and Google Maps.
- Apple:Apple’s focus on design and user experience has resulted in iconic products like the iPhone and iPad.
Role in Problem-Solving and Innovation
Creative thinking plays a crucial role in problem-solving and innovation:
- It enables individuals to generate novel ideas and solutions.
- It promotes experimentation and risk-taking, leading to breakthroughs.
li>It helps organizations adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements.
Link to Cognitive Flexibility
Creative thinking is closely linked to cognitive flexibility, the ability to switch between different perspectives and adapt to changing situations:
- It allows individuals to break away from conventional thinking patterns.
- It enhances the ability to see problems from multiple angles.
- It promotes divergent thinking and the generation of diverse ideas.
Importance in Education
Fostering creative thinking in educational settings is essential:
- It prepares students for a rapidly changing world that demands innovative solutions.
- It enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- It creates a positive and stimulating learning environment.
Short Story: The Power of Creative Thinking
In a small village, a group of children were playing by the river. Suddenly, they noticed a young boy struggling in the water. The children panicked, but one girl, Anya, remained calm. She quickly devised a plan using a nearby rope and a stick.
She tied the rope to the stick and extended it towards the boy. With the help of her friends, she pulled the boy to safety. Anya’s creative thinking and quick action saved the boy’s life.
Identify Barriers to Creative Thinking
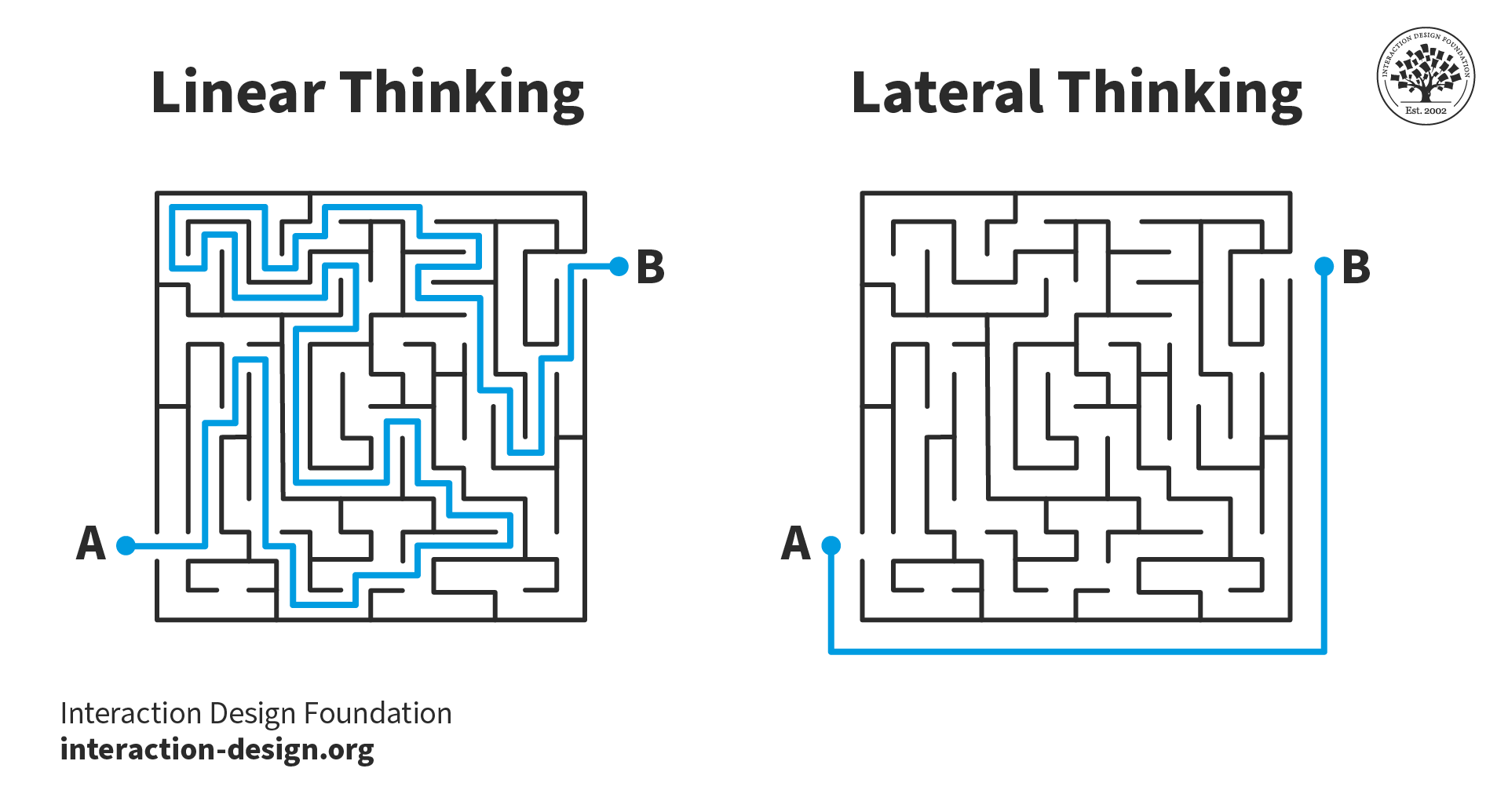
Creative thinking can be stifled by various obstacles and challenges. Identifying these barriers is crucial for fostering an environment that nurtures creativity.Common obstacles to creative thinking include:
Fear of Failure
- Apprehension about making mistakes or producing subpar ideas can hinder risk-taking and exploration.
- To overcome this barrier, encourage a supportive environment where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities rather than setbacks.
Cognitive Biases
- Unconscious mental shortcuts can lead to rigid thinking and limit the generation of novel ideas.
- To mitigate this, encourage active questioning, challenge assumptions, and seek diverse perspectives.
Groupthink
- Pressure to conform within a group can suppress individual creativity and lead to unoriginal solutions.
- To counter this, promote open dialogue, encourage diverse opinions, and foster an environment where individuals feel comfortable expressing their unique ideas.
Environmental Factors
- External factors such as time constraints, lack of resources, or a stressful work environment can stifle creative thinking.
- To address this, provide sufficient time for ideation, allocate necessary resources, and create a work environment that encourages relaxation and free-flowing ideas.
Discuss the Role of Collaboration in Creative Thinking

Collaboration is essential for stimulating and enhancing creative thinking. It brings together diverse perspectives, experiences, and expertise, fostering a fertile environment for generating innovative ideas.
Successful collaborations have led to groundbreaking outcomes, such as the Wright brothers’ invention of the airplane, the development of the internet, and the creation of the iPhone.
Brainstorming is another term for creative thinking, a process that often leads to a bunch of ideas. But where do you store all those creative options? That’s where creative options storage comes in. It’s like a filing cabinet for your ideas, helping you keep track of them and find the ones you need when you need them for brainstorming.
Types of Collaboration
Different types of collaboration exist, each with its impact on creative thinking:
- Formal Collaboration:Structured and goal-oriented, with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Informal Collaboration:Spontaneous and less structured, often occurring in casual settings like coffee breaks or social events.
- Virtual Collaboration:Remote collaboration using digital tools, allowing individuals from different locations to work together.
- Face-to-Face Collaboration:Direct and in-person interaction, enabling non-verbal cues and immediate feedback.
Challenges and Benefits of Collaboration
Collaboration presents challenges and benefits:
- Challenges:Managing different perspectives, resolving conflicts, and overcoming communication barriers.
- Benefits:Cross-fertilization of ideas, enhanced problem-solving, and increased motivation.
Design a Creative Thinking Exercise
To foster creative thinking, structured exercises can be invaluable. Here’s a step-by-step guide to create an engaging and effective creative thinking exercise:
Define the Objective
Begin by clearly defining the purpose of the exercise. Identify the specific creative thinking skills you aim to enhance, such as problem-solving, idea generation, or divergent thinking.
Gather Materials
Determine the materials required for the exercise. Consider using readily available and cost-effective items like paper, pens, markers, or digital drawing tools. Visual aids, such as whiteboards or sticky notes, can also be beneficial.
Another term for creative thinking is divergent thinking, which encourages you to explore different possibilities. If you’re looking for a fun and creative activity for kids, check out creativity for kids glow-in-the-dark paracord wristbands. This project is perfect for kids of all ages and helps develop their creativity and fine motor skills.
Plus, the wristbands glow in the dark, making them a fun and unique accessory.
Establish Guidelines
Provide clear instructions and guidelines to participants. Explain the exercise’s objective, time constraints, and any specific rules or constraints that apply.
Encourage Exploration
Foster an environment that encourages participants to think creatively and explore multiple perspectives. Encourage them to challenge assumptions, experiment with ideas, and embrace unconventional approaches.
Incorporate Collaboration
Consider incorporating elements of collaboration into the exercise. Divide participants into small groups to promote teamwork, idea sharing, and cross-pollination of perspectives.
Set Time Limits
Establish clear time limits for the exercise to maintain focus and encourage participants to work efficiently. Time constraints can also stimulate creative thinking by adding an element of urgency.
Facilitate Debriefing
Plan a debriefing session after the exercise to help participants reflect on their experience and apply their learnings. Guide them through a discussion of their ideas, challenges encountered, and potential applications of the techniques used.
Workshop Objectives and Learning Outcomes
Workshop ObjectivesThe primary objective of this workshop is to equip participants with the knowledge, skills, and techniques to enhance their creative thinking abilities. By the end of the workshop, participants will be able to:
- Define and understand the concept of creative thinking
- Identify and overcome barriers to creative thinking
- Develop and implement strategies to foster creative thinking
- Collaborate effectively in creative environments
Specific Learning OutcomesUpon completion of the workshop, participants will be able to:
- Articulate the key characteristics of creative thinkers
- Apply techniques to generate and evaluate creative ideas
- Understand the benefits of creative thinking in various contexts
- Foster a supportive environment for creative collaboration
- Design and facilitate creative thinking exercises
Create a Visual Representation of Creative Thinking
Visual representations can help us understand complex concepts more easily. They can also be used to generate new ideas and solve problems. In this section, we will create a visual representation of creative thinking.
There are many different ways to create a visual representation of creative thinking. One common method is to use a mind map. A mind map is a diagram that shows the relationships between different ideas. To create a mind map, start by writing down the main topic in the center of a page.
Then, draw branches off of the main topic and write down related ideas on the branches. You can continue to add branches and ideas until you have a complete mind map.
Another way to create a visual representation of creative thinking is to use an infographic. An infographic is a graphic that presents information in a visually appealing way. Infographics can include charts, graphs, images, and text. To create an infographic, start by gathering the information you want to present.
Then, choose a design that will make the information easy to understand and visually appealing.
Flowchart or Diagram of the Creative Thinking Process
A flowchart or diagram can be used to illustrate the steps involved in the creative thinking process. The flowchart should start with the problem identification stage and end with the solution implementation stage. The flowchart should also include the key elements of creative thinking, such as divergent thinking, convergent thinking, and idea generation.
Examples of Creative Thinking in Different Fields
Creative thinking is used in all fields of human endeavor. Here are a few examples of creative thinking in different fields:
- Science:Scientists use creative thinking to develop new theories and solve problems.
- Art:Artists use creative thinking to create new works of art.
- Business:Business people use creative thinking to develop new products and services.
– Write a table summarizing key concepts in creative thinking.
Creative thinking involves generating new and original ideas. It’s a crucial skill for problem-solving, innovation, and personal growth. Here’s a table summarizing key concepts in creative thinking:
| Concept | Definition | Example | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divergent thinking | Generating multiple, unconventional ideas | Brainstorming a list of ideas for a new product | Problem-solving, innovation |
| Convergent thinking | Narrowing down to a single best solution | Choosing the most feasible idea from a brainstorm | Decision-making, critical thinking |
| Lateral thinking | Solving problems by looking at them from unconventional angles | Using a different perspective to solve a puzzle | Problem-solving, creative writing |
| Brainstorming | Generating a large number of ideas without judgment | Holding a brainstorming session with a team | Idea generation, problem-solving |
| Mind mapping | Creating a visual representation of ideas and their connections | Using a mind map to organize notes for a presentation | Note-taking, planning, problem-solving |
| Freewriting | Writing down whatever comes to mind without stopping | Freewriting for 10 minutes to generate ideas for a story | Idea generation, creative writing, self-reflection |
Compare and Contrast Creative Thinking Styles: Another Term For Creative Thinking
Creative thinking encompasses diverse styles, each with unique strengths, weaknesses, and applications. Understanding these styles empowers individuals to leverage their natural inclinations and enhance their creative problem-solving abilities.
Analytic Style
- Strengths:Logical, structured, and analytical. Focuses on breaking down problems, identifying patterns, and developing rational solutions.
- Weaknesses:May prioritize logic over imagination and struggle with abstract concepts or intuitive leaps.
- Applications:Engineering, research, data analysis, and tasks requiring precise and logical thinking.
Intuitive Style
- Strengths:Imaginative, insightful, and open-minded. Relies on gut feelings, hunches, and sudden flashes of inspiration.
- Weaknesses:May struggle with structured analysis and logical reasoning, and ideas may be difficult to articulate or justify.
- Applications:Art, design, writing, and tasks requiring a leap of imagination and original perspectives.
Hybrid Style
- Strengths:Combines the strengths of both analytic and intuitive styles. Balances logical analysis with creative exploration.
- Weaknesses:May not excel in either style specifically, but provides a well-rounded approach to creative thinking.
- Applications:Problem-solving, innovation, and tasks requiring both analytical and imaginative abilities.
– Elaborate on the Impact of Creative Thinking in Various Fields

Creative thinking is a valuable asset in numerous fields, fostering innovation, problem-solving, and decision-making. Its impact extends across diverse disciplines, including science, technology, art, and business.
Science
In science, creative thinking fuels groundbreaking discoveries and theories. Albert Einstein’s revolutionary theory of relativity, for instance, emerged from his imaginative thought experiments.
Technology
Technology thrives on creative thinking, driving the development of innovative products and solutions. The invention of the smartphone, for example, was a testament to the convergence of creative ideas from engineers and designers.
Art
Art is a canvas for creative expression, where artists push boundaries and explore new perspectives. Pablo Picasso’s Cubist paintings revolutionized the art world, challenging conventional representations of reality.
Business
Creative thinking is a catalyst for innovation in business, leading to new products, services, and strategies. Apple’s iPhone, for instance, emerged from the convergence of creative ideas from engineers, designers, and marketers.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Creative thinking aids in solving complex problems and making informed decisions. It encourages the exploration of multiple perspectives, fostering a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
Cognitive Abilities
Creative thinking complements other cognitive abilities, such as intelligence and memory. It enhances problem-solving capabilities, improves memory recall, and fosters a flexible approach to learning.
Fostering Creative Thinking, Another term for creative thinking
Fostering creative thinking in various fields requires:
- Encouraging curiosity and exploration.
- Promoting collaboration and idea-sharing.
- Providing opportunities for experimentation and risk-taking.
- Valuing diversity and unconventional perspectives.
- Creating a supportive and open environment.
Detail the Process of Creative Problem Solving
Creative problem solving is a structured approach to finding innovative solutions to challenges. It involves a series of steps that guide individuals through the process of generating ideas, evaluating options, and implementing effective solutions.
Steps in Creative Problem Solving
- Identify the problem:Clearly define the challenge or issue that needs to be addressed.
- Gather information:Research the problem and collect relevant data to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Generate ideas:Brainstorm and explore a wide range of potential solutions, encouraging unconventional thinking.
- Evaluate ideas:Analyze the feasibility, practicality, and potential impact of each idea.
- Select and implement the best solution:Choose the most promising idea and develop a plan to put it into action.
- Monitor and evaluate:Track the progress of the implemented solution and make adjustments as needed.
Each step in the creative problem-solving process plays a crucial role in fostering innovation. By systematically working through these steps, individuals can increase their chances of finding effective and original solutions to complex problems.
Design a Creative Thinking Assessment Tool
Evaluating creative thinking abilities is crucial for identifying individuals with exceptional problem-solving and innovation skills. To facilitate this assessment, a comprehensive tool or questionnaire can be developed, providing valuable insights into an individual’s creative potential.
The assessment tool should encompass a range of criteria that measure different aspects of creative thinking, such as:
- Fluency:The ability to generate a large number of ideas.
- Flexibility:The ability to think in different ways and come up with novel solutions.
- Originality:The ability to produce unique and uncommon ideas.
- Elaboration:The ability to develop and refine ideas.
- Evaluation:The ability to assess the value and feasibility of ideas.
Administration and Interpretation
To administer the assessment, individuals can be presented with a series of prompts or scenarios that encourage creative thinking. The responses can be analyzed based on the predefined criteria, and a score can be assigned for each category.
The interpretation of the results should consider the individual’s performance across all criteria, providing a comprehensive evaluation of their creative thinking abilities. Individuals with high scores in multiple categories demonstrate exceptional creative potential and may be suitable for roles that require innovative problem-solving and idea generation.
Illustrate the Evolution of Creative Thinking Theories

Creative thinking has been a subject of study for centuries, with various theories emerging over time. Here’s an overview of the evolution of these theories:
Timeline of Creative Thinking Theories
- Ancient Greece: Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle recognized the importance of imagination and creativity in problem-solving.
- Renaissance: Leonardo da Vinci emphasized the role of observation, experimentation, and intuition in creative thinking.
- 19th Century: Romanticism placed a high value on imagination and subjective experiences as sources of creativity.
- Early 20th Century: Gestalt psychology focused on the role of perception and problem-solving in creativity.
- Mid-20th Century: Cognitive psychology emerged, emphasizing the role of mental processes like problem-solving, divergent thinking, and insight in creativity.
- Late 20th Century: Social and cultural factors were recognized as influential in creative thinking, leading to theories like social cognition and cultural psychology.
- 21st Century: Interdisciplinary approaches emerged, combining insights from cognitive science, neuroscience, and other fields to understand creativity.
Key Contributors and their Contributions
- J.P. Guilford: Developed the “Structure of Intellect” model, classifying different types of creative abilities.
- E.P. Torrance: Created the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking, widely used to assess creative potential.
- Howard Gardner: Proposed the theory of multiple intelligences, including “creative intelligence.”
- Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi: Developed the concept of “flow,” a state of intense concentration and creativity.
- Edward de Bono: Introduced the concept of “lateral thinking” and developed tools like the “Six Thinking Hats” to enhance creativity.
FAQ Section
What is creative thinking?
Creative thinking is the ability to generate new ideas and solutions. It is a skill that is essential for success in many different fields.
How can I enhance my creative thinking abilities?
There are many ways to enhance your creative thinking abilities. Some of the most effective methods include brainstorming, mind mapping, and freewriting.
What are the benefits of creative thinking?
Creative thinking can lead to a number of benefits, including increased productivity, improved problem-solving skills, and enhanced innovation.