Creative and critical thinking are the cornerstones of innovation, problem-solving, and decision-making. This comprehensive guide explores the essential skills, strategies, and applications of these cognitive processes, empowering you to harness their potential in all aspects of life.
From brainstorming techniques to critical analysis frameworks, we delve into the intricacies of both creative and critical thinking, providing practical insights and examples to enhance your cognitive abilities.
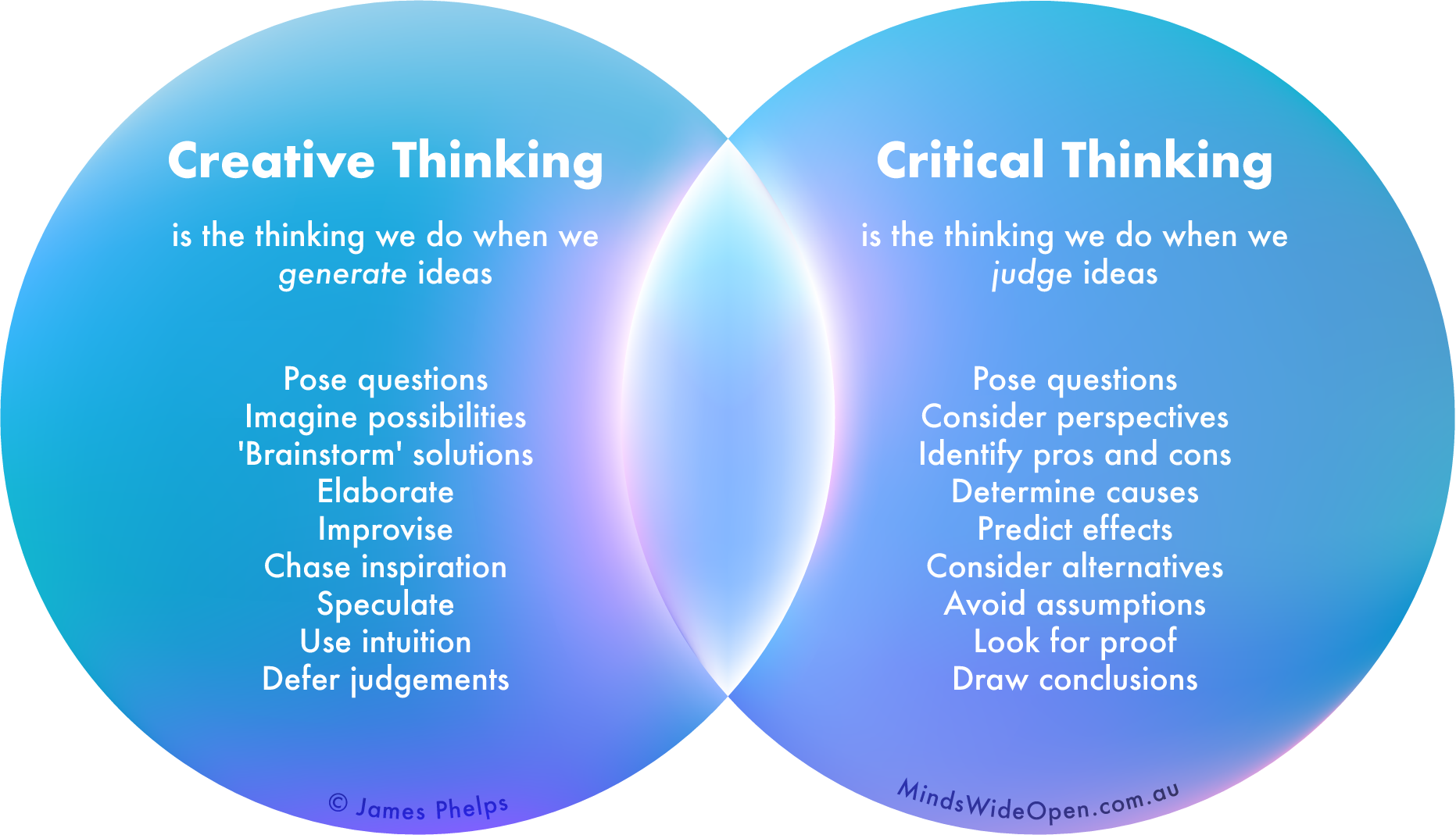
Creative Thinking Skills
Creative thinking involves generating novel ideas, approaches, or solutions to challenges. It entails skills such as brainstorming, divergent thinking, and idea generation.
To foster creative thinking, engage in exercises like:
- Brainstorming:Generate as many ideas as possible, no matter how unconventional.
- Divergent Thinking:Explore multiple perspectives and consider unconventional approaches to a problem.
- Idea Generation:Use techniques like mind mapping, freewriting, or sketching to generate and connect ideas.
– Define critical thinking and discuss its key components, such as analysis, evaluation, synthesis, and application.
Critical thinking is a higher-order cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, synthesizing, and applying information to make informed judgments and decisions. It goes beyond memorizing facts and encompasses a range of skills, including:
Analysis
Breaking down information into its constituent parts to understand its structure, relationships, and implications.
Evaluation
Examining information objectively, considering its strengths, weaknesses, and biases to determine its credibility and value.
Synthesis
Combining information from multiple sources to create new ideas, perspectives, or solutions.
Application
Using information to solve problems, make decisions, or take actions effectively.
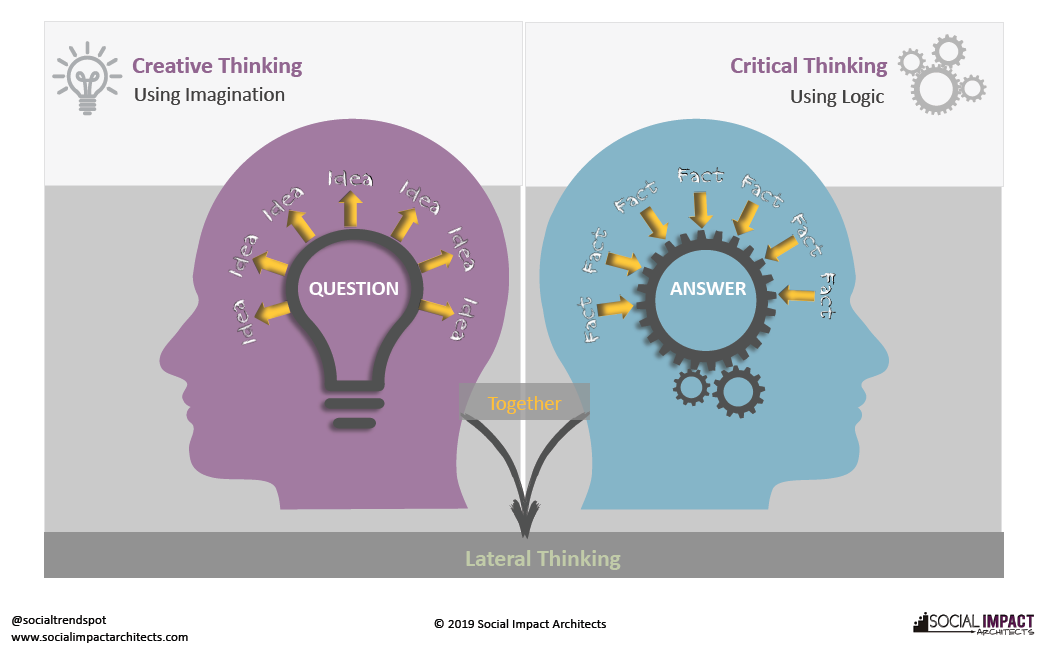
The Interplay of Creativity and Critical Thinking

Creativity and critical thinking are two essential skills for problem-solving and decision-making. They are often seen as opposites, but in reality, they complement each other. Creativity is the ability to generate new ideas, while critical thinking is the ability to evaluate and refine those ideas.
When used together, these skills can lead to innovative and effective solutions.
Role of Critical Thinking in Evaluating and Refining Creative Ideas
Critical thinking is essential for evaluating and refining creative ideas. It allows us to identify the strengths and weaknesses of an idea, and to make sure that it is feasible and effective. For example, a creative idea for a new product may be very innovative, but it may not be practical to manufacture or market.
Critical thinking can help us to identify these potential problems and to develop solutions.
Creative and Critical Thinking in Education
Fostering both creative and critical thinking skills in educational settings is paramount. Creative thinking enables individuals to generate novel ideas, explore possibilities, and find innovative solutions. Critical thinking, on the other hand, empowers them to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to form sound judgments.
Integrating Creative and Critical Thinking in Lesson Plans
Integrating these skills into various subjects enhances student learning and promotes a holistic approach to education.
Example 1: Language Arts
- Creative Thinking: Encourage students to write imaginative stories, poems, or plays that showcase their creativity and divergent thinking.
- Critical Thinking: Assign analytical essays or debates that require students to evaluate arguments, analyze evidence, and form their own perspectives.
Example 2: Science
- Creative Thinking: Engage students in hands-on experiments that encourage them to explore, innovate, and propose hypotheses.
- Critical Thinking: Guide students in designing experiments, interpreting data, and drawing logical conclusions based on scientific evidence.
Example 3: Mathematics
- Creative Thinking: Present students with open-ended problems that allow them to explore multiple solution pathways and develop creative approaches.
- Critical Thinking: Introduce problem-solving strategies that require students to analyze, evaluate, and apply mathematical concepts to solve complex problems.
Creative and Critical Thinking in the Workplace
Creative and critical thinking are essential skills for success in today’s workplace. They allow employees to come up with new ideas, solve problems, and make decisions that can benefit their organizations.In a recent study by IBM, researchers found that companies that encourage creative and critical thinking are more likely to be innovative and successful.
The study found that these companies are more likely to develop new products and services, enter new markets, and increase their profits.There are many examples of how creative and critical thinking have contributed to innovation and problem-solving in different industries.
For example, in the healthcare industry, creative thinking has led to the development of new drugs and treatments. In the technology industry, critical thinking has helped companies develop new products and services that meet the needs of consumers.
Case Studies
* Google:Google is a company that is known for its innovative culture. The company encourages its employees to be creative and to think outside the box. This has led to the development of many new products and services, including Gmail, Google Maps, and YouTube.
3M
3M is another company that is known for its innovative culture. The company has a long history of developing new products, including Scotch tape, Post-it notes, and the Thinsulate insulation. 3M encourages its employees to be creative and to take risks.
This has led to the development of many new products that have benefited consumers around the world.
Measuring Creative and Critical Thinking Skills
Assessing and evaluating creative and critical thinking abilities is crucial for developing and fostering these skills in individuals. Various methods and tools exist to measure these abilities, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods rely on standardized tests and assessments to measure specific aspects of creative and critical thinking. These tests typically provide numerical scores or ratings that can be compared to norms or benchmarks. Examples include:
Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT)
A widely used battery of tests that measures different aspects of creativity, such as fluency, originality, and flexibility.
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA)
A standardized test that assesses critical thinking skills, including analysis, evaluation, inference, and deduction.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods involve observing and analyzing individuals’ thinking processes and products. These methods provide more in-depth insights into the nature and quality of creative and critical thinking. Examples include:
Thinking Aloud Protocols
Participants verbalize their thoughts and reasoning processes while completing tasks that require creative or critical thinking.
Portfolio Analysis
Examining individuals’ work products, such as essays, presentations, or projects, to assess their creative and critical thinking abilities.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the availability of various measurement tools, assessing creative and critical thinking skills presents challenges and limitations:
Cultural Bias
Tests and assessments may be biased towards certain cultural norms or values, potentially underestimating the abilities of individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Reliability and Validity
The reliability and validity of measurement tools can vary, affecting the accuracy and consistency of assessments.
Subjectivity
Qualitative methods rely on subjective judgments, which can introduce bias or inconsistency in evaluations.
– Provide a detailed description of the creative and critical thinking processes involved in decision-making.
Decision-making is a complex process that involves both creative and critical thinking. Creative thinking allows us to generate new ideas and solutions, while critical thinking allows us to evaluate those ideas and solutions and make informed decisions. The creative and critical thinking processes are complementary and work together to help us make better decisions.
The creative thinking process involves generating new ideas and solutions. This can be done through brainstorming, freewriting, or other creative thinking techniques. Once we have generated a number of ideas, we can use critical thinking to evaluate those ideas and select the best one.
Creative and critical thinking skills are crucial for innovation and problem-solving. To cultivate these skills, it’s essential to immerse yourself in environments that foster creativity. One such environment is creative vibes , where you’ll find inspiration and collaboration opportunities. By surrounding yourself with creative energy, you can enhance your ability to generate new ideas and critically evaluate them, ultimately boosting your creative and critical thinking capabilities.
The critical thinking process involves analyzing the pros and cons of each idea, identifying potential risks and benefits, and making a decision based on the evidence.
The role of intuition and biases in decision-making
Intuition and biases can play a role in decision-making. Intuition is a feeling or hunch that something is true or correct. Biases are preconceived notions or beliefs that can influence our decisions. While intuition and biases can sometimes be helpful, they can also lead to poor decision-making.
It is important to be aware of our own biases and to be critical of our own intuition.
How to mitigate the impact of intuition and biases
There are a number of things we can do to mitigate the impact of intuition and biases on our decision-making. First, we can be aware of our own biases and try to control for them. Second, we can seek out information from a variety of sources to get a more complete picture of the situation.
Third, we can consult with others to get their input and feedback.
– Define cognitive biases and explain how they can influence our thoughts and actions.
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts that our brains use to make quick decisions. While these shortcuts can be helpful in some situations, they can also lead us to make flawed judgments and decisions. Cognitive biases can influence our thoughts and actions in many ways, including:
- By making us more likely to believe information that confirms our existing beliefs.This is known as confirmation bias, and it can lead us to ignore evidence that contradicts our beliefs and to seek out information that supports them.
- By making us more likely to remember information that is consistent with our existing beliefs.This is known as the Einstellung effect, and it can lead us to recall information that supports our beliefs more easily than information that contradicts them.
- By making us more likely to interpret information in a way that is consistent with our existing beliefs.This is known as the framing effect, and it can lead us to make different decisions depending on how information is presented to us.
Cognitive biases can have a significant impact on our lives. They can lead us to make poor decisions, to have difficulty solving problems, and to be less effective at communicating with others.
Cultural Influences on Creative and Critical Thinking

Culture plays a significant role in shaping the development and expression of creative and critical thinking skills. Cultural norms, values, and beliefs influence how individuals perceive, interpret, and respond to the world around them.
For instance, cultures that emphasize conformity and respect for authority may discourage individuals from questioning established norms and ideas, which can hinder critical thinking. Conversely, cultures that value individuality and encourage open-mindedness may foster critical thinking skills.
Key Cultural Influences
The table below summarizes the key cultural influences on creative and critical thinking, along with examples from different cultures:
| Cultural Influence | Impact on Creative and Critical Thinking | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Conformity and respect for authority | May discourage questioning and critical thinking | East Asian cultures (e.g., China, Japan) |
| Individualism and open-mindedness | May foster critical thinking and creativity | Western cultures (e.g., United States, Europe) |
| Cultural diversity and exposure to different perspectives | May enhance creativity and critical thinking | Multicultural societies (e.g., Canada, Australia) |
| Education and access to information | Plays a crucial role in developing critical thinking skills | Developed countries with high literacy rates (e.g., Finland, Norway) |
| Social and economic conditions | Can influence access to education and opportunities for creative expression | Developing countries with limited resources (e.g., Sub-Saharan Africa) |
Technology and Creative and Critical Thinking
Technology has profoundly influenced the way we think and solve problems. It has become an indispensable tool for enhancing our creative and critical thinking abilities.
One of the key benefits of technology is its ability to provide us with access to vast amounts of information and resources. The internet has made it possible for us to research any topic imaginable, find inspiration, and connect with experts in our field.
This wealth of information can help us to generate new ideas, evaluate different perspectives, and make more informed decisions.
Potential Challenges, Creative and critical thinking
- Distraction and Overload:Technology can also be a source of distraction, making it difficult to focus on deep thinking and problem-solving. The constant bombardment of notifications, messages, and social media updates can fragment our attention and reduce our ability to engage in sustained critical thinking.
- Echo Chambers:Technology can also contribute to the creation of echo chambers, where we are only exposed to information and opinions that align with our own. This can lead to confirmation bias, where we seek out information that supports our existing beliefs and ignore evidence that contradicts them.
- Over-reliance on Technology:While technology can be a valuable tool, it is important to avoid becoming overly reliant on it. We need to be able to think critically and solve problems without always relying on external sources.
Future Trends in Creative and Critical Thinking
The field of creative and critical thinking is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. These trends are being driven by a number of factors, including advances in technology, the changing nature of the workplace, and the increasing complexity of the world around us.
One of the most important trends in creative and critical thinking is the growing emphasis on interdisciplinary approaches. In the past, creativity and critical thinking were often seen as separate disciplines, but today it is increasingly recognized that they are closely intertwined.
This is because creativity is essential for generating new ideas, while critical thinking is essential for evaluating and refining those ideas.
Another important trend is the increasing use of technology to enhance creativity and critical thinking. Technology can be used to provide access to information, facilitate collaboration, and create new learning opportunities. For example, online brainstorming tools can help people to generate new ideas, while virtual reality simulations can provide immersive experiences that allow people to explore complex problems from different perspectives.
The future of creative and critical thinking is bright. These skills are essential for success in the 21st century workplace, and they are also important for personal growth and development. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends in creative and critical thinking, you can ensure that you are well-equipped to meet the challenges of the future.
Research
The latest theoretical and methodological advancements in the study of creative and critical thinking are providing new insights into these complex processes. For example, cognitive neuroscience research is helping us to understand the neural mechanisms that underlie creativity and critical thinking.
This research is providing valuable information that can be used to develop new educational programs and interventions to improve these skills.
Another emerging area of research is computational creativity. Computational creativity is the use of computers to generate creative artifacts, such as music, art, and literature. This research is helping us to understand the computational processes that underlie creativity, and it is also leading to the development of new tools that can be used to enhance human creativity.
Finally, there is a growing interest in critical thinking in complex systems. Complex systems are systems that are made up of many interconnected parts, and they can be very difficult to understand and predict. Critical thinking in complex systems is essential for making decisions in a complex world, and it is an area of research that is likely to grow in importance in the years to come.
Practice
There are a number of innovative approaches to teaching and developing creative and critical thinking skills. One popular approach is project-based learning. Project-based learning is a type of learning in which students work on projects that are designed to challenge their creativity and critical thinking skills.
These projects can be anything from designing a new product to creating a work of art.
Another effective approach to teaching creative and critical thinking is through the use of technology. Technology can be used to provide access to information, facilitate collaboration, and create new learning opportunities. For example, online brainstorming tools can help students to generate new ideas, while virtual reality simulations can provide immersive experiences that allow students to explore complex problems from different perspectives.
Finally, it is important to remember that creative and critical thinking skills can be developed in any setting. It is not necessary to take a special class or workshop to develop these skills. You can simply start by incorporating more creative and critical thinking activities into your daily life.
For example, you can try to come up with new solutions to problems, or you can try to evaluate the arguments that you hear in the media.
Implications
The trends in creative and critical thinking have important implications for the future of education, the workplace, and society as a whole.
In education, there is a growing need for teachers to develop students’ creative and critical thinking skills. This is because these skills are essential for success in the 21st century workplace. In the workplace, creative and critical thinking skills are essential for innovation, problem-solving, and decision-making.
In society as a whole, creative and critical thinking skills are essential for addressing global challenges and promoting democratic values.
The future of creative and critical thinking is bright. These skills are essential for success in the 21st century, and they are also important for personal growth and development. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends in creative and critical thinking, you can ensure that you are well-equipped to meet the challenges of the future.
Best Practices for Fostering Creative and Critical Thinking

Nurturing creative and critical thinking abilities is crucial for individuals, organizations, and educational institutions. By implementing effective strategies, we can foster an environment that encourages innovation, problem-solving, and well-informed decision-making.
Educational Institutions
- Encourage Inquiry-Based Learning:Promote active learning methods like problem-based learning, case studies, and simulations to stimulate curiosity and critical thinking.
- Foster Collaboration:Create opportunities for students to work in groups, share ideas, and challenge each other’s perspectives.
- Provide Constructive Feedback:Offer specific and actionable feedback that helps students identify areas for improvement and develop their critical thinking skills.
Workplaces
- Promote a Culture of Innovation:Encourage employees to question the status quo, generate new ideas, and take calculated risks.
- Establish Cross-Functional Teams:Bring together individuals with diverse perspectives to foster creative problem-solving and critical analysis.
- Provide Opportunities for Professional Development:Offer training and workshops to enhance employees’ critical thinking and creative abilities.
Individuals
- Practice Active Reading:Engage in deep reading, question assumptions, and evaluate the credibility of information.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives:Expose yourself to different viewpoints, engage in discussions, and challenge your own biases.
- Take Time for Reflection:Dedicate time to contemplate experiences, identify patterns, and develop insights.
Examples of Creative and Critical Thinking in Action
Creative and critical thinking are essential skills for success in various aspects of life. They enable us to approach problems with originality, evaluate information objectively, and make well-informed decisions. Here are a few examples of creative and critical thinking in action:
Art
- Example:Pablo Picasso’s painting “Guernica” (1937)
- Explanation:This iconic painting demonstrates creative thinking in its unique and powerful depiction of the horrors of war, while critical thinking is evident in its use of symbolism and abstraction to convey a complex message.
Science
- Example:Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity (1905)
- Explanation:Einstein’s groundbreaking theory showcases creative thinking in its imaginative and unconventional approach to understanding the universe, while critical thinking is reflected in the rigorous experimentation and logical reasoning that supported his ideas.
Business
- Example:Apple’s iPhone (2007)
- Explanation:The iPhone exemplifies creative thinking in its innovative design and integration of multiple technologies, while critical thinking is evident in the careful market research and user testing that informed its development.
Everyday Life
- Example:Solving a complex puzzle or riddle
- Explanation:Puzzles and riddles require both creative thinking to generate possible solutions and critical thinking to evaluate and select the most likely one.
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between creative and critical thinking?
Creative thinking focuses on generating new ideas and exploring possibilities, while critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to form sound judgments.
How can I improve my creative thinking skills?
Engage in brainstorming, divergent thinking exercises, and mind mapping techniques to stimulate your imagination and generate a wide range of ideas.
What are the key components of critical thinking?
Critical thinking involves analysis, evaluation, synthesis, and application of information to reach well-reasoned conclusions.
How can I apply creative and critical thinking in my workplace?
Utilize creative thinking to generate innovative solutions and critical thinking to evaluate and refine ideas, leading to more effective problem-solving and decision-making.