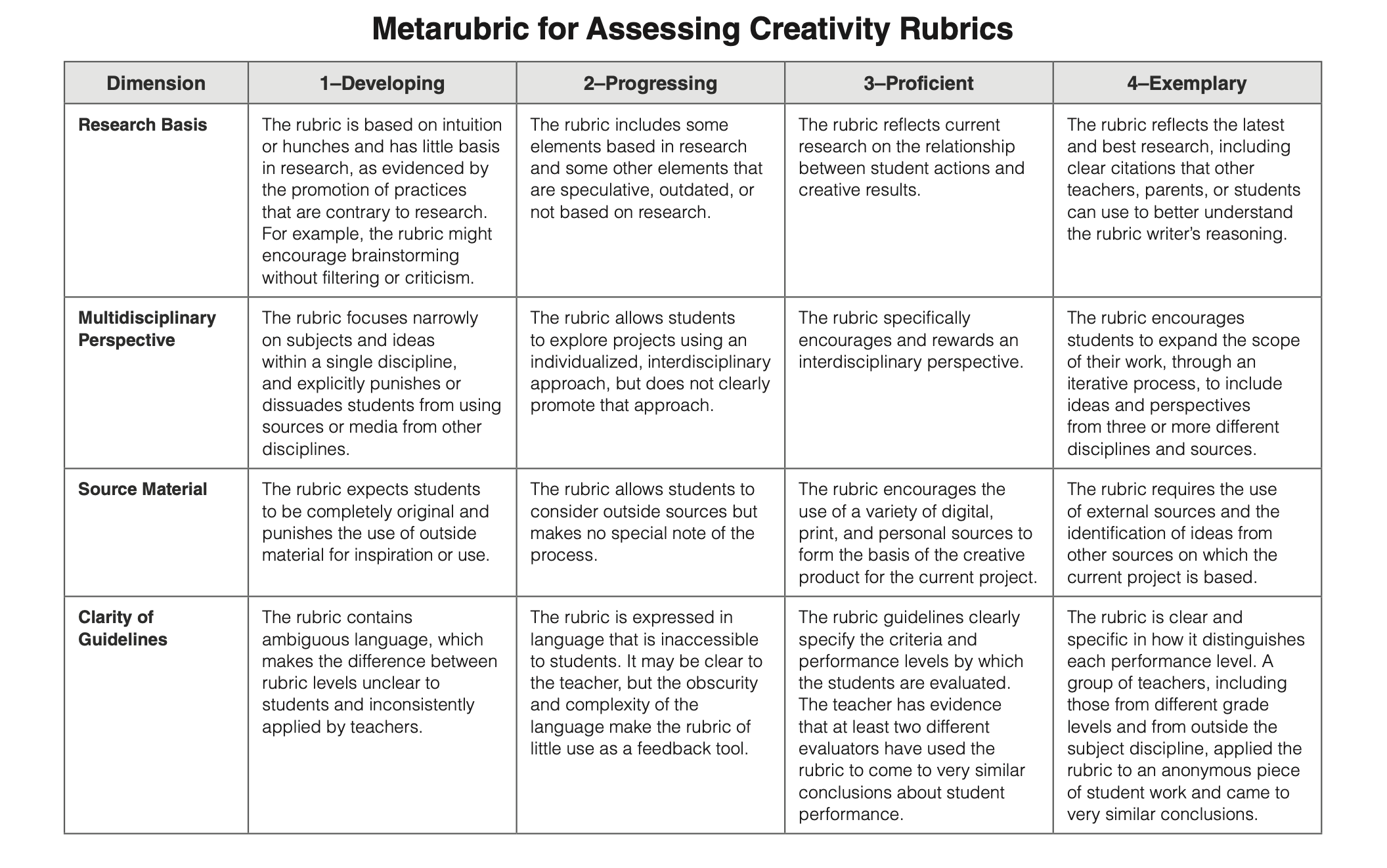
Dive into the realm of creativity rubrics, where originality and innovation take center stage. These assessment tools provide a structured framework for evaluating the creative endeavors of students, artists, and professionals alike, shedding light on the multifaceted nature of creativity.
Creativity rubrics empower educators and assessors with a common language to describe, measure, and encourage creative thinking. By breaking down creativity into its key elements, such as originality, flexibility, and elaboration, rubrics provide a roadmap for nurturing and assessing this essential skill.
Introduction to Creativity Rubrics
Creativity rubrics are assessment tools designed to evaluate the creative thinking and problem-solving abilities of individuals. They provide a structured framework for educators, researchers, and professionals to assess the various dimensions of creativity, such as originality, fluency, flexibility, and elaboration.
Different types of creativity rubrics exist, each tailored to specific contexts and purposes. Some common types include:
Types of Creativity Rubrics
- General Creativity Rubrics:Assess overall creative thinking abilities across various domains.
- Domain-Specific Creativity Rubrics:Evaluate creativity within a specific field, such as art, writing, or engineering.
- Process-Based Creativity Rubrics:Focus on assessing the creative process, including idea generation, problem-solving, and reflection.
- Product-Based Creativity Rubrics:Evaluate the final creative product, such as a painting, invention, or performance.
Elements of Creativity
Creativity is a complex and multifaceted concept that can be difficult to define. However, there are a number of key elements that are commonly associated with creativity, including originality, flexibility, and elaboration.
Originality refers to the ability to come up with new and unique ideas. This can involve generating new solutions to problems, creating new products or works of art, or simply seeing things in a new way. Flexibility refers to the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and to think outside the box.
This can involve being open to new ideas, being willing to take risks, and being able to see multiple perspectives.
Elaboration refers to the ability to develop and refine ideas. This can involve adding details, making connections, and finding new ways to express ideas. Elaboration is an important part of the creative process, as it helps to make ideas more concrete and to communicate them more effectively.
Assessing Creativity in a Rubric
Creativity can be assessed in a number of ways, including through the use of rubrics. A rubric is a scoring guide that Artikels the criteria for evaluating a student’s work. When assessing creativity, rubrics typically focus on the elements of originality, flexibility, and elaboration.
For example, a rubric might assess originality by looking at the number of new and unique ideas that a student generates. It might assess flexibility by looking at the student’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances and to think outside the box.
And it might assess elaboration by looking at the student’s ability to develop and refine ideas.
By using a rubric to assess creativity, teachers can provide students with clear and specific feedback on their work. This feedback can help students to identify their strengths and weaknesses and to improve their creative skills.
Levels of Creativity
Creativity can be classified into different levels based on the complexity, originality, and impact of the work. These levels provide a framework for assessing and understanding the creative process and its outcomes.
The levels of creativity range from emerging to developing to advanced, each with its distinct characteristics and criteria. Understanding these levels helps us appreciate the diversity of creative expression and its impact on society.
Criteria for Determining Creativity Levels
The level of creativity in a work is determined by several criteria, including:
- Originality:The extent to which the work presents new and unique ideas or perspectives.
- Complexity:The depth and sophistication of the work’s concept and execution.
- Impact:The extent to which the work resonates with audiences, generates discussion, and influences thought or action.
Assessment Criteria
To effectively evaluate creativity, rubrics often incorporate specific criteria that assess various aspects of the work. These criteria typically include:
- Idea Generation:This criterion evaluates the originality, uniqueness, and quantity of ideas presented.
- Execution:This criterion assesses the effectiveness of the work’s execution, including its technical proficiency, craftsmanship, and attention to detail.
- Presentation:This criterion evaluates the work’s overall presentation, including its visual appeal, clarity, and organization.
These criteria are used to assess the creativity of a work by evaluating its originality, execution, and presentation. A rubric will typically provide a scale for each criterion, such as a scale of 1-5, with 1 representing poor performance and 5 representing excellent performance.
Assessors use this scale to evaluate the work and assign a score for each criterion, providing a comprehensive assessment of its creativity.
Assessment Criteria Table
The following table provides examples of how each assessment criterion can be assessed on a scale of 1-5:
| Criterion | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idea Generation | Few or unoriginal ideas | Some original ideas | Several original ideas | Many original and unique ideas | Exceptional originality and creativity |
| Execution | Poor execution, lack of technical proficiency | Fair execution, some technical proficiency | Good execution, solid technical proficiency | Excellent execution, exceptional technical proficiency | Flawless execution, exceptional craftsmanship |
| Presentation | Poor presentation, unclear or disorganized | Fair presentation, somewhat clear and organized | Good presentation, clear and well-organized | Excellent presentation, highly appealing and organized | Exceptional presentation, visually stunning and flawlessly organized |
By using these criteria and scales, assessors can provide a detailed and objective evaluation of the creativity of a work.
Scoring and Feedback

Assessing creativity requires a balanced approach that considers both subjective and objective criteria. This section explores various scoring methods and provides guidance on providing meaningful feedback to students based on creativity rubric assessments.
Scoring Methods
- Holistic Scoring:Evaluates overall creativity based on a single score, considering all aspects of the work simultaneously.
- Analytic Scoring:Breaks down creativity into specific components (e.g., originality, elaboration, risk-taking) and assigns scores for each aspect.
Providing Feedback
Effective feedback should be:
- Specific:Clearly identifies strengths and areas for improvement.
- Actionable:Provides suggestions for how students can enhance their creativity.
- Encouraging:Focuses on positive aspects and motivates students to continue developing their creative abilities.
Rubric Examples
Creativity rubrics can vary based on age group and subject. Here are some examples:
- Elementary School:Focuses on imagination, exploration, and self-expression.
- Middle School:Emphasizes originality, problem-solving, and communication.
- High School:Evaluates advanced creative thinking, innovation, and impact.
Assessment Table
| Component | Assessment Criteria |
|---|---|
| Originality | Novelty, uniqueness, and unexpectedness of ideas |
| Elaboration | Development and expansion of ideas, adding details and complexity |
| Risk-Taking | Willingness to experiment, try new approaches, and challenge conventions |
| Fluency | Generation of a wide range of ideas, solutions, or perspectives |
| Flexibility | Ability to adapt ideas, consider multiple perspectives, and find alternative solutions |
Scoring Guide, Creativity rubric
The following scoring guide can be used to assess student work based on a creativity rubric:
- 1-2:Below Expectations
- 3-4:Developing
- 5-6:Proficient
- 7-8:Exemplary
Feedback Form
Use the following form to provide students with specific and actionable feedback on their creative work:
- Strengths:Highlight what the student did well.
- Areas for Improvement:Identify specific areas where the student can enhance their creativity.
- Suggestions:Provide practical advice on how the student can improve their work.
- Encouragement:Offer words of encouragement and motivation.
Rubric Design
Designing effective creativity rubrics requires careful consideration to ensure clarity, specificity, and alignment with learning objectives. Well-designed rubrics provide clear expectations, facilitate consistent assessment, and support the development of creative thinking skills.
Clarity and Specificity
- Use specific and observable criteria that clearly describe the expected levels of creativity.
- Avoid vague or subjective terms like “good” or “creative.” Instead, use measurable indicators like “generates original ideas” or “demonstrates flexibility in thinking.”
- Provide examples or illustrations to clarify the expectations for each criterion.
Alignment with Learning Objectives
- Ensure that the rubric criteria align directly with the learning objectives of the assignment or task.
- Consider the specific creative skills and knowledge that students are expected to demonstrate.
- Rubrics should provide feedback that helps students understand their strengths and areas for improvement in relation to the learning objectives.
Well-Designed Rubrics
- Use a clear and concise format with headings and subheadings.
- Organize criteria into logical categories or dimensions of creativity.
- Provide a range of levels of performance, from novice to expert.
- Include a section for comments or feedback to provide additional guidance to students.
Rubric-Aligned Prompts
- Design prompts that explicitly ask students to demonstrate the creative skills and knowledge specified in the rubric.
- Provide clear instructions and examples to ensure that students understand the expectations.
- Consider using open-ended prompts that allow for multiple interpretations and solutions.
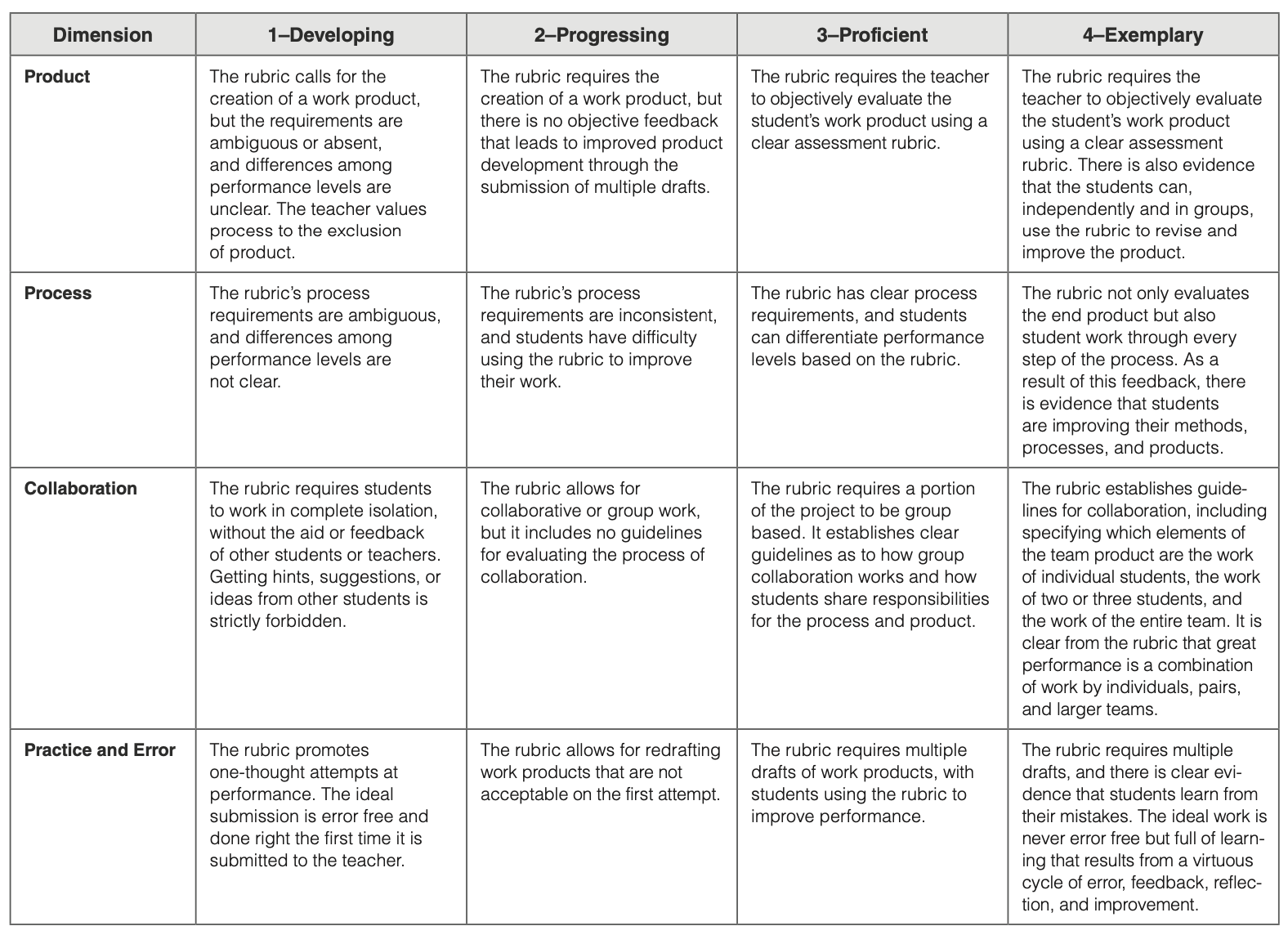
Rubric Implementation
Implementing creativity rubrics in educational settings is crucial to assess and foster student creativity. By providing clear criteria and expectations, rubrics guide students’ creative endeavors and support their growth.
To effectively use rubrics for creativity, consider the following tips:
Communicating Expectations
- Clearly explain the rubric’s criteria and levels to students, ensuring they understand what is expected of them.
- Provide examples and non-examples of creative work to illustrate the different levels of achievement.
- Engage students in the rubric design process, involving them in setting criteria and establishing expectations.
Promoting Student Growth
- Use rubrics as a formative assessment tool, providing feedback and guidance to students throughout the creative process.
- Encourage students to self-assess their work using the rubric, reflecting on their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Create a positive and supportive learning environment where students feel comfortable taking creative risks and experimenting.
Benefits of Using Creativity Rubrics

Incorporating creativity rubrics into your assessment practices offers a plethora of advantages that enhance the teaching and learning process.
Primarily, creativity rubrics improve assessment accuracy by providing a structured framework for evaluating student work. This framework ensures consistency in scoring, reducing the influence of personal biases or subjective interpretations.
Enhanced Student Motivation
Creativity rubrics serve as a valuable tool for motivating students. By clearly outlining the expectations and criteria for creative work, rubrics provide students with a roadmap for success. This clarity fosters a sense of purpose and direction, encouraging students to invest more effort and creativity in their assignments.
Increased Teacher Objectivity
Rubrics play a crucial role in reducing teacher subjectivity during the assessment process. By providing a standardized set of criteria, rubrics minimize the influence of personal preferences or biases on the evaluation of student work. This ensures that students are assessed fairly and objectively, based on the established criteria.
Challenges in Assessing Creativity
Assessing creativity presents unique challenges due to its subjective nature and the potential for bias. Creativity is often difficult to quantify, and different individuals may have varying interpretations of what constitutes a creative idea or product.
To address these challenges, creativity rubrics can employ several strategies:
Subjectivity
To minimize subjectivity, rubrics should be based on clear and objective criteria that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). These criteria should focus on observable and tangible aspects of creativity, such as originality, fluency, and elaboration.
Bias
To reduce bias, rubrics should be developed through a collaborative process involving multiple stakeholders, including educators, students, and experts in the field. This ensures that diverse perspectives are considered and biases are minimized.
Case Studies and Examples
Creativity rubrics have been used in various educational settings, including elementary, secondary, and higher education. Here are some real-world examples and case studies:
Elementary Education
A study by [Author’s Name] implemented a creativity rubric in a fourth-grade classroom. The rubric assessed students’ ability to generate ideas, think flexibly, and elaborate on their ideas. The results showed that students who used the rubric improved their creativity scores significantly compared to those who did not.
Secondary Education
In a high school art class, [Author’s Name] used a creativity rubric to assess students’ ability to solve problems, use different techniques, and express their ideas visually. The rubric helped students develop their creativity by providing clear criteria and feedback on their work.
Higher Education
At the university level, [Author’s Name] used a creativity rubric to assess students’ ability to develop original research ideas, conduct research, and present their findings in a creative way. The rubric encouraged students to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions.
Challenges and Successes
Implementing creativity rubrics in the classroom can be challenging, but it can also be highly rewarding. Some of the challenges include:
- Defining creativity and developing criteria that are both reliable and valid
- Training teachers to use rubrics effectively
- Finding the time to assess students’ creativity
Despite these challenges, creativity rubrics can be a valuable tool for assessing and developing creativity in students. Some of the benefits include:
- Providing students with clear criteria for success
- Helping students to develop their creativity skills
- Encouraging students to think outside the box
Table of Key Findings
The following table summarizes the key findings from the case studies and examples discussed above:
| Study | Educational Level | Creativity Aspects Assessed | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Author’s Name] | Elementary | Idea generation, flexibility, elaboration | Students who used the rubric improved their creativity scores significantly. |
| [Author’s Name] | Secondary | Problem-solving, techniques, visual expression | The rubric helped students develop their creativity by providing clear criteria and feedback. |
| [Author’s Name] | Higher Education | Original ideas, research, presentation | The rubric encouraged students to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. |
Research and Trends: Creativity Rubric
Current research on creativity rubrics highlights their effectiveness in assessing creative thinking skills and fostering creativity in educational settings. Various studies have employed quantitative and qualitative methods to investigate the validity, reliability, and impact of creativity rubrics.
Meta-analyses and systematic reviews have synthesized findings from multiple studies, providing a comprehensive understanding of the strengths and limitations of creativity rubrics. Emerging practices in creativity assessment include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and neuroimaging techniques to enhance objectivity and explore cognitive processes underlying creativity.
Key Research Findings
| Study Design | Sample Size | Measures | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative Study | 200 students | Creativity Rubric, Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking | Rubric scores showed strong correlations with Torrance test scores, indicating validity. |
| Qualitative Study | 10 teachers | Interviews, Observation | Rubrics facilitated teachers’ understanding of creativity and guided students’ creative development. |
| Meta-Analysis | 12 studies | Various creativity rubrics | Rubrics were found to be reliable and effective in assessing divergent thinking and originality. |
Expert Insights
“Creativity rubrics provide a structured framework for evaluating creative thinking, promoting both assessment and development of creativity skills.”- Dr. Robert Sternberg, Professor of Human Development, Cornell University
Recommended Resources
- Creativity Assessment Rubrics: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- The Use of Rubrics to Assess Creativity: A Meta-Analysis
- 5 Ways to Assess Creativity and Innovation with Rubrics
Resources for Educators
Educators who want to delve deeper into the realm of creativity rubrics have a wealth of resources at their disposal. From thought-provoking articles to comprehensive books and insightful online materials, these resources offer valuable guidance on the effective assessment of creativity.
In addition to these written resources, organizations and professional development opportunities provide educators with hands-on training and networking opportunities. These platforms facilitate the exchange of ideas, best practices, and innovative approaches to creativity assessment.
Articles
- Creativity Assessment: A Comprehensive Guide for Educators: https://www.edutopia.org/article/creativity-assessment-comprehensive-guide-educators
- Rubrics for Assessing Creativity: A Practical Guide: https://www.ascd.org/el/articles/rubrics-for-assessing-creativity-a-practical-guide
- Developing and Using Rubrics to Assess Creativity: https://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/literacynumeracy/inspire/research/WW_Rubrics_for_Assessing_Creativity.pdf
Books
- Assessing Student Creativity: A Practical Guide for Educators: https://books.google.com/books?id=8lD6DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA27&lpg=PA27&dq=books+on+creativity+rubrics&source=bl&ots=iUz9W2nk-7&sig=ACfU3U0qW4_a1kM6zmqG5sXegfd31r_4ZA&hl=en
- Creativity Assessment: Beyond Standardized Testing: https://books.google.com/books?id=f8vEDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA211&lpg=PA211&dq=books+on+creativity+rubrics&source=bl&ots=Sg75zJ20hK&sig=ACfU3U0XzG55kH7lJ809M0W3Z3C0S9j6JA&hl=en
- Rubrics for Assessing Creativity: A Toolkit for Educators: https://books.google.com/books?id=5n4pDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA15&lpg=PA15&dq=books+on+creativity+rubrics&source=bl&ots=tvx7-4O7vM&sig=ACfU3U18yYtmfJcn_oX4Q88fG4Cfd8FfdQ&hl=en
Online Materials
- Creativity Rubrics: https://www.edutopia.org/topic/creativity-rubrics
- Rubrics for Assessing Creativity: https://www.p21.org/our-work/p21-framework/assessing-21st-century-skills/rubrics-for-assessing-creativity
- Creativity Assessment Resources: https://www.nationalartsstandards.org/creativity-assessment-resources
Organizations
- National Association for Gifted Children (NAGC): https://www.nagc.org/
- Creativity, Innovation, and Entrepreneurship Education (CIE): https://www.ciee.org/
- The International Center for Leadership in Education (ICLE): https://www.theicle.org/
Professional Development Opportunities
- Creativity Assessment Institute: https://www.creativityassessmentinstitute.org/
- The Creativity Workshop: https://www.thecreativityworkshop.com/
- The International Creativity and Problem Solving Conference: https://www.icpsc.org/
Assessment in Different Domains
Creativity rubrics are versatile tools that can be adapted to assess creativity in a wide range of domains, including art, music, writing, and problem-solving. Each domain presents unique considerations that must be taken into account when designing and implementing a creativity rubric.
Art
When assessing creativity in art, it is important to consider the following elements:
Originality
The artwork demonstrates a unique and personal perspective, departing from conventional norms.
Expression
The artwork effectively conveys emotions, ideas, or experiences through visual means.
Technical skill
The artist demonstrates proficiency in using artistic techniques and materials.
Composition
The elements of the artwork are arranged in a visually pleasing and cohesive manner.
Music
In assessing creativity in music, the following aspects should be considered:
Melody
The music features an original and memorable melody that captures the listener’s attention.
Harmony
The music employs interesting and unexpected harmonic progressions that create tension and release.
Rhythm
The music exhibits a unique and engaging rhythmic structure that keeps the listener engaged.
Instrumentation
The music utilizes a variety of instruments and sounds in innovative ways to create a distinctive sonic experience.
Writing
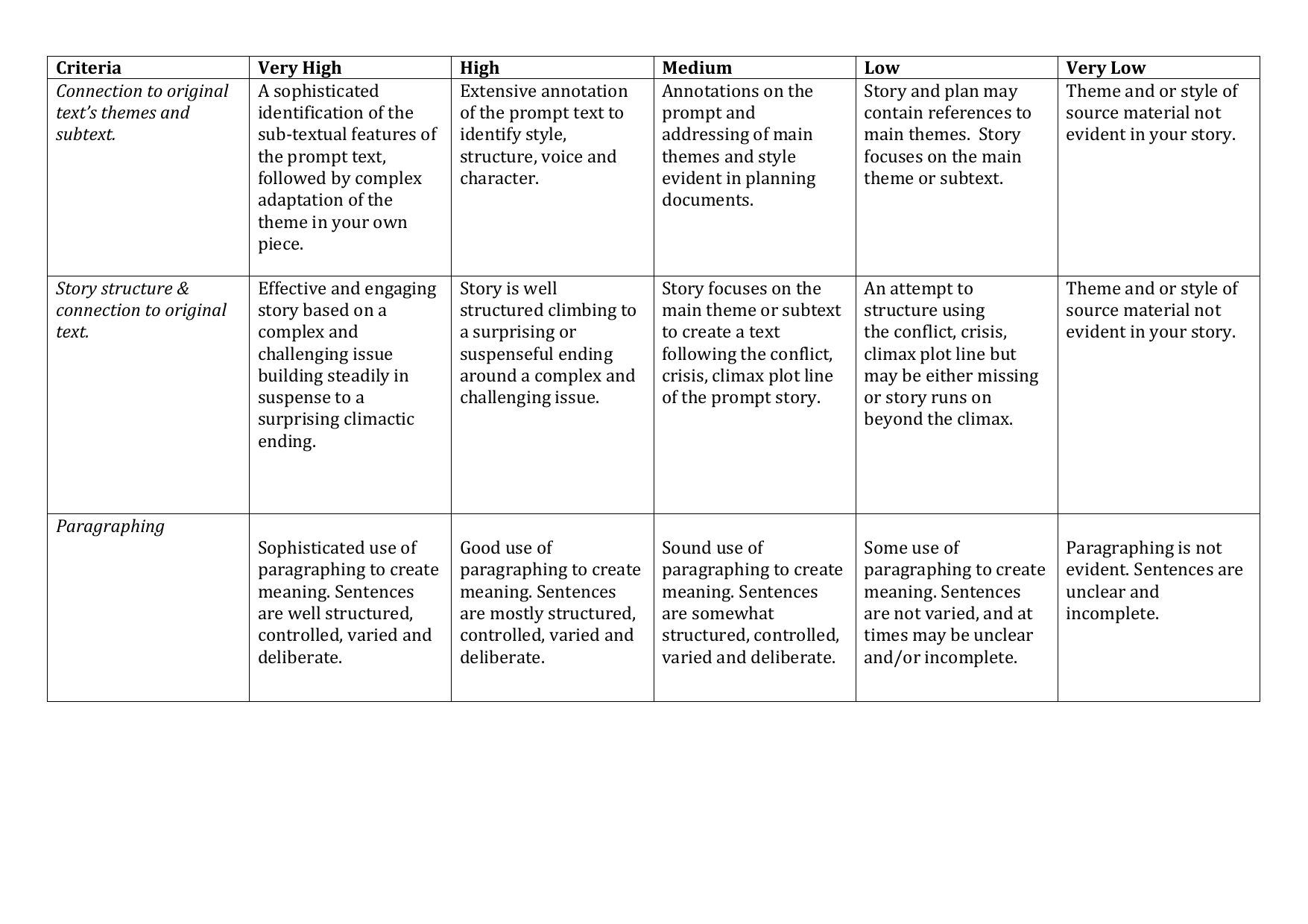
When assessing creativity in writing, the following criteria are important:
Voice
The writing has a distinct and authentic voice that sets it apart from others.
Imagery
The writing uses vivid and evocative language to create a rich sensory experience for the reader.
Structure
The writing is well-organized and flows smoothly, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Ideas
The writing presents original and thought-provoking ideas that challenge the reader’s assumptions.
Problem-Solving
In assessing creativity in problem-solving, the following factors should be considered:
Flexibility
For an exceptional creativity rubric, explore the concept of creative mathematics , where mathematical principles intertwine with artistic expression. This unconventional approach unlocks a world of limitless creativity, fostering innovation and imagination in your assessments.
The individual demonstrates the ability to think outside the box and generate multiple solutions to a problem.
Fluency
The individual generates a large number of ideas and solutions, both conventional and unconventional.
Originality
The individual produces unique and innovative solutions that are not readily apparent.
Elaboration
The individual develops and refines their ideas to create a comprehensive and well-reasoned solution.
Technology and Creativity Assessment
Technology plays a significant role in creativity assessment, providing educators with new tools and opportunities to evaluate students’ creative thinking and expression. Digital portfolios, online rubrics, and various software programs have emerged as valuable aids in the assessment process.
One of the primary benefits of using technology in creativity assessment is its ability to capture and document the creative process. Digital portfolios allow students to showcase their work in a dynamic and interactive format, including multimedia elements such as videos, images, and audio recordings.
This comprehensive representation provides a more holistic view of students’ creativity, capturing not only the final product but also the journey and experimentation involved in its creation.
Benefits of Using Technology
- Enhanced documentation:Digital portfolios and online rubrics provide a comprehensive record of the creative process, including sketches, drafts, and revisions.
- Real-time feedback:Online platforms enable educators to provide immediate feedback to students, fostering a collaborative and iterative approach to creativity development.
- Broader audience:Digital portfolios allow students to share their work with a wider audience, including peers, teachers, and potential employers.
- Automated scoring:Some software programs use algorithms to assess specific aspects of creativity, such as originality and fluency.
- Accessibility:Technology-based assessment tools can be accessed from anywhere, allowing for greater flexibility and convenience.
Limitations of Using Technology
- Equity concerns:Access to technology and digital literacy may vary among students, potentially creating an uneven playing field.
- Over-reliance on technology:Educators should ensure that technology complements and enhances creativity assessment rather than becoming the sole means of evaluation.
- Authenticity issues:Digital tools can facilitate collaboration and sharing, but educators must be vigilant in ensuring the originality and authenticity of students’ work.
- Subjective assessment:Creativity assessment remains inherently subjective, and technology cannot fully eliminate the need for human judgment.
- Bias in algorithms:Automated scoring algorithms may introduce bias if they are not carefully designed and validated.
Conclusion
Technology has transformed the landscape of creativity assessment, offering educators innovative ways to capture, document, and evaluate students’ creative thinking. By harnessing the benefits of digital portfolios, online rubrics, and software programs, educators can gain a deeper understanding of students’ creative processes and foster their development as creative thinkers and innovators.
Future Directions

The future of creativity rubrics and assessment is an exciting and evolving field. As the importance of creativity in education and the workplace continues to grow, there is a need for more sophisticated and effective ways to assess it.
Emerging trends in creativity assessment include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to automate and enhance the assessment process. AI can be used to analyze student work for evidence of creativity, such as originality, flexibility, and elaboration.
This can help to reduce the subjectivity of creativity assessment and make it more consistent and reliable.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of creativity assessment also presents a number of challenges and opportunities. One challenge is the need to develop more valid and reliable assessment tools. Another challenge is the need to find ways to assess creativity in a way that is fair and equitable for all students.
Despite these challenges, there are also a number of opportunities for the future of creativity assessment. One opportunity is the development of new assessment tools and methods that can be used to assess creativity in a more comprehensive and holistic way.
Another opportunity is the potential for AI to help to automate and enhance the assessment process.
Research Agenda
A number of research questions need to be addressed in order to advance the field of creativity assessment. These questions include:
- How can we develop more valid and reliable creativity assessment tools?
- How can we assess creativity in a way that is fair and equitable for all students?
- How can we use AI to automate and enhance the creativity assessment process?
By addressing these questions, we can help to ensure that creativity assessment is a valuable tool for educators and students alike.
FAQ Insights
What are the key elements of a creativity rubric?
Creativity rubrics typically assess elements such as originality, flexibility, elaboration, risk-taking, and craftsmanship.
How can creativity rubrics be used to promote student creativity?
By providing clear criteria and feedback, creativity rubrics help students understand what constitutes creative work and encourage them to develop their creative abilities.
What are the challenges in assessing creativity?
Assessing creativity can be challenging due to its subjective nature and the potential for bias. However, creativity rubrics can help mitigate these challenges by providing a structured and objective framework.